Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Where Are American Dog Ticks Found?


Common Health Issues
Where Are American Dog Ticks Found?
Published: February 5, 2024
Learn about the common health issues associated with American dog ticks and where they are typically found. Protect your pets with this essential information.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
American dog ticks, scientifically known as Dermacentor variabilis, are a common ectoparasite found in the United States. These ticks are notorious for transmitting various diseases, making them a significant concern for both humans and animals. Understanding the behavior, habitats, and geographic distribution of American dog ticks is crucial for effectively managing the risks associated with their presence.
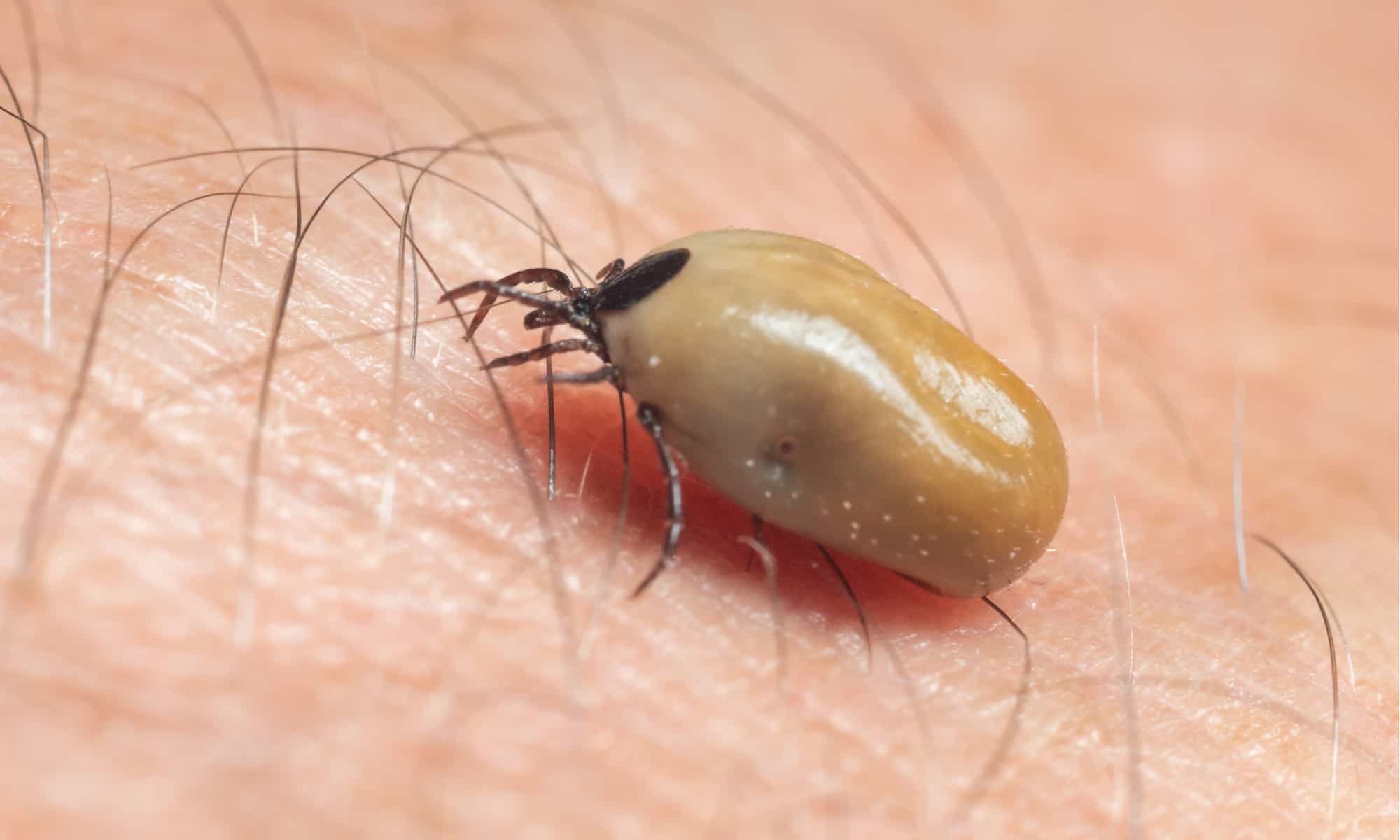
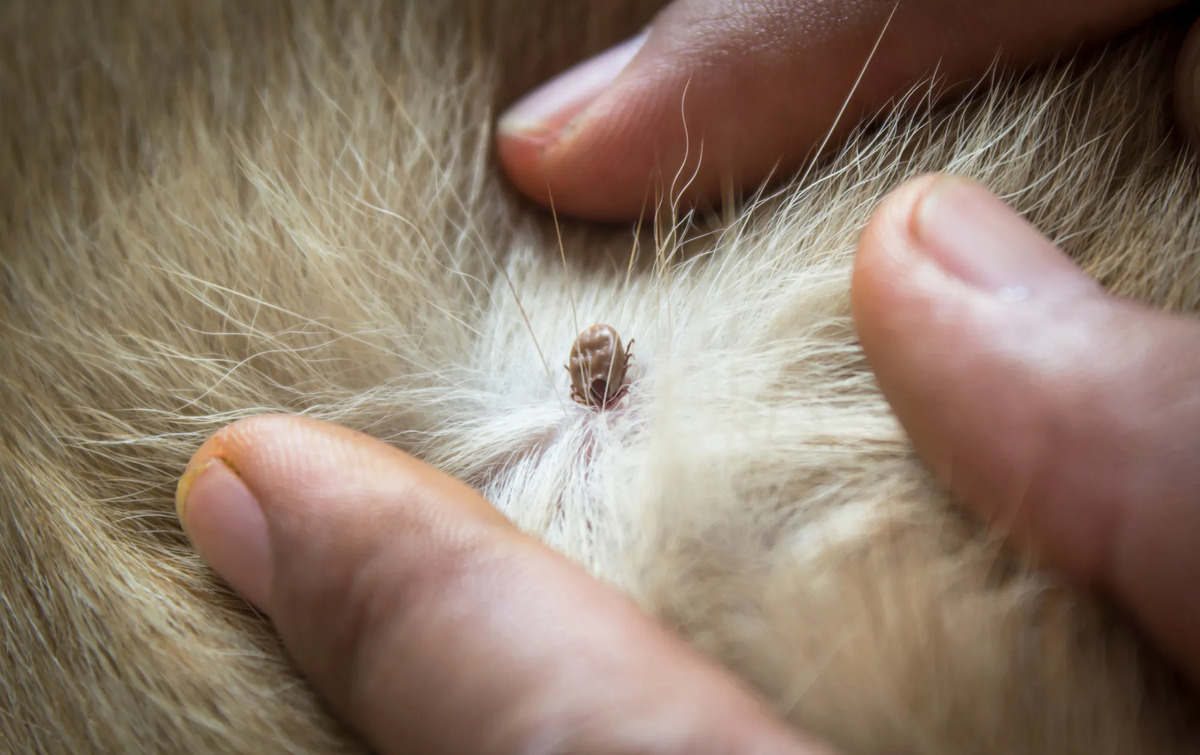
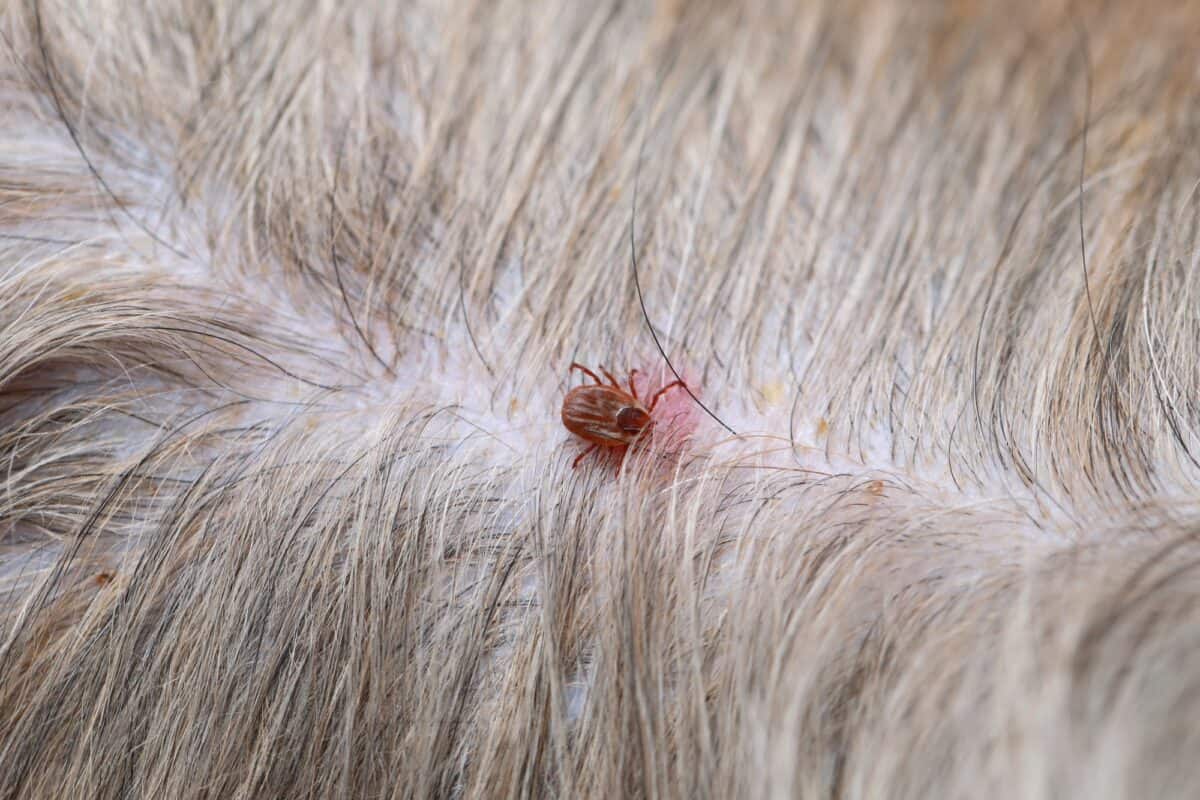
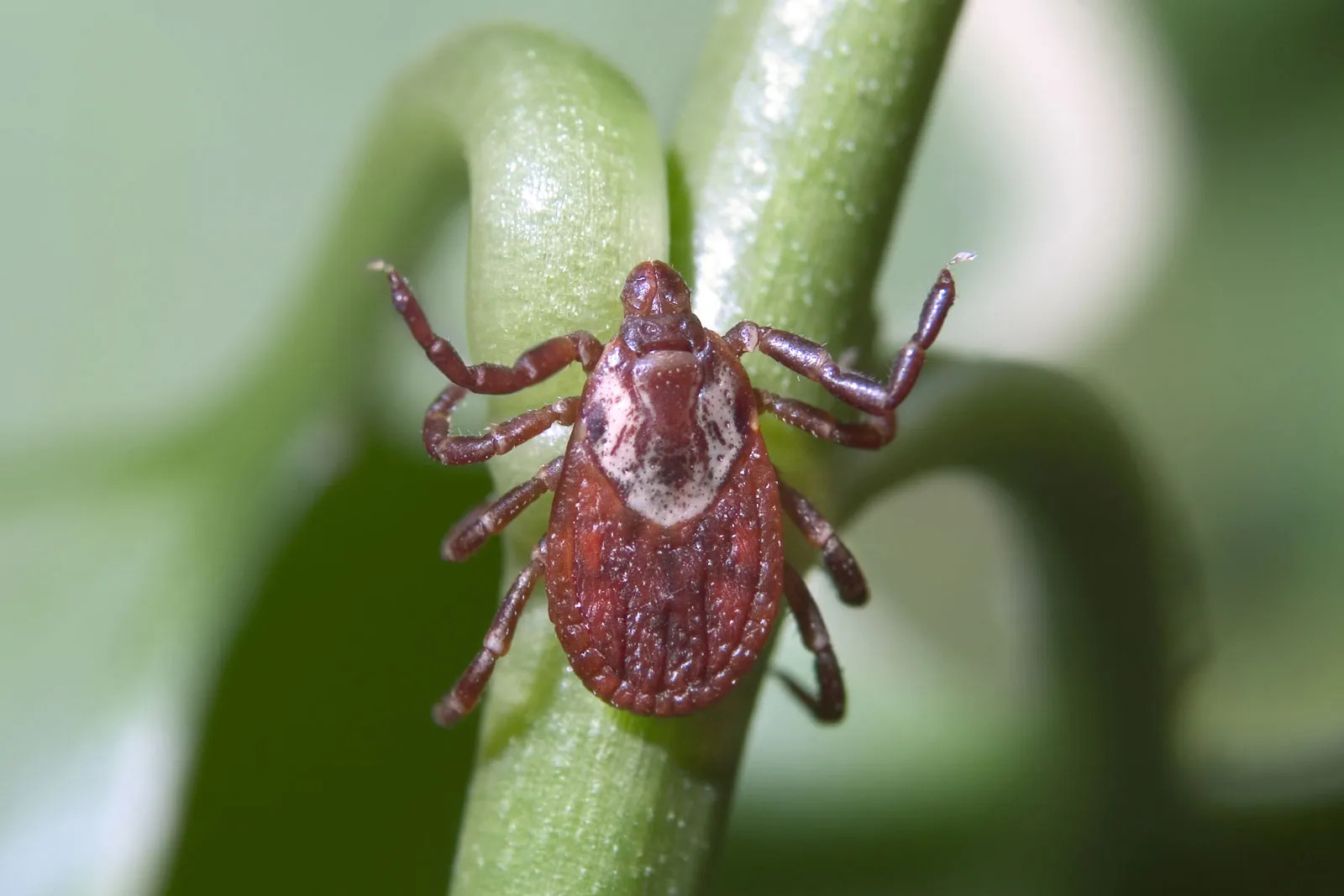
These blood-sucking arachnids are known for their distinctive appearance, featuring a reddish-brown body with white or gray markings. They have a hard exoskeleton and are typically found in grassy, wooded areas, as well as along trails and the edges of forests. American dog ticks are particularly active during the warmer months, posing a greater threat to outdoor enthusiasts, hikers, and individuals with pets.
Given their potential to transmit diseases such as Rocky Mountain spotted fever and tularemia, American dog ticks are a significant public health concern. Furthermore, they can cause tick paralysis in animals, making it essential for pet owners to be vigilant in protecting their furry companions from these parasites.
In this article, we will delve into the habitats and geographic distribution of American dog ticks, shedding light on the regions where they are most prevalent. Additionally, we will explore the associated risks and effective prevention strategies to minimize the likelihood of encountering these troublesome parasites. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of American dog ticks, individuals can take proactive measures to safeguard themselves and their pets from the potential health hazards posed by these blood-feeding arachnids.
Read more: Where Do Dogs Get Ticks?
Understanding American Dog Ticks
American dog ticks, scientifically known as Dermacentor variabilis, are ectoparasites that belong to the arachnid family. These ticks are commonly found in grassy and wooded areas, where they latch onto passing hosts to feed on their blood. Recognizable by their reddish-brown bodies adorned with white or gray markings, American dog ticks are known for their distinctive appearance and potential health risks.
These blood-feeding arachnids have a complex life cycle, progressing through four stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. During each stage, American dog ticks seek out hosts to feed on, with the potential to transmit diseases during their blood meals. While they are commonly associated with dogs, American dog ticks are opportunistic feeders and can latch onto a wide range of hosts, including humans, deer, and other mammals.
American dog ticks are particularly active during the warmer months, from spring to fall, when outdoor activities are at their peak. Their habitats typically include grassy areas, wooded regions, and the edges of forests, where they lie in wait for suitable hosts to pass by. When a potential host brushes against the vegetation where the ticks are situated, they quickly grasp onto the host's skin, beginning their blood-feeding process.
In addition to their feeding habits, American dog ticks are known for their ability to transmit various diseases to their hosts. One of the most concerning diseases associated with these ticks is Rocky Mountain spotted fever, a potentially severe illness characterized by fever, headache, and rash. Furthermore, American dog ticks can transmit tularemia, a bacterial infection that can cause flu-like symptoms and, if left untreated, may lead to serious health complications.
Understanding the behavior and characteristics of American dog ticks is crucial for individuals who frequent outdoor environments, as well as pet owners. By recognizing the habitats where these ticks are commonly found and being aware of their potential health risks, individuals can take proactive measures to minimize the likelihood of encountering these parasites. In the following sections, we will explore the specific habitats and geographic distribution of American dog ticks, as well as effective prevention strategies to mitigate the risks associated with their presence.
Habitats of American Dog Ticks
American dog ticks, also known as wood ticks, are commonly found in grassy and wooded areas, as well as along the edges of forests. These habitats provide the ideal environment for American dog ticks to thrive, as they offer ample opportunities to latch onto passing hosts for their blood meals. The ticks are particularly prevalent in regions where suitable hosts, such as deer, rodents, and other mammals, frequent the vegetation, providing ample opportunities for the ticks to find their next meal.
Grassy areas, including fields, meadows, and parks, serve as prime habitats for American dog ticks. The tall grass and vegetation in these areas provide ideal hiding spots for the ticks as they await potential hosts. Additionally, wooded regions, characterized by dense foliage and leaf litter, offer suitable environments for American dog ticks to lie in wait for passing animals or humans. The humid and shaded conditions within wooded areas create favorable microclimates for the ticks, allowing them to remain active and seek out hosts for feeding.
Moreover, the edges of forests, where the vegetation transitions from dense woodland to open spaces, are favored habitats for American dog ticks. These transitional zones provide an abundance of wildlife and offer opportunities for the ticks to latch onto passing animals as they move between the forest and open areas. Furthermore, these areas are commonly frequented by outdoor enthusiasts, hikers, and individuals with pets, increasing the likelihood of human and pet encounters with American dog ticks.
It is important to note that American dog ticks are not limited to rural environments; they can also be found in urban and suburban areas with suitable habitats. Parks, recreational areas, and even residential yards with overgrown vegetation can harbor American dog ticks, posing a potential risk to individuals and their pets.
Understanding the specific habitats favored by American dog ticks is essential for individuals who spend time in outdoor environments, as well as pet owners. By recognizing the typical habitats where these ticks are prevalent, individuals can take proactive measures to minimize their exposure and reduce the risk of encountering these blood-feeding parasites. In the following sections, we will delve into the geographic distribution of American dog ticks, shedding light on the regions where they are most commonly found. Additionally, we will explore the associated risks and effective prevention strategies to mitigate the potential health hazards posed by these troublesome parasites.
Geographic Distribution
The geographic distribution of American dog ticks spans a significant portion of the United States, with specific regions exhibiting higher prevalence due to environmental factors and host populations. These ticks are commonly found in the eastern, central, and midwestern states, where suitable habitats and hosts facilitate their survival and reproduction. The states with the highest reported cases of American dog tick encounters include but are not limited to, Pennsylvania, New York, New Jersey, North Carolina, Virginia, and Maryland.
In the eastern United States, American dog ticks are prevalent in regions characterized by dense woodlands, grassy areas, and a diverse range of wildlife. States such as Pennsylvania and New York, known for their expansive forests and abundant wildlife populations, provide ideal environments for American dog ticks to thrive. Additionally, the humid climate and ample vegetation in these regions create favorable conditions for the ticks, allowing them to persist and seek out hosts for their blood meals.
Moving towards the central and midwestern states, American dog ticks are commonly encountered in areas with a mix of wooded habitats, grasslands, and transitional zones. States such as North Carolina, Virginia, and Maryland exhibit a notable presence of American dog ticks, particularly in regions where forests meet open spaces. These transitional zones serve as hotspots for tick activity, as they attract a diverse array of wildlife and human outdoor enthusiasts, increasing the likelihood of tick encounters.
While the eastern, central, and midwestern states are known for their higher prevalence of American dog ticks, it is important to note that these ticks can also be found in other parts of the country. As the climate and environmental conditions continue to evolve, the geographic distribution of American dog ticks may shift, impacting their presence in various regions. Therefore, individuals residing in or visiting areas with suitable tick habitats should remain vigilant and implement preventive measures to minimize the risk of tick encounters.
Understanding the geographic distribution of American dog ticks is crucial for individuals residing in or traveling to regions where these ticks are prevalent. By being aware of the specific states and environments where American dog ticks are commonly found, individuals can take proactive steps to protect themselves and their pets from potential tick encounters. In the subsequent section, we will explore the associated risks and effective prevention strategies to mitigate the potential health hazards posed by these troublesome parasites.
Risks and Prevention
The presence of American dog ticks poses significant health risks to both humans and animals due to their potential to transmit various diseases during their blood-feeding process. One of the most concerning diseases associated with American dog ticks is Rocky Mountain spotted fever, a potentially severe illness characterized by fever, headache, and rash. Additionally, these ticks can transmit tularemia, a bacterial infection that can cause flu-like symptoms and, if left untreated, may lead to serious health complications. Furthermore, American dog ticks can cause tick paralysis in animals, making it essential for pet owners to be vigilant in protecting their furry companions from these parasites.
To mitigate the risks associated with American dog ticks, individuals can implement effective prevention strategies to minimize the likelihood of encountering these troublesome parasites. Here are some key measures to consider:
-
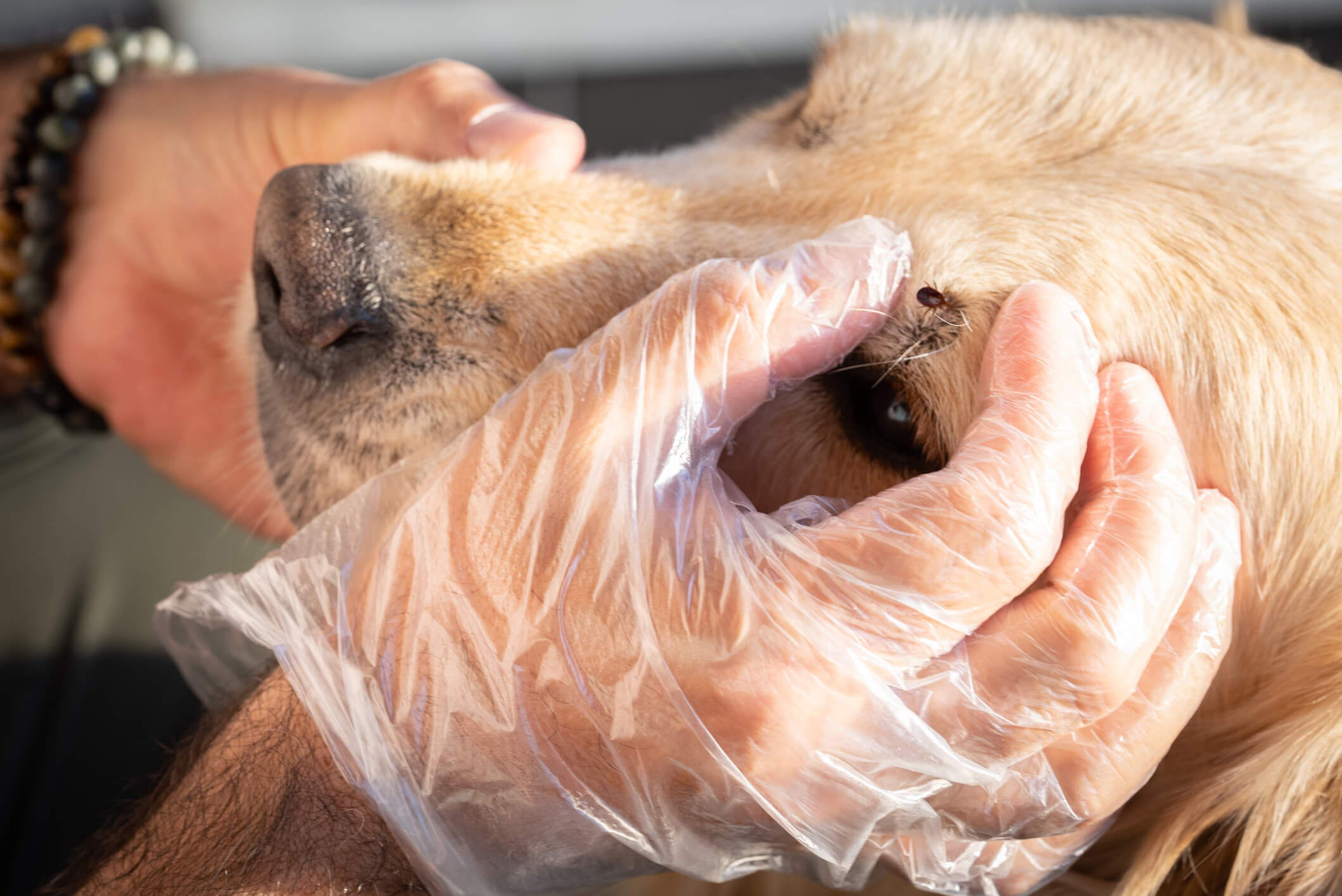
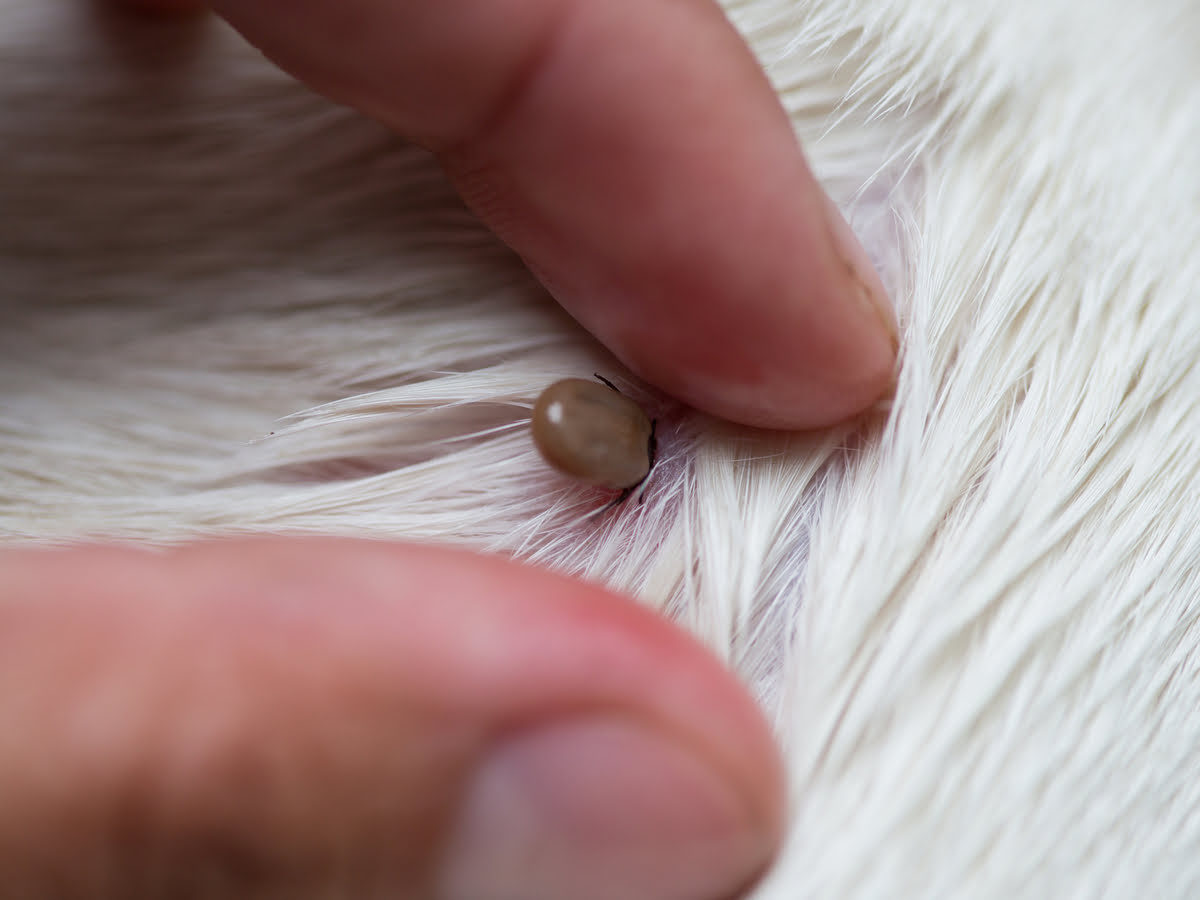
Tick Checks: After spending time in outdoor environments, individuals should conduct thorough tick checks on themselves, their children, and pets. Pay close attention to areas such as the scalp, behind the ears, under the arms, and around the waist and knees, as ticks prefer warm and moist areas to attach.
-
Protective Clothing: Wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and closed-toe shoes can act as a physical barrier, reducing the likelihood of ticks making direct contact with the skin. Tucking pants into socks and wearing light-colored clothing can also make ticks more visible, aiding in prompt removal.
-
Tick Repellents: The use of EPA-registered insect repellents containing DEET or picaridin can effectively repel ticks. Applying repellents to exposed skin and clothing can provide added protection against tick bites.
-
Environmental Modifications: Keeping grassy and wooded areas around homes well-maintained can reduce tick habitats. Regularly mowing the lawn, removing leaf litter, and creating a barrier of wood chips or gravel between lawns and wooded areas can help minimize tick populations.
-
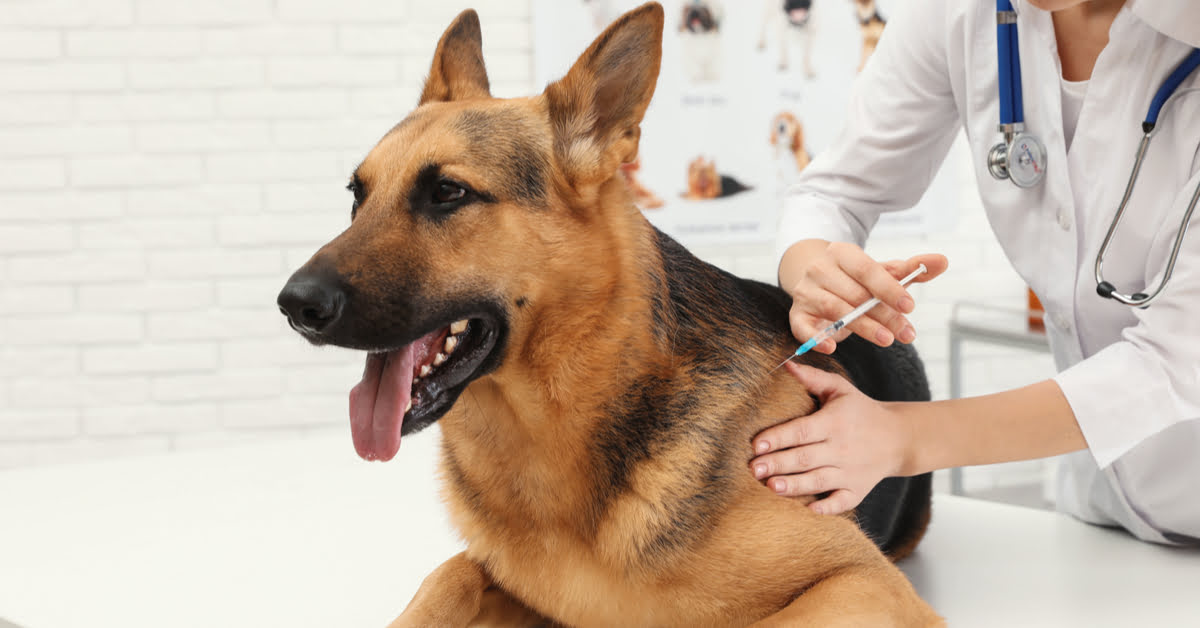
Tick Control for Pets: Pet owners should consider using veterinarian-recommended tick control products for their animals. These may include topical treatments, collars, or oral medications designed to repel and kill ticks, reducing the risk of tick-borne diseases in pets.
-
Prompt Tick Removal: If a tick is found attached to the skin, it should be promptly and carefully removed using fine-tipped tweezers. Grasping the tick as close to the skin's surface as possible and pulling upward with steady, even pressure can aid in complete removal.
By implementing these preventive measures, individuals can significantly reduce the risk of encountering American dog ticks and minimize the potential health hazards associated with tick-borne diseases. Additionally, staying informed about the geographic distribution and habitats of American dog ticks can empower individuals to make informed decisions when venturing into outdoor environments, ultimately contributing to a safer and more enjoyable outdoor experience for both humans and their furry companions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, American dog ticks, with their distinct appearance and potential to transmit diseases, pose a significant health risk to both humans and animals. Understanding the habitats and geographic distribution of these blood-feeding parasites is crucial for individuals who frequent outdoor environments, as well as pet owners. By recognizing the specific habitats favored by American dog ticks, such as grassy areas, wooded regions, and the edges of forests, individuals can take proactive measures to minimize their exposure and reduce the risk of encountering these troublesome parasites.
The geographic distribution of American dog ticks spans a significant portion of the United States, with specific regions exhibiting higher prevalence due to environmental factors and host populations. While the eastern, central, and midwestern states are known for their higher prevalence of American dog ticks, it is important to note that these ticks can also be found in other parts of the country. As the climate and environmental conditions continue to evolve, the geographic distribution of American dog ticks may shift, impacting their presence in various regions.
To mitigate the risks associated with American dog ticks, individuals can implement effective prevention strategies, including conducting thorough tick checks, wearing protective clothing, using tick repellents, making environmental modifications, and employing tick control products for pets. These measures can significantly reduce the risk of encountering American dog ticks and minimize the potential health hazards associated with tick-borne diseases.
By staying informed about the behavior, habitats, and geographic distribution of American dog ticks, individuals can make informed decisions when venturing into outdoor environments, ultimately contributing to a safer and more enjoyable outdoor experience for both humans and their furry companions. With vigilance and proactive prevention, the risks posed by American dog ticks can be effectively managed, allowing individuals to continue enjoying the beauty of the great outdoors while safeguarding their health and the well-being of their beloved pets.