Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Why Do Ticks Bite When Dogs Take Tick Medicine

Common Health Issues
Why Do Ticks Bite When Dogs Take Tick Medicine
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn why ticks still bite dogs even when they are on tick medicine and how to address this common health issue effectively. Discover the best solutions for tick prevention and treatment.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to protecting our furry friends from pesky parasites like ticks, many pet owners turn to tick medicine as a reliable solution. However, despite the use of tick medicine, some dogs still experience tick bites. This phenomenon can be perplexing and concerning for pet owners who are dedicated to safeguarding their canine companions from the potential dangers associated with tick infestations.
Understanding the reasons behind why ticks still bite dogs on tick medicine is crucial for pet owners and veterinarians alike. By delving into the intricacies of tick medicine and the behavior of ticks, we can gain valuable insights into this perplexing occurrence. In this article, we will explore the mechanisms of tick medicine, the factors influencing tick bites on dogs receiving tick medicine, and the underlying reasons why ticks may still latch onto our canine companions despite the protective measures in place.
By shedding light on this topic, we aim to empower pet owners with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions about tick prevention and to ensure the well-being of their beloved pets. Let's embark on a journey to unravel the mystery of why ticks bite when dogs take tick medicine.
Read more: When Should Dogs Take Flea And Tick Medicine
Understanding Tick Medicine for Dogs
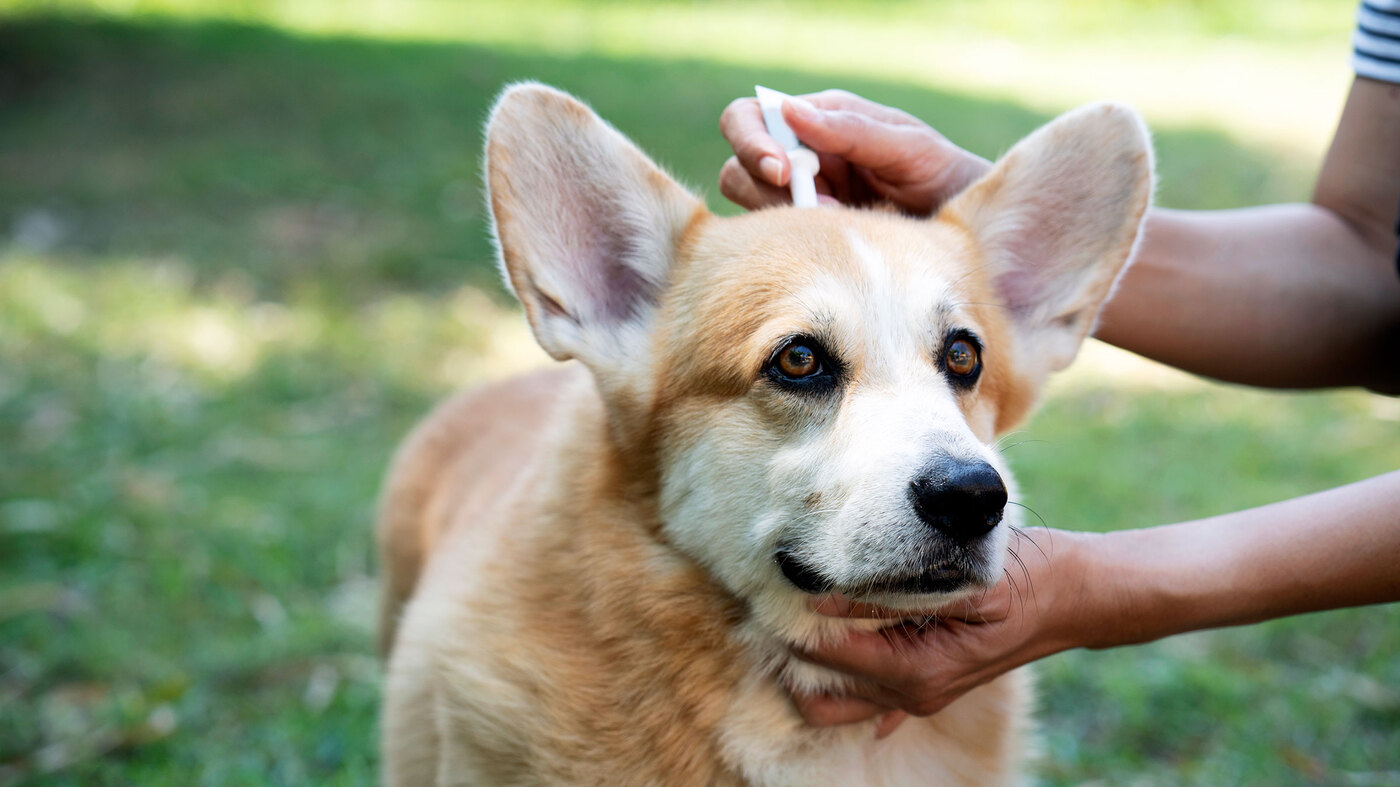
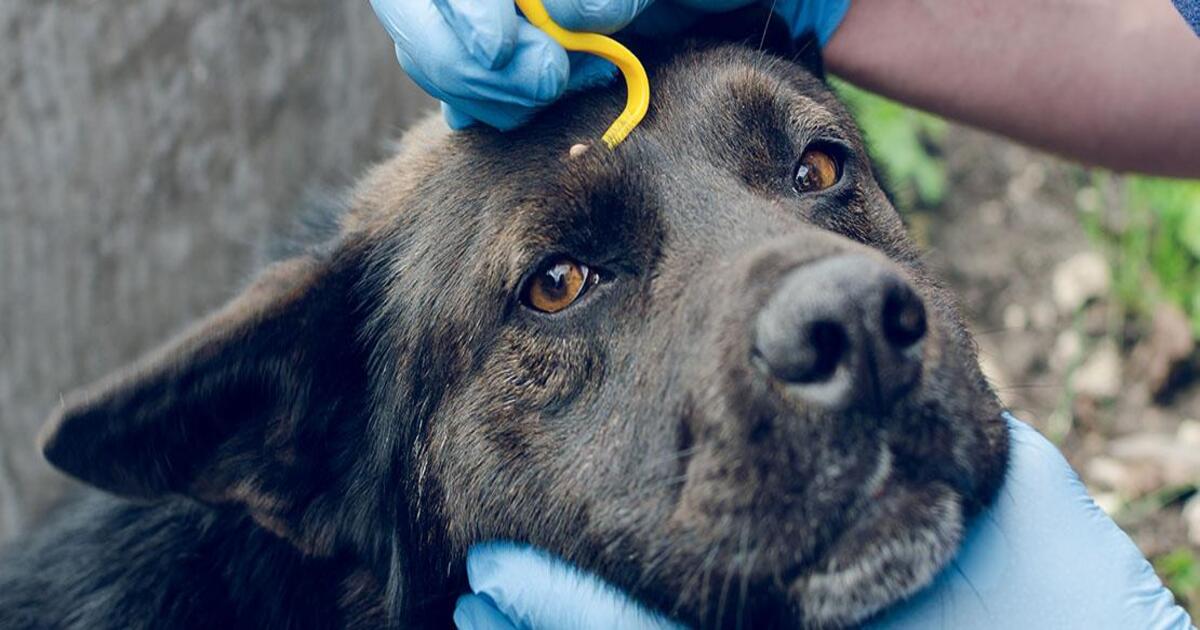
Tick medicine for dogs plays a pivotal role in safeguarding our furry companions from the perils of tick infestations. These medications are specifically formulated to repel ticks, prevent them from attaching to the dog's skin, and eliminate existing ticks. There are various forms of tick medicine available, including topical treatments, oral medications, and collars, each designed to provide effective protection against ticks.
Topical tick medications are applied directly to the dog's skin, typically between the shoulder blades, where the dog cannot lick it off. These treatments work by spreading across the skin's surface, creating a barrier that repels ticks and other parasites. Oral tick medications, on the other hand, are administered internally and work by circulating through the dog's bloodstream, effectively killing ticks upon contact. Tick collars are another popular form of tick medicine, emitting active ingredients that repel ticks and prevent infestations.
The active ingredients in tick medicine are crucial to their effectiveness. Common ingredients such as fipronil, permethrin, and fluralaner target ticks at various stages of their life cycle, disrupting their ability to feed on the dog and reproduce. These ingredients are carefully formulated to ensure the safety and well-being of the dog while effectively combating tick infestations.
It's important to note that tick medicine for dogs should be chosen based on the dog's specific needs and health considerations. Factors such as the dog's age, weight, breed, and any existing health conditions should be taken into account when selecting the most suitable tick medication. Additionally, consulting with a veterinarian is essential to determine the most appropriate tick prevention strategy for each individual dog.
By understanding the mechanisms and variations of tick medicine for dogs, pet owners can make informed decisions regarding the most suitable and effective tick prevention measures for their beloved canine companions. This knowledge empowers pet owners to take proactive steps in protecting their dogs from the potential harm posed by tick infestations, ensuring their continued health and well-being.
How Tick Medicine Works
Tick medicine for dogs operates through a multifaceted approach to combat and prevent tick infestations. These medications are designed to disrupt the life cycle of ticks, repel them from attaching to the dog's skin, and eliminate existing ticks. Understanding the mechanisms behind how tick medicine works is essential for pet owners seeking to protect their canine companions from the potential dangers posed by ticks.
The active ingredients in tick medicine play a pivotal role in its effectiveness. Commonly used ingredients such as fipronil, permethrin, and fluralaner are carefully formulated to target ticks at various stages of their life cycle. These ingredients work by interfering with the ticks' nervous system, leading to paralysis and ultimately death. Additionally, some ingredients disrupt the ticks' ability to feed on the dog, effectively preventing them from obtaining the blood meal necessary for their survival and reproduction.
Topical tick medications, when applied to the dog's skin, create a protective barrier that repels ticks and other parasites. These treatments spread across the skin's surface, forming a shield against tick infestations. Oral tick medications, when ingested by the dog, circulate through the bloodstream, effectively killing ticks upon contact. This internal approach ensures that ticks are targeted systemically, providing comprehensive protection against infestations.
Tick collars, another form of tick medicine, emit active ingredients that repel ticks and prevent infestations. These collars release the active ingredients gradually, creating a protective zone around the dog that deters ticks from latching on. This sustained release mechanism ensures long-lasting efficacy, offering continuous protection against tick infestations.
It's important to note that the effectiveness of tick medicine is not limited to killing ticks on the dog; it also plays a crucial role in preventing reinfestation. By repelling ticks and disrupting their life cycle, tick medicine helps to create an inhospitable environment for ticks, reducing the risk of infestations in the dog's living spaces.
Understanding how tick medicine works empowers pet owners to make informed decisions regarding the most suitable and effective tick prevention measures for their beloved canine companions. By leveraging the multifaceted mechanisms of tick medicine, pet owners can proactively safeguard their dogs from the potential harm posed by tick infestations, ensuring their continued health and well-being.
Why Ticks Still Bite Dogs on Tick Medicine
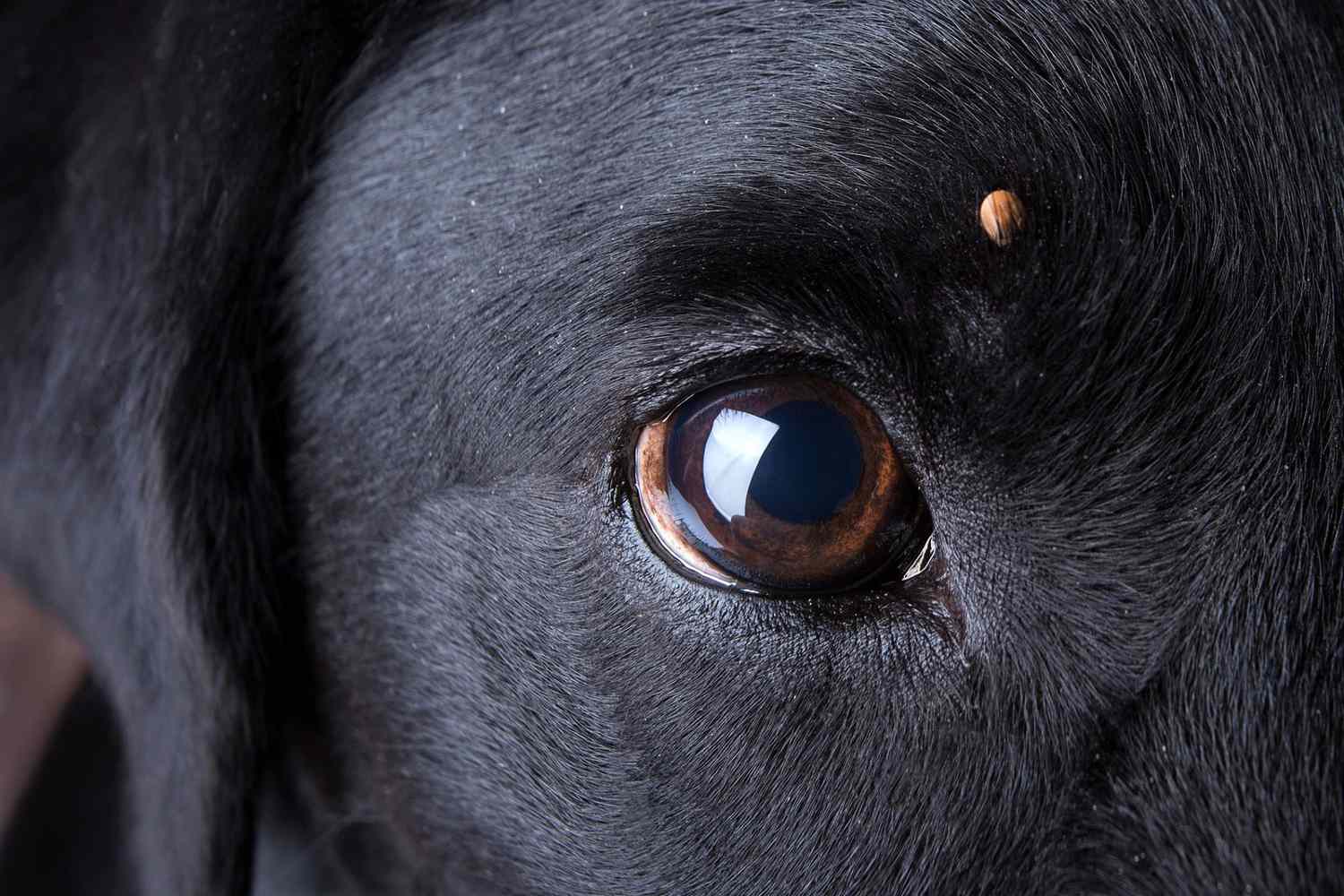
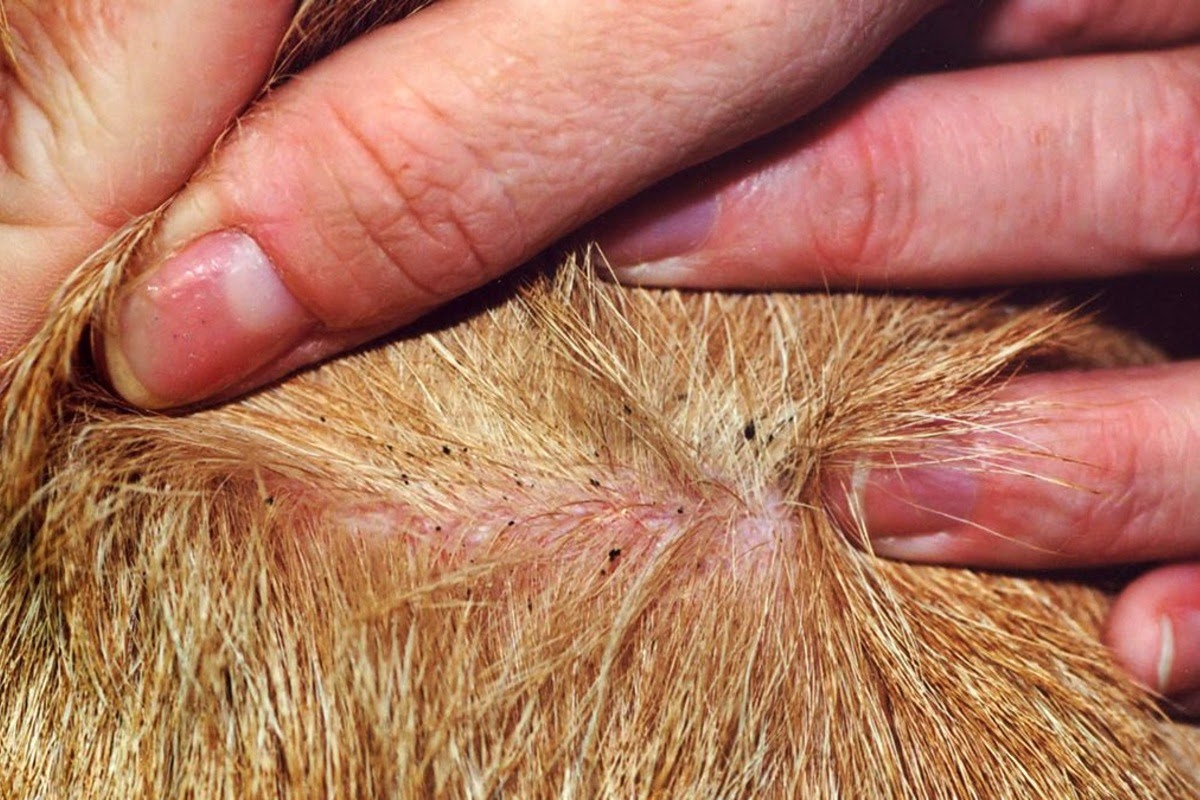
Despite the diligent use of tick medicine, some dogs may still experience tick bites, leaving pet owners perplexed and concerned. This phenomenon raises a fundamental question: why do ticks still bite dogs on tick medicine? Understanding the underlying reasons behind this occurrence is crucial for pet owners and veterinarians alike.
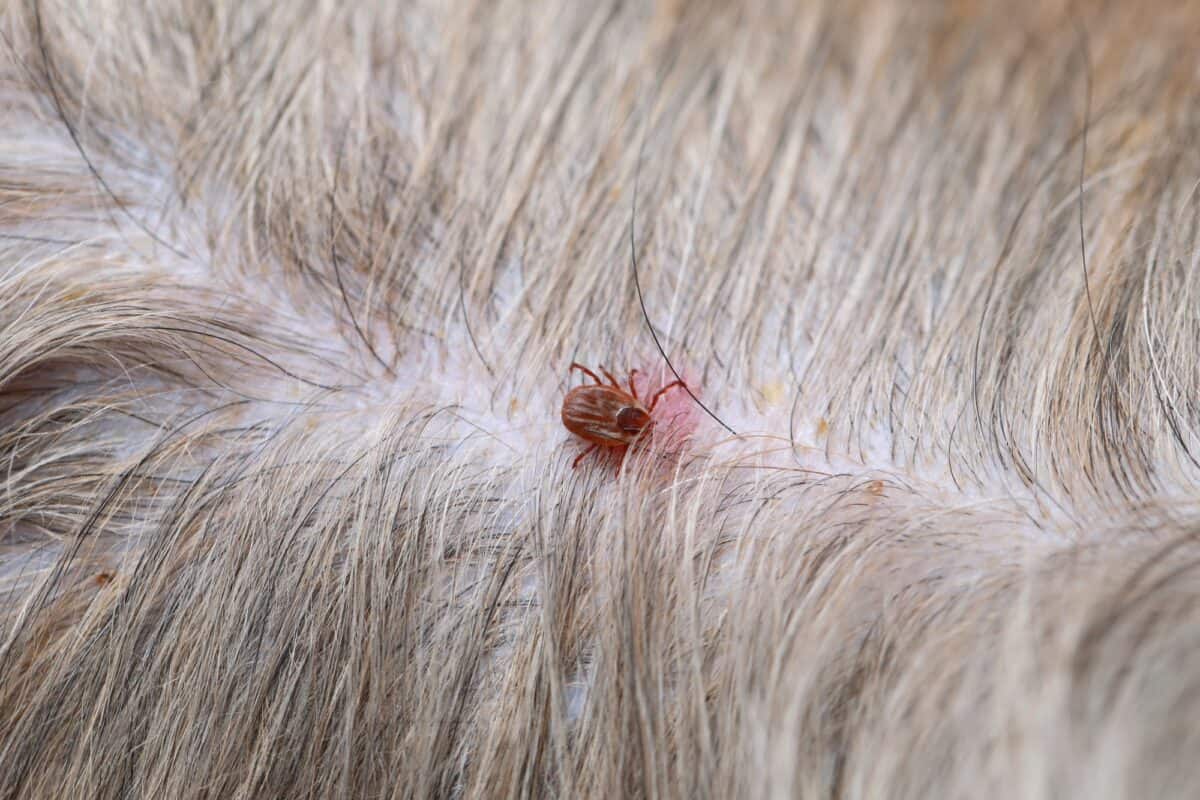
One of the primary factors contributing to ticks biting dogs on tick medicine is the persistence and adaptability of ticks. Ticks are resilient parasites with a remarkable ability to adapt to various environmental conditions and host defenses. While tick medicine is designed to repel and eliminate ticks, certain species of ticks may still manage to latch onto the dog's skin before succumbing to the effects of the medication. Additionally, ticks may encounter the dog before the tick medicine has taken full effect, leading to potential bites before the parasites are repelled or eliminated.
Furthermore, the timing of tick medicine application plays a crucial role in its effectiveness. In some cases, pet owners may inadvertently delay the application of tick medicine, leaving a window of vulnerability during which ticks can latch onto the dog. Consistent and timely application of tick medicine is essential to ensure continuous protection against tick infestations.
Another contributing factor is the potential for incomplete coverage of the dog's body with tick medicine. If the application of topical tick medication is not thorough or if the dog removes the medication by licking or grooming, certain areas of the dog's body may remain unprotected, providing an opportunity for ticks to attach and feed.
Moreover, variations in the efficacy of tick medicine products can influence the likelihood of ticks biting dogs. Different formulations and brands of tick medicine may exhibit varying degrees of effectiveness against specific tick species, potentially leaving room for some ticks to evade the protective measures.
Additionally, environmental factors, such as high tick populations in certain regions or habitats, can pose challenges even with the use of tick medicine. In areas where ticks are abundant, the risk of exposure to ticks remains elevated, increasing the likelihood of tick bites despite the use of preventive measures.
Understanding the multifaceted reasons why ticks still bite dogs on tick medicine empowers pet owners to take proactive steps in enhancing tick prevention strategies. By addressing these factors and ensuring consistent, thorough application of tick medicine, pet owners can minimize the risk of tick bites and provide comprehensive protection for their beloved canine companions.
Factors Affecting Tick Bites on Dogs with Tick Medicine
Several factors can influence the likelihood of tick bites on dogs despite the use of tick medicine. Understanding these factors is essential for pet owners seeking to optimize tick prevention strategies and ensure comprehensive protection for their beloved canine companions.
-
Tick Species and Resistance: Different species of ticks exhibit varying levels of resistance to tick medicine. Some ticks may possess genetic adaptations that render them less susceptible to certain active ingredients in tick medications. This resistance can diminish the effectiveness of tick medicine, potentially allowing resistant ticks to evade the protective measures and bite dogs.
-
Application Consistency and Thoroughness: The consistent and thorough application of tick medicine is crucial for its efficacy. Inadequate coverage or irregular application of topical treatments can create opportunities for ticks to attach and feed on untreated areas of the dog's body. Ensuring that the entire body is adequately protected with tick medicine is essential for minimizing the risk of tick bites.
-
Environmental Factors: Environmental conditions, such as high tick populations in specific regions or habitats, can pose challenges for tick prevention efforts. In areas where ticks are abundant, the risk of exposure to ticks remains elevated, increasing the likelihood of tick bites despite the use of preventive measures. Additionally, outdoor activities in wooded or grassy areas can heighten the dog's exposure to ticks, potentially leading to bites even with the use of tick medicine.
-
Tick Life Cycle and Behavior: Understanding the life cycle and behavior of ticks is crucial for effective prevention. Ticks exhibit distinct behaviors at different stages of their life cycle, and their activity levels may vary based on environmental factors. Some ticks may be more resilient or active during specific seasons, increasing the risk of encounters with dogs despite the use of tick medicine.
-
Product Efficacy and Variability: The efficacy of tick medicine products can vary based on their formulations and active ingredients. Different brands and formulations may exhibit varying degrees of effectiveness against specific tick species. It is essential for pet owners to select tick medicine products that are well-suited to the prevalent tick species in their region and to consider any variations in product efficacy when implementing tick prevention measures.
By considering these factors and taking proactive measures to address potential vulnerabilities, pet owners can enhance their tick prevention strategies and minimize the risk of tick bites on dogs receiving tick medicine. Consistent application, environmental awareness, and a thorough understanding of tick behavior and resistance can collectively contribute to comprehensive tick prevention for canine companions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the perplexing occurrence of ticks biting dogs despite the use of tick medicine underscores the multifaceted nature of tick prevention and the resilience of these parasitic pests. While tick medicine plays a crucial role in safeguarding dogs from tick infestations, several factors can contribute to the persistence of tick bites. Understanding the underlying reasons behind this phenomenon empowers pet owners to optimize their tick prevention strategies and provide comprehensive protection for their beloved canine companions.
Consistency and thoroughness in the application of tick medicine are paramount. Ensuring that the entire body of the dog is adequately protected with tick medicine, and adhering to the recommended application schedules, can significantly reduce the risk of tick bites. Additionally, environmental awareness and an understanding of regional tick populations and behaviors are essential for implementing effective tick prevention measures. By being mindful of high-risk areas and seasonal variations in tick activity, pet owners can proactively mitigate the risk of tick encounters.
Furthermore, the selection of tick medicine should be based on the prevalent tick species in the dog's environment, as well as the product's efficacy against specific ticks. Different formulations and brands of tick medicine may exhibit varying degrees of effectiveness, and pet owners should consult with veterinarians to identify the most suitable tick prevention solutions for their dogs.
While the persistence of tick bites on dogs receiving tick medicine can be concerning, it is important for pet owners to remain vigilant and proactive in their tick prevention efforts. By addressing the factors influencing tick bites and leveraging a comprehensive approach to tick prevention, pet owners can minimize the risk of tick infestations and ensure the continued health and well-being of their canine companions.
Ultimately, the well-being of our furry friends is a top priority, and by staying informed and proactive in tick prevention, pet owners can create a safe and nurturing environment for their dogs. Through a combination of consistent tick medicine application, environmental awareness, and informed decision-making, pet owners can effectively mitigate the risk of tick bites and provide their dogs with the protection they deserve.