Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How To Get Rid Of A Parasite In Dogs


Common Health Issues
How To Get Rid Of A Parasite In Dogs
Modified: March 1, 2024
Learn how to address common health issues in dogs, including how to get rid of parasites. Discover effective solutions for a healthier, happier pet.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Parasites are a common concern for dog owners, as these pesky organisms can cause a range of health issues for our beloved pets. From intestinal worms to external pests like fleas and ticks, parasites can wreak havoc on a dog's well-being if left unchecked. As responsible pet owners, it's crucial to understand the risks associated with parasite infestations and take proactive measures to protect our furry companions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of parasites in dogs, exploring the signs and symptoms of infestation, common types of parasites, preventive measures, treatment options, and natural remedies. By gaining a deeper understanding of these topics, you'll be better equipped to safeguard your dog's health and provide the care they deserve.
Stay tuned as we unravel the complexities of parasite infestations in dogs, empowering you with the knowledge to identify, prevent, and address these common health concerns. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to ensure the well-being of our canine friends.
Read more: How To Get Rid Of Fleas In A Dog Pen
Understanding Parasites in Dogs
Parasites are organisms that live on or inside another organism, known as the host, and derive nutrients at the host's expense. In the case of dogs, parasites can cause a myriad of health issues, ranging from mild discomfort to severe illnesses. Understanding the nature of these parasites is crucial for dog owners to effectively protect their pets from infestations.
Parasites that commonly affect dogs can be broadly categorized into internal and external parasites. Internal parasites, such as roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, and tapeworms, reside within the dog's body, often in the gastrointestinal tract. These parasites can cause symptoms like diarrhea, weight loss, and anemia, and in severe cases, they may even lead to life-threatening complications.
On the other hand, external parasites, including fleas, ticks, and mites, infest the dog's skin and fur. These parasites not only cause discomfort and skin irritation but also transmit diseases such as Lyme disease and ehrlichiosis. Additionally, mosquitoes, which are vectors for heartworm disease, pose a significant threat to dogs in many regions.
Understanding the life cycles of different parasites is essential for effective prevention and treatment. For instance, knowing that fleas have a complex life cycle involving eggs, larvae, pupae, and adult stages can help dog owners implement targeted control measures at each stage to break the cycle of infestation.
Moreover, certain parasites, such as ticks and mosquitoes, are more prevalent during specific seasons or in particular geographic regions. Being aware of these environmental factors can aid in devising a tailored parasite prevention strategy based on the dog's lifestyle and the prevalent parasites in their surroundings.
By comprehending the diverse nature of parasites that can afflict dogs, pet owners can proactively take steps to minimize the risk of infestation and protect their canine companions from the associated health complications. This knowledge forms the foundation for implementing preventive measures and seeking timely veterinary care to ensure the overall well-being of dogs.
Signs and Symptoms of Parasite Infestation
Detecting the signs and symptoms of parasite infestation in dogs is crucial for timely intervention and effective management of these health concerns. While the specific indicators may vary depending on the type of parasite involved, there are several common manifestations that dog owners should be vigilant about.
Internal Parasites:
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Dogs infested with internal parasites may exhibit symptoms such as diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort. Persistent gastrointestinal issues, especially when accompanied by changes in appetite and weight loss, could signal the presence of worms or other internal parasites.
- Anemia: Certain internal parasites, particularly hookworms, can cause anemia in dogs, leading to pale gums, weakness, and lethargy. Anemic dogs may also display reduced stamina and exercise intolerance.
- Visible Worms in Stool: In some cases, segments of tapeworms or adult worms may be visible in the dog's feces, indicating an active infestation.
External Parasites:
- Skin Irritation and Scratching: Fleas, ticks, and mites can cause intense itching and skin irritation in dogs. Constant scratching, biting, or licking of the skin, particularly in localized areas, may indicate the presence of external parasites.
- Hair Loss and Skin Lesions: Infestations with external parasites can lead to hair loss, redness, and the formation of skin lesions. These visible changes in the dog's coat and skin should prompt a closer examination for the presence of fleas, ticks, or mites.
- Presence of Parasites: Direct observation of fleas, ticks, or mites on the dog's fur or skin is a clear indication of infestation and warrants immediate attention.
Read more: How To Get Rid Of Fleas And Ticks On My Dog
General Indicators:
- Lethargy and Weakness: Dogs suffering from parasite infestations may exhibit lethargy, weakness, and a lack of energy. A noticeable decrease in activity levels and reluctance to engage in regular physical activities can be indicative of underlying health issues related to parasites.
- Changes in Appetite: Parasite infestations can impact a dog's appetite, leading to decreased food intake or, in some cases, increased hunger due to the body's efforts to combat the parasites' drain on nutrients.
Recognizing these signs and symptoms of parasite infestation empowers dog owners to promptly seek veterinary care and implement appropriate measures to address the underlying issues. Regular monitoring for these indicators, coupled with preventive measures, can significantly contribute to maintaining the health and well-being of dogs, ensuring they lead happy and active lives free from the burdens of parasitic infestations.
Common Types of Parasites in Dogs
Intestinal Worms
Intestinal worms are a prevalent concern for dogs, with several species posing health risks. Roundworms, also known as ascarids, are among the most common intestinal parasites in dogs. These worms can cause digestive disturbances, stunted growth in puppies, and, in severe cases, intestinal blockages. Hookworms, another type of intestinal parasite, feed on the dog's blood, leading to anemia and potentially life-threatening complications, especially in young or debilitated dogs. Whipworms and tapeworms are additional intestinal parasites that can affect dogs, causing symptoms such as diarrhea, weight loss, and nutritional deficiencies.
Fleas
Fleas are notorious external parasites that infest dogs, causing intense itching, skin irritation, and allergic reactions. These tiny, agile insects reproduce rapidly and can quickly establish infestations in the dog's environment. Flea bites can lead to dermatitis and discomfort, and in some cases, dogs may develop flea allergy dermatitis, characterized by severe itching and skin inflammation. Additionally, fleas can transmit tapeworms when ingested by the dog, further complicating the infestation.
Read more: How To Get Rid Of Dog Fleas And Lice
Ticks
Ticks are external parasites that pose significant health risks to dogs. These blood-feeding arachnids can transmit various diseases, including Lyme disease, ehrlichiosis, and Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Dogs infested with ticks may exhibit symptoms such as fever, joint pain, and lethargy. Prompt removal of ticks and preventive measures, such as using tick-repellent products, are essential for protecting dogs from the potential consequences of tick infestations.
Heartworms
Heartworm disease, caused by the parasitic worm Dirofilaria immitis, is a serious and potentially fatal condition in dogs. Transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes, heartworm larvae migrate to the dog's heart and lungs, leading to respiratory distress, heart failure, and other severe complications. Prevention through regular administration of heartworm preventives is crucial, as treatment for established heartworm infections can be complex and risky.
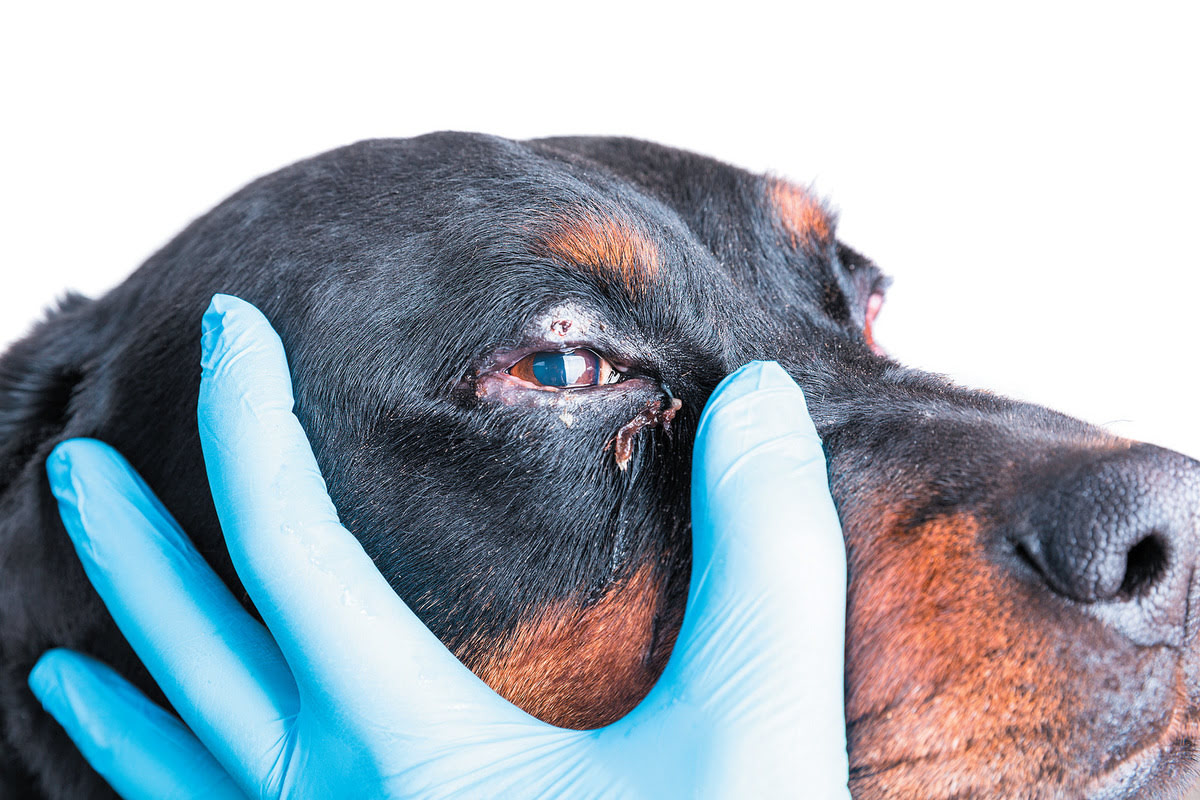
Ear Mites
Ear mites are common parasites that infest the ear canals of dogs, causing irritation, itching, and discomfort. Dogs with ear mite infestations may frequently shake their heads or scratch at their ears. If left untreated, ear mite infestations can lead to secondary ear infections and exacerbate the dog's discomfort. Regular ear examinations and prompt treatment of ear mite infestations are essential for maintaining the ear health of dogs.
Sarcoptic Mange Mites
Sarcoptic mange, or scabies, is a skin condition caused by infestations of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. Dogs affected by sarcoptic mange may experience intense itching, hair loss, and skin inflammation. The relentless scratching associated with sarcoptic mange can lead to self-inflicted injuries and secondary bacterial infections. Timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment are crucial for managing sarcoptic mange infestations and alleviating the dog's discomfort.
By familiarizing themselves with these common types of parasites that can affect dogs, pet owners can proactively implement preventive measures and seek timely veterinary care to safeguard their canine companions from the detrimental effects of parasitic infestations.
Prevention of Parasite Infestation
Preventing parasite infestations in dogs is a fundamental aspect of responsible pet ownership. By implementing proactive measures and adhering to preventive protocols, dog owners can significantly reduce the risk of their pets falling victim to the detrimental effects of parasites. Here are essential strategies for preventing parasite infestations in dogs:
Regular Veterinary Care:
Scheduling routine veterinary examinations is crucial for maintaining the overall health of dogs and preventing parasite infestations. Veterinarians can conduct comprehensive wellness checks and recommend appropriate preventive measures based on the dog's lifestyle, geographic location, and specific risk factors. Regular check-ups also facilitate early detection of any potential parasite-related issues, enabling prompt intervention.
Parasite Control Products:
Utilizing veterinarian-recommended parasite control products, such as monthly flea and tick preventives, heartworm preventives, and deworming medications, is essential for comprehensive parasite protection. These products are available in various formulations, including topical treatments, oral medications, and collars, offering flexibility and convenience for dog owners. Selecting the right products tailored to the dog's needs and adhering to the prescribed dosing schedules are critical for effective parasite prevention.
Environmental Management:
Maintaining a clean and hygienic living environment for dogs is pivotal in preventing parasite infestations. Regularly cleaning and vacuuming the indoor spaces, washing the dog's bedding, and implementing environmental control measures can help minimize the presence of fleas, ticks, and other parasites in the dog's surroundings. Additionally, practicing proper waste disposal and minimizing exposure to areas with high parasite prevalence contribute to a healthier living environment for dogs.
Preventive Measures for Outdoor Activities:
Dogs that spend time outdoors, whether for walks, hikes, or playtime, are susceptible to encountering parasites. Implementing preventive measures such as using tick-repellent products, avoiding areas with known parasite infestations, and conducting thorough post-outdoor activity checks for ticks and other external parasites can help mitigate the risk of infestation. Furthermore, minimizing contact with wildlife and stray animals reduces the likelihood of exposure to parasites.
Hygiene and Grooming Practices:
Regular grooming and hygiene practices play a vital role in preventing external parasite infestations. Maintaining a consistent grooming routine, including bathing with veterinarian-approved shampoos, brushing the dog's coat, and inspecting the skin for any signs of parasites, contributes to early detection and prevention. Additionally, keeping the dog's ears clean and dry helps prevent ear mite infestations and related ear health issues.
By integrating these preventive strategies into their care routines, dog owners can effectively shield their pets from the perils of parasite infestations. Proactive prevention not only safeguards the health and well-being of dogs but also fosters a harmonious and fulfilling bond between pets and their devoted owners.
Treatment Options for Parasite Infestation
When a dog is diagnosed with a parasite infestation, prompt and effective treatment is essential to alleviate the pet's discomfort and prevent the escalation of health complications. The choice of treatment options depends on the type of parasite involved, the severity of the infestation, and the dog's overall health status. Here are the primary treatment options for addressing parasite infestations in dogs:
Deworming Medications:
For internal parasite infestations, such as roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, and tapeworms, deworming medications are commonly prescribed. These medications are designed to target and eliminate the parasites residing within the dog's gastrointestinal tract. Dewormers may come in various formulations, including oral tablets, liquids, or injectables, and are administered based on the specific parasite species and the dog's weight. It's crucial to follow the veterinarian's dosage instructions and complete the full course of treatment to ensure the effective eradication of internal parasites.
Flea and Tick Control Products:
External parasite infestations, particularly fleas and ticks, necessitate the use of specialized control products. Topical spot-on treatments, oral medications, and collars formulated to repel or eliminate fleas and ticks are commonly recommended. These products work by disrupting the parasites' life cycles, killing adult fleas and ticks, and preventing reinfestation. Regular application of flea and tick control products, as directed by the veterinarian, is vital for sustained protection against these external parasites.
Heartworm Treatment:
In cases of heartworm infestations, treatment protocols are more complex and may involve multiple stages. The primary goal of heartworm treatment is to eliminate the adult heartworms residing in the dog's heart and pulmonary arteries. Treatment typically includes a series of injections administered under the supervision of a veterinarian. Additionally, strict rest and activity restrictions may be imposed to minimize the risk of complications during and after the treatment process. Following treatment, preventive measures are crucial to protect the dog from future heartworm infestations.
Medications for Ear and Skin Parasites:
Parasitic infestations affecting the ears, such as ear mites, and the skin, such as sarcoptic mange mites, require targeted medications to address the specific parasites. Ear mite treatments may include ear drops or topical medications to eliminate the mites and alleviate the associated irritation. Similarly, sarcoptic mange infestations may necessitate medicated shampoos, dips, or oral medications to combat the mites and soothe the dog's skin.
Supportive Care and Monitoring:
In addition to specific parasite-targeted treatments, supportive care measures, such as nutritional support, hydration, and symptomatic relief, may be recommended to aid the dog's recovery. Regular monitoring by the veterinarian to assess the treatment's effectiveness, evaluate the dog's response, and detect any potential complications is integral to ensuring the successful resolution of parasite infestations.
By leveraging these treatment options in conjunction with veterinary guidance, dog owners can effectively combat parasite infestations and restore their pets' health and vitality. Timely intervention, adherence to treatment protocols, and ongoing preventive measures are pivotal in safeguarding dogs from the detrimental effects of parasitic infestations, allowing them to thrive in a safe and parasite-free environment.
Read more: How To Naturally Get Rid Of Fleas From A Dog
Natural Remedies for Parasite Infestation
In addition to conventional treatments, natural remedies can complement the management of parasite infestations in dogs. While these remedies may not entirely replace prescribed medications, they can offer supportive benefits and contribute to the overall well-being of the dog. It's important to consult with a veterinarian before implementing natural remedies to ensure they are safe and appropriate for the specific parasite infestation and the dog's health status.
Herbal Supplements:
Certain herbal supplements are known for their potential to deter parasites and support the dog's immune system. For instance, garlic, when used in controlled amounts, is believed to have natural anti-parasitic properties. However, it's crucial to exercise caution with garlic, as excessive consumption can be toxic to dogs. Other herbs such as wormwood, clove, and neem are also recognized for their potential anti-parasitic effects and may be incorporated into the dog's diet under veterinary guidance.
Diatomaceous Earth:
Food-grade diatomaceous earth, composed of fossilized remains of diatoms, is a natural substance that can be used to combat external parasites such as fleas and ticks. When applied to the dog's coat, diatomaceous earth acts by dehydrating and disrupting the exoskeleton of these parasites, ultimately leading to their demise. It's important to use diatomaceous earth specifically labeled as safe for pets and to follow application guidelines to prevent inhalation.
Probiotics:
Maintaining a healthy gut flora through the use of probiotics can support the dog's digestive health and potentially aid in combating certain types of internal parasites. Probiotic supplements containing beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium can contribute to a balanced intestinal environment, potentially reducing the susceptibility to certain parasitic infestations. Additionally, probiotics may help mitigate the gastrointestinal disturbances associated with parasite infestations.
Read more: How To Get Rid Of Fleas On My Cat And Dog
Essential Oils:
Certain essential oils, when used cautiously and in diluted forms, may offer natural repellent properties against external parasites. Oils such as cedarwood, lavender, and peppermint are known for their potential to deter fleas and ticks. However, it's imperative to use essential oils sparingly and with careful dilution, as dogs can be sensitive to concentrated forms of these oils. Additionally, some essential oils are toxic to dogs and should be avoided altogether.
Nutritional Support:
A balanced and nutritious diet plays a crucial role in supporting the dog's overall health and immune function, which can aid in combating parasite infestations. Incorporating high-quality, species-appropriate food, rich in essential nutrients and immune-supporting ingredients, can contribute to the dog's resilience against parasites. Additionally, certain dietary supplements, such as omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E, may offer anti-inflammatory and immune-modulating benefits.
By integrating these natural remedies into a comprehensive parasite management plan, dog owners can potentially enhance the effectiveness of conventional treatments and promote the well-being of their pets. However, it's essential to approach natural remedies with prudence and seek professional guidance to ensure their safety and suitability for the individual dog's needs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, safeguarding our canine companions from the perils of parasite infestations is a fundamental aspect of responsible pet ownership. By gaining a deeper understanding of the diverse parasites that can afflict dogs, recognizing the signs and symptoms of infestations, and implementing proactive preventive measures, we can significantly mitigate the risks and protect our pets' well-being.
From intestinal worms to external pests like fleas, ticks, and mites, parasites can pose a range of health threats to dogs. Understanding the nature of these parasites and their life cycles empowers us to tailor preventive strategies based on our dogs' specific needs and environmental factors. By prioritizing regular veterinary care, utilizing parasite control products, and maintaining a clean living environment, we can create a robust defense against potential infestations.
In the event of a parasite infestation, timely intervention and effective treatment are paramount. Deworming medications, flea and tick control products, and targeted treatments for heartworms, ear mites, and skin parasites play pivotal roles in alleviating the dog's discomfort and restoring their health. Additionally, natural remedies, when used prudently and under veterinary guidance, can complement conventional treatments and contribute to the overall well-being of our pets.
By integrating these insights and strategies into our approach to canine care, we can create a safe and nurturing environment where our dogs can thrive free from the burdens of parasitic infestations. Our commitment to their well-being, coupled with proactive measures and informed decision-making, ensures that our beloved canine companions lead healthy, active, and fulfilling lives.
As we embark on this journey of responsible pet ownership, let us continue to prioritize the health and happiness of our dogs, standing as steadfast guardians against the threats posed by parasites. Through knowledge, vigilance, and unwavering dedication, we can create a harmonious and parasite-free environment where our dogs can flourish as cherished members of our families.