Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>Why Does My Dog Lick My Other Dog’s Eye


Eye and Ear Health
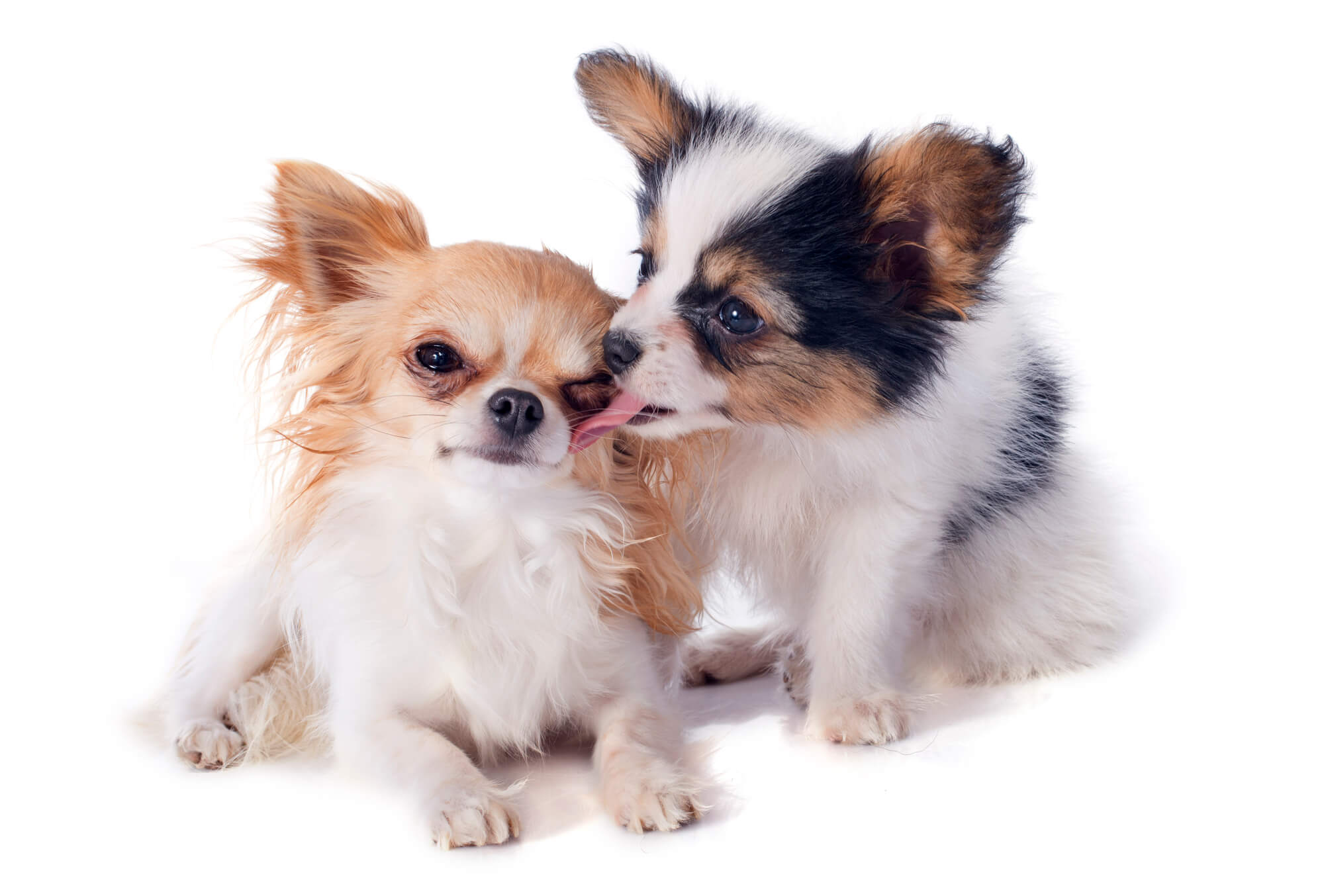
Why Does My Dog Lick My Other Dog’s Eye
Published: February 13, 2024
Learn why dogs lick each other's eyes and how it relates to their eye and ear health. Understand the reasons behind this behavior and how to ensure your dogs' eye and ear health.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
As a dog owner, you may have observed some peculiar behaviors in your furry companions. One such behavior that often raises eyebrows is when one dog licks the eyes of another. This seemingly unusual act can prompt a range of questions and concerns. Why does it happen? Is it a cause for worry? Understanding the reasons behind this behavior is crucial for ensuring the well-being of your canine friends. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of canine behavior and explore the various factors that may lead to one dog licking another's eyes. From social dynamics to potential medical implications, we will unravel the mysteries behind this behavior and provide insights into how to address it. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey to gain a deeper understanding of why dogs engage in the curious act of licking each other's eyes.
Read more: Why Does My Senior Dog Lick So Much?
Understanding Canine Behavior
Understanding canine behavior is essential for deciphering the intricate ways in which dogs communicate and interact with one another. Dogs are social animals with a rich and complex set of behaviors that are deeply rooted in their evolutionary history and pack dynamics.
Canine behavior is heavily influenced by their ancestry as pack animals. In the wild, dogs rely on a sophisticated system of body language, vocalizations, and actions to convey messages and maintain social order within their packs. This intricate communication system is ingrained in their DNA and continues to shape their behavior in domestic settings.
One fundamental aspect of canine behavior is their inclination towards social bonding and hierarchy establishment. Dogs form close-knit social structures within their packs, and this social cohesion is maintained through various behaviors, including grooming, playing, and, notably, licking. Licking is a multifaceted behavior that serves as a means of communication, affection, and social bonding among dogs.
Furthermore, dogs are highly attuned to non-verbal cues and sensory information. They rely on their acute sense of smell, taste, and touch to interpret the world around them and communicate with their fellow pack members. Licking, including licking of the eyes, is a form of tactile communication that conveys a range of messages, from affection and reassurance to submission and respect within the pack hierarchy.
In addition to social dynamics, canine behavior is also influenced by individual personalities, past experiences, and environmental factors. Each dog has its own unique temperament and behavioral tendencies, which can shape their interactions with other dogs. Understanding these nuances is crucial for interpreting the motivations behind specific behaviors, such as eye licking, and addressing them effectively.
By delving into the intricacies of canine behavior, we gain valuable insights into the motivations and meanings behind their actions. This understanding forms the foundation for addressing and managing various behaviors, including the intriguing phenomenon of one dog licking another's eyes. As we continue our exploration, we will uncover the specific reasons why dogs engage in this behavior and how it can be approached from both a behavioral and medical standpoint.
Reasons for Eye Licking
Dogs engage in a myriad of behaviors to communicate, bond, and navigate their social dynamics. When it comes to the act of licking another dog's eyes, several compelling reasons underpin this intriguing behavior. Understanding these motivations is essential for interpreting the underlying messages and addressing any potential concerns. Let's explore the diverse reasons why dogs may exhibit eye licking behavior:
-
Social Bonding and Affection: Licking, including licking of the eyes, is a common expression of affection and social bonding among dogs. It serves as a tactile form of communication that conveys warmth, reassurance, and a sense of belonging. When one dog licks another's eyes, it can be a display of affection and a way to strengthen their social connection.
-
Grooming and Hygiene: Dogs are naturally inclined to engage in grooming behaviors to maintain cleanliness and hygiene within their pack. Licking, particularly around the facial area, is a way for dogs to assist in grooming each other. By licking the eyes, dogs may be exhibiting a grooming behavior aimed at removing debris, tear stains, or foreign particles from the eye area of their fellow canine companion.
-
Submission and Respect: In the intricate hierarchy of pack dynamics, submissive behaviors play a crucial role in maintaining social order. Licking, including licking of the eyes, can be a submissive gesture aimed at showing deference and respect to a higher-ranking or dominant dog. This act of submission helps reinforce the pack hierarchy and minimize potential conflicts.
-
Stress Relief and Comfort: Dogs may engage in licking behaviors, including licking the eyes of another dog, as a means of seeking comfort and alleviating stress. The act of licking releases endorphins, which can have a calming effect on both the licker and the recipient. In situations of anxiety or tension, dogs may resort to licking as a self-soothing mechanism, and this behavior can extend to comforting their fellow pack members.
-
Communication and Signaling: Licking, particularly in the sensitive area around the eyes, can serve as a form of communication and signaling among dogs. It can convey messages of reassurance, empathy, and a desire for mutual understanding. Dogs rely on tactile cues to convey their emotions and intentions, and licking the eyes can be a subtle yet powerful way to communicate within their social group.
By unraveling the multifaceted reasons behind eye licking behavior, we gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of canine communication and social dynamics. These insights pave the way for effectively addressing and managing this behavior, whether it stems from affectionate bonding, grooming instincts, social hierarchy, stress relief, or nuanced forms of communication. As we delve further into this exploration, we will delve into the potential medical concerns associated with eye licking and strategies for addressing this behavior.
Social and Pack Behavior
Social and pack behavior plays a pivotal role in shaping the interactions and dynamics among dogs. Dogs are inherently social animals with a strong inclination towards forming cohesive groups, or packs, which are governed by a complex set of social rules and hierarchies. Within these packs, dogs engage in a wide array of behaviors aimed at maintaining social order, fostering bonds, and communicating with one another.
One of the fundamental aspects of social behavior in dogs is the establishment of a hierarchical structure within the pack. This hierarchy is characterized by dominant and submissive roles, with each dog occupying a specific position based on their assertiveness, confidence, and interactions with other pack members. The intricate dance of dominance and submission is woven into the fabric of canine social dynamics, shaping their interactions and behaviors, including the act of licking each other's eyes.
In the context of social and pack behavior, the act of one dog licking another's eyes can be deeply rooted in the dynamics of dominance and submission. Dogs may engage in eye licking as a submissive gesture, acknowledging the authority and status of the recipient. By offering this display of deference, the licking dog reaffirms the existing pack hierarchy and minimizes potential conflicts within the group.
Furthermore, eye licking can also serve as a means of reinforcing social bonds and strengthening the cohesion of the pack. Dogs rely on tactile communication to convey emotions, establish connections, and foster a sense of unity within the group. When one dog licks another's eyes, it can be a gesture of affection and solidarity, fostering a deeper sense of camaraderie and mutual understanding among pack members.
In addition to hierarchical dynamics and social bonding, the act of licking another dog's eyes can also be a manifestation of grooming behavior within the pack. Grooming plays a vital role in maintaining hygiene and cleanliness, and dogs often engage in mutual grooming as a way of caring for one another. By licking the eyes of their fellow pack members, dogs may be participating in a grooming ritual aimed at removing debris, soothing irritations, and fostering a sense of well-being within the group.
Understanding the intricate interplay of dominance, submission, bonding, and grooming within the context of social and pack behavior provides valuable insights into the motivations behind eye licking among dogs. These behaviors are deeply ingrained in their evolutionary heritage as pack animals and continue to shape their interactions in domestic settings. By recognizing the significance of social and pack behavior, we gain a deeper appreciation for the complexities of canine communication and social dynamics, laying the groundwork for effectively addressing and managing eye licking behavior among dogs.
Medical Concerns
While the act of one dog licking another's eyes can often be attributed to social bonding, grooming, and communication within the pack, it's essential to consider potential medical concerns associated with this behavior. The delicate nature of the eyes and the potential implications of excessive or prolonged licking warrant careful attention from dog owners and caregivers.
One of the primary medical concerns related to eye licking behavior is the risk of introducing harmful bacteria or irritants into the recipient dog's eyes. Dogs' tongues, while serving as a grooming tool, can harbor bacteria and microorganisms that may pose a risk when in contact with the sensitive ocular area. This can lead to eye infections, irritations, or other ocular issues, especially if the recipient dog has pre-existing eye conditions or a compromised immune system.
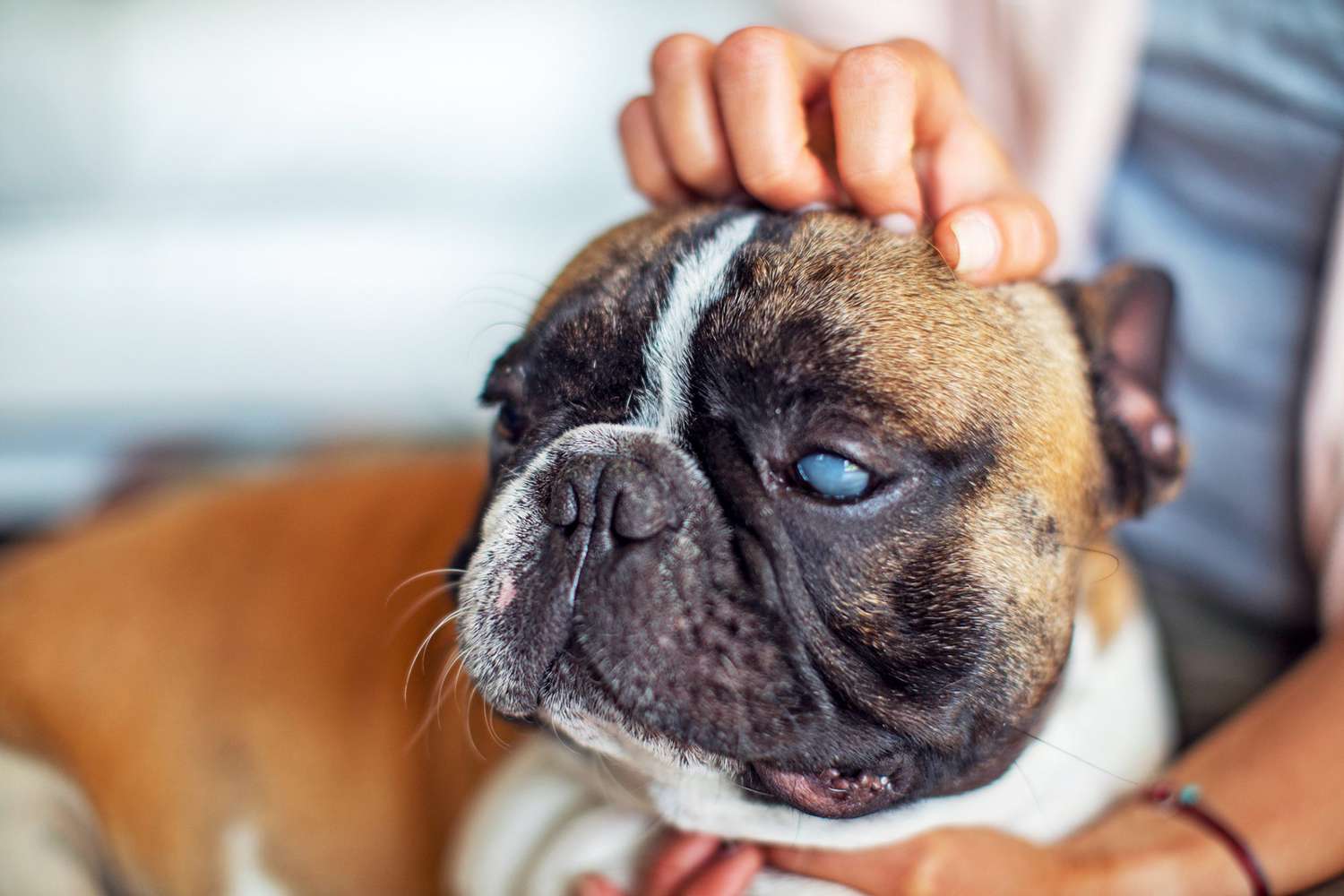
Furthermore, excessive licking of the eyes can result in mechanical irritation and trauma to the delicate tissues surrounding the eyes. The constant moisture and friction from licking can lead to inflammation, redness, and potential abrasions, predisposing the affected dog to discomfort and potential secondary infections. Additionally, dogs with protruding eyes, such as brachycephalic breeds, may be particularly susceptible to mechanical trauma from excessive licking due to the anatomical characteristics of their eye structures.
In some cases, persistent eye licking behavior may be indicative of underlying medical conditions in the licking dog, such as allergies, skin irritations, or ocular discomfort. Dogs may resort to licking as a self-soothing mechanism in response to itching, pain, or discomfort in the eye area. Identifying and addressing the root cause of the licking behavior is crucial for ensuring the overall well-being of both the licking dog and the recipient.
Moreover, certain systemic health issues, such as gastrointestinal disturbances or dietary sensitivities, can manifest as compulsive licking behaviors in dogs. Addressing these underlying health concerns is essential for mitigating the behavioral manifestations and promoting holistic wellness in canine companions.
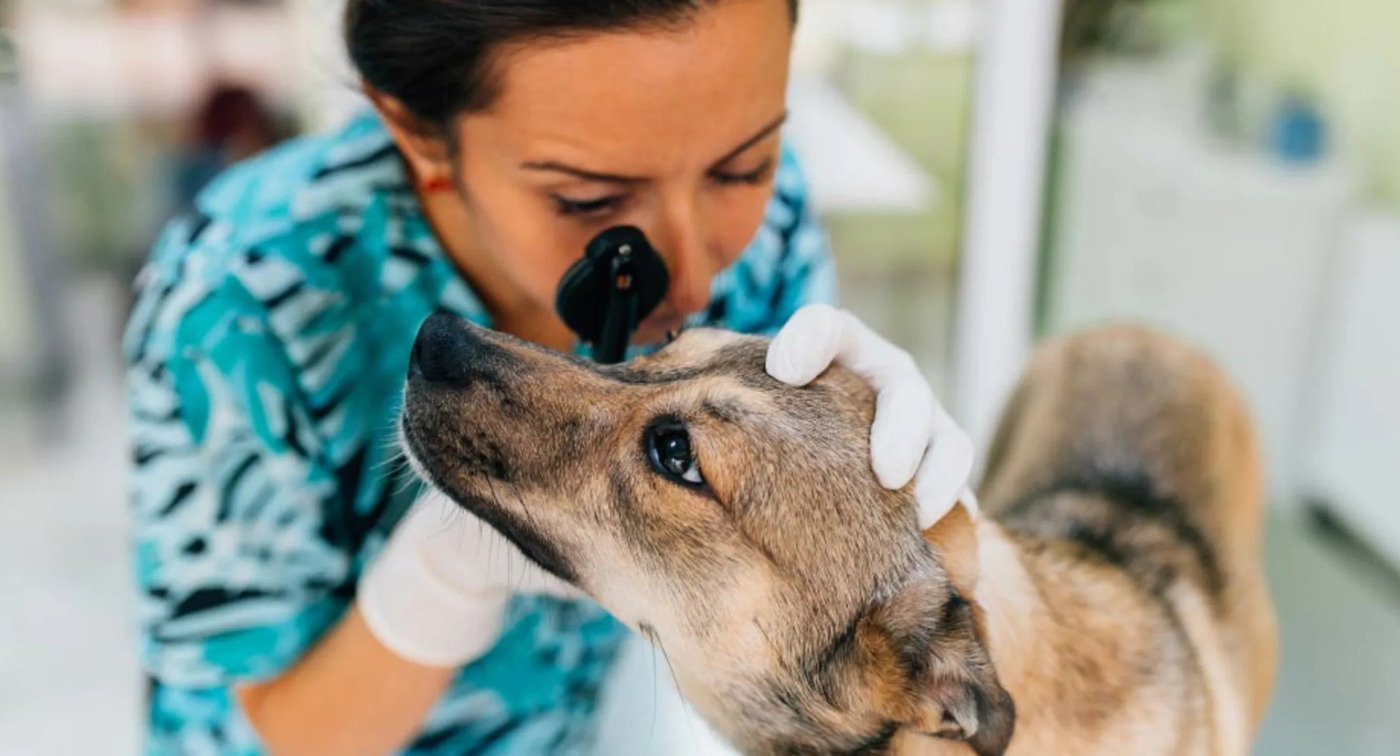
As responsible pet owners, it is imperative to monitor and assess the frequency and intensity of eye licking behavior among dogs. Any signs of ocular irritation, redness, discharge, or discomfort should prompt a thorough veterinary evaluation to rule out potential medical issues and ensure appropriate care for the affected dogs.
By acknowledging the potential medical concerns associated with eye licking behavior, dog owners can take proactive measures to safeguard their pets' ocular health and well-being. This awareness underscores the importance of a holistic approach to canine care, encompassing both behavioral and medical considerations to promote the optimal health and happiness of our beloved canine companions.
Read more: Why Does My Dog Have A Bump By Her Eye
How to Address Eye Licking Behavior
Addressing eye licking behavior in dogs requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses both behavioral interventions and attentive care. By understanding the underlying motivations and potential implications of this behavior, dog owners can implement effective strategies to manage and address eye licking in their canine companions.
-
Behavioral Modification: Employing positive reinforcement techniques and redirection strategies can help modify the behavior of the licking dog. By rewarding alternative, desirable behaviors and redirecting their attention towards interactive toys, puzzles, or engaging activities, dog owners can effectively discourage excessive eye licking. Consistency and patience are key in implementing behavioral modifications, and gradual progress can be achieved through persistent training and reinforcement.
-
Environmental Enrichment: Enriching the living environment of dogs can alleviate stress and boredom, which are common triggers for compulsive licking behaviors. Providing ample opportunities for physical exercise, mental stimulation, and social interaction can help channel their energy in constructive ways, reducing the likelihood of engaging in excessive licking. Interactive toys, puzzle feeders, and regular playtime can contribute to a fulfilling and enriching environment for dogs.
-
Ocular Care and Monitoring: Regularly monitoring the ocular health of both the licking dog and the recipient is essential. Keeping the eyes clean, free from debris, and ensuring optimal ocular hygiene can mitigate the risk of ocular irritations and infections. Additionally, seeking veterinary guidance for appropriate ocular care products and preventive measures can contribute to maintaining ocular health in dogs.
-
Veterinary Evaluation: If the eye licking behavior persists or is accompanied by signs of ocular discomfort or irritation, seeking a comprehensive veterinary evaluation is imperative. A thorough examination by a veterinarian can help identify any underlying medical issues, ocular conditions, or systemic health concerns that may be contributing to the behavior. Addressing these underlying factors is crucial for devising an effective management plan.
-
Nutritional and Health Considerations: Ensuring a balanced and nutritious diet, tailored to the specific needs of individual dogs, is essential for promoting overall well-being and addressing potential underlying health issues. Dietary sensitivities, allergies, or nutritional deficiencies can manifest as compulsive behaviors, including excessive licking. Consulting with a veterinarian to optimize the dog's diet and address any nutritional concerns is integral to holistic care.
-
Professional Behavioral Consultation: In cases where the eye licking behavior persists despite behavioral interventions, seeking guidance from a certified professional dog behaviorist or trainer can provide valuable insights and tailored strategies for addressing the behavior. Professional consultation can offer personalized behavioral modification plans and support for dog owners navigating challenging behavioral issues.
By integrating these proactive measures and tailored interventions, dog owners can effectively address and manage eye licking behavior in their canine companions, promoting their overall well-being and fostering harmonious interactions within the pack dynamic. Understanding the nuanced interplay of behavioral, environmental, and medical factors is pivotal in devising a comprehensive approach to addressing and mitigating eye licking behavior in dogs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the act of one dog licking another's eyes is a fascinating behavior deeply rooted in the intricate tapestry of canine communication, social dynamics, and pack behavior. Through our exploration, we have gained valuable insights into the multifaceted reasons behind this behavior, encompassing social bonding, grooming instincts, hierarchical dynamics, stress relief, and nuanced forms of communication. Dogs rely on tactile cues and sensory communication to convey emotions, establish connections, and navigate their social world, with eye licking serving as a tangible expression of their complex social interactions.
While the behavior of eye licking among dogs is often driven by benign motivations such as affection, grooming, and social bonding, it is crucial to remain mindful of potential medical concerns associated with this behavior. The delicate nature of the eyes and the risk of ocular irritation, infections, and mechanical trauma underscore the importance of vigilant monitoring and proactive care. By recognizing the interplay of behavioral and medical considerations, dog owners can implement a holistic approach to addressing and managing eye licking behavior in their beloved canine companions.
Effective strategies for addressing eye licking encompass behavioral modification, environmental enrichment, ocular care, veterinary evaluation, nutritional considerations, and professional behavioral consultation. By integrating these proactive measures, dog owners can promote the overall well-being of their dogs and foster harmonious interactions within the pack dynamic. Understanding the nuanced interplay of behavioral, environmental, and medical factors is pivotal in devising a comprehensive approach to addressing and mitigating eye licking behavior in dogs.
As responsible caregivers, our commitment to understanding and addressing the behaviors of our canine companions is instrumental in nurturing a thriving and harmonious bond with them. By delving into the depths of canine behavior and communication, we not only gain a deeper appreciation for the rich tapestry of their social world but also empower ourselves to provide attentive care and support for their holistic well-being. Through this journey of understanding, we embark on a shared path of companionship, empathy, and mutual understanding with our loyal and beloved canine friends.