Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>Why Does My Dog Keep Closing One Eye?

Eye and Ear Health
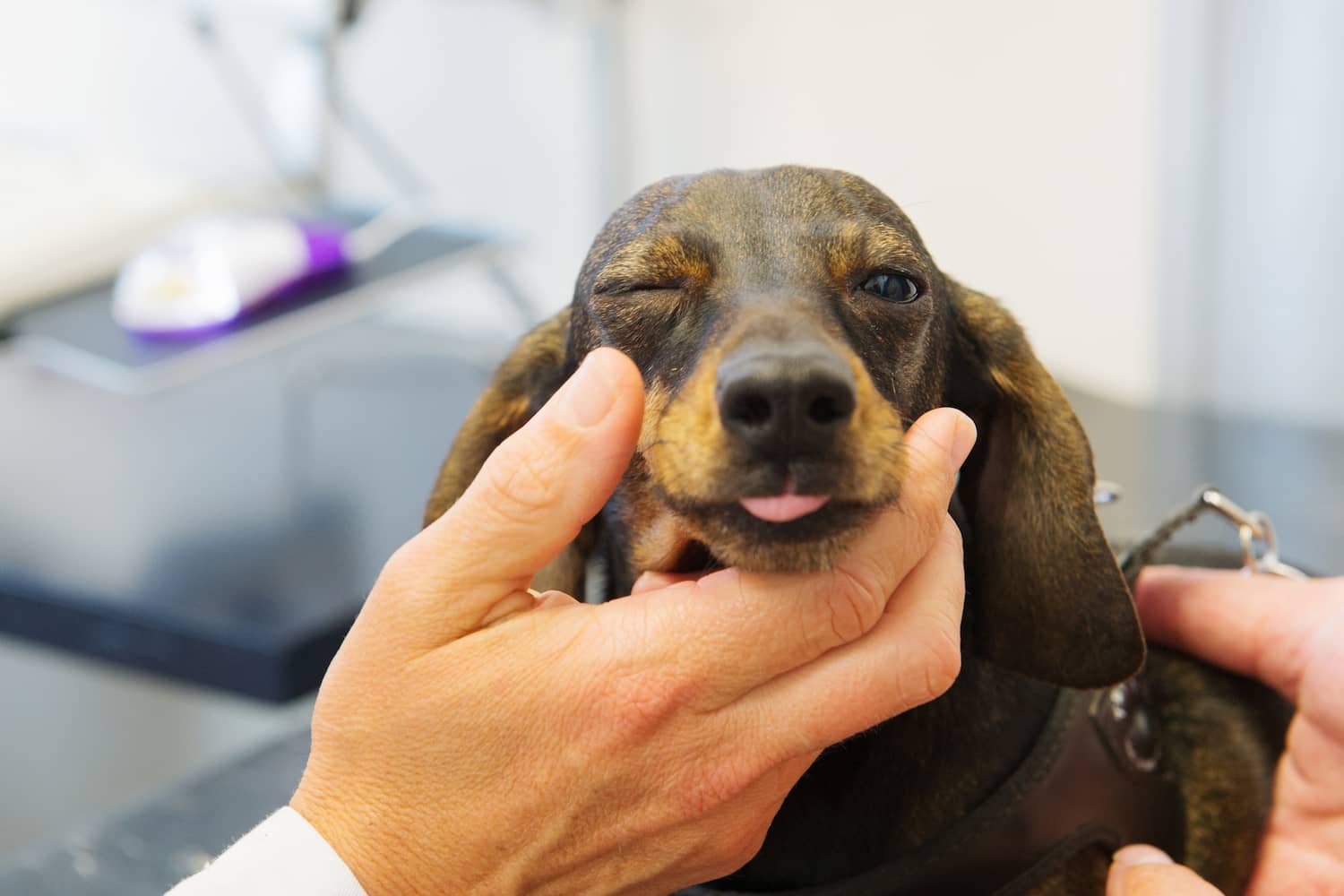
Why Does My Dog Keep Closing One Eye?
Published: February 11, 2024
Discover the reasons why your dog may be closing one eye and learn how to maintain their eye and ear health. Find expert tips and advice here.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Dogs are known for their expressive eyes, often communicating a wide range of emotions through their gaze. As a pet owner, you may have noticed your furry companion intermittently closing one eye, prompting the question, "Why does my dog keep closing one eye?" This behavior can be perplexing, but it's essential to delve into the potential reasons behind this action to ensure the well-being of your canine friend.
Understanding the underlying causes of one eye closure in dogs requires a comprehensive exploration of both medical and behavioral factors. While it may initially appear as a harmless quirk, it's crucial to recognize that this behavior could signify an underlying issue that necessitates attention and care. By gaining insight into the potential triggers for this behavior, you can effectively address any concerns and ensure the optimal health and happiness of your beloved pet.
In the following sections, we will delve into the possible medical reasons for one eye closure in dogs, exploring various conditions that may lead to this behavior. Additionally, we will examine the behavioral aspects that could contribute to this action, shedding light on the emotional and environmental factors that may influence your dog's eye behavior. Furthermore, we will discuss practical strategies for addressing one eye closure in dogs, providing guidance on how to support your pet's well-being and seek appropriate care when necessary.
By delving into these key aspects, you will gain valuable insights into the potential reasons behind your dog's one eye closure, empowering you to take proactive steps to ensure their health and happiness. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the mystery behind your dog's eye behavior and discover actionable approaches to support their well-being.
Possible Medical Reasons for One Eye Closure
When a dog repeatedly closes one eye, it can be indicative of various underlying medical conditions that require attention. Understanding these potential medical reasons is crucial for identifying and addressing any health issues affecting your pet. Here are some possible medical reasons for one eye closure in dogs:
-
Eye Irritation or Injury: Dogs may close one eye in response to irritation or injury to the affected eye. Foreign objects, such as dust, debris, or small particles, can cause discomfort, leading the dog to squint or close the affected eye. Additionally, scratches or minor injuries to the eye can prompt this behavior as a protective mechanism to alleviate discomfort.
-
Conjunctivitis: Also known as pink eye, conjunctivitis is a common eye condition in dogs characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva. This condition can lead to eye redness, discharge, and discomfort, prompting the dog to close the affected eye. Conjunctivitis can be caused by allergies, infections, or environmental irritants.
-
Corneal Ulcers: Corneal ulcers, or injuries to the cornea, can result in significant discomfort for dogs. When a dog experiences a corneal ulcer, they may exhibit signs of eye pain, excessive blinking, and squinting or closing of the affected eye. Prompt veterinary attention is crucial to address corneal ulcers and prevent potential complications.
-
Glaucoma: Glaucoma is a serious eye condition characterized by increased pressure within the eye, leading to pain and potential vision loss. Dogs with glaucoma may exhibit symptoms such as eye redness, squinting, and partial or complete closure of the affected eye. Timely diagnosis and management are essential to mitigate the impact of glaucoma on a dog's eye health.
-
Entropion or Ectropion: Entropion, a condition where the eyelid rolls inward, or ectropion, where the eyelid turns outward, can cause discomfort and irritation for dogs. These eyelid abnormalities can lead to excessive tearing, redness, and squinting or closing of the affected eye as the dog attempts to alleviate discomfort.
-
Foreign Body Ingestion: In some cases, dogs may close one eye due to the presence of a foreign body lodged in the eye or eyelid. This can cause significant discomfort and prompt the dog to exhibit protective behaviors such as eye closure or squinting.
-
Underlying Health Conditions: Certain systemic health issues, such as allergies, autoimmune diseases, or neurological disorders, can manifest with ocular symptoms, including eye closure. Identifying and addressing these underlying health conditions is crucial for supporting the overall well-being of the dog.
Understanding these potential medical reasons for one eye closure in dogs underscores the importance of proactive veterinary care and attention to your pet's eye health. If you observe your dog repeatedly closing one eye or displaying any signs of ocular discomfort, seeking prompt veterinary evaluation is essential to identify and address any underlying medical issues. By prioritizing your dog's eye health, you can ensure their comfort and well-being, fostering a strong bond based on care and attentiveness.
Behavioral Reasons for One Eye Closure
In addition to medical factors, behavioral aspects can also contribute to a dog's tendency to close one eye. Understanding these behavioral reasons is essential for gaining insight into your pet's emotional well-being and environmental interactions. Here are some behavioral reasons for one eye closure in dogs:
-
Discomfort or Pain: Dogs may close one eye as a response to discomfort or pain, which can stem from various sources. Environmental factors, such as bright sunlight or exposure to strong winds, may prompt a dog to squint or partially close one eye to reduce discomfort. Additionally, underlying pain or discomfort in the eye or surrounding areas can lead to this behavior as a protective mechanism.
-
Stress or Anxiety: Dogs, like humans, can exhibit stress or anxiety through physical behaviors, including eye closure. Stressors such as loud noises, unfamiliar environments, or changes in routine can induce anxiety in dogs, prompting them to display signs of distress, including closing one eye. Understanding and addressing the underlying sources of stress can help alleviate this behavior.
-
Eye Contact and Communication: Dogs rely heavily on nonverbal communication, and eye contact plays a significant role in their interactions. Closing one eye can be a subtle form of communication or expression, conveying emotions such as relaxation, contentment, or even playfulness. Observing your dog's overall body language and context can provide valuable clues about the intent behind this behavior.
-
Environmental Stimuli: Dogs are highly sensitive to their surroundings, and certain environmental stimuli can prompt them to close one eye as a response. For example, exposure to strong odors, airborne particles, or sudden movements may lead a dog to partially close one eye as a protective measure against potential irritants.
-
Habitual Behavior: In some cases, dogs may develop habitual behaviors, including intermittently closing one eye, without any underlying medical or emotional distress. This behavior may stem from individual preferences or past experiences, and while it may not necessarily indicate a problem, it's essential to monitor and understand your dog's unique behavioral patterns.
Understanding the behavioral reasons for one eye closure in dogs provides valuable insights into their emotional state and environmental interactions. By recognizing the potential influences behind this behavior, pet owners can cultivate a deeper understanding of their canine companions and provide appropriate support to ensure their overall well-being.
By acknowledging the interplay of medical and behavioral factors in a dog's eye behavior, pet owners can approach the issue with a holistic perspective, addressing any underlying health concerns while also considering the emotional and environmental influences on their pet's behavior. This comprehensive approach fosters a nurturing and supportive environment for dogs, promoting their physical comfort and emotional contentment.
How to Address One Eye Closure in Dogs
Addressing one eye closure in dogs requires a proactive and attentive approach to ensure the well-being of your canine companion. Whether the behavior stems from medical issues, behavioral factors, or a combination of both, pet owners can take specific steps to address and manage this concern effectively.
-
Veterinary Evaluation: If you observe your dog repeatedly closing one eye or displaying signs of ocular discomfort, seeking prompt veterinary evaluation is paramount. A thorough examination by a veterinarian can help identify any underlying medical conditions, such as eye injuries, infections, or systemic health issues. Based on the diagnosis, appropriate treatment and management strategies can be implemented to address the root cause of the eye closure behavior.
-
Ocular Care and Hygiene: Maintaining good ocular hygiene is essential for supporting your dog's eye health. Regularly cleaning the area around the eyes and ensuring that there are no foreign objects or irritants lodged in the eye can help alleviate potential sources of discomfort. Additionally, following veterinary recommendations for eye care, including prescribed eye drops or ointments, can aid in managing specific eye conditions.
-
Environmental Considerations: Assessing and addressing environmental factors that may contribute to eye closure in dogs is crucial. Providing a comfortable and safe living environment, minimizing exposure to potential irritants, and ensuring adequate protection from harsh weather conditions can help reduce the likelihood of ocular discomfort and stress-related eye closure.
-
Behavioral Support: Understanding and addressing behavioral triggers for one eye closure is essential for promoting your dog's emotional well-being. Creating a calm and predictable routine, offering reassurance during stressful situations, and providing enriching activities can help alleviate stress and anxiety, potentially reducing the occurrence of stress-related eye closure behaviors.
-
Nutritional and Health Support: A balanced and nutritious diet plays a vital role in supporting overall health, including ocular health. Providing a high-quality diet rich in essential nutrients, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to optimal eye health in dogs. Additionally, addressing any underlying systemic health issues through veterinary guidance can positively impact ocular comfort and function.
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Communication: Regularly monitoring your dog's eye behavior and overall well-being is essential for detecting any changes or concerns. Open communication with your veterinarian, including reporting any persistent or worsening eye closure behaviors, can facilitate proactive management and timely intervention when necessary.
By implementing these proactive measures and maintaining a keen focus on your dog's eye health and emotional well-being, you can effectively address one eye closure in dogs. This comprehensive approach encompasses attentive care, environmental considerations, and proactive communication with veterinary professionals, ultimately fostering a supportive and nurturing environment for your beloved canine companion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the behavior of a dog repeatedly closing one eye can stem from a myriad of factors, encompassing both medical and behavioral dimensions. Understanding the potential medical reasons, including eye irritation, conjunctivitis, corneal ulcers, glaucoma, eyelid abnormalities, and underlying health conditions, underscores the importance of proactive veterinary care and attention to a dog's eye health. Prompt identification and management of these medical issues are essential for ensuring the comfort and well-being of our canine companions.
Moreover, delving into the behavioral reasons for one eye closure sheds light on the emotional and environmental influences that can prompt this behavior. Factors such as discomfort, stress, communication, environmental stimuli, and habitual behaviors play a significant role in a dog's tendency to close one eye. Recognizing and addressing these behavioral triggers is crucial for fostering a supportive and enriching environment that promotes the emotional contentment of our beloved pets.
Addressing one eye closure in dogs requires a holistic approach that encompasses veterinary evaluation, ocular care and hygiene, environmental considerations, behavioral support, nutritional and health support, and ongoing monitoring. By integrating these proactive measures into our pet care routines, we can effectively address and manage this concern, ensuring the optimal well-being of our canine companions.
Ultimately, the bond between a pet owner and their dog is built on a foundation of care, attentiveness, and understanding. By unraveling the mystery behind a dog's eye behavior and taking proactive steps to address any underlying issues, we demonstrate our unwavering commitment to the health and happiness of our furry friends. Through this journey of discovery and attentive care, we cultivate a nurturing environment where our dogs can thrive, fostering a harmonious and fulfilling companionship that enriches both our lives and theirs.
