Home>Health & Wellness>Behavior & Cognitive Care>Why Does My Senior Dog Lick So Much?
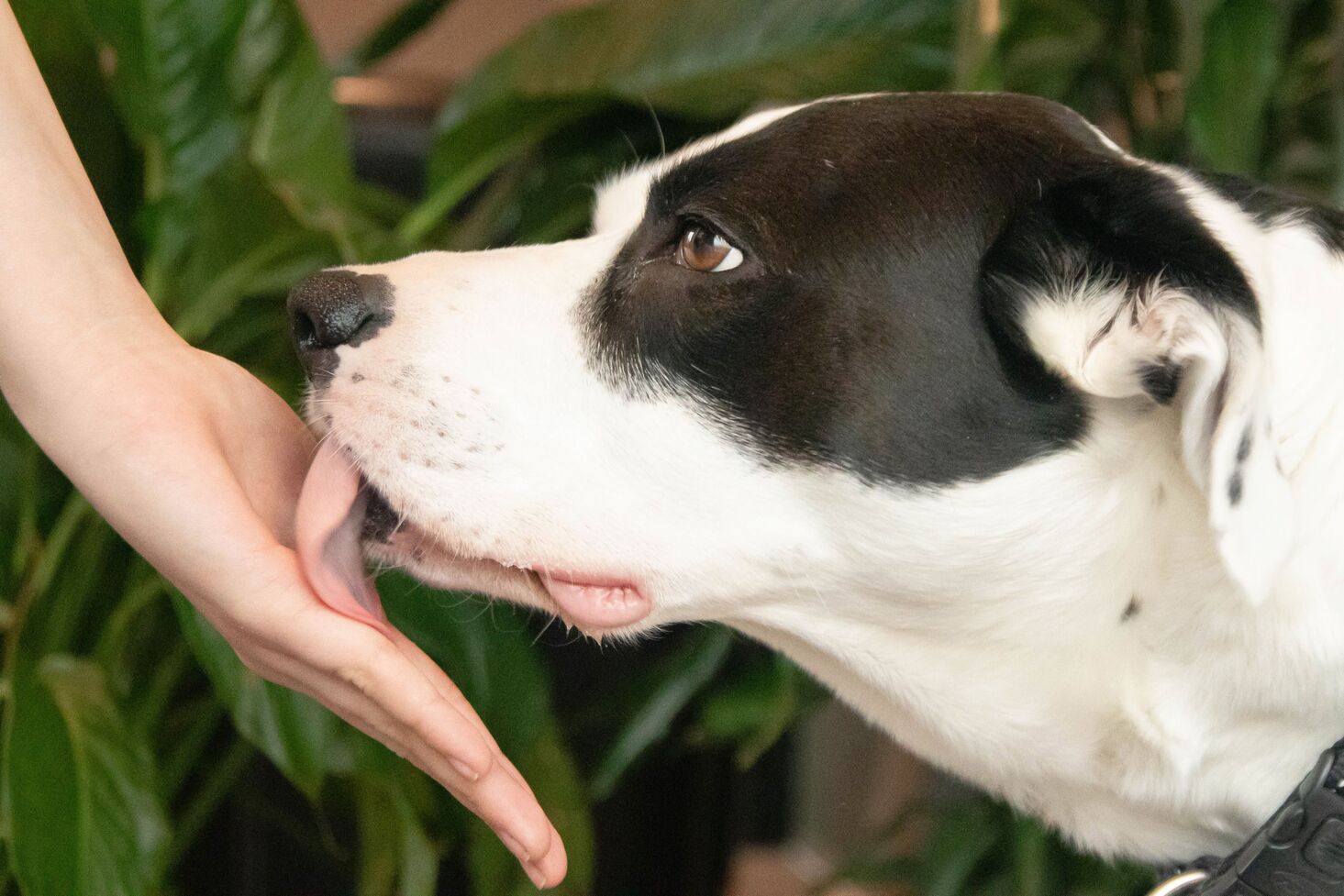


Behavior & Cognitive Care
Why Does My Senior Dog Lick So Much?
Published: February 1, 2024
Discover why senior dogs lick excessively and learn how to address this behavior with effective behavior and cognitive care strategies. Keep your senior dog happy and healthy!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Senior dogs are cherished members of many families, offering years of companionship, loyalty, and love. As our furry friends age, they may exhibit various behavioral changes, one of which is excessive licking. This behavior can be concerning for pet parents, prompting them to seek understanding and solutions.
Excessive licking in senior dogs can stem from a range of factors, including medical conditions, cognitive changes, and emotional distress. It's essential for pet owners to recognize the underlying reasons behind this behavior and take appropriate steps to address it. By delving into the potential causes and effective management strategies, we can ensure the well-being and comfort of our beloved senior canine companions.
Understanding the reasons behind excessive licking in senior dogs is crucial for providing them with the care and support they need in their later years. Whether the root cause is physical discomfort, anxiety, or a combination of factors, a compassionate and informed approach is key to helping senior dogs lead fulfilling and contented lives.
Read more: Why Is My Senior Dog Peeing So Much?
Understanding the reasons behind excessive licking in senior dogs
Excessive licking in senior dogs can be attributed to various factors, encompassing both medical and behavioral aspects. Understanding these reasons is pivotal in addressing this behavior and ensuring the well-being of our aging canine companions.
Medical Causes
Senior dogs may engage in excessive licking as a response to physical discomfort. Arthritic pain, skin allergies, and other underlying health issues can trigger this behavior. For instance, osteoarthritis, a common ailment in older dogs, may lead to joint pain and stiffness, prompting them to lick the affected areas in an attempt to alleviate discomfort. Similarly, skin conditions such as dermatitis or hot spots can provoke incessant licking as a means of soothing irritation or pain.
Cognitive Changes
As dogs age, they may experience cognitive decline, leading to altered behaviors, including excessive licking. Canine cognitive dysfunction (CCD), akin to Alzheimer's disease in humans, can manifest in senior dogs, causing confusion, anxiety, and repetitive actions such as excessive licking. This condition can result in heightened stress and a compulsive need for self-soothing behaviors, contributing to the prevalence of excessive licking in senior dogs.
Emotional Distress
Senior dogs may undergo emotional upheaval due to various factors, such as changes in their environment, loss of companions, or diminished sensory perception. These emotional stressors can trigger excessive licking as a coping mechanism, providing a form of self-soothing and comfort during periods of distress or anxiety.
Read more: Why Is My Diabetic Dog Shaking So Much
Sensory Perception Changes
Aging can bring about sensory changes in dogs, affecting their perception of touch, taste, and smell. Diminished sensory input may lead to increased licking behavior, as senior dogs seek tactile stimulation or attempt to explore and interact with their environment through heightened oral activity.
Social and Environmental Factors
Changes in the social and environmental dynamics of a senior dog's life can also contribute to excessive licking. Factors such as reduced social interaction, altered daily routines, or the introduction of new stimuli can prompt stress and anxiety, leading to heightened licking behavior as a response to these changes.
By comprehending the multifaceted reasons behind excessive licking in senior dogs, pet parents can approach this behavior with empathy and targeted interventions. This understanding lays the groundwork for effectively addressing the underlying causes and implementing strategies to support the well-being of senior dogs as they navigate the complexities of aging.
Medical causes of excessive licking in senior dogs
Senior dogs, like humans, are susceptible to a range of medical conditions that can contribute to excessive licking behavior. Understanding these underlying health issues is crucial in addressing and managing this behavior effectively.
Arthritic pain is a prevalent medical cause of excessive licking in senior dogs. As dogs age, they are prone to developing osteoarthritis, a degenerative joint disease characterized by inflammation and pain in the joints. This discomfort can lead to incessant licking as a means of alleviating the associated pain and stiffness. Dogs may target specific areas, such as their paws or joints, where arthritis-related discomfort is most pronounced, exhibiting a repetitive licking pattern in response to the persistent discomfort.
In addition to arthritis, senior dogs may experience skin allergies and dermatological conditions that prompt excessive licking. Skin irritations, hot spots, and allergic reactions can trigger intense itching and discomfort, compelling dogs to engage in excessive licking as a form of self-soothing. The act of licking may provide temporary relief from the itching sensation, albeit exacerbating the underlying skin issues and perpetuating a cycle of irritation and licking.
Furthermore, dental problems can contribute to excessive licking behavior in senior dogs. Periodontal disease, tooth decay, or oral discomfort can lead to heightened oral activity, including excessive licking of the lips and mouth. Dogs may exhibit this behavior in an attempt to alleviate dental pain or discomfort, signaling the need for prompt veterinary attention to address underlying dental issues and alleviate the associated discomfort driving the excessive licking behavior.
Moreover, systemic health issues such as gastrointestinal disturbances or metabolic imbalances can manifest in excessive licking behavior. Dogs experiencing gastrointestinal discomfort, nausea, or acid reflux may engage in excessive licking as a response to the associated digestive distress. Similarly, metabolic conditions such as thyroid imbalances can influence a dog's behavior, potentially leading to heightened licking activity as a manifestation of the underlying physiological imbalance.
By recognizing and addressing these medical causes of excessive licking in senior dogs, pet parents can take proactive measures to alleviate discomfort and improve their canine companions' quality of life. Seeking veterinary guidance and appropriate medical interventions is essential in identifying and managing these underlying health issues, ultimately promoting the well-being and comfort of senior dogs as they navigate the complexities of aging.
Behavioral causes of excessive licking in senior dogs
Behavioral causes of excessive licking in senior dogs encompass a spectrum of psychological, emotional, and environmental factors that can influence this repetitive behavior. Understanding these behavioral triggers is pivotal in addressing and managing excessive licking in senior dogs, fostering their emotional well-being and overall contentment in their later years.
Anxiety and Stress: Senior dogs may experience heightened anxiety and stress due to various factors, including changes in their environment, separation from their human companions, or the presence of unfamiliar stimuli. These emotional stressors can manifest in excessive licking behavior, as dogs seek self-soothing mechanisms to cope with their heightened emotional distress. The act of licking provides a form of tactile comfort and can serve as a repetitive, calming ritual in response to anxiety-inducing situations.
Boredom and Understimulation: Lack of mental and physical stimulation can contribute to excessive licking in senior dogs. As dogs age, they may experience reduced mobility or diminished sensory input, leading to boredom and under-stimulation. In the absence of engaging activities and environmental enrichment, dogs may resort to excessive licking as a means of occupying themselves and seeking sensory stimulation. Addressing this behavioral cause involves providing senior dogs with mentally stimulating toys, interactive games, and gentle physical activities tailored to their individual capabilities.
Compulsive Behavior: Some senior dogs may develop compulsive behaviors, including excessive licking, as a result of cognitive changes or emotional distress. Canine cognitive dysfunction (CCD) can lead to compulsive tendencies, prompting dogs to engage in repetitive actions such as excessive licking. Similarly, emotional upheaval or distress can trigger compulsive behavior patterns, further exacerbating the frequency of licking episodes. Understanding and addressing the underlying factors contributing to compulsive licking is essential in managing this behavior and promoting the psychological well-being of senior dogs.
Environmental Triggers: Changes in a senior dog's living environment, such as relocation, introduction of new pets, or alterations in daily routines, can instigate excessive licking behavior. These environmental triggers may induce stress and anxiety, prompting dogs to seek solace through repetitive licking. By identifying and mitigating these environmental stressors, pet parents can help alleviate the emotional burden on senior dogs, reducing the likelihood of excessive licking as a coping mechanism.
By recognizing and addressing these behavioral causes of excessive licking in senior dogs, pet parents can implement targeted interventions to support their canine companions' emotional health and well-being. Creating a nurturing and stimulating environment, providing emotional reassurance, and engaging in gentle, positive interactions can contribute to mitigating excessive licking behavior and fostering a harmonious and contented life for senior dogs.
Read more: Why Does My Dog Lick My Other Dog’s Eye
How to address excessive licking in senior dogs
Addressing excessive licking in senior dogs necessitates a comprehensive approach that encompasses both medical and behavioral considerations. By integrating targeted interventions and supportive measures, pet parents can effectively manage this behavior, promoting the well-being and comfort of their aging canine companions.
Veterinary Evaluation
Initiating the process of addressing excessive licking in senior dogs involves seeking a thorough veterinary evaluation to identify and address any underlying medical issues contributing to this behavior. A comprehensive physical examination, along with diagnostic tests as deemed necessary, can help pinpoint potential health concerns such as arthritis, skin allergies, dental problems, or systemic conditions. By addressing these medical factors, pet parents can alleviate discomfort and reduce the impetus for excessive licking.
Treatment of Underlying Health Issues
Upon identifying medical causes of excessive licking, implementing targeted treatment plans in collaboration with a veterinarian is essential. This may involve pain management for arthritis, dermatological interventions for skin conditions, dental care, or addressing systemic health issues through medication or dietary adjustments. By addressing these underlying health issues, pet parents can alleviate physical discomfort and reduce the need for excessive licking as a coping mechanism.
Environmental Enrichment
Creating a stimulating and comforting environment for senior dogs is pivotal in addressing behavioral causes of excessive licking. Providing mentally enriching toys, gentle physical activities, and interactive engagement can help alleviate boredom and under-stimulation, reducing the likelihood of excessive licking as a result of emotional distress or compulsive behavior.
Read more: Why Does My Senior Dog Keep Whining?
Emotional Support and Reassurance
Senior dogs benefit from emotional support and reassurance from their human companions. Maintaining a consistent and nurturing presence, offering gentle affection, and minimizing stress-inducing factors in their environment can contribute to reducing anxiety and emotional distress, thereby mitigating the need for excessive licking as a self-soothing mechanism.
Behavioral Modification Techniques
Implementing positive reinforcement techniques and redirecting excessive licking behavior through gentle, consistent training can be beneficial. Encouraging alternative soothing behaviors, such as providing calming massages or offering interactive play, can help senior dogs manage their emotional state without resorting to excessive licking.
Holistic Approaches
Exploring holistic approaches, such as acupuncture, massage therapy, or aromatherapy, in consultation with a qualified professional, can complement traditional interventions in addressing excessive licking in senior dogs. These holistic modalities can contribute to overall relaxation and well-being, potentially reducing the frequency of excessive licking episodes.
By integrating these multifaceted strategies, pet parents can effectively address excessive licking in senior dogs, promoting their physical comfort, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life as they navigate the unique challenges of aging. Through a compassionate and proactive approach, senior dogs can experience contentment and fulfillment in their later years, supported by attentive care and understanding from their human companions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, excessive licking in senior dogs can stem from a myriad of factors, encompassing both medical and behavioral causes. Understanding the underlying reasons behind this behavior is pivotal in providing comprehensive care and support for aging canine companions. Medical conditions such as arthritis, skin allergies, and dental problems can prompt excessive licking as a response to physical discomfort. Additionally, cognitive changes, emotional distress, and environmental triggers can contribute to this behavior, highlighting the complex interplay of physical and psychological factors in senior dogs.
Addressing excessive licking in senior dogs requires a holistic approach that integrates veterinary evaluation, targeted medical interventions, environmental enrichment, emotional support, and behavioral modification techniques. By identifying and addressing underlying health issues, pet parents can alleviate physical discomfort, reducing the impetus for excessive licking. Furthermore, creating a nurturing and stimulating environment, providing emotional reassurance, and engaging in positive interactions can help mitigate behavioral causes of excessive licking, fostering the emotional well-being of senior dogs.
Through a compassionate and informed approach, pet parents can ensure that their senior dogs receive the care and support they need to navigate the complexities of aging. By recognizing the multifaceted nature of excessive licking and implementing tailored interventions, senior dogs can experience comfort, contentment, and a high quality of life in their later years. It is through our dedication to understanding and addressing the unique needs of senior dogs that we can honor their unwavering companionship and enrich their lives as cherished members of our families.