Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Parasite Can Be Transferred Between Dogs With Brushes And Combs?
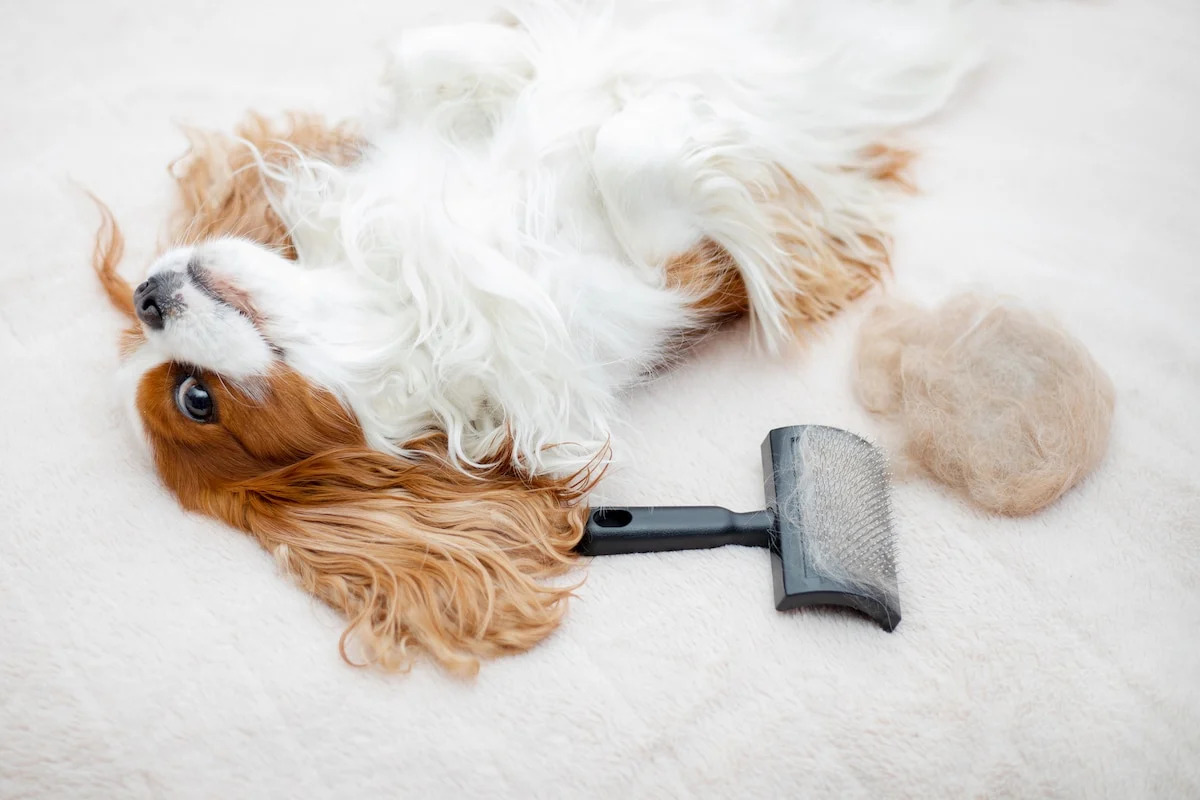


Common Health Issues
What Parasite Can Be Transferred Between Dogs With Brushes And Combs?
Published: February 7, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs and how parasites can be transferred between them through brushes and combs. Protect your pet's health with proper grooming practices.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to the health and well-being of our furry companions, it's essential to be aware of the potential risks they may face. Parasites are a common concern for dog owners, as these pesky organisms can cause a range of health issues for our beloved pets. From itching and discomfort to more serious conditions, the presence of parasites can significantly impact a dog's quality of life.
In particular, the transfer of parasites through brushes and combs is a topic that deserves attention. As dog owners, we often use grooming tools such as brushes and combs to keep our pets looking and feeling their best. However, these tools can inadvertently become vehicles for the transmission of parasites if proper precautions are not taken.
Understanding the types of parasites that can affect dogs and how they can be transferred through grooming tools is crucial for ensuring the health and safety of our canine companions. By gaining insight into this aspect of pet care, we can take proactive measures to prevent parasite transmission and safeguard the well-being of our furry friends.
In the following sections, we will delve into the common parasites that affect dogs, explore how these parasites can be transmitted through brushes and combs, and discuss effective strategies for preventing parasite transfer. By arming ourselves with this knowledge, we can become more informed and responsible pet owners, actively contributing to the overall health and happiness of our canine companions.
Common Parasites in Dogs
Parasites are unwelcome guests that can take up residence in a dog's body, causing a range of health issues. Understanding the common parasites that affect dogs is essential for proactive pet care. Here are some of the most prevalent parasites that dog owners should be aware of:
1. Fleas
Fleas are tiny, wingless insects that survive by feeding on the blood of their hosts. These pesky parasites can cause intense itching, skin irritation, and allergic reactions in dogs. In severe infestations, fleas can lead to anemia, especially in young or small dogs.
2. Ticks
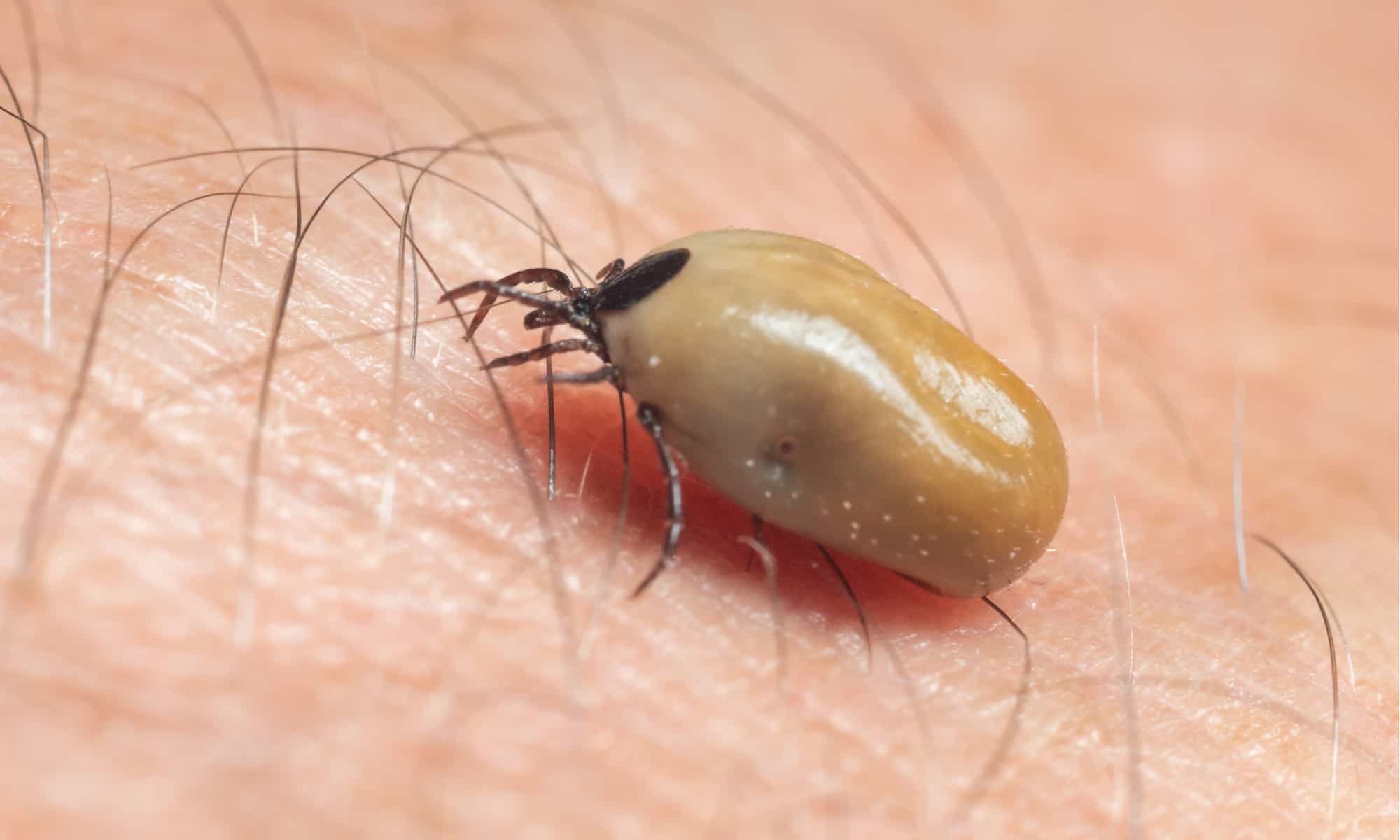
Ticks are external parasites that attach themselves to a dog's skin and feed on their blood. In addition to causing discomfort and skin irritation, ticks can transmit serious diseases such as Lyme disease and Rocky Mountain spotted fever.
3. Mites
Mites are microscopic parasites that can cause a variety of skin conditions in dogs, including mange. Sarcoptic mange, also known as scabies, is a highly contagious skin disease caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, leading to intense itching and hair loss.
4. Lice
Lice are another type of external parasite that can infest dogs. While less common than fleas or ticks, lice can still cause itching and skin irritation. In severe cases, lice infestations can lead to hair loss and anemia.
5. Intestinal Parasites
Intestinal parasites such as roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, and tapeworms can take up residence in a dog's gastrointestinal tract, leading to digestive issues, weight loss, and nutrient deficiencies. These parasites can be transmitted through ingestion of contaminated soil, water, or feces.
6. Heartworms
Heartworms are transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. These parasites take up residence in the dog's heart and lungs, leading to severe respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Heartworm disease can be life-threatening if left untreated.
By being aware of these common parasites, dog owners can take proactive measures to protect their pets from infestations and related health issues. Regular grooming, parasite prevention medications, and routine veterinary check-ups are essential components of a comprehensive parasite control strategy for dogs.
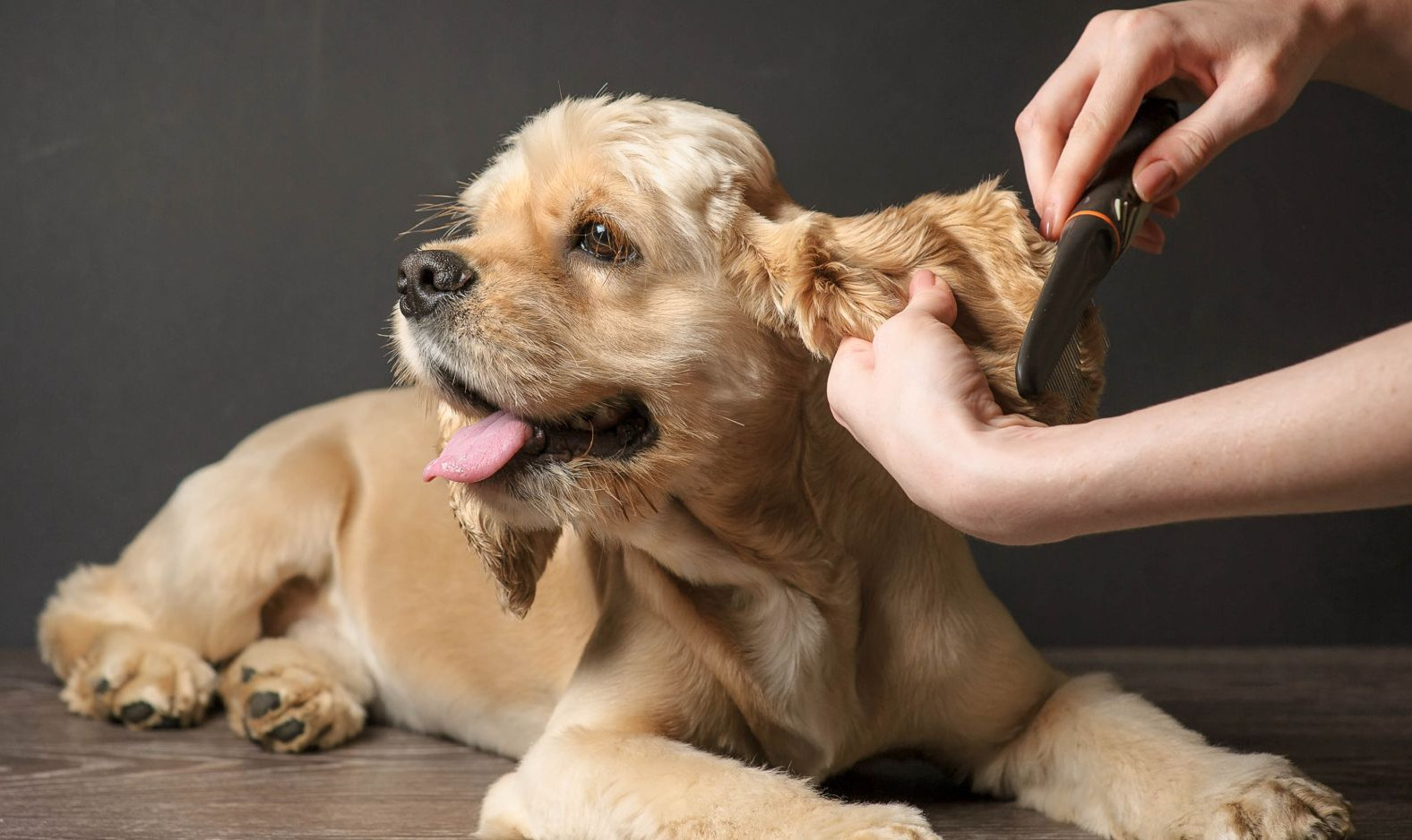
Transmission of Parasites through Brushes and Combs
Grooming tools such as brushes and combs play a crucial role in maintaining a dog's hygiene and appearance. However, these tools can inadvertently become vehicles for the transmission of parasites if proper precautions are not taken. Understanding how parasites can be transferred through brushes and combs is essential for preventing infestations and protecting the health of our canine companions.
-
Fleas and Eggs: Fleas and their eggs can easily cling to the bristles of a brush or the teeth of a comb. When grooming an infested dog, these parasites can transfer onto the grooming tools, ready to be deposited onto the next unsuspecting host.
-
Ticks: Ticks can also hitch a ride on grooming tools. These blood-sucking parasites can attach themselves to the bristles or teeth of a brush, waiting to latch onto a dog's skin during the next grooming session.
-
Mites and Lice: While less common, mites and lice can also be transferred through brushes and combs. These microscopic parasites may find their way onto grooming tools, posing a risk of infestation for other dogs.
-
Eggs of Intestinal Parasites: The eggs of intestinal parasites such as roundworms and hookworms can be present in a dog's fur. When grooming, these eggs can be transferred onto brushes and combs, potentially leading to the ingestion and subsequent infestation of other dogs.
To mitigate the risk of parasite transmission through grooming tools, dog owners should implement the following preventive measures:
-
Regular Cleaning: Thoroughly clean and disinfect grooming tools after each use to remove any potential parasites or eggs.
-
Individual Tools: If grooming multiple dogs, use separate brushes and combs for each dog to prevent cross-contamination.
-
Parasite Control: Ensure that all dogs in the household are on a comprehensive parasite control program, including regular flea and tick prevention.
-
Routine Grooming: Regular grooming sessions provide an opportunity to inspect a dog's skin and coat for signs of parasites, allowing for early detection and intervention.
By being mindful of the potential for parasite transmission through brushes and combs, dog owners can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of infestations. Through regular cleaning, individualized grooming tools, and comprehensive parasite control, the transfer of parasites through grooming tools can be effectively mitigated, contributing to the overall health and well-being of our furry companions.
Read more: What Is Giardia Parasite In Dogs?
Preventing Parasite Transfer
Preventing the transfer of parasites through grooming tools is a crucial aspect of responsible pet care. By implementing proactive measures, dog owners can significantly reduce the risk of infestations and protect the health of their canine companions. Here are effective strategies for preventing parasite transfer through brushes and combs:
1. Regular Cleaning and Disinfection
Thoroughly cleaning and disinfecting grooming tools after each use is essential for removing any potential parasites or eggs that may have latched onto the bristles or teeth. Using pet-safe disinfectants or hot water can help eliminate any lingering parasites, preventing their transfer to other dogs during subsequent grooming sessions.
2. Individualized Tools for Each Dog
When grooming multiple dogs, it's important to use separate brushes and combs for each dog to prevent cross-contamination. This practice ensures that parasites from one dog do not inadvertently spread to another, minimizing the risk of infestations within the household.
3. Comprehensive Parasite Control Program
Ensuring that all dogs in the household are on a comprehensive parasite control program is vital for preventing infestations. Regular use of flea and tick prevention products, as well as deworming medications, can significantly reduce the likelihood of parasites taking hold and being transferred through grooming tools.
4. Routine Grooming and Inspection
Regular grooming sessions provide an opportunity to inspect a dog's skin and coat for signs of parasites. By carefully examining the pet's fur and skin, dog owners can detect any potential infestations early, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment. This proactive approach helps prevent the transfer of parasites to other dogs and mitigates the impact of infestations on the affected pet.
5. Environmental Management
In addition to grooming tools, environmental management plays a crucial role in preventing parasite transfer. Regularly cleaning and vacuuming the areas where dogs spend time, such as bedding, carpets, and furniture, can help eliminate any parasites or eggs that may have been shed from infested dogs, reducing the risk of reinfestation and transfer through grooming tools.
By incorporating these preventive measures into their pet care routine, dog owners can effectively minimize the risk of parasite transfer through brushes and combs. Proactive parasite control, individualized grooming tools, and routine inspection and cleaning contribute to a healthy and parasite-free environment for dogs, promoting their overall well-being and quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the potential transfer of parasites through grooming tools such as brushes and combs is a significant consideration for dog owners seeking to safeguard the health and well-being of their pets. By understanding the common parasites that affect dogs and how they can be transmitted through grooming tools, pet owners can take proactive measures to prevent infestations and minimize the risk of parasite transfer.
The presence of parasites such as fleas, ticks, mites, lice, and intestinal parasites can lead to a range of health issues for dogs, including itching, skin irritation, anemia, digestive disturbances, and more severe conditions if left untreated. The transfer of these parasites through grooming tools poses a potential risk of infestation for other dogs in the household, making it essential for dog owners to be vigilant and proactive in their parasite control efforts.
Implementing preventive strategies such as regular cleaning and disinfection of grooming tools, individualized tools for each dog, comprehensive parasite control programs, routine grooming and inspection, and environmental management can significantly reduce the risk of parasite transfer. By incorporating these measures into their pet care routine, dog owners can create a healthy and parasite-free environment for their canine companions, promoting their overall well-being and quality of life.
Ultimately, responsible pet ownership involves not only providing love and care but also taking proactive steps to protect pets from potential health risks. By staying informed about parasite control and transmission, dog owners can play a pivotal role in ensuring the health and happiness of their furry friends. Through diligence, preventive measures, and regular veterinary care, pet owners can create a safe and nurturing environment where their dogs can thrive free from the burden of parasitic infestations.
In essence, by being mindful of the potential for parasite transfer through grooming tools and taking proactive steps to mitigate this risk, dog owners can contribute to the overall health and well-being of their beloved pets, fostering a strong and enduring bond built on trust, care, and a commitment to providing the best possible life for their canine companions.