Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Far Between Shots Of Dog Vaccination

Common Health Issues
How Far Between Shots Of Dog Vaccination
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about the common health issues in dogs and how far between shots of dog vaccination to keep your pet healthy and protected. Find out the best vaccination schedule for your furry friend.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Vaccination is a crucial aspect of responsible pet ownership, playing a pivotal role in safeguarding the health and well-being of our beloved canine companions. Just as vaccinations are essential for humans, they are equally vital for dogs to protect them from a myriad of potentially life-threatening diseases. As a pet parent, ensuring that your furry friend receives the necessary vaccinations is a proactive measure that can significantly contribute to their longevity and quality of life.
Vaccines work by stimulating a dog's immune system to produce antibodies against specific diseases, effectively preparing their body to combat these illnesses should they encounter them in the future. By bolstering their immunity, vaccinations help prevent the onset of various contagious and often fatal conditions, thereby sparing dogs from unnecessary suffering and potential premature death.
As responsible pet owners, it is our duty to prioritize the health and well-being of our canine companions. This involves adhering to a comprehensive vaccination schedule recommended by veterinarians to ensure that our dogs are adequately protected from a range of infectious diseases. Understanding the importance of dog vaccination and the recommended time intervals between shots is crucial for every pet parent, as it empowers them to make informed decisions regarding their dog's healthcare.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve into the significance of dog vaccination, explore the recommended time intervals between shots, and consider the various factors that can influence a dog's vaccination schedule. By gaining a deeper understanding of these aspects, pet owners can take proactive steps to safeguard their dog's health and contribute to a thriving and vibrant canine community.
Read more: How Much Is The Heartworm Shot For Dogs?
Importance of Dog Vaccination
Vaccinating dogs is a fundamental aspect of responsible pet ownership, serving as a crucial preventive measure against a spectrum of potentially life-threatening diseases. These vaccinations are designed to stimulate a dog's immune system, prompting the production of antibodies that can effectively combat specific diseases. By bolstering their immunity, vaccinations play a pivotal role in shielding dogs from a myriad of contagious and often fatal conditions, thereby contributing to their overall health and well-being.
One of the primary reasons for vaccinating dogs is to prevent the spread of infectious diseases within the canine population. By immunizing dogs against prevalent diseases such as rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and canine hepatitis, pet owners can significantly reduce the risk of their furry companions contracting these illnesses. Moreover, vaccination also helps in curbing the transmission of these diseases to other dogs, thereby fostering a healthier and safer environment for the entire canine community.
Furthermore, dog vaccinations are instrumental in safeguarding human health. Diseases such as rabies, which can be transmitted from infected dogs to humans, pose a significant public health concern. Through routine vaccination, the risk of zoonotic diseases, which are those that can be transmitted from animals to humans, is mitigated, thereby protecting both dogs and the human population.
In addition to preventing the onset of contagious diseases, vaccinations also contribute to reducing the economic burden associated with treating these illnesses. The cost of treating a dog suffering from preventable diseases can be substantial, often exceeding the expense of routine vaccinations. By investing in a comprehensive vaccination regimen, pet owners can potentially save on veterinary expenses while ensuring the long-term health and well-being of their canine companions.
Moreover, vaccinations provide peace of mind to pet owners, knowing that they have taken proactive measures to protect their dogs from potentially devastating diseases. This proactive approach not only benefits the individual dog but also contributes to the collective immunity of the entire canine population, thereby fostering a healthier and more resilient community of dogs.
In essence, the importance of dog vaccination cannot be overstated. By prioritizing routine vaccinations, pet owners play a pivotal role in safeguarding the health and well-being of their beloved canine companions, while also contributing to the broader public health landscape. Through vaccination, dogs can lead healthier, happier lives, free from the threat of preventable diseases, thereby enriching the bond between pets and their human caregivers.
Recommended Time Between Shots
The recommended time intervals between dog vaccinations are essential for ensuring the effectiveness of the immunization process and providing comprehensive protection against a range of infectious diseases. Understanding the optimal timing for administering different vaccines is crucial for pet owners, as it directly impacts the efficacy of the immunization and the overall health of their canine companions.
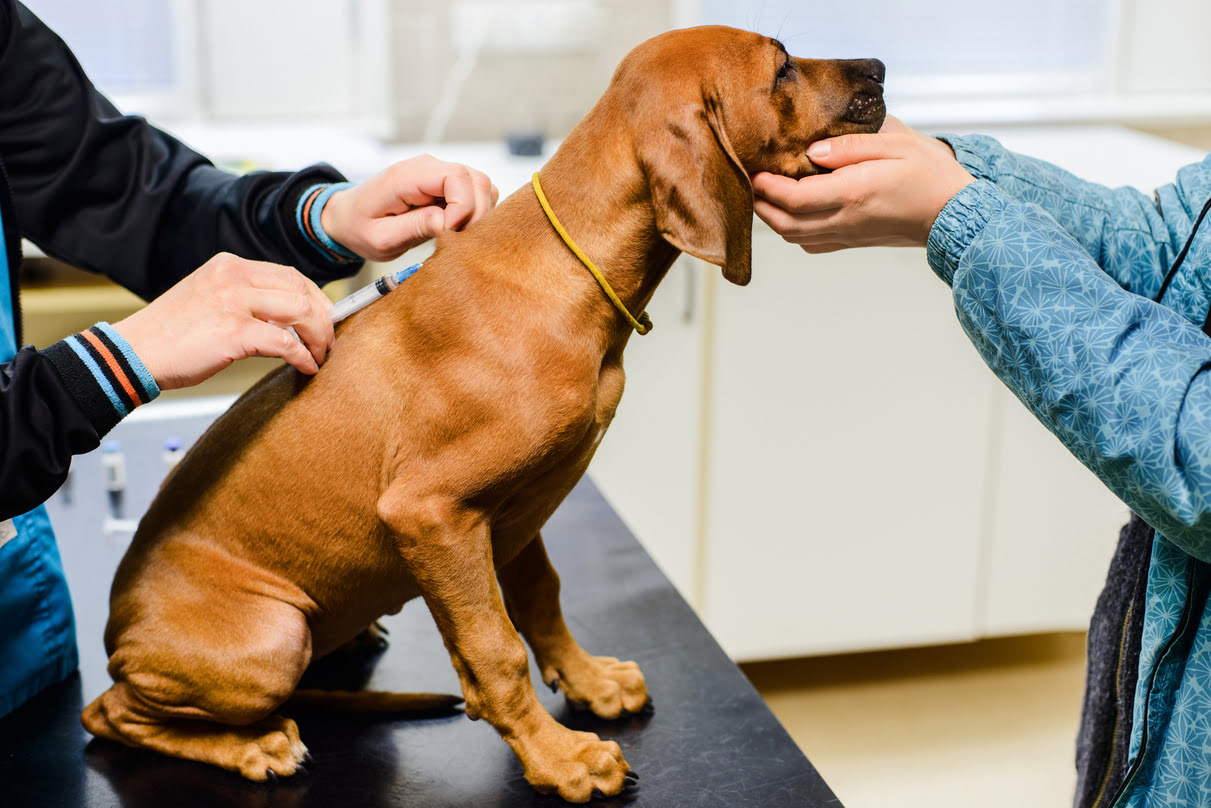
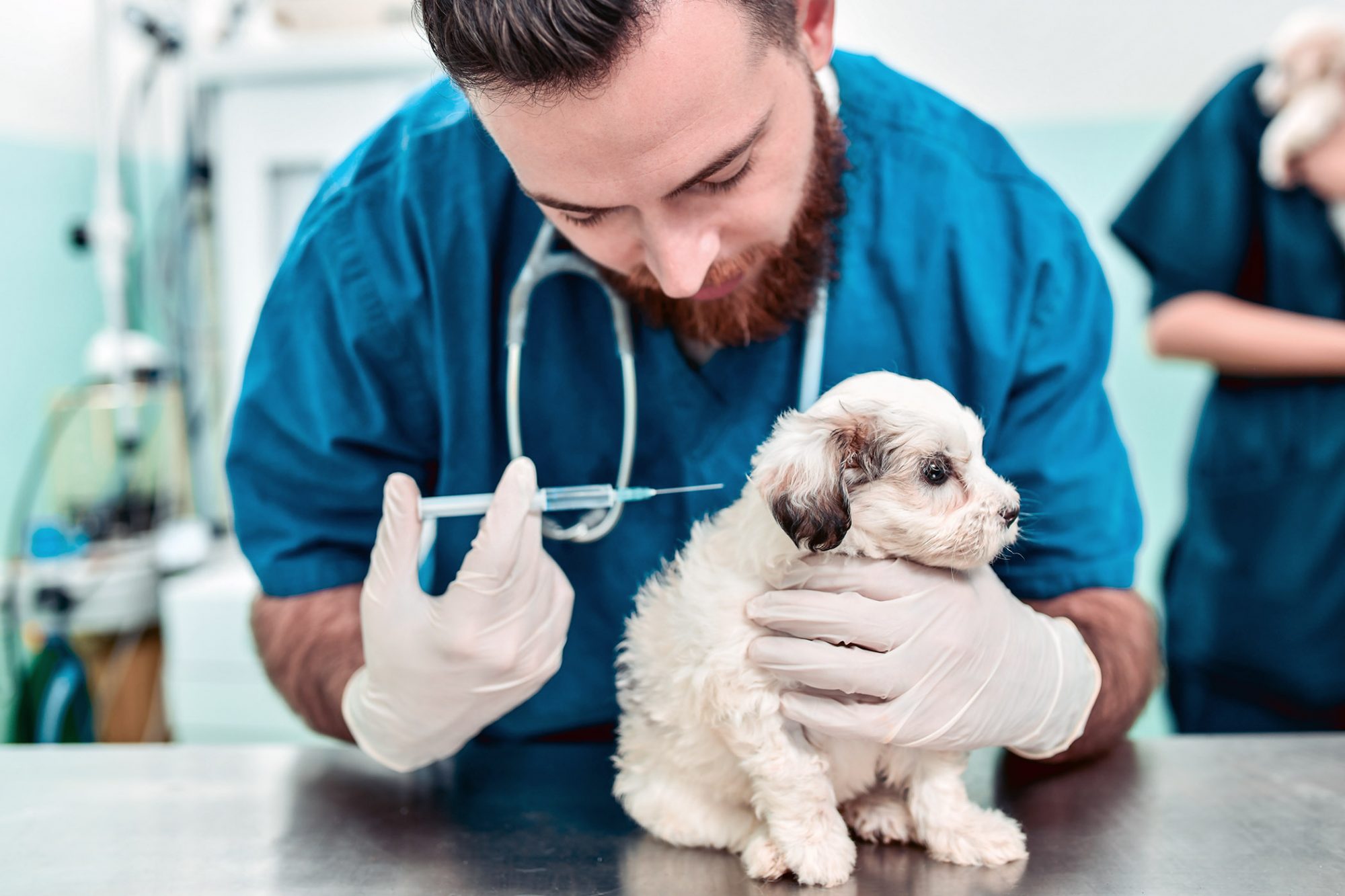
In general, the recommended time between shots of dog vaccination is determined by the specific vaccine being administered and the age of the dog. Puppies typically receive a series of vaccinations, with each vaccine requiring multiple doses to establish robust immunity. The initial vaccination schedule for puppies usually begins at around 6-8 weeks of age, with subsequent doses administered at 3-4 week intervals until the puppy reaches 16 weeks of age. This schedule may vary slightly based on the specific vaccine protocols recommended by veterinarians.
For adult dogs, the recommended time between shots is influenced by the duration of immunity provided by each vaccine. Some vaccines, such as core vaccines against diseases like rabies and distemper, offer long-lasting immunity and may require less frequent administration, typically every 1-3 years. Non-core vaccines, which protect against diseases based on a dog's lifestyle and risk factors, may have varying intervals between shots, often ranging from annual to triennial boosters.
It is important to note that the recommended time between shots may also be influenced by local regulations and guidelines, as well as the prevalence of specific diseases in a particular geographic region. Therefore, pet owners should consult with their veterinarians to develop a tailored vaccination schedule that aligns with their dog's individual needs and the prevalent disease risks in their environment.
Adhering to the recommended time intervals between shots is crucial for ensuring that dogs receive optimal protection against infectious diseases. Deviating from the prescribed vaccination schedule can compromise the effectiveness of the immunization, leaving dogs vulnerable to potentially life-threatening illnesses. By diligently following the recommended time between shots, pet owners can proactively safeguard the health and well-being of their furry companions, contributing to a thriving and resilient canine community.
In essence, understanding and adhering to the recommended time intervals between shots of dog vaccination is a cornerstone of responsible pet ownership, ensuring that dogs receive comprehensive protection against a spectrum of infectious diseases. By prioritizing a tailored vaccination schedule in consultation with veterinarians, pet owners can play a pivotal role in promoting the long-term health and well-being of their beloved canine companions.
Factors Affecting Vaccination Schedule
Several factors can influence a dog's vaccination schedule, necessitating a tailored approach to ensure optimal protection against infectious diseases. Understanding these factors is crucial for pet owners and veterinarians alike, as it enables them to develop a vaccination regimen that aligns with the individual needs and lifestyle of each dog. By considering these influential factors, pet owners can proactively safeguard the health and well-being of their furry companions, contributing to a thriving and resilient canine community.
1. Age and Developmental Stage
The age and developmental stage of a dog play a pivotal role in determining the appropriate vaccination schedule. Puppies, for instance, require a series of vaccinations to establish robust immunity, as their maternal antibodies wane and their own immune systems mature. The initial vaccination schedule for puppies typically begins at 6-8 weeks of age, with subsequent doses administered at specific intervals to ensure comprehensive protection. Understanding the developmental milestones of puppies is essential for determining the optimal timing of vaccinations and ensuring their effectiveness.
Read more: What Is In An Allergy Shot For Dogs
2. Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
The lifestyle and environmental factors to which a dog is exposed can significantly influence their vaccination needs. Dogs that frequent dog parks, boarding facilities, or areas with a high prevalence of certain diseases may require additional vaccinations to mitigate the heightened risk of exposure. Similarly, dogs that engage in activities such as hiking, camping, or hunting may benefit from vaccines tailored to protect against specific environmental hazards. By considering the lifestyle and environmental factors relevant to each dog, veterinarians can tailor a vaccination schedule that provides targeted protection against prevalent risks.
3. Health Status and Medical History
The health status and medical history of a dog are critical considerations when devising a vaccination schedule. Dogs with underlying health conditions or a history of vaccine-related adverse reactions may require a modified vaccination approach to minimize potential risks. Additionally, the presence of certain medical conditions may impact the dog's immune response to vaccines, necessitating a personalized vaccination plan tailored to their specific health needs. By taking into account the individual health status and medical history of each dog, veterinarians can ensure that vaccinations are administered in a manner that prioritizes both safety and efficacy.
4. Local Regulations and Guidelines
Local regulations and guidelines pertaining to dog vaccinations can also influence the vaccination schedule. Certain jurisdictions may have specific requirements regarding the administration of core vaccines, such as rabies, and may mandate the frequency of booster shots to maintain compliance. Pet owners should familiarize themselves with the prevailing regulations in their area and work closely with veterinarians to ensure that their dogs receive vaccinations in accordance with local mandates.
5. Prevailing Disease Risks
The prevalent disease risks in a particular geographic region can significantly impact the vaccination needs of dogs. Certain diseases may be more prevalent in specific areas, necessitating tailored vaccination protocols to address the heightened risk of exposure. By assessing the prevalent disease risks in their environment, veterinarians can recommend targeted vaccinations that provide optimal protection against locally endemic diseases, thereby mitigating the risk of illness within the canine population.
In essence, a myriad of factors can influence a dog's vaccination schedule, underscoring the importance of a personalized and tailored approach to immunization. By considering the age and developmental stage, lifestyle and environmental factors, health status and medical history, local regulations, and prevailing disease risks, veterinarians can collaborate with pet owners to devise a vaccination schedule that prioritizes the individual needs of each dog. This proactive and personalized approach to vaccination scheduling is instrumental in safeguarding the health and well-being of dogs, contributing to a resilient and thriving community of canine companions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dog vaccination is an indispensable pillar of responsible pet ownership, serving as a proactive measure to safeguard the health and well-being of our beloved canine companions. By adhering to a comprehensive vaccination schedule, pet owners play a pivotal role in protecting their dogs from a spectrum of infectious diseases, thereby contributing to a thriving and resilient canine community. The significance of dog vaccination extends beyond individual pets, encompassing broader public health implications and economic considerations. Through routine vaccination, pet owners not only prioritize the health of their furry companions but also contribute to the collective immunity of the entire canine population, fostering a safer and healthier environment for dogs and humans alike.
Understanding the recommended time intervals between shots of dog vaccination is essential for ensuring the effectiveness of the immunization process. By adhering to the prescribed vaccination schedule, pet owners can proactively safeguard their dogs from potentially life-threatening diseases, thereby promoting their long-term health and well-being. Moreover, considering the various factors that can influence a dog's vaccination schedule, such as age, lifestyle, health status, and prevailing disease risks, enables veterinarians and pet owners to develop tailored vaccination regimens that align with the individual needs of each dog. This personalized approach to vaccination scheduling ensures that dogs receive optimal protection against prevalent risks, contributing to a resilient and thriving community of canine companions.
As responsible pet owners, it is imperative to prioritize routine vaccinations and collaborate closely with veterinarians to develop a vaccination schedule tailored to the specific needs of our dogs. By doing so, we not only fulfill our duty to safeguard the health of our furry companions but also contribute to the broader public health landscape. Through proactive vaccination, we can mitigate the spread of infectious diseases, reduce the economic burden associated with treating preventable illnesses, and foster a community of healthy and thriving dogs.
In essence, dog vaccination is a cornerstone of responsible pet ownership, embodying our commitment to prioritizing the health and well-being of our beloved canine companions. By understanding the importance of vaccination, adhering to recommended time intervals between shots, and considering the influential factors that shape a dog's vaccination schedule, pet owners can play a pivotal role in promoting a vibrant and resilient community of dogs. Through proactive vaccination, we can enrich the lives of our furry companions, ensuring that they lead healthy, happy, and fulfilling lives free from the threat of preventable diseases.