Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Often Is Rabies Vaccination Required For Dogs In California

Common Health Issues
How Often Is Rabies Vaccination Required For Dogs In California
Published: January 31, 2024
Ensure your dog's health with regular rabies vaccinations in California. Learn about this and other common health issues for your furry friend.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Rabies is a viral disease that affects the central nervous system of mammals, including humans. It is a highly fatal disease that poses a significant public health concern. In California, as in many other states, rabies vaccination for dogs is a crucial aspect of responsible pet ownership and public safety. The state has specific requirements and regulations in place to ensure that dogs are adequately protected against this deadly disease.
Rabies is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected animal, with dogs being one of the most common carriers of the virus. Due to the potential risk of transmission to humans and other animals, the state of California has implemented strict guidelines regarding the vaccination of dogs against rabies. These regulations not only safeguard the health and well-being of pets but also contribute to the overall public health and safety of communities.
Understanding the importance of rabies vaccination for dogs is essential for every pet owner. It not only protects the individual dog from the devastating effects of the disease but also prevents the potential spread of rabies within the community. By adhering to the vaccination requirements set forth by the state, dog owners play a vital role in mitigating the risk of rabies transmission and upholding the welfare of their beloved pets.
In the subsequent sections, we will delve into the specific rabies vaccination requirements for dogs in California, including the frequency of vaccination, exemptions, and special circumstances. This comprehensive exploration aims to provide dog owners with a clear understanding of their responsibilities in ensuring the health and safety of their canine companions, as well as the broader community. Let's embark on this informative journey to unravel the essential aspects of rabies vaccination for dogs in the Golden State.
Read more: How Often Do Dogs Get Rabies Vaccinations
Rabies Vaccination Requirements in California
In California, the rabies vaccination requirements for dogs are established and enforced by the California Department of Public Health (CDPH) and local county authorities. These regulations are designed to protect both the canine population and the public from the threat of rabies, a potentially fatal viral disease.
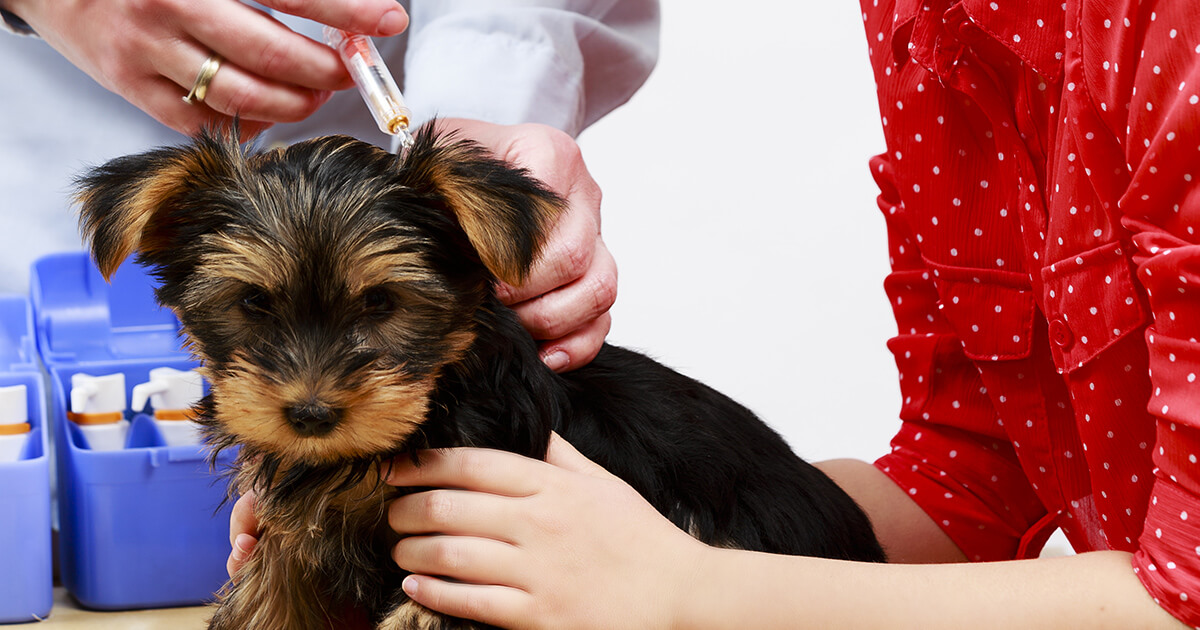
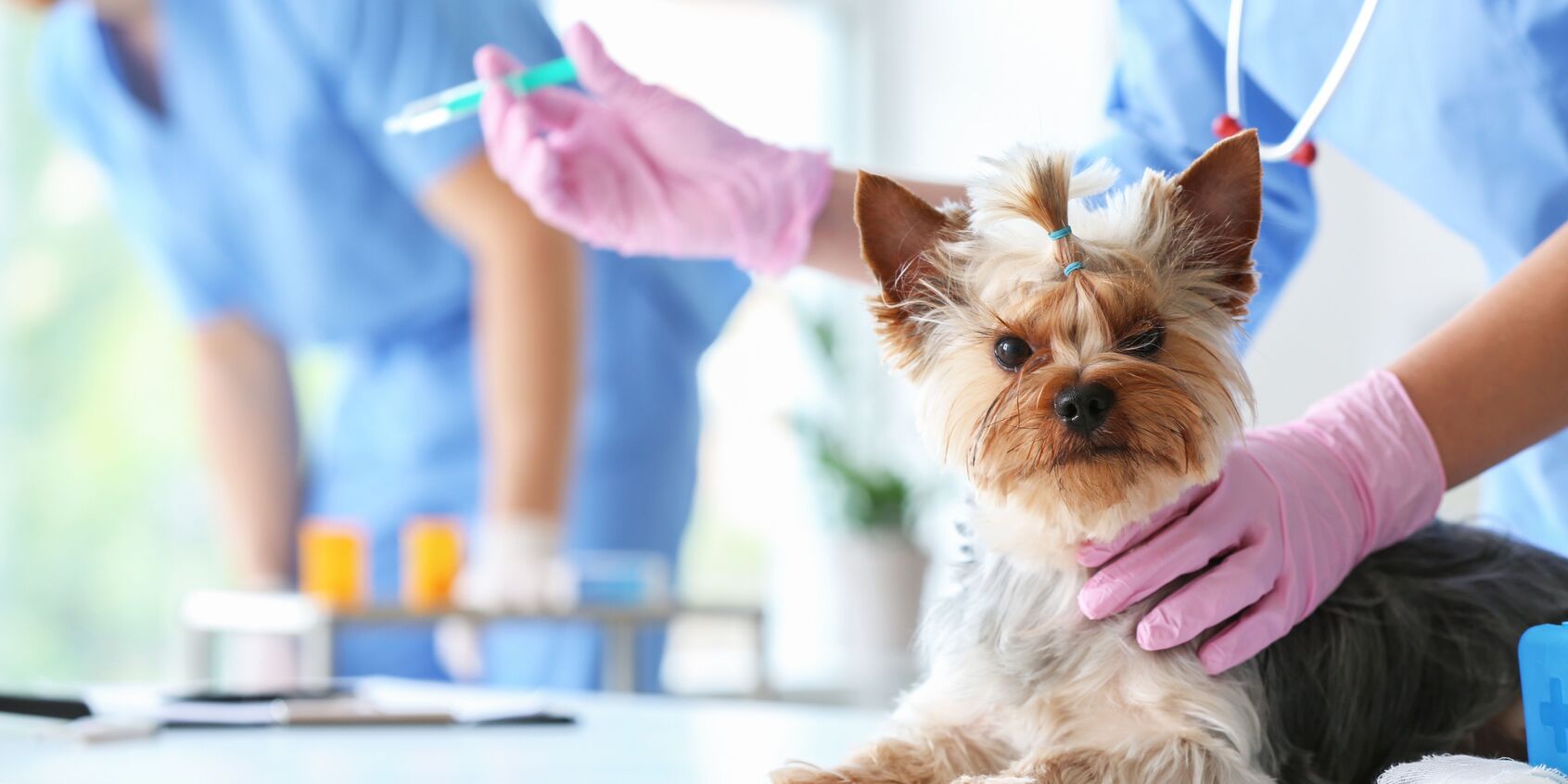
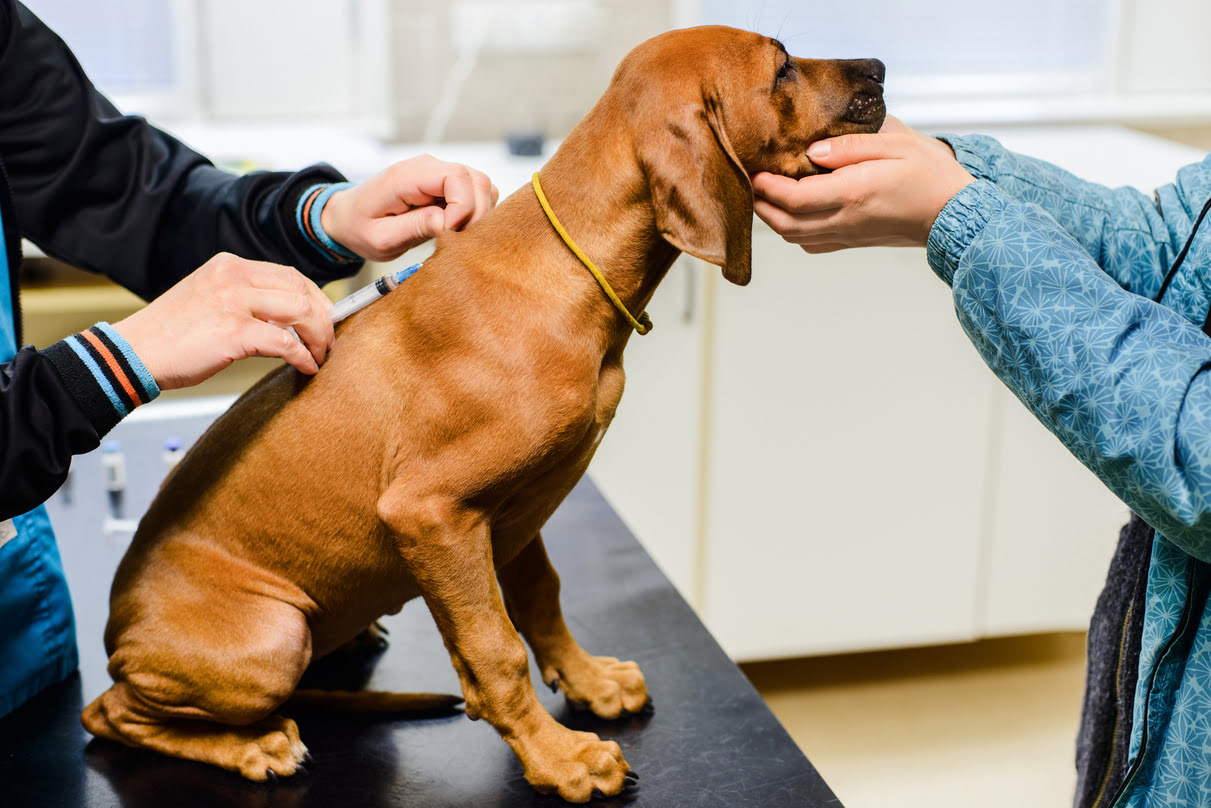
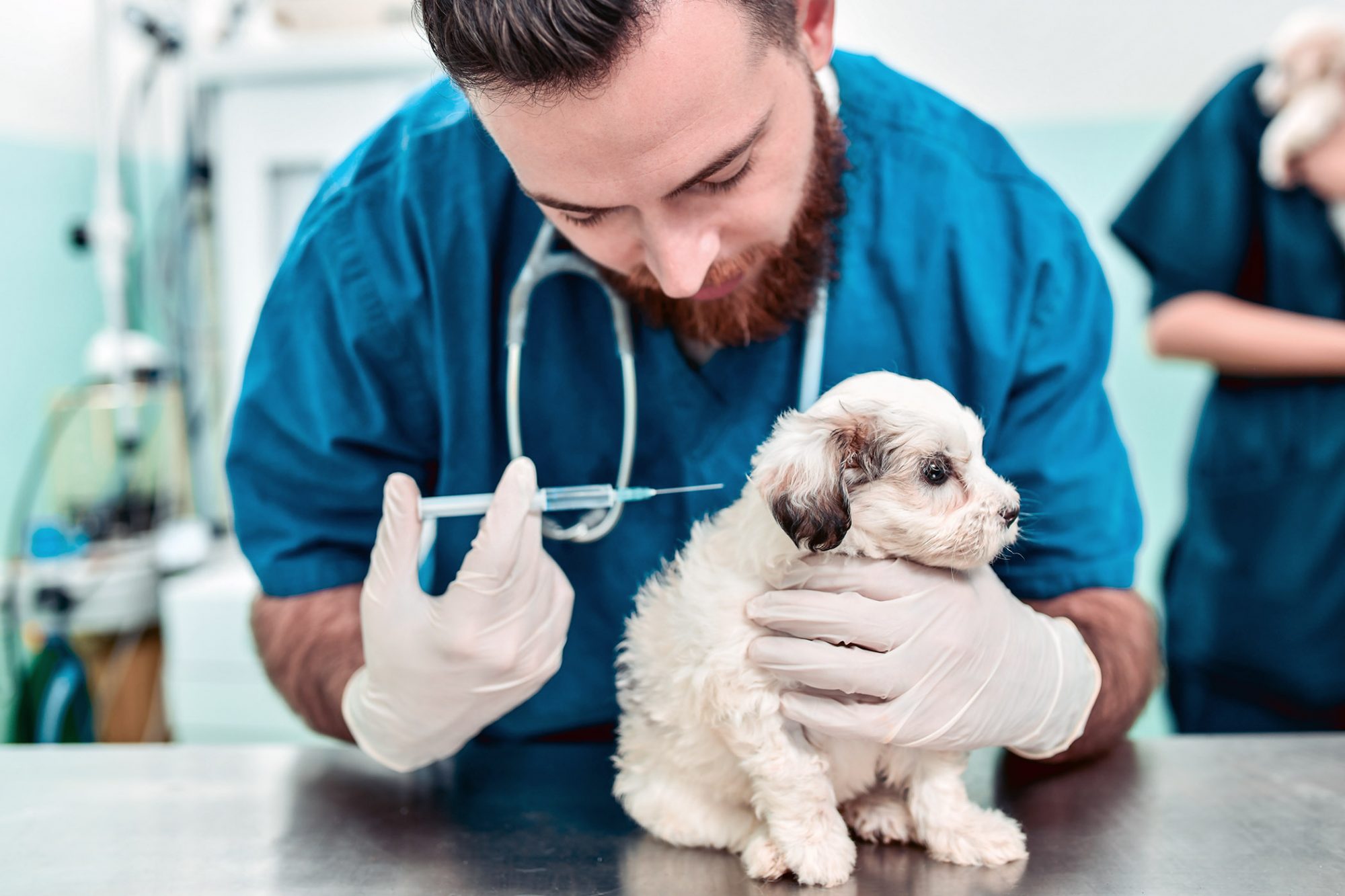
According to California state law, all dogs are required to be vaccinated against rabies by a licensed veterinarian. The initial vaccination should be administered when the dog is around 16 weeks of age. Subsequently, a booster shot is typically required within one year of the initial vaccination. Following the initial booster, the frequency of rabies vaccination for dogs in California may vary based on the type of vaccine used and local county regulations.
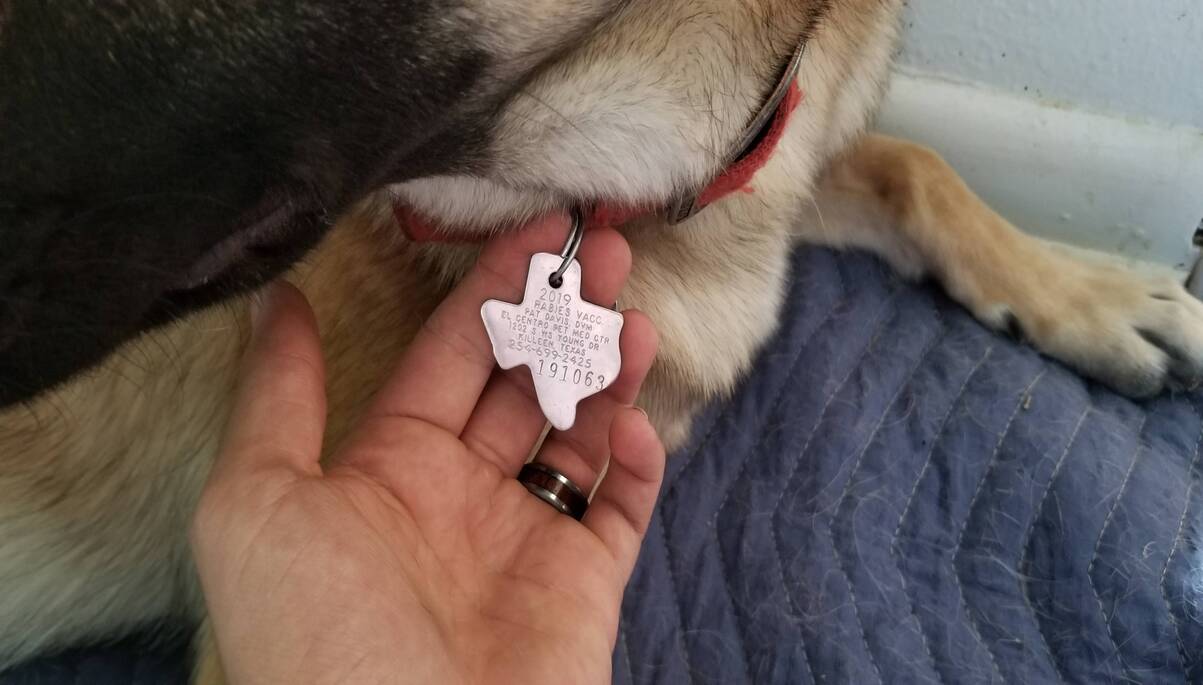
It's important to note that the rabies vaccination must be performed by a licensed veterinarian, and the vaccine used should be approved by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) for use in dogs. Additionally, the vaccination should be accompanied by a certificate issued by the administering veterinarian, documenting the details of the vaccination, including the date of administration, the type of vaccine used, and the duration of immunity.
In California, the standard duration of immunity for rabies vaccination in dogs is typically three years for adult dogs. However, some counties may have specific regulations that require more frequent vaccination, such as an annual booster, to ensure continuous protection against rabies.
Furthermore, the CDPH emphasizes the importance of maintaining accurate vaccination records for dogs, as these records serve as crucial documentation of compliance with state and local rabies vaccination requirements. Dog owners are advised to keep copies of vaccination certificates and ensure that the information is up to date and easily accessible.
Failure to comply with rabies vaccination requirements in California can result in legal consequences, including fines and potential quarantine of the dog. Moreover, unvaccinated dogs may be at risk of exposure to rabies, posing a threat to their health and the safety of the community.
Overall, the rabies vaccination requirements in California are established to safeguard the well-being of dogs and mitigate the risk of rabies transmission. By adhering to these regulations, dog owners contribute to the collective effort of maintaining public health and safety, while ensuring the protection of their cherished canine companions.
Frequency of Rabies Vaccination for Dogs
The frequency of rabies vaccination for dogs in California is a critical aspect of responsible pet ownership and public health protection. After the initial vaccination at around 16 weeks of age, dogs typically receive a booster shot within one year to ensure the establishment of immunity against rabies. Following this initial booster, the frequency of rabies vaccination may vary based on the type of vaccine used and local county regulations.
In California, the standard duration of immunity for rabies vaccination in adult dogs is typically three years. This means that most adult dogs require a rabies booster shot every three years to maintain protection against the virus. However, it's important to note that some counties may have specific regulations that mandate more frequent vaccination, such as an annual booster, to ensure continuous immunity against rabies.
The decision regarding the frequency of rabies vaccination for dogs is influenced by various factors, including the type of vaccine used, the prevalence of rabies in the region, and local public health considerations. Additionally, the recommendations provided by the American Animal Hospital Association (AAHA) and the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) serve as valuable guidelines for determining the appropriate vaccination schedule for dogs.
It's crucial for dog owners to stay informed about the specific vaccination requirements in their local area, as county regulations may differ regarding the frequency of rabies vaccination. By remaining proactive and attentive to these regulations, dog owners can ensure that their pets receive timely and adequate protection against rabies, thereby contributing to the overall public health and safety of their communities.
Maintaining accurate vaccination records for dogs is paramount, as these records serve as documentation of compliance with state and local rabies vaccination requirements. Dog owners should retain copies of vaccination certificates and ensure that the information is up to date and easily accessible. This proactive approach not only facilitates compliance with regulations but also provides a comprehensive record of the dog's vaccination history, which can be invaluable for future reference.
In summary, the frequency of rabies vaccination for dogs in California is contingent upon various factors, including the type of vaccine, local county regulations, and the standard duration of immunity. By adhering to the recommended vaccination schedule and staying informed about local requirements, dog owners play a pivotal role in safeguarding the health and well-being of their beloved pets, while contributing to the broader efforts of rabies prevention and public safety.
Exemptions and Special Circumstances
In certain situations, exemptions from rabies vaccination requirements may be granted to dogs based on specific circumstances and medical considerations. It's important to recognize that while rabies vaccination is a fundamental aspect of responsible pet ownership, there are instances where exemptions may be warranted to accommodate the health and well-being of individual dogs.
One of the primary considerations for exemptions from rabies vaccination is related to the health of the dog. In cases where a licensed veterinarian determines that a dog's health condition precludes the safe administration of the rabies vaccine, an exemption may be granted. This could apply to dogs with underlying medical conditions or those undergoing treatments that may pose a risk in conjunction with vaccination. It's crucial for such determinations to be made by qualified veterinary professionals, taking into account the specific health status of the dog.
Additionally, exemptions from rabies vaccination requirements may be considered for dogs with documented allergic reactions to components of the rabies vaccine. Allergic reactions to vaccines, although rare, can pose significant health risks to dogs. In such instances, alternative measures for protecting the dog against rabies, while ensuring public safety, may be explored in consultation with a veterinarian and local public health authorities.
Furthermore, special circumstances related to the lifestyle and environment of certain dogs may warrant exemptions from standard vaccination requirements. For example, dogs that are certified as working animals, such as service dogs or law enforcement K-9 units, may be subject to distinct considerations regarding rabies vaccination. These dogs often have unique exposure risks and may require tailored vaccination protocols to align with their specific roles and responsibilities.
It's important to emphasize that exemptions from rabies vaccination are not granted lightly and should be approached with careful consideration of both the individual dog's health needs and public health implications. Any exemptions granted should be well-documented, transparent, and in compliance with applicable state and local regulations.
In summary, exemptions from rabies vaccination requirements for dogs in California may be granted in specific circumstances, such as health-related considerations and unique environmental factors. These exemptions are carefully evaluated and should be guided by the expertise of licensed veterinarians and relevant public health authorities. By recognizing and accommodating exemptions where warranted, the welfare of individual dogs can be upheld while maintaining a commitment to public health and safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rabies vaccination requirements for dogs in California are integral to the protection of both canine companions and public health. The state's regulations, overseen by the California Department of Public Health and local county authorities, establish clear guidelines for the vaccination of dogs against rabies. These regulations not only serve to safeguard individual pets from the devastating effects of the disease but also contribute to the broader efforts of rabies prevention and public safety.
Understanding the frequency of rabies vaccination and adhering to the recommended schedule is paramount for dog owners. After the initial vaccination at approximately 16 weeks of age, dogs typically receive a booster shot within one year, followed by subsequent vaccinations based on the type of vaccine used and local county regulations. Maintaining accurate vaccination records is essential, as it ensures compliance with state and local requirements and provides a comprehensive history of the dog's vaccinations.
Exemptions from rabies vaccination requirements may be granted in specific circumstances, such as health-related considerations and unique environmental factors. These exemptions are carefully evaluated and should be guided by the expertise of licensed veterinarians and relevant public health authorities, ensuring that the welfare of individual dogs is upheld while maintaining a commitment to public health and safety.
By upholding the rabies vaccination requirements for dogs in California, pet owners play a crucial role in mitigating the risk of rabies transmission and contributing to the overall well-being of their communities. Compliance with these regulations not only protects individual pets but also fosters a safer environment for all residents. It is a testament to responsible pet ownership and a collective commitment to public health and safety.
In essence, the importance of rabies vaccination for dogs cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental aspect of responsible pet ownership and a vital component of public health protection. By staying informed about the requirements, maintaining accurate vaccination records, and seeking guidance from qualified veterinary professionals, dog owners can fulfill their role in ensuring the health and safety of their beloved canine companions and the community at large.