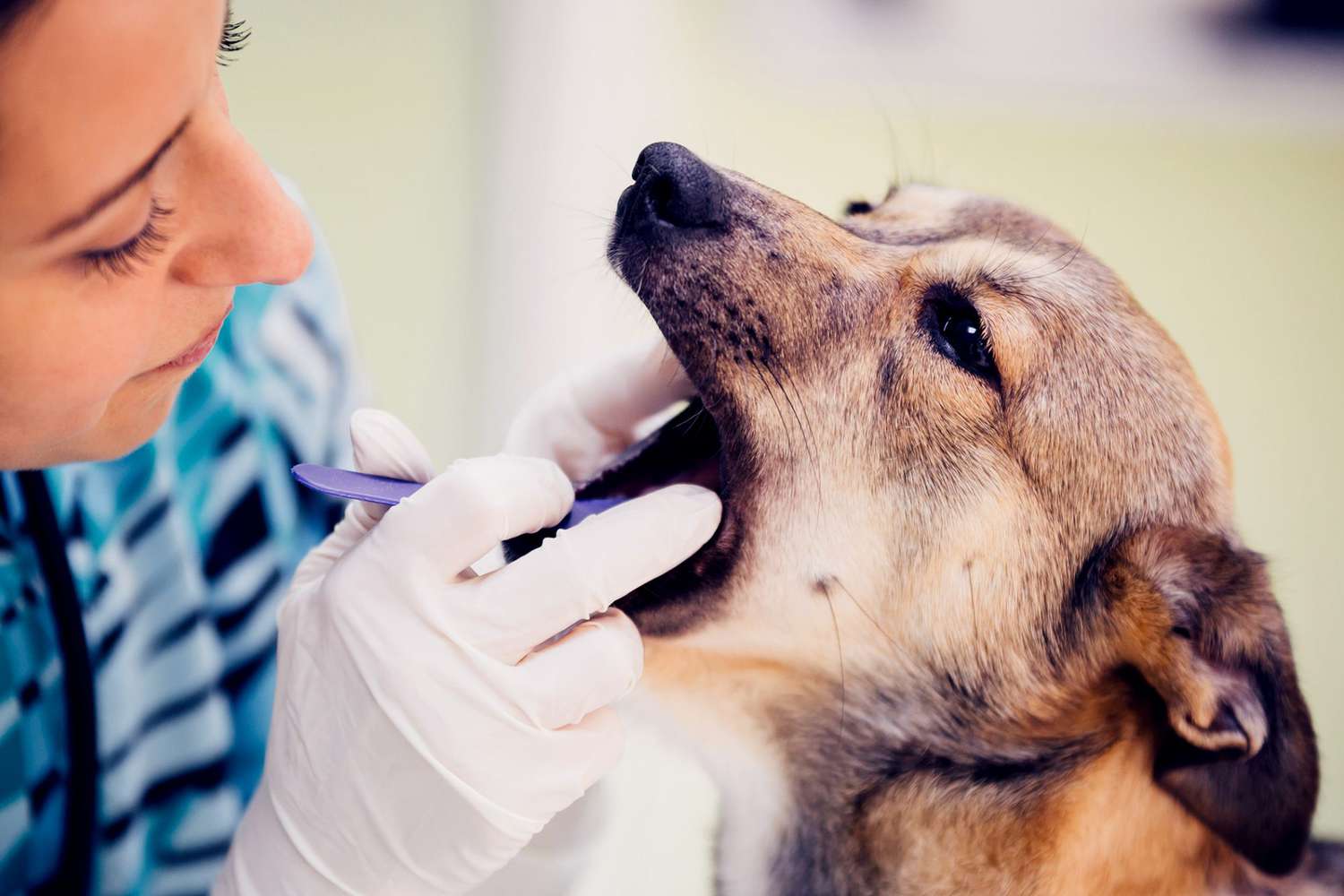
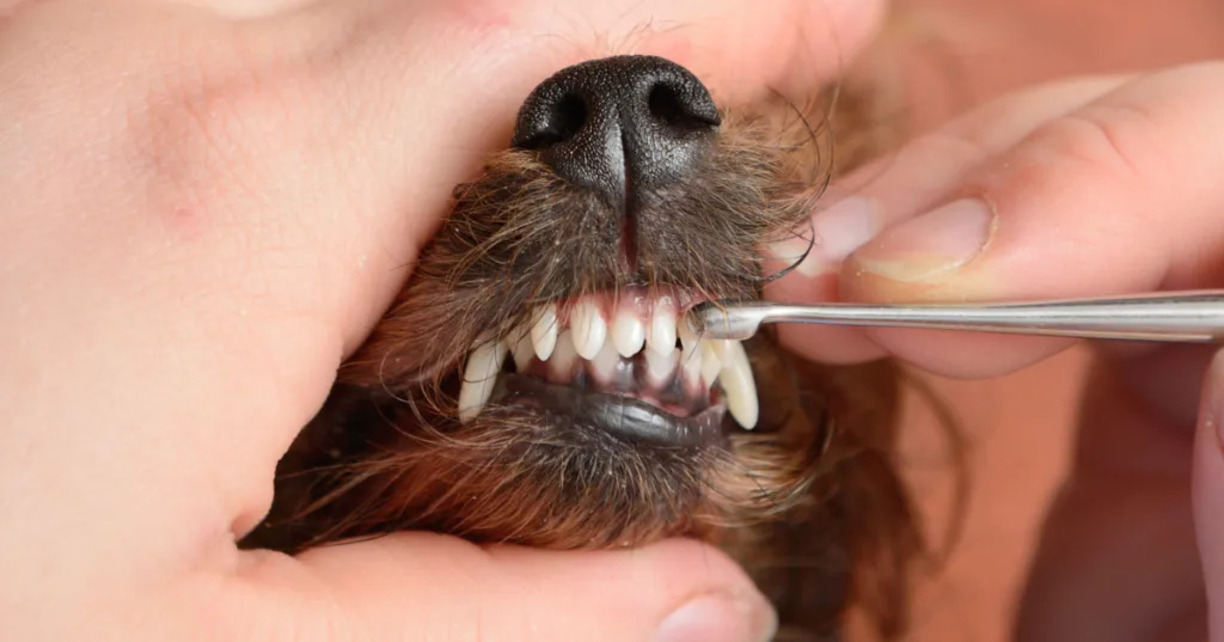
Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How To Treat A Dental Infection In A Dog


Common Health Issues
How To Treat A Dental Infection In A Dog
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn how to address common health issues in dogs, including dental infections. Discover effective treatments and preventive measures to keep your pet healthy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Dental infections in dogs can cause discomfort and distress, impacting their overall well-being. Just like humans, dogs can experience dental issues, including infections, which can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. As responsible pet owners, it's crucial to understand the signs, symptoms, and treatment options for dental infections in dogs to ensure their optimal health and happiness.
Dental infections in dogs can stem from various factors, such as plaque and tartar buildup, fractured teeth, or advanced periodontal disease. These infections can result in pain, difficulty eating, and even systemic health problems if bacteria from the mouth enter the bloodstream. Therefore, being proactive in recognizing and addressing dental infections is essential for maintaining your dog's quality of life.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of dental infections in dogs, covering everything from understanding the root causes to effective treatment options and preventive measures. By gaining insight into this common health issue, you'll be better equipped to provide the necessary care and support for your canine companion, ensuring their dental health and overall well-being.
Understanding the impact of dental infections on dogs and learning how to identify and address these issues is a vital aspect of responsible pet ownership. With the right knowledge and proactive measures, you can help your furry friend maintain a healthy and happy life, free from the discomfort and complications associated with dental infections. Let's embark on this informative journey to empower you as a pet owner in safeguarding your dog's dental health.
Read more: What Is The Safest Dental Dog Treat?
Understanding Dental Infections in Dogs
Dental infections in dogs, also known as periodontal disease, encompass a range of oral health issues that can affect the teeth, gums, and surrounding structures. These infections often stem from the accumulation of plaque and tartar, which harbor harmful bacteria, leading to inflammation and potential tissue damage. Additionally, factors such as fractured teeth, oral trauma, or underlying health conditions can contribute to the development of dental infections in dogs.
Periodontal disease typically progresses through various stages, starting with the formation of plaque, a sticky film comprised of bacteria, saliva, and food particles. If not adequately removed through regular brushing or professional dental cleanings, plaque can mineralize and harden into tartar, also known as dental calculus. Tartar accumulation can irritate the gums, causing inflammation known as gingivitis, which is an early stage of periodontal disease.
As the infection advances, the bacteria within the tartar can penetrate beneath the gum line, leading to more severe forms of periodontal disease. This can result in gum recession, destruction of the tooth's supporting structures, and the formation of periodontal pockets, which further harbor bacteria and exacerbate the infection. Left untreated, dental infections can lead to tooth loss, abscess formation, and even systemic health issues as bacteria from the oral cavity enter the bloodstream.
Understanding the progression and impact of dental infections in dogs is crucial for pet owners. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of periodontal disease, such as bad breath, swollen or bleeding gums, reluctance to eat, and pawing at the mouth, can prompt timely intervention to address the underlying infection. Moreover, being aware of the risk factors, including breed predispositions, age, and diet, can aid in implementing preventive measures to mitigate the development of dental infections in dogs.
By comprehending the intricate nature of dental infections in dogs, pet owners can take proactive steps to prioritize their canine companions' oral health. From regular dental examinations to implementing effective home care routines, a thorough understanding of periodontal disease empowers pet owners to advocate for their dogs' well-being and ensure they receive the necessary support and treatment to combat dental infections.
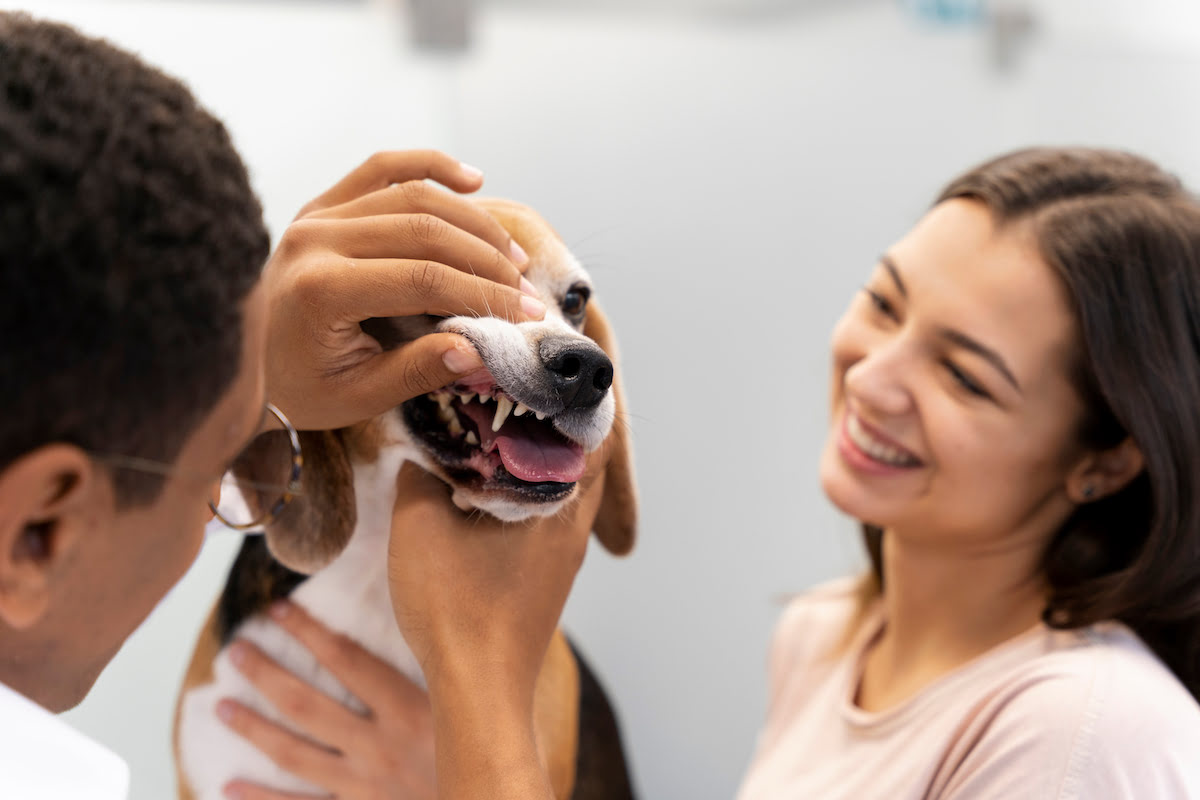
Signs and Symptoms of Dental Infections
Identifying the signs and symptoms of dental infections in dogs is pivotal in addressing these oral health issues promptly and effectively. By recognizing the subtle indicators of periodontal disease, pet owners can take proactive measures to seek veterinary care and implement appropriate treatment strategies. Here are the key signs and symptoms to watch for:
-
Bad Breath (Halitosis): Persistent foul breath is often an early indication of dental infections in dogs. The accumulation of bacteria and decaying food particles in the oral cavity contributes to the unpleasant odor, signaling potential oral health issues.
-
Gum Abnormalities: Observing changes in the gums can provide valuable insights into a dog's dental health. Look for signs of inflammation, such as redness, swelling, or tenderness, as well as bleeding or receding gums. These abnormalities often accompany periodontal disease and warrant immediate attention.
-
Difficulty Eating or Chewing: Dogs experiencing dental infections may exhibit reluctance to eat, particularly when it involves chewing hard or crunchy food. This reluctance can stem from oral discomfort, tooth pain, or sensitivity associated with the infection.
-
Excessive Drooling: Unexplained or excessive drooling, especially when it deviates from a dog's typical behavior, can indicate oral discomfort or pain linked to dental infections. Monitor changes in drooling patterns to assess potential dental issues.
-
Pawing at the Mouth: Dogs may instinctively paw at their mouths when experiencing oral discomfort. Persistent pawing or rubbing at the face and mouth area can signal underlying dental problems, prompting further investigation.
-
Visible Tartar or Discoloration: Inspect your dog's teeth for visible tartar buildup, discoloration, or visible plaque. These visual cues can indicate the presence of dental infections and the need for professional dental assessment and treatment.
-
Behavioral Changes: Keep an eye out for changes in your dog's behavior, such as irritability, restlessness, or reluctance to engage in play or social interactions. Dental infections can cause discomfort, leading to alterations in a dog's typical demeanor.
-
Reluctance to Be Touched Around the Mouth: Dogs experiencing oral pain or discomfort may display aversion to having their mouths touched or examined. Notice any signs of reluctance or sensitivity when handling the mouth area during grooming or routine care.
By remaining vigilant and attuned to these signs and symptoms, pet owners can promptly address potential dental infections in their dogs, ensuring timely veterinary intervention and appropriate treatment. Early detection and proactive management of dental issues are instrumental in safeguarding a dog's oral health and overall well-being.
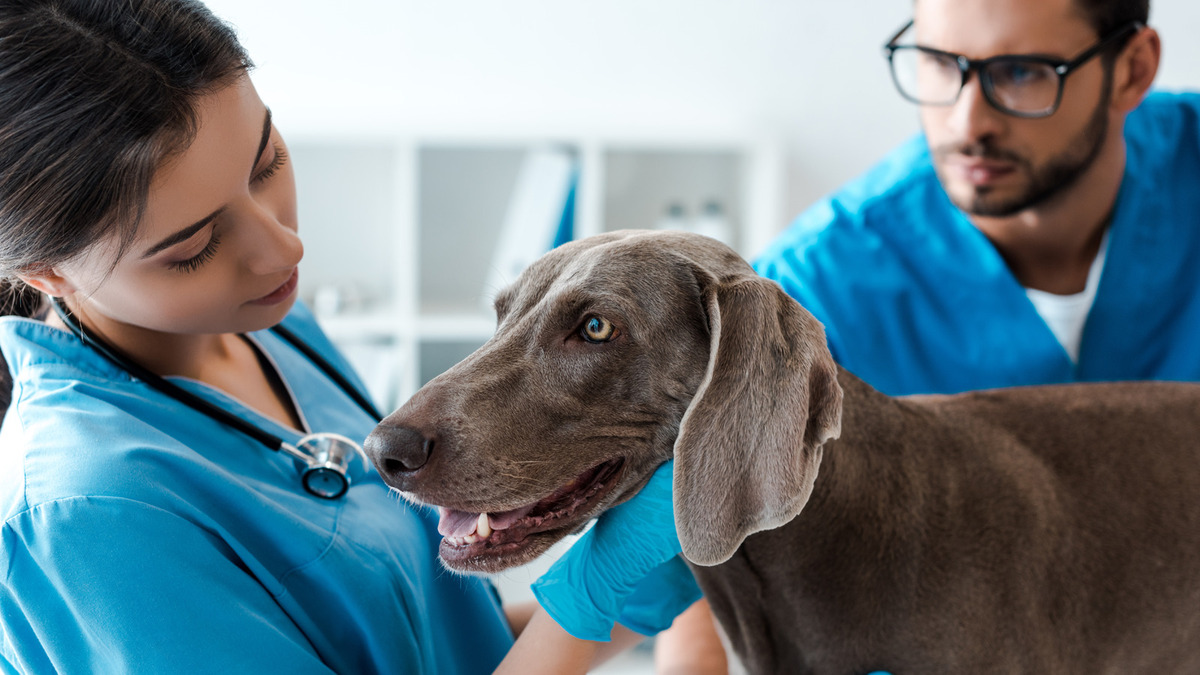
Seeking Veterinary Care
Seeking prompt veterinary care is paramount when suspecting dental infections in dogs. Upon observing any signs or symptoms indicative of periodontal disease, such as persistent bad breath, gum abnormalities, or changes in eating habits, it is imperative to schedule a comprehensive veterinary examination for your canine companion. Veterinary professionals possess the expertise and resources to conduct thorough oral assessments, diagnose dental infections, and recommend tailored treatment plans to address the underlying issues.
During the veterinary visit, the veterinarian will perform a comprehensive oral examination, evaluating the teeth, gums, and oral cavity for signs of infection, inflammation, or dental abnormalities. This assessment may involve dental probing to assess periodontal pockets, dental X-rays to visualize underlying structures, and a thorough evaluation of the oral tissues to identify potential sources of discomfort or infection.
Based on the findings, the veterinarian will formulate a personalized treatment approach to address the dental infections in your dog. This may encompass professional dental cleanings to remove tartar and plaque, periodontal therapy to address gum disease, or extractions of severely affected teeth to alleviate pain and prevent further complications. Additionally, the veterinarian may prescribe antibiotics or pain management medications to combat the infection and alleviate discomfort.
Furthermore, the veterinary team will provide guidance on post-treatment care and home oral hygiene practices to support your dog's recovery and prevent the recurrence of dental infections. This may include recommendations for regular tooth brushing, dental diets or chews, and the use of oral hygiene products tailored to your dog's specific needs.
In some cases, the veterinarian may collaborate with veterinary dental specialists to ensure comprehensive and specialized care for complex dental infections or advanced periodontal disease. This collaborative approach underscores the commitment to delivering optimal oral health outcomes for dogs experiencing dental infections.
By proactively seeking veterinary care and adhering to the recommended treatment protocols, pet owners can effectively address dental infections in their dogs, alleviating discomfort, preserving oral health, and promoting overall well-being. Timely veterinary intervention is instrumental in mitigating the progression of dental infections and safeguarding a dog's oral health, underscoring the pivotal role of professional veterinary care in managing periodontal disease in dogs.
Treatment Options for Dental Infections
Upon diagnosis of dental infections in dogs, various treatment options may be recommended to address the underlying oral health issues and alleviate discomfort. The treatment approach is tailored to the specific needs of the dog, considering the extent of the infection, the presence of complicating factors, and the overall oral health status. Here are the key treatment options for dental infections in dogs:
-
Professional Dental Cleanings: Professional dental cleanings, performed under general anesthesia, are a cornerstone of managing dental infections in dogs. This procedure involves the removal of plaque and tartar from the teeth and beneath the gum line, addressing the primary source of bacterial proliferation and inflammation. Veterinary professionals utilize specialized instruments to thoroughly clean the teeth and perform a comprehensive oral assessment to identify any additional treatment needs.
-
Periodontal Therapy: In cases of advanced gum disease associated with dental infections, periodontal therapy may be indicated. This may involve techniques such as subgingival scaling and root planing to address deep-seated tartar and bacteria within periodontal pockets. By meticulously cleaning and disinfecting the affected areas, periodontal therapy aims to halt the progression of gum disease and promote periodontal tissue healing.
-
Tooth Extractions: Severely affected teeth that cannot be salvaged may require extraction to eliminate a source of infection and alleviate pain. Veterinary professionals carefully evaluate the affected teeth and may recommend extractions to prevent the spread of infection and preserve the overall oral health of the dog. Post-extraction care and pain management are integral components of this treatment approach.
-
Antibiotic Therapy: In conjunction with other treatment modalities, antibiotic therapy may be prescribed to combat the bacterial infection associated with dental infections. Antibiotics can help mitigate the spread of bacteria, reduce inflammation, and support the healing process. It is essential to adhere to the prescribed antibiotic regimen and follow the veterinarian's guidance regarding administration and monitoring for potential side effects.
-
Pain Management: Dogs experiencing dental infections may endure discomfort and oral pain. Therefore, pain management strategies, such as analgesic medications or anti-inflammatory agents, may be incorporated into the treatment plan to enhance the dog's comfort and well-being during the recovery process.
-
Home Care Recommendations: Following professional treatment, the veterinarian will provide guidance on home care practices to maintain oral health and prevent the recurrence of dental infections. This may include recommendations for regular tooth brushing, the use of dental diets or chews, and the application of oral hygiene products tailored to the dog's specific needs.
By leveraging a comprehensive approach that encompasses professional dental interventions, targeted therapies, and diligent home care, the treatment options for dental infections in dogs aim to mitigate the impact of periodontal disease, alleviate discomfort, and promote sustained oral health. Pet owners play a pivotal role in supporting their dogs' recovery by adhering to the recommended treatment protocols and implementing proactive oral care practices to safeguard their canine companions' dental well-being.
Home Care for Dental Infections
Implementing effective home care practices is integral in supporting the recovery from dental infections in dogs and maintaining their oral health. After professional treatment and intervention for dental infections, pet owners play a crucial role in implementing proactive measures to prevent the recurrence of periodontal disease and promote sustained oral well-being for their canine companions.
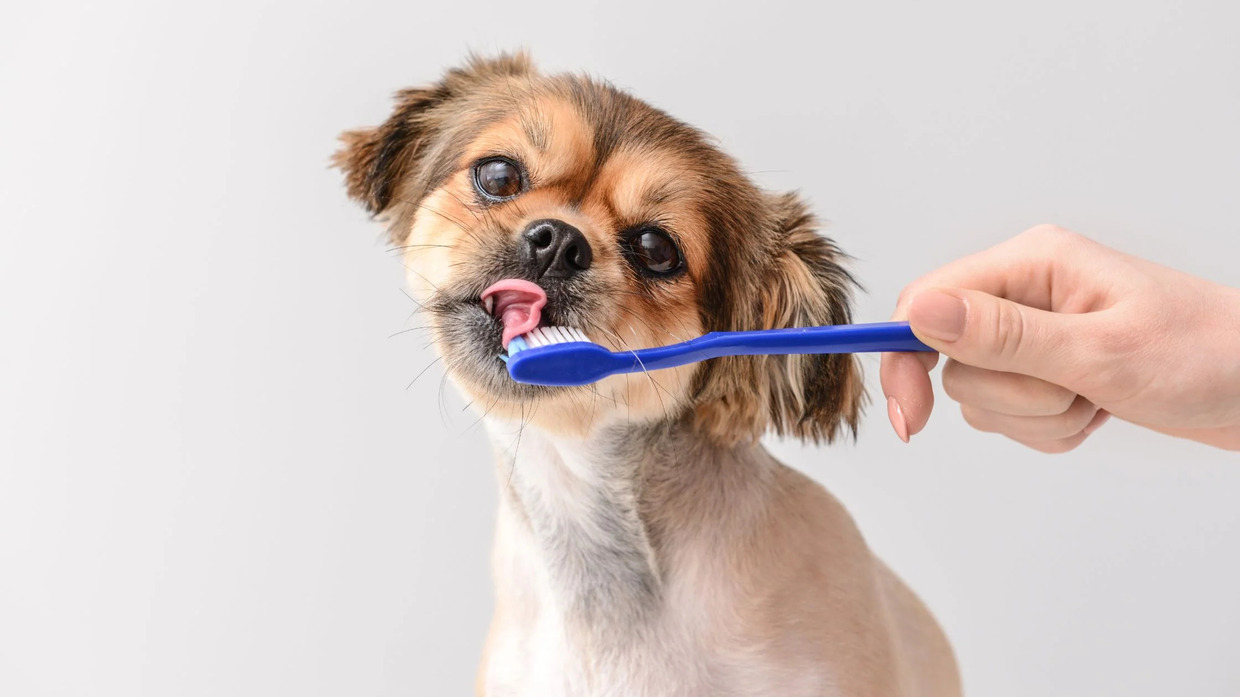
Regular Tooth Brushing
Regular tooth brushing is a cornerstone of home dental care for dogs. Utilizing a soft-bristled toothbrush and veterinary-approved toothpaste, pet owners can establish a routine for brushing their dog's teeth. This practice helps remove plaque, prevent tartar buildup, and mitigate the proliferation of harmful bacteria in the oral cavity. By incorporating tooth brushing into the daily care regimen, pet owners can significantly contribute to their dog's oral health and reduce the risk of dental infections.
Dental Diets and Chews
Specialized dental diets and chews designed to promote oral health can complement home care efforts. These products are formulated to aid in plaque and tartar control, support gum health, and provide mechanical cleansing benefits. Additionally, they can serve as enjoyable treats for dogs while contributing to their dental well-being. When selecting dental diets and chews, pet owners should seek guidance from veterinary professionals to ensure the products align with their dog's specific oral health needs.
Oral Hygiene Products
An array of oral hygiene products, including dental rinses, gels, and water additives, are available to augment home care for dental infections in dogs. These products are designed to combat plaque, freshen breath, and promote oral hygiene. When used in accordance with veterinary recommendations, oral hygiene products can serve as valuable adjuncts to regular tooth brushing, contributing to comprehensive oral care for dogs.
Read more: How To Treat Dog Ear Infection With Steroids
Routine Veterinary Examinations
Scheduling routine veterinary examinations is essential for monitoring a dog's oral health and addressing any emerging dental concerns. Veterinary professionals can conduct thorough oral assessments, provide guidance on home care practices, and identify early signs of dental infections. By prioritizing regular veterinary visits, pet owners demonstrate a commitment to proactive oral health management for their dogs.
Ongoing Monitoring and Observation
Consistent monitoring and observation of a dog's oral health are fundamental aspects of home care for dental infections. Pet owners should remain vigilant for any changes in their dog's eating habits, drooling patterns, or oral discomfort. Additionally, routinely inspecting the teeth and gums for signs of plaque, tartar, or abnormalities enables early detection of potential dental issues, facilitating timely intervention and treatment.
By integrating these home care practices into their daily routines, pet owners can actively contribute to their dog's oral health and well-being, fostering a supportive environment for recovery from dental infections and promoting sustained oral hygiene. The collaborative efforts of veterinary professionals and dedicated pet owners are instrumental in ensuring optimal dental care for dogs, mitigating the impact of dental infections, and nurturing a lifetime of oral health for canine companions.
Preventing Dental Infections in Dogs
Preventing dental infections in dogs is a proactive endeavor that encompasses various strategies aimed at preserving oral health and mitigating the risk of periodontal disease. By implementing preventive measures, pet owners can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their canine companions' dental well-being and reducing the likelihood of dental infections. Here are key approaches to prevent dental infections in dogs:
Regular Dental Care
Establishing a consistent dental care routine is fundamental in preventing dental infections. Regular tooth brushing, using veterinary-approved toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush, helps remove plaque, minimize tartar buildup, and mitigate the proliferation of harmful bacteria in the oral cavity. By incorporating tooth brushing into the daily care regimen, pet owners can significantly contribute to their dog's oral health and reduce the risk of dental infections.
Dental Diets and Chews
Specialized dental diets and chews designed to promote oral health can complement home care efforts. These products are formulated to aid in plaque and tartar control, support gum health, and provide mechanical cleansing benefits. Additionally, they can serve as enjoyable treats for dogs while contributing to their dental well-being. When selecting dental diets and chews, pet owners should seek guidance from veterinary professionals to ensure the products align with their dog's specific oral health needs.
Oral Hygiene Products
An array of oral hygiene products, including dental rinses, gels, and water additives, are available to augment home care for dental infections in dogs. These products are designed to combat plaque, freshen breath, and promote oral hygiene. When used in accordance with veterinary recommendations, oral hygiene products can serve as valuable adjuncts to regular tooth brushing, contributing to comprehensive oral care for dogs.
Read more: How To Treat Dog Ear Infection With Steroids
Routine Veterinary Examinations
Scheduling routine veterinary examinations is essential for monitoring a dog's oral health and addressing any emerging dental concerns. Veterinary professionals can conduct thorough oral assessments, provide guidance on home care practices, and identify early signs of dental infections. By prioritizing regular veterinary visits, pet owners demonstrate a commitment to proactive oral health management for their dogs.
Ongoing Monitoring and Observation
Consistent monitoring and observation of a dog's oral health are fundamental aspects of home care for dental infections. Pet owners should remain vigilant for any changes in their dog's eating habits, drooling patterns, or oral discomfort. Additionally, routinely inspecting the teeth and gums for signs of plaque, tartar, or abnormalities enables early detection of potential dental issues, facilitating timely intervention and treatment.
By integrating these preventive measures into their daily routines, pet owners can actively contribute to their dog's oral health and well-being, fostering a supportive environment for preventing dental infections and promoting sustained oral hygiene. The collaborative efforts of veterinary professionals and dedicated pet owners are instrumental in ensuring optimal dental care for dogs, mitigating the risk of dental infections, and nurturing a lifetime of oral health for canine companions.
Read more: What To Treat A Dog’s Ear Infection With
Conclusion
In conclusion, the management and prevention of dental infections in dogs are pivotal aspects of responsible pet ownership. Dental infections, encompassing periodontal disease and associated oral health issues, can significantly impact a dog's well-being if left unaddressed. By understanding the root causes, signs, and treatment options for dental infections, pet owners can proactively advocate for their canine companions' oral health and ensure they receive the necessary care and support.
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of dental infections, such as persistent bad breath, gum abnormalities, and changes in eating habits, empowers pet owners to seek timely veterinary care and intervention. Veterinary professionals play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating dental infections, utilizing comprehensive oral assessments, professional dental cleanings, and targeted therapies to address the underlying issues and alleviate discomfort in affected dogs.
Moreover, the implementation of home care practices, including regular tooth brushing, dental diets and chews, and ongoing monitoring, serves as a fundamental component of preventing dental infections and supporting the recovery of dogs following professional treatment. By integrating these proactive measures into their daily routines, pet owners actively contribute to their dogs' oral health, fostering a supportive environment for sustained oral hygiene and mitigating the risk of dental infections.
The collaborative efforts of veterinary professionals and dedicated pet owners are instrumental in ensuring optimal dental care for dogs, nurturing a lifetime of oral health and well-being for canine companions. By prioritizing regular veterinary examinations, adhering to home care recommendations, and remaining vigilant for any emerging dental concerns, pet owners demonstrate a commitment to proactive oral health management, ultimately safeguarding their dogs from the impact of dental infections.
In essence, the journey to combat dental infections in dogs encompasses awareness, proactive intervention, and ongoing commitment to oral health. By embracing this holistic approach, pet owners can empower themselves to advocate for their dogs' well-being, ensuring they lead healthy, happy lives free from the discomfort and complications associated with dental infections. Through education, collaboration, and dedicated care, pet owners can make a profound difference in their dogs' oral health, fostering a lifetime of smiles and wagging tails.