Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Happens If You Get Bitten By A Dog Tick


Common Health Issues
What Happens If You Get Bitten By A Dog Tick
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about the common health issues that can arise if you get bitten by a dog tick. Understand the potential risks and how to protect yourself.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Dog ticks are small, blood-sucking parasites that can pose a significant health risk to both humans and animals. These tiny creatures belong to the arachnid family and are commonly found in grassy, wooded areas, and on domestic animals such as dogs. When a dog tick bites a human, it can transmit various diseases, making it crucial to understand the potential consequences of such an encounter.
Understanding the behavior and impact of dog ticks is essential for safeguarding one's health and well-being. This article will delve into the intricacies of dog tick bites, including their symptoms, potential risks, and appropriate measures for treatment and prevention. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of these aspects, individuals can effectively protect themselves and their loved ones from the potential harm associated with dog tick encounters.
As we explore the topic of dog tick bites, it's important to approach the information with a sense of awareness and preparedness. By equipping ourselves with knowledge about dog ticks and their effects, we can take proactive steps to minimize the likelihood of encountering these parasites and mitigate the potential consequences if a bite occurs. Let's embark on this journey to unravel the nuances of dog tick bites and empower ourselves with the necessary insights to navigate this aspect of common health issues.
Understanding Dog Ticks
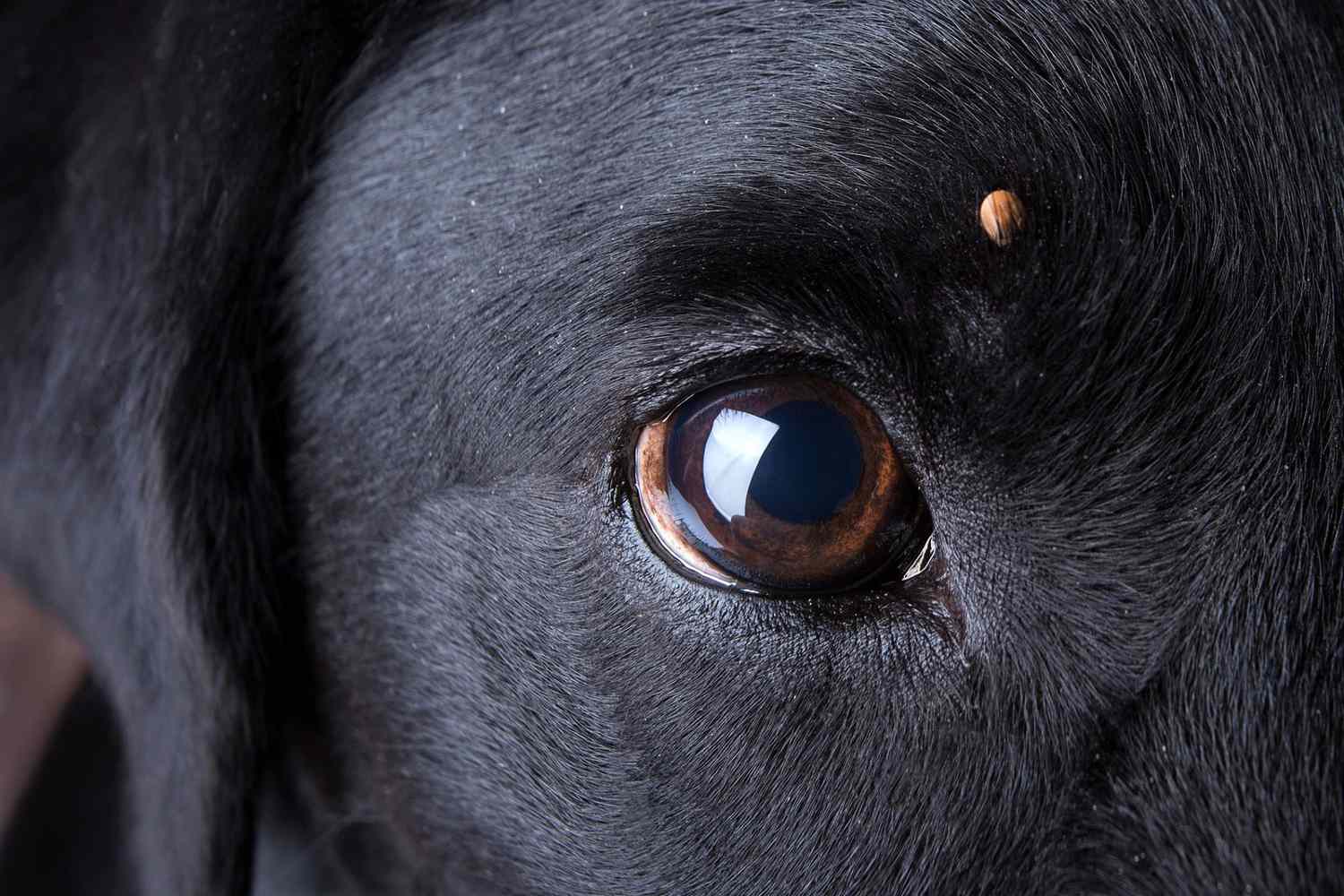
Dog ticks, scientifically known as Dermacentor variabilis, are ectoparasites that belong to the arachnid family. These blood-feeding creatures are commonly found in grassy and wooded areas, where they latch onto passing hosts to feed on their blood. Dog ticks are also frequently encountered on domestic animals, particularly dogs, as they seek out warm and furry hosts for sustenance.
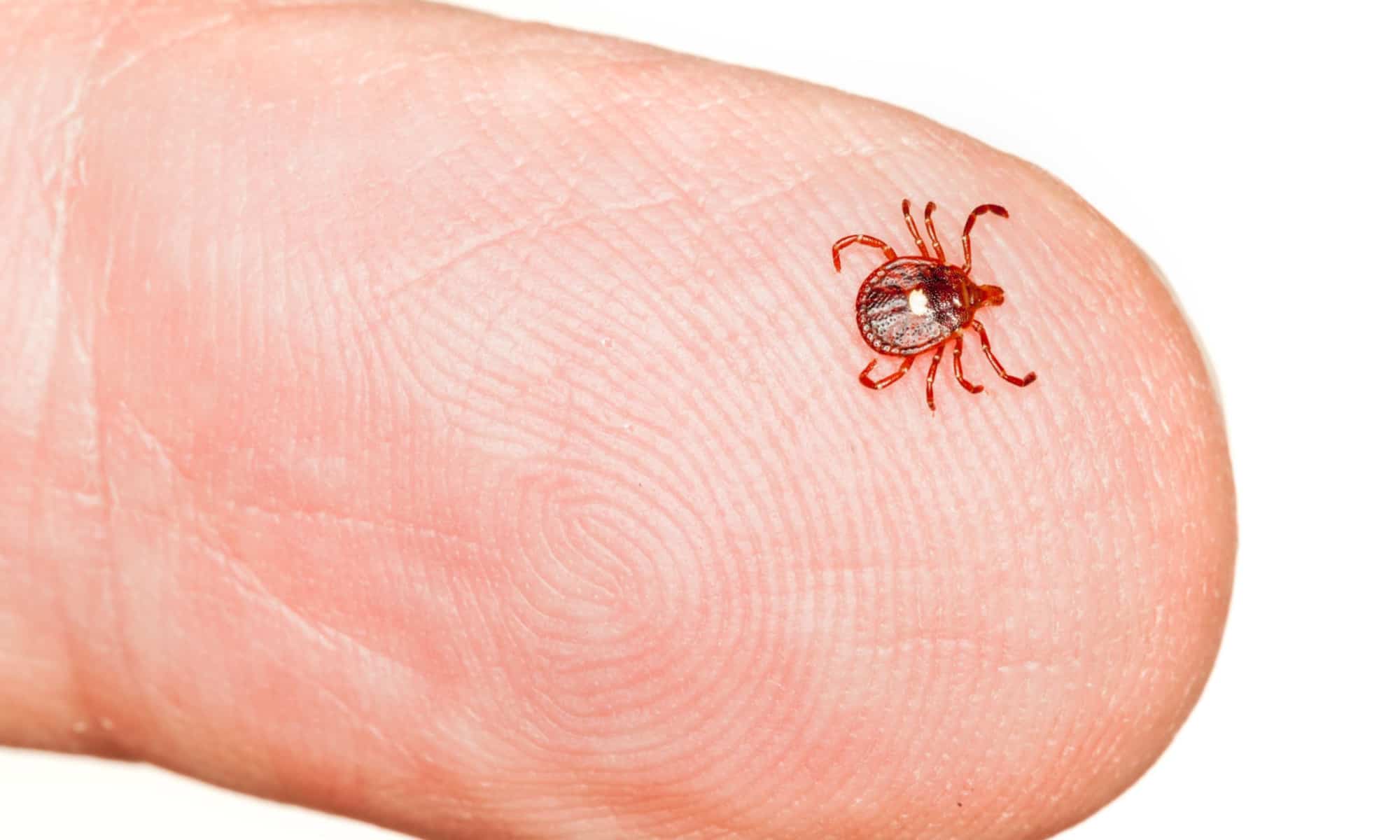
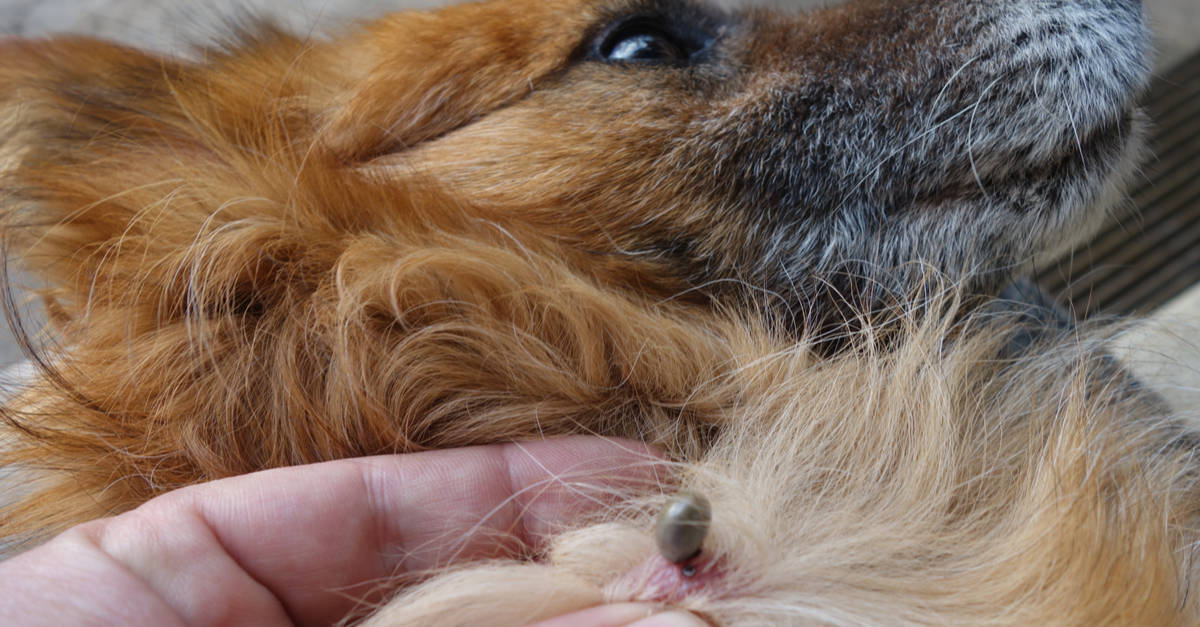
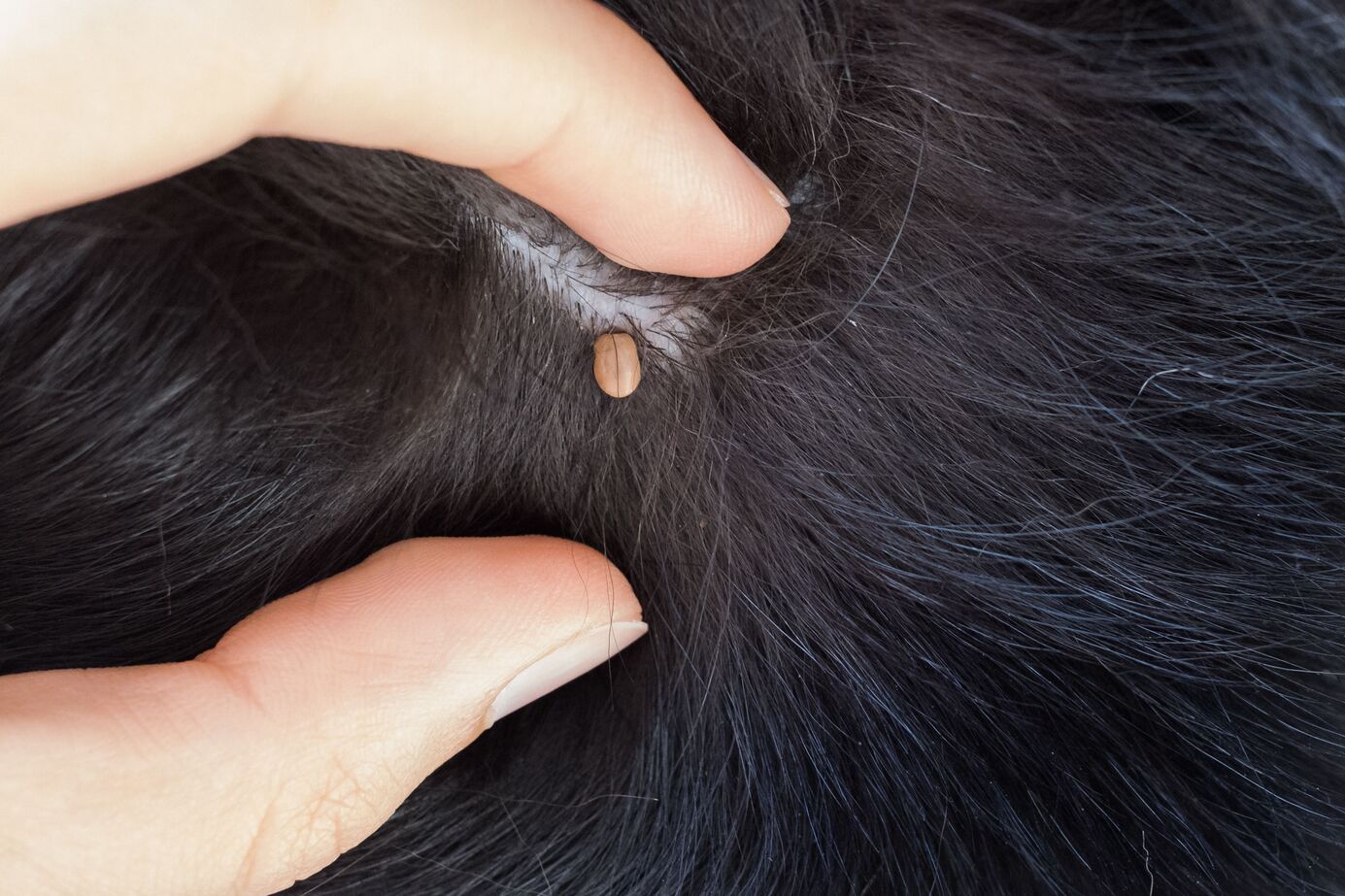
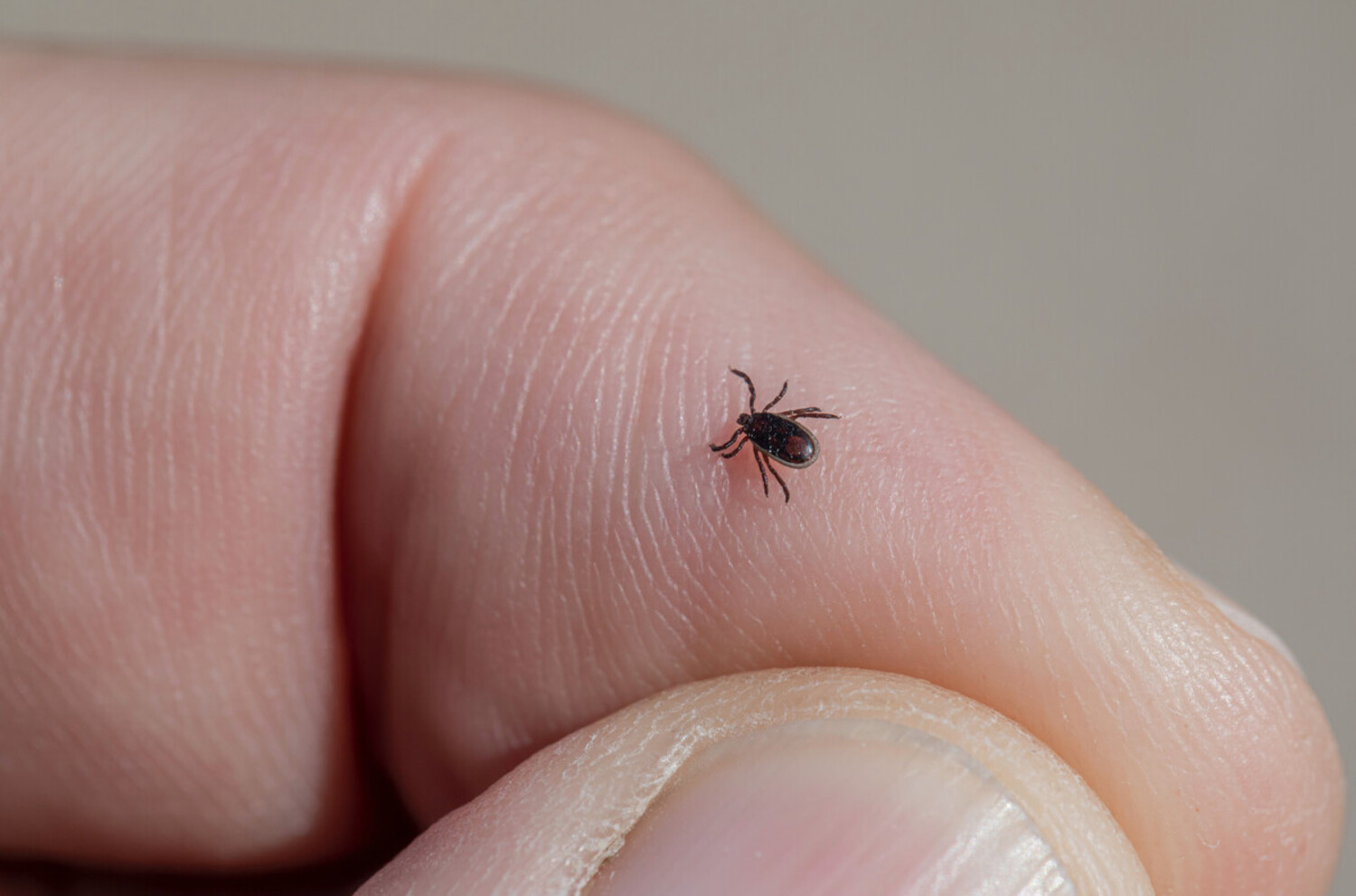
These parasites have a distinct appearance, characterized by their small size and flattened bodies. When unfed, dog ticks appear relatively flat, but once they engorge themselves with blood, their bodies become engorged and rounded. This transformation is particularly noticeable after a tick has fed on a host for an extended period.
Dog ticks are known for their remarkable ability to detect hosts through sensory organs that enable them to perceive changes in temperature, carbon dioxide levels, and other cues emitted by potential hosts. Once a suitable host is detected, the tick latches onto the host's skin using specialized mouthparts designed for piercing and sucking blood. This feeding process can last for several days, during which the tick may transmit disease-causing pathogens to the host.
In addition to their feeding habits, dog ticks are notorious for their ability to transmit various diseases, including Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and ehrlichiosis. These diseases are caused by bacteria and other pathogens that the tick may carry, making their bites a potential source of serious health concerns for both humans and animals.
Understanding the behavior and characteristics of dog ticks is crucial for identifying potential risks and taking appropriate preventive measures. By recognizing the habitats where dog ticks thrive and learning to recognize their physical attributes, individuals can enhance their ability to minimize the likelihood of encountering these parasites and reduce the risk of tick-borne diseases.
In summary, dog ticks are small but formidable creatures that pose a significant health risk to humans and animals. By gaining a deeper understanding of their behavior and potential impact, individuals can better equip themselves to mitigate the risks associated with dog tick encounters and safeguard their well-being.
Symptoms of a Dog Tick Bite
Upon being bitten by a dog tick, individuals may experience various symptoms that can serve as indicators of the encounter. It's important to note that the manifestation of symptoms can vary depending on factors such as the individual's immune response, the duration of tick attachment, and the presence of disease-causing pathogens within the tick. Understanding these symptoms is crucial for promptly identifying a potential dog tick bite and seeking appropriate medical attention.
-
Skin Irritation: One of the most common initial symptoms of a dog tick bite is localized skin irritation at the site of the bite. This may include redness, swelling, and itchiness, often resembling a small bump or rash. The skin may also feel warm to the touch, indicating a localized inflammatory response to the tick's bite.
-
Erythema Migrans: In cases where the dog tick is carrying the bacteria responsible for Lyme disease, an erythema migrans rash may develop. This distinctive rash often appears as a red, expanding bull's-eye pattern around the bite site. It is important to note that not all individuals with Lyme disease will develop this rash, and other symptoms may manifest instead.
-
Flu-Like Symptoms: Some individuals may experience flu-like symptoms following a dog tick bite, including fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, and fatigue. These symptoms can be indicative of the body's immune response to potential pathogens transmitted by the tick.
-
Joint Pain: In cases where the dog tick transmits disease-causing agents such as those responsible for Lyme disease or ehrlichiosis, joint pain and swelling may occur. This can manifest as discomfort in the knees, elbows, or other joints, potentially leading to reduced mobility and discomfort.
-
Neurological Symptoms: In rare instances, particularly with certain tick-borne diseases, individuals may experience neurological symptoms such as confusion, dizziness, and facial paralysis. These symptoms warrant immediate medical attention and evaluation for potential tick-borne illnesses.
It's important to emphasize that the presence of these symptoms following a dog tick bite should prompt individuals to seek medical evaluation, especially if the tick was attached for an extended period or if there is uncertainty about the tick's potential exposure to disease-causing pathogens. Early detection and appropriate management of tick-borne illnesses are crucial for preventing potential complications and promoting recovery.
By recognizing these symptoms and remaining vigilant after potential dog tick encounters, individuals can take proactive steps to address any health concerns promptly. Additionally, seeking medical advice and evaluation can provide reassurance and appropriate guidance in managing the aftermath of a dog tick bite.
Risks and Complications
Encountering a dog tick and sustaining a bite can pose various risks and potential complications, particularly if the tick is carrying disease-causing pathogens. Understanding these risks is essential for individuals to recognize the gravity of a dog tick bite and take appropriate measures to address any potential health concerns.
One of the primary risks associated with dog tick bites is the transmission of tick-borne illnesses. Dog ticks are known vectors for a range of diseases, including Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis, and anaplasmosis, among others. When a tick bites a human and transmits these pathogens into the bloodstream, it can lead to the onset of debilitating illnesses if left untreated. The severity of these diseases can vary, with symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to serious neurological and cardiac complications.
Furthermore, the prolonged attachment of a dog tick can exacerbate the risks of disease transmission and potential complications. As the tick feeds on its host's blood, disease-causing pathogens present within the tick's body can be introduced into the host's bloodstream. If the tick remains attached for an extended period, the likelihood of pathogen transmission increases, heightening the risk of developing tick-borne illnesses.
In addition to the direct health risks posed by tick-borne diseases, dog tick bites can lead to secondary complications related to the body's immune response and the physiological impact of the bite. For instance, individuals may experience allergic reactions to components in the tick's saliva, leading to localized swelling, itching, and discomfort at the bite site. In some cases, individuals with heightened sensitivity to tick bites may develop more pronounced allergic reactions, necessitating medical attention to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
Moreover, the psychological impact of a dog tick bite should not be overlooked. The potential transmission of serious illnesses and the discomfort associated with tick encounters can induce anxiety and distress in affected individuals. This psychological burden can contribute to the overall impact of a dog tick bite, affecting one's mental well-being and quality of life.
By recognizing these risks and potential complications, individuals can appreciate the gravity of dog tick encounters and prioritize preventive measures and prompt medical evaluation. Proactive steps, such as thorough tick checks after outdoor activities, prompt tick removal, and seeking medical advice in the event of a bite, are crucial for mitigating these risks and safeguarding one's health.
In summary, dog tick bites carry inherent risks, encompassing the transmission of tick-borne illnesses, potential allergic reactions, and psychological implications. By acknowledging these risks and remaining vigilant, individuals can take proactive measures to address potential complications and prioritize their well-being in the aftermath of a dog tick encounter.
Treatment for Dog Tick Bites
Upon discovering a dog tick bite, prompt and appropriate treatment is essential to address potential health concerns and minimize the risk of complications. The following measures are recommended for the treatment of dog tick bites:
-
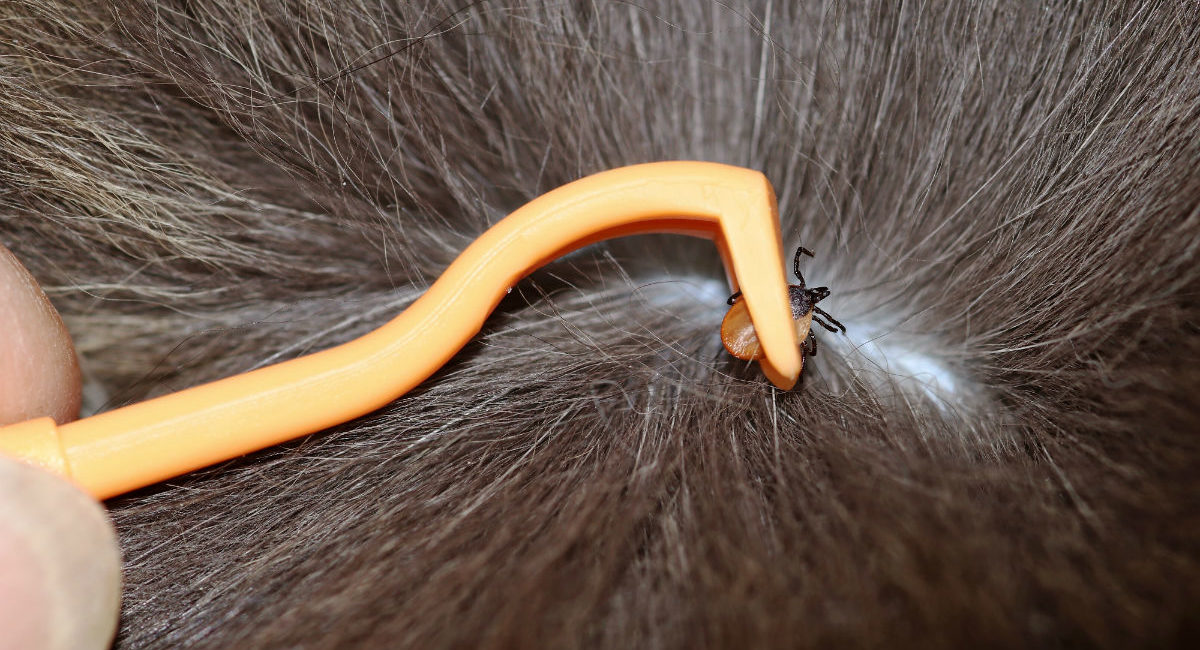
Tick Removal: The first step in treating a dog tick bite is to safely remove the tick from the skin. This should be done with caution to prevent any parts of the tick from remaining embedded in the skin, which can lead to infection. Using fine-tipped tweezers, grasp the tick as close to the skin's surface as possible and pull upward with steady, even pressure. Avoid twisting or jerking the tick, as this can cause the mouthparts to break off and remain in the skin. After removal, clean the bite area and hands with rubbing alcohol, an iodine scrub, or soap and water.
-
Seek Medical Evaluation: Following tick removal, individuals should seek medical evaluation, especially if the tick was attached for an extended period or if there is uncertainty about the tick's potential exposure to disease-causing pathogens. Medical professionals can assess the bite site, provide guidance on potential disease transmission, and recommend appropriate measures based on the specific circumstances of the bite.
-
Monitoring for Symptoms: It is crucial to monitor the bite site and the individual's overall health for any signs of infection or the onset of tick-borne illnesses. If symptoms such as rash, fever, joint pain, or flu-like symptoms develop, prompt medical attention should be sought to evaluate potential disease transmission and initiate appropriate management.
-
Treatment for Tick-Borne Illnesses: In cases where a dog tick bite leads to the transmission of tick-borne illnesses, medical intervention is necessary to address the specific disease. Treatment may involve the administration of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, and supportive care to manage symptoms and promote recovery. The specific approach to treatment will depend on the diagnosed tick-borne illness and the individual's overall health status.
-
Preventative Measures: Individuals who have experienced a dog tick bite should take proactive measures to prevent future encounters and minimize the risk of additional bites. This includes employing tick repellents, wearing protective clothing in tick-prone areas, and conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities. Additionally, seeking guidance from healthcare providers on preventive strategies can further reduce the likelihood of future tick bites.
By adhering to these treatment measures, individuals can effectively address the aftermath of a dog tick bite and mitigate potential health risks. Prompt tick removal, medical evaluation, and proactive monitoring are crucial steps in ensuring the appropriate management of dog tick bites and promoting overall well-being.
Read more: What Happens When A Dog Gets Tick Paralysis
Prevention of Dog Tick Bites
Preventing dog tick bites is paramount in safeguarding against the potential health risks associated with these parasitic encounters. By adopting proactive measures and integrating preventive strategies into daily routines, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of dog tick bites and minimize the risk of tick-borne illnesses. Here are essential steps to prevent dog tick bites:
-
Tick Repellents: Utilizing tick repellents containing DEET or permethrin can effectively deter ticks from latching onto the skin. Applying these repellents to exposed skin and clothing before venturing into tick-prone areas can serve as a crucial line of defense against tick bites.
-
Protective Clothing: Wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and closed-toe shoes can act as a physical barrier, reducing skin exposure to ticks. Additionally, tucking pants into socks or boots can further prevent ticks from gaining access to the skin.
-
Tick-Proof Landscaping: Maintaining a well-groomed yard can help minimize tick habitats around residential areas. Regularly mowing the lawn, removing leaf litter, and creating a barrier of wood chips or gravel between lawns and wooded areas can deter ticks from encroaching on outdoor living spaces.
-
Tick Checks: Conducting thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors is essential for promptly identifying and removing any ticks before they have a chance to bite. Paying close attention to hidden areas such as the scalp, behind the ears, and along the hairline can aid in detecting ticks early.
-
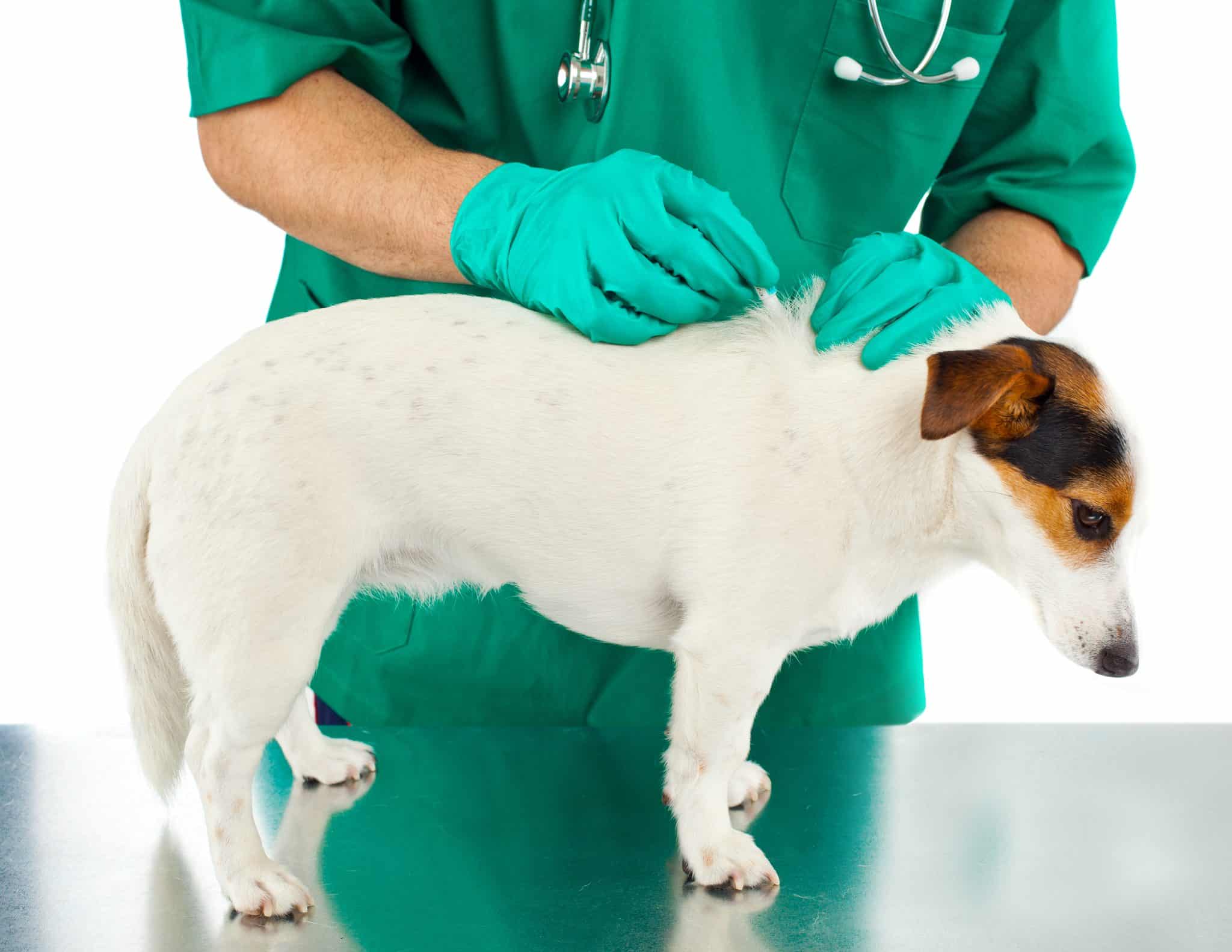
Pet Protection: Ensuring that pets are treated with veterinarian-recommended tick preventatives can reduce the likelihood of ticks being introduced into the home environment. Regular grooming and inspection of pets for ticks can also prevent potential tick infestations.
-
Awareness of Tick Habitats: Being mindful of tick habitats and avoiding direct contact with areas where ticks are prevalent, such as tall grass, wooded areas, and leaf litter, can minimize the risk of encountering ticks.
-
Prompt Tick Removal: In the event of a tick attachment, promptly removing the tick using fine-tipped tweezers and cleaning the bite site can prevent potential disease transmission.
By integrating these preventive measures into daily routines and outdoor activities, individuals can fortify their defenses against dog tick bites and reduce the risk of tick-borne illnesses. Additionally, seeking guidance from healthcare providers on effective tick prevention strategies tailored to specific environments and activities can further enhance the effectiveness of these preventive measures.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the potential consequences of a dog tick bite extend beyond the initial discomfort at the bite site. Understanding the symptoms, risks, and appropriate measures for treatment and prevention is crucial for individuals to navigate the aftermath of a dog tick encounter effectively. By recognizing the significance of dog tick bites and adopting proactive strategies, individuals can safeguard their health and well-being in tick-prone environments.
The symptoms of a dog tick bite, ranging from skin irritation to flu-like symptoms and neurological manifestations, serve as vital indicators of potential health risks. Prompt recognition of these symptoms and seeking medical evaluation can facilitate early intervention and mitigate the impact of tick-borne illnesses. Additionally, understanding the risks and potential complications associated with dog tick bites underscores the importance of preventive measures and prompt treatment to address any health concerns.
Treatment for dog tick bites encompasses safe tick removal, medical evaluation, and monitoring for symptoms of tick-borne illnesses. By adhering to these treatment measures, individuals can effectively manage the aftermath of a dog tick bite and minimize the risk of complications. Furthermore, the implementation of preventive strategies, including tick repellents, protective clothing, and tick checks, plays a pivotal role in reducing the likelihood of dog tick encounters and mitigating the risk of tick-borne illnesses.
The psychological impact of dog tick bites should not be overlooked, as the potential transmission of serious illnesses and the discomfort associated with tick encounters can induce anxiety and distress. By acknowledging these psychological implications and fostering awareness of effective preventive measures, individuals can navigate dog tick encounters with resilience and confidence.
In essence, the comprehensive understanding of dog tick bites empowers individuals to make informed decisions and take proactive steps to protect themselves and their loved ones. By integrating knowledge, vigilance, and preventive measures into daily routines, individuals can minimize the impact of dog tick encounters and prioritize their well-being in tick-prone environments. Ultimately, by embracing a proactive and informed approach, individuals can effectively mitigate the potential consequences of dog tick bites and foster a safer and healthier lifestyle.