Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Muscular and Joint Health>Dog Joint Pain: Recognizing and Addressing Discomfort in Old Dogs


Muscular and Joint Health
Dog Joint Pain: Recognizing and Addressing Discomfort in Old Dogs
Modified: November 27, 2023
Understanding the signs and possible causes of joint pain in old dogs is crucial for pet owners. Read on to find out more.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
As our canine companions age, joint pain often becomes a part of their lives. Understanding the signs and possible causes of joint pain in old dogs is crucial for pet owners. This blog post is designed to help you recognize the early signs of discomfort in your senior dog and understand the underlying causes.
Early Signs of Joint Pain in Old Dogs
- Reluctance to Move: One of the first signs is a noticeable reluctance to move or participate in activities they once enjoyed.
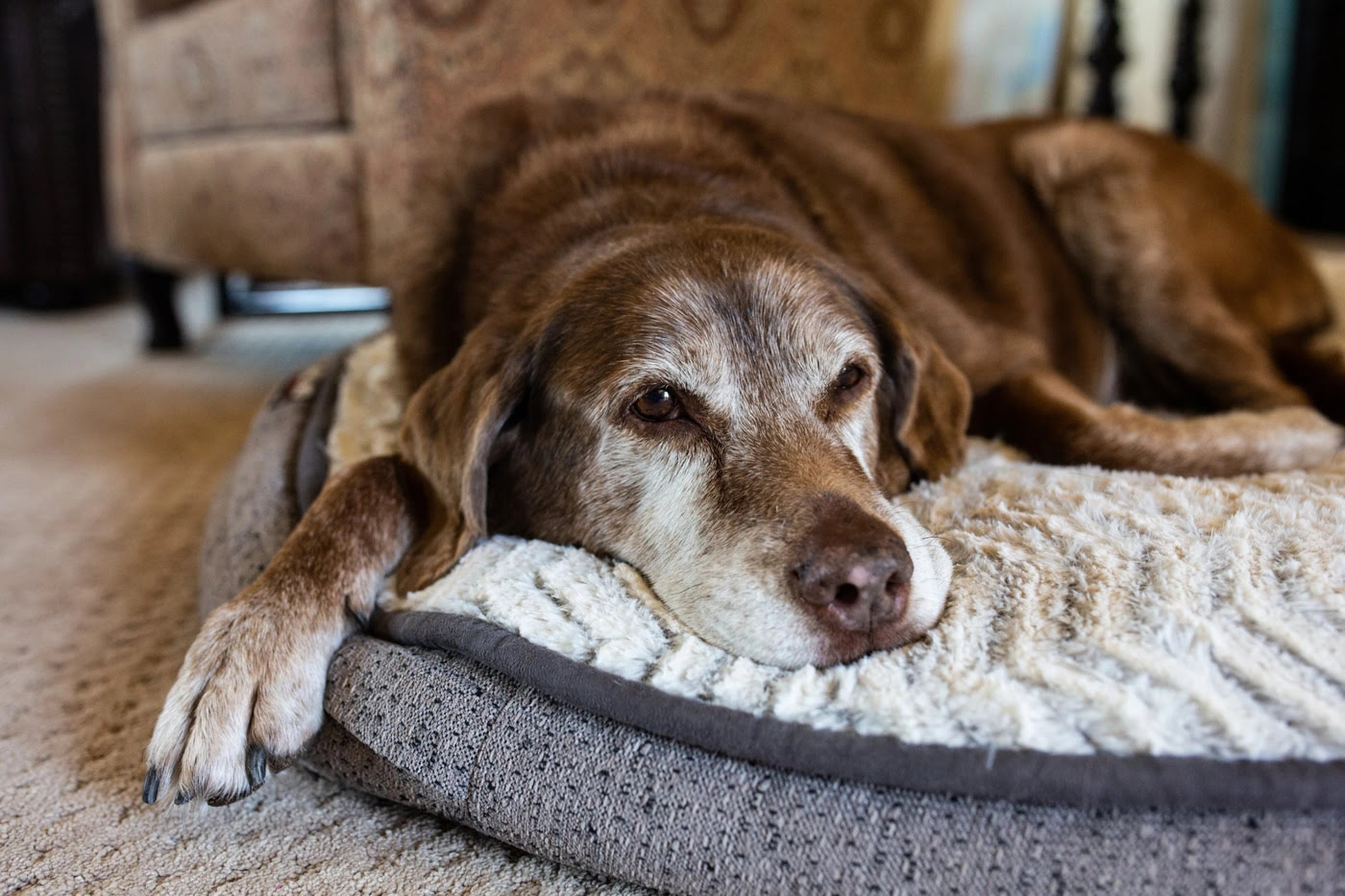
- Stiffness After Resting: Dogs might show stiffness or discomfort after getting up from a resting position.
- Limping: An obvious sign is limping or favoring one leg over others.
- Difficulty Climbing Stairs: Struggling with stairs or jumping can be a sign of joint pain.
- Changes in Behavior: You might notice changes in their behavior, like irritability or withdrawal, due to discomfort.
Common Causes of Joint Pain in Senior Dogs
- Osteoarthritis: This degenerative disease is common in older dogs, leading to the breakdown of cartilage in the joints.
- Hip Dysplasia: A genetic condition, often seen in larger breeds, where the hip joint doesn’t fit together perfectly.
- Obesity: Extra weight can put additional strain on your dog’s joints, exacerbating pain.
- Previous Injuries: Old injuries can lead to joint pain later in life.
- Breed Predispositions: Some breeds are more susceptible to joint issues due to their size and genetics.
Managing Your Dog’s Joint Pain
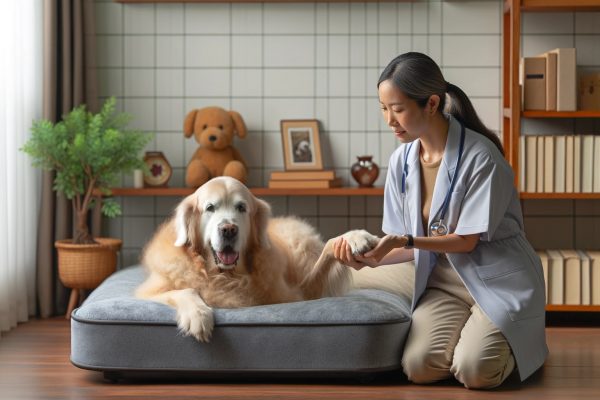
- Veterinary Care: Regular check-ups with your vet are crucial for managing joint pain.
- Weight Management: Keeping your dog at a healthy weight reduces stress on their joints.
- Appropriate Exercise: Regular, gentle exercise helps maintain joint mobility.
- Joint Supplements: Supplements like glucosamine and chondroitin can support joint health.
- Pain Relief: Your vet may prescribe medications to help manage pain and inflammation.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Comfort
- Comfortable Bedding: Provide a soft, supportive bed to ease joint pain during rest.
- Accessibility: Make your home more accessible, for example, using ramps for getting in and out of cars or onto furniture.
- Gentle Handling: Be gentle when playing with or handling your dog to avoid causing pain.
Recognizing When to Seek Help
- Persistent Limping: If limping persists or worsens, it’s time to consult your vet.
- Changes in Appetite or Behavior: Significant changes could indicate that the pain is affecting their overall well-being.
- Difficulty with Daily Activities: If your dog struggles with routine activities, professional advice is necessary.
The Emotional Aspect of Joint Pain
Remember that joint pain can affect your dog’s emotional state. Provide extra love and attention to help them cope with the discomfort.
Alternative Therapies
- Physical Therapy: Can improve mobility and reduce discomfort.
- Acupuncture: Some owners find acupuncture beneficial for pain relief.
- Massage Therapy: Gentle massage can improve circulation and ease sore muscles.
Final Thoughts on Caring for a Dog with Joint Pain
Caring for a senior dog with joint pain requires patience, understanding, and sometimes creative solutions. By staying vigilant to the signs and working closely with your vet, you can help your furry friend maintain a good quality of life in their golden years.