Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>What To Do With An Infection In A Dog’s Eye


Eye and Ear Health
What To Do With An Infection In A Dog’s Eye
Published: February 11, 2024
Learn how to identify and treat infections in your dog's eyes and ears. Keep your pet's eye and ear health in top condition with our expert tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Eye health is a crucial aspect of a dog's overall well-being. Just like humans, dogs can experience eye infections that require prompt attention and care. As a responsible pet owner, it's essential to be vigilant about your furry friend's ocular health and be prepared to address any signs of discomfort or infection.
Understanding the common signs, causes, treatment options, and preventive measures for dog eye infections is vital for ensuring your pet's comfort and long-term health. This article will delve into the various aspects of eye infections in dogs, equipping you with the knowledge to identify, manage, and prevent these issues effectively.
By gaining insight into the symptoms and potential causes of eye infections in dogs, you can take proactive measures to safeguard your pet's vision and overall quality of life. Additionally, learning about home remedies and when to seek professional veterinary care will empower you to provide the best possible support for your canine companion.
In the following sections, we will explore the signs of eye infections in dogs, the underlying causes, treatment options, home remedies, and preventive strategies. By the end of this comprehensive guide, you will be well-equipped to recognize, address, and prevent eye infections in your beloved canine companion.
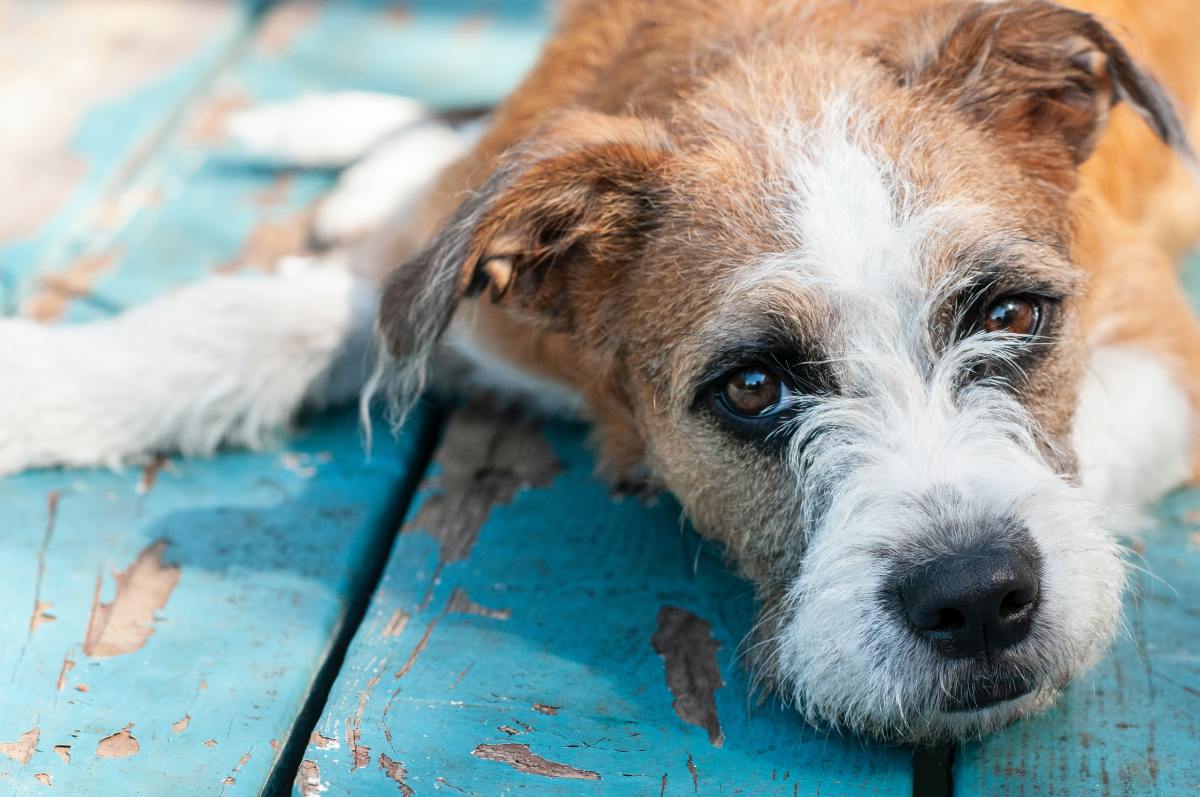
Signs of an Eye Infection in Dogs
Recognizing the signs of an eye infection in dogs is crucial for timely intervention and effective management. Dogs, like humans, can experience a range of ocular issues, and being attuned to the subtle indicators of an eye infection can make a significant difference in your pet's well-being. Here are the key signs to watch for:
1. Excessive Tearing or Discharge
One of the primary indicators of an eye infection in dogs is excessive tearing or the presence of abnormal discharge. If you notice an increase in tear production or observe any pus-like or mucus-like discharge around your dog's eyes, it could signal an underlying infection.
2. Redness and Irritation
Redness and irritation in and around the eyes are common manifestations of an eye infection. Your dog may exhibit signs of discomfort, such as frequent blinking, rubbing or pawing at the affected eye, and sensitivity to light. These symptoms often indicate inflammation and the need for prompt attention.
3. Swelling and Inflammation
Swelling and inflammation of the eyelids or the tissues surrounding the eyes can be indicative of an underlying infection. If you notice any abnormal bulging, puffiness, or redness in the eye area, it's essential to investigate further to determine the cause and initiate appropriate measures.
4. Squinting or Excessive Blinking
Dogs experiencing eye discomfort due to an infection may squint or blink excessively. This behavior is a natural response to alleviate discomfort and protect the affected eye. Persistent squinting or frequent blinking should prompt a closer examination of your dog's eyes.
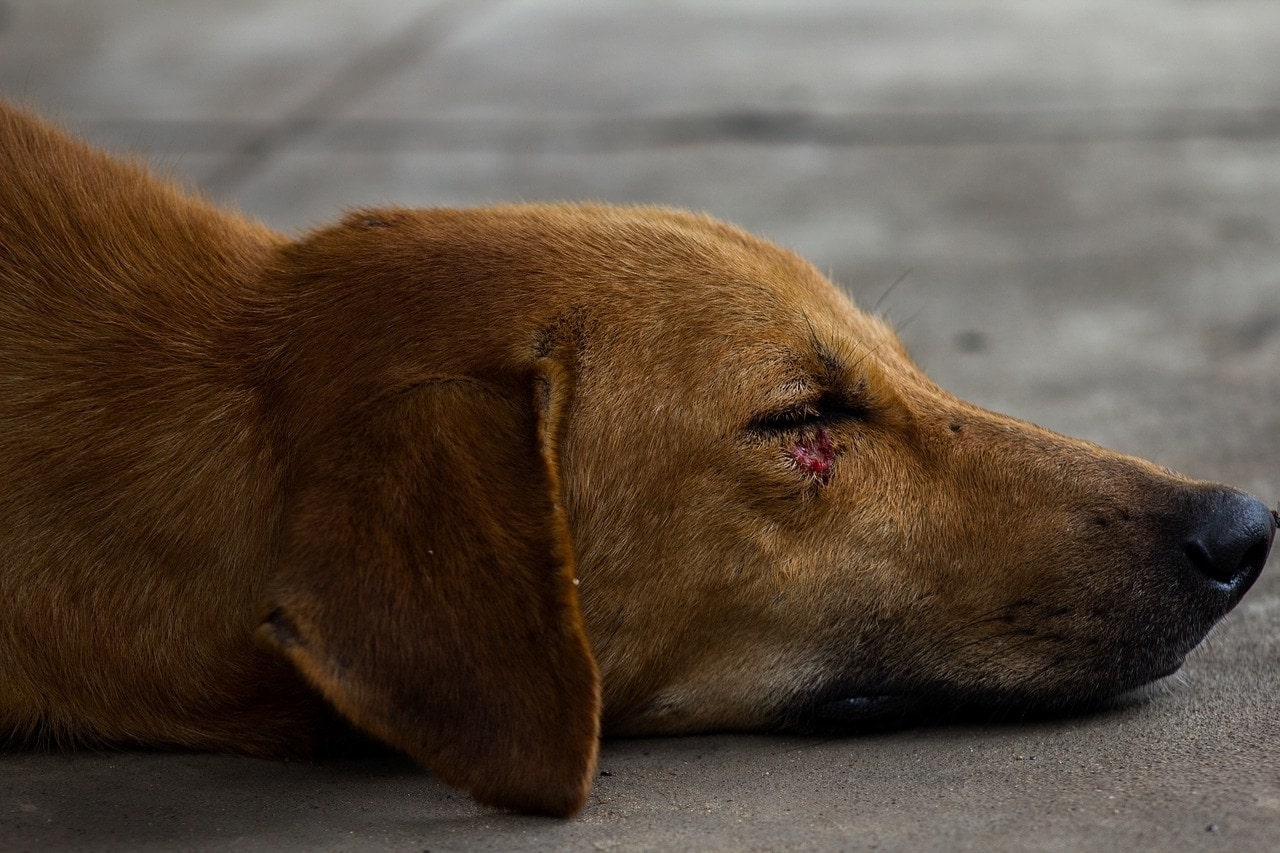
5. Changes in Eye Appearance
An eye infection can lead to noticeable changes in the appearance of the affected eye. This may include cloudiness, opacity, or the presence of a visible film over the eye surface. Any alterations in the normal appearance of the eyes should be carefully evaluated by a veterinarian.
6. Avoidance of Light
Sensitivity to light, medically known as photophobia, is a common symptom of eye infections in dogs. If your dog seems to be avoiding bright light or displays signs of discomfort when exposed to light, it could indicate an underlying ocular issue requiring attention.
7. Behavioral Changes
In some cases, dogs with eye infections may exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased restlessness, agitation, or reluctance to engage in activities they typically enjoy. These behavioral shifts can be linked to the discomfort and distress associated with an eye infection.
By being attentive to these signs, you can promptly identify potential eye infections in your dog and take the necessary steps to address the issue. Early detection and intervention are key to preventing the progression of eye infections and minimizing any discomfort experienced by your furry companion.
Causes of Eye Infections in Dogs
Eye infections in dogs can stem from various factors, ranging from environmental irritants to underlying health conditions. Understanding the potential causes of these infections is essential for implementing preventive measures and addressing the root of the issue. Here are the primary factors that can contribute to eye infections in dogs:
-
Foreign Objects and Irritants: Dogs are naturally curious and may come into contact with foreign objects or irritants that can lead to eye infections. Dust, pollen, dirt, and debris can enter the eyes, causing irritation and potential infection. Additionally, exposure to chemicals or airborne pollutants can also trigger ocular issues in dogs.
-
Bacterial Infections: Bacterial organisms, such as Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species, can infiltrate the eyes, leading to bacterial conjunctivitis or other forms of bacterial eye infections. These infections can result from poor hygiene, contaminated environments, or contact with other infected animals.
-
Viral Infections: Viruses, including the canine distemper virus and herpesvirus, can cause severe ocular complications in dogs. Viral eye infections are highly contagious and can spread rapidly among dogs, particularly in settings with close contact, such as kennels or dog parks.
-
Allergies: Dogs can develop allergic reactions to various substances, including pollen, mold, dust mites, and certain foods. Allergic conjunctivitis, characterized by redness, itching, and discharge, is a common manifestation of allergies in dogs and can predispose them to secondary bacterial or fungal eye infections.
-
Trauma or Injury: Physical trauma to the eye, such as scratches, abrasions, or blunt force impact, can create openings for bacteria or fungi to invade, leading to infections. Additionally, foreign bodies lodged in the eye can cause irritation and infection if not promptly removed.
-
Anatomical Abnormalities: Certain breeds are predisposed to anatomical abnormalities, such as shallow eye sockets or prominent eyelids, which can increase the risk of eye infections. These structural features may impede proper tear drainage or predispose the eyes to chronic irritation and infection.
-
Underlying Health Conditions: Dogs with systemic health issues, such as autoimmune diseases, diabetes, or hormonal imbalances, may experience compromised immune function, making them more susceptible to eye infections. Chronic conditions that affect tear production or quality can also contribute to ocular infections.
-
Poor Hygiene and Grooming Practices: Inadequate grooming, poor hygiene, and the accumulation of ocular discharge can create an environment conducive to bacterial or fungal growth, leading to recurrent eye infections in dogs.
By recognizing these potential causes, pet owners can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of eye infections in their dogs. Implementing regular eye examinations, maintaining a clean living environment, and seeking prompt veterinary care for any signs of ocular discomfort are essential strategies for mitigating the impact of these diverse contributing factors.
Treatment Options for Dog Eye Infections
When it comes to addressing dog eye infections, prompt and appropriate treatment is essential for alleviating discomfort, preventing complications, and promoting swift recovery. The choice of treatment options depends on the underlying cause of the infection, the severity of symptoms, and the veterinarian's assessment. Here are the primary treatment modalities commonly employed for managing dog eye infections:
-
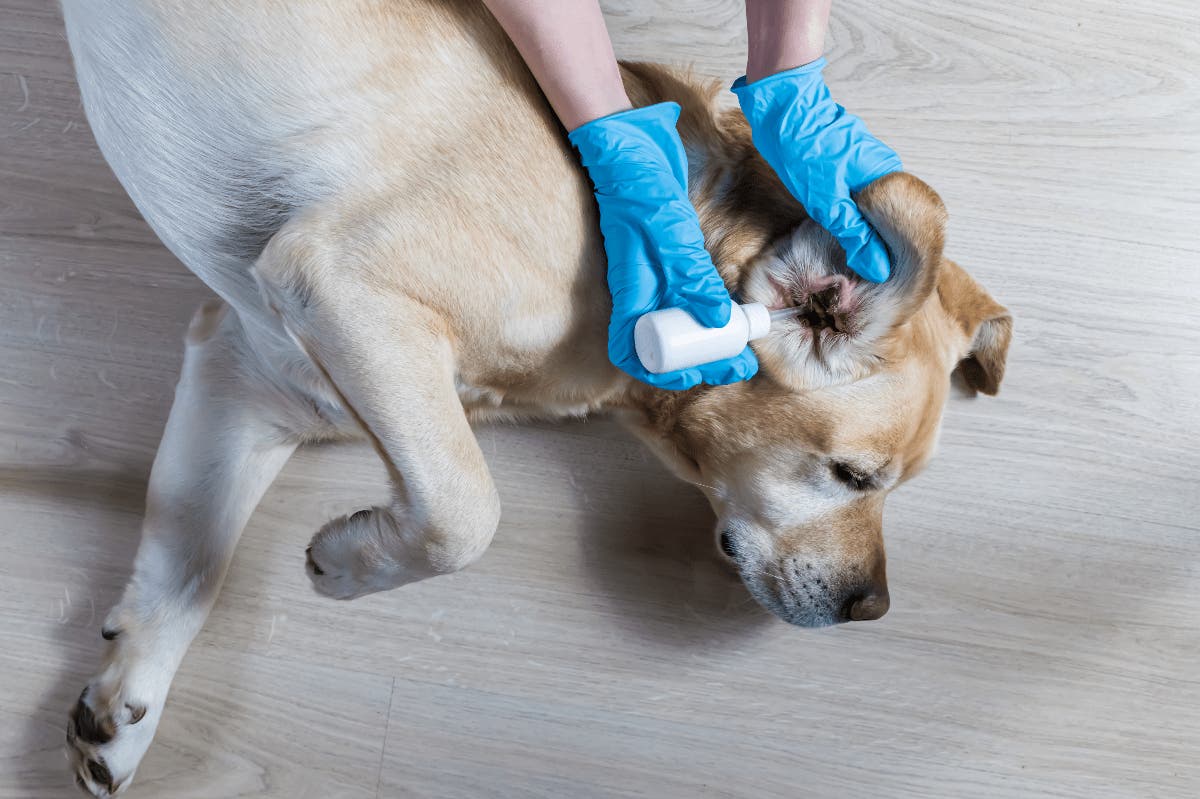
Topical Antibiotics: In cases of bacterial eye infections, topical antibiotic ointments or drops are often prescribed to combat the underlying bacterial pathogens. These medications target the specific bacteria responsible for the infection and help eliminate the source of ocular inflammation and discharge.
-
Antiviral Medications: For viral eye infections, such as those caused by the canine distemper virus or herpesvirus, antiviral medications may be recommended. These medications aim to suppress viral replication and reduce the severity and duration of the infection.
-
Anti-inflammatory Agents: Inflammation is a common feature of eye infections, and anti-inflammatory medications, such as corticosteroids or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may be prescribed to alleviate swelling, redness, and discomfort in the affected eye.
-
Tear Stimulants and Lubricants: In cases where the dog's tear production is compromised or inadequate, tear stimulants and lubricating eye drops may be utilized to maintain proper ocular moisture and promote healing. These products help prevent dryness and protect the eye surface from further irritation.
-
Warm Compresses and Eye Irrigation: To aid in the removal of discharge, debris, or irritants from the eye, warm compresses and gentle eye irrigation techniques may be recommended. These measures can help cleanse the eye area and provide relief from discomfort.
-
Surgical Intervention: In instances of severe trauma, corneal ulcers, or anatomical abnormalities contributing to recurrent infections, surgical intervention may be necessary. Procedures such as corneal debridement, eyelid correction, or tear duct clearance can be performed to address underlying issues and prevent future infections.
-
Complementary Therapies: In addition to conventional medications, complementary therapies, such as herbal eye washes, homeopathic remedies, or nutritional supplements, may be incorporated to support overall ocular health and enhance the effectiveness of primary treatment modalities.
It's important to note that the specific treatment approach will be tailored to the individual dog's condition, and pet owners should strictly adhere to the veterinarian's instructions regarding medication administration, dosage, and duration of treatment. Additionally, regular follow-up appointments may be necessary to monitor the dog's progress and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
By leveraging these diverse treatment options and collaborating closely with veterinary professionals, pet owners can effectively address dog eye infections and facilitate the restoration of optimal ocular health for their beloved canine companions.
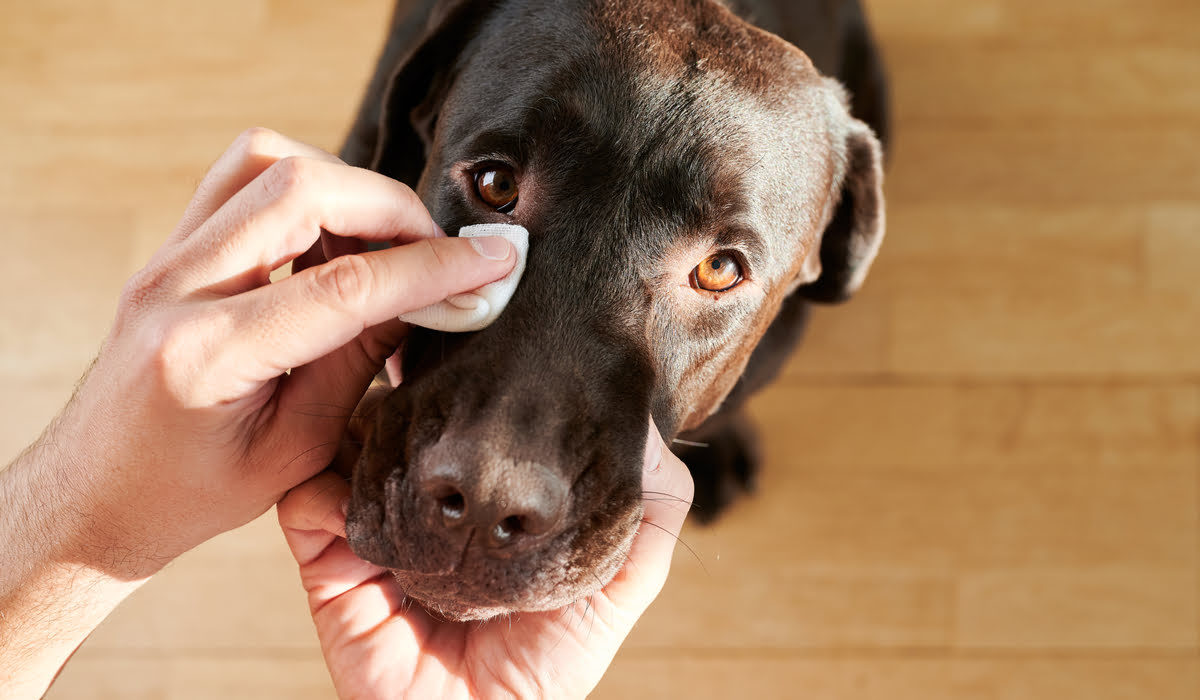
Home Remedies for Dog Eye Infections
In addition to professional veterinary care, home remedies can play a supportive role in managing mild cases of dog eye infections and promoting overall ocular health. While these remedies are not substitutes for veterinary treatment, they can offer supplementary relief and aid in the recovery process. Here are several effective home remedies for dog eye infections:
-
Saline Solution Rinse: A gentle saline solution can be used to rinse your dog's eyes, helping to flush out debris, reduce irritation, and maintain cleanliness. To prepare the solution, mix one teaspoon of salt in a cup of warm water and use a clean, lint-free cloth or sterile gauze to gently wipe the eye area.
-
Chamomile Tea Compress: Chamomile possesses soothing and anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit dogs with eye infections. Brew a weak chamomile tea, allow it to cool, and then use a soft, clean cloth soaked in the tea as a warm compress over the affected eye. This can help alleviate discomfort and reduce inflammation.
-
Cold Compress: In cases of swelling or inflammation, a cold compress can provide relief to your dog. Wrap a few ice cubes in a cloth and apply it gently to the affected eye for short intervals. Be sure to avoid direct contact between the ice and the eye to prevent frostbite.
-
Honey: Raw, organic honey has natural antibacterial and soothing properties. A small amount of honey can be diluted with sterile water and used as an eye wash to help combat infection and promote healing. It's important to use this remedy with caution and under veterinary guidance, especially for dogs with certain health conditions.
-
Nutritional Supplements: Supporting your dog's overall immune function and ocular health through proper nutrition is essential. Omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin E, and vitamin C supplements can contribute to eye health and bolster the immune system. Consult with your veterinarian to determine the appropriate supplements and dosages for your dog.
-
Environmental Modifications: Creating a clean and allergen-free environment can aid in preventing recurrent eye infections. Regularly dusting and vacuuming your home, using air purifiers, and minimizing exposure to potential irritants can help reduce the risk of allergic reactions and subsequent eye issues.
It's important to note that while these home remedies can offer relief and support, they should be used under the guidance of a veterinarian. Additionally, any persistent or worsening symptoms should prompt immediate veterinary attention to ensure the proper diagnosis and treatment of the underlying cause.
By integrating these home remedies into a comprehensive approach to dog eye infection management, pet owners can contribute to their dog's comfort and well-being while working in tandem with professional veterinary care.
Preventing Eye Infections in Dogs
Preventing eye infections in dogs is a proactive endeavor that involves a combination of attentive care, environmental management, and preventive measures. By implementing the following strategies, pet owners can significantly reduce the risk of ocular issues and promote long-term eye health for their canine companions.
-
Regular Eye Examinations: Schedule routine eye examinations with a veterinarian to monitor your dog's ocular health and detect any early signs of infection or underlying conditions. Proactive monitoring allows for timely intervention and preventive measures.
-
Maintaining Cleanliness: Keep your dog's living environment clean and free from potential eye irritants, such as dust, pollen, and chemicals. Regularly clean and dust your home, and ensure that your dog's bedding and living areas are kept free from debris and allergens.
-
Proper Hygiene Practices: Practice good grooming and hygiene habits to prevent the accumulation of ocular discharge and debris around your dog's eyes. Regularly clean the area around the eyes with a damp cloth to remove any buildup that could contribute to infection.
-
Eye Protection: In situations where your dog may be exposed to airborne irritants or debris, such as during outdoor activities or walks, consider using protective eyewear designed for dogs. These can help shield the eyes from potential irritants and reduce the risk of infection.
-
Healthy Nutrition: Provide a balanced and nutritious diet that supports overall immune function and ocular health. Incorporate foods rich in essential nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin E, and vitamin C, which contribute to eye health and bolster the immune system.
-
Regular Exercise and Mental Stimulation: Engage your dog in regular exercise and mental stimulation to support overall well-being. Physical activity and mental enrichment contribute to a strong immune system, which plays a role in preventing infections, including those affecting the eyes.
-
Preventative Veterinary Care: Stay up to date with your dog's vaccinations and preventive medications to minimize the risk of infectious diseases that can lead to ocular complications. Additionally, discuss preventive measures with your veterinarian, such as parasite control, to safeguard your dog's health.
-
Prompt Treatment of Underlying Conditions: Address any underlying health conditions, such as allergies or systemic diseases, promptly and comprehensively. By managing these conditions effectively, you can reduce the likelihood of secondary eye infections stemming from compromised immune function or allergic reactions.
By integrating these preventive strategies into your dog's care routine, you can create a supportive environment that minimizes the risk of eye infections and promotes optimal ocular health. Additionally, maintaining open communication with your veterinarian and seeking guidance on preventive measures tailored to your dog's specific needs can further enhance your efforts in preventing eye infections.
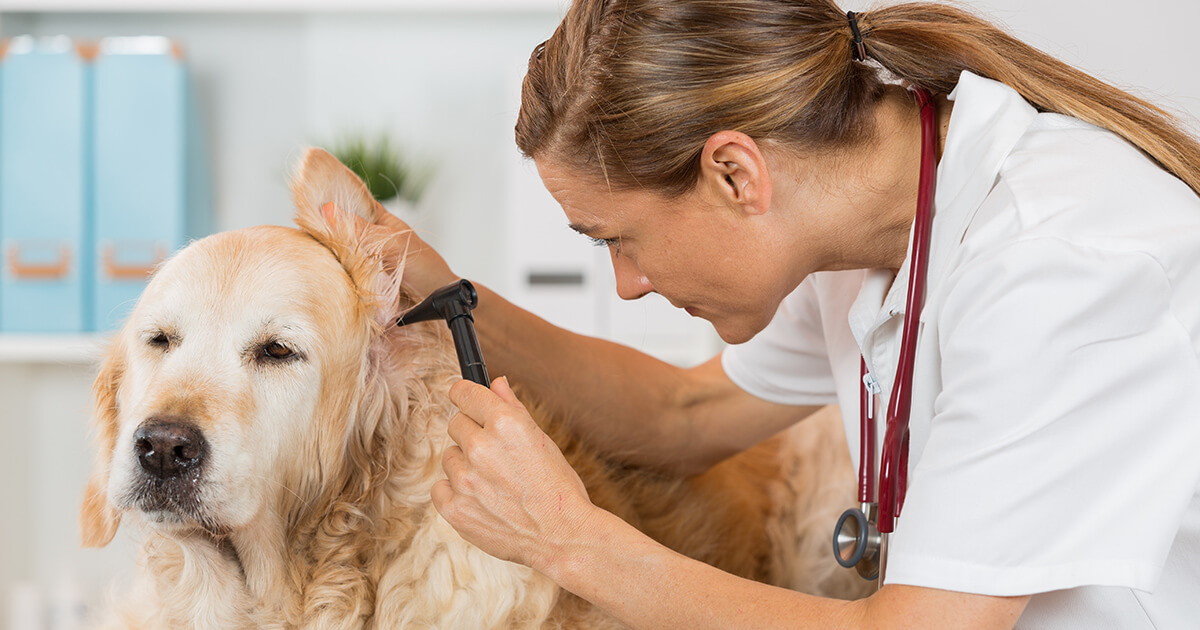
When to See a Veterinarian
Prompt veterinary attention is crucial when dealing with potential eye infections in dogs. While home care and remedies can offer supportive measures, certain circumstances warrant immediate evaluation and treatment by a veterinarian. Recognizing the signs that necessitate professional intervention can prevent the escalation of ocular issues and ensure the appropriate management of your dog's eye health.
-
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms: If your dog exhibits persistent or worsening symptoms of an eye infection, such as increased redness, swelling, discharge, or discomfort, it is imperative to seek veterinary care promptly. Unresolved symptoms can indicate a more severe underlying condition that requires professional assessment and treatment.
-
Visible Eye Trauma or Injury: In cases where your dog experiences visible eye trauma, such as scratches, lacerations, or foreign objects embedded in the eye, immediate veterinary attention is essential. Prompt intervention can prevent complications and mitigate the risk of infection stemming from the injury.
-
Sudden Onset of Severe Symptoms: The sudden onset of severe symptoms, such as acute pain, pronounced swelling, or significant changes in the appearance of the eye, warrants immediate veterinary evaluation. These indicators may signal a critical condition that demands urgent attention.
-
History of Chronic Eye Issues: Dogs with a history of recurrent or chronic eye infections, underlying health conditions affecting ocular health, or anatomical abnormalities predisposing them to eye problems should receive regular veterinary monitoring. Any exacerbation of existing issues necessitates timely veterinary assessment.
-
Changes in Behavior or Appetite: If your dog displays changes in behavior, such as increased agitation, reluctance to engage in activities, or a decrease in appetite accompanied by signs of ocular discomfort, it is advisable to consult a veterinarian. Behavioral changes can indicate underlying pain or distress related to eye issues.
-
Preexisting Health Conditions: Dogs with preexisting health conditions, such as autoimmune disorders, diabetes, or allergies, may be more susceptible to eye infections. Any signs of ocular discomfort in dogs with underlying health issues should prompt veterinary evaluation to address potential complications.
-
Concerns About Medication or Home Remedies: If you have concerns about the effectiveness of prescribed medications, adverse reactions to treatment, or the use of home remedies, seeking veterinary guidance is essential. Your veterinarian can provide clarity and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
By remaining vigilant and responsive to these indicators, pet owners can ensure that their dogs receive timely and appropriate veterinary care for any potential eye infections. Early intervention and professional assessment are pivotal in safeguarding your dog's ocular health and promoting a swift and effective resolution of eye-related concerns.