Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>What To Do For An Ulcer In A Dog’s Eye


Eye and Ear Health
What To Do For An Ulcer In A Dog’s Eye
Published: February 13, 2024
Learn effective ways to treat an ulcer in your dog's eye and maintain their overall eye and ear health. Expert tips and advice for pet owners.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Ulcers in a Dog's Eye
Ulcers in a dog's eye are a common and concerning condition that can cause discomfort and potential vision impairment for our beloved canine companions. An ulcer, also known as a corneal ulcer, refers to a defect or erosion in the outermost layer of the eye, the cornea. The cornea is a transparent, dome-shaped structure that covers the front part of the eye, allowing light to enter and protecting the delicate inner structures. When an ulcer occurs, it disrupts the smooth surface of the cornea, leading to pain, inflammation, and potential complications if left untreated.
Corneal ulcers in dogs can be caused by a variety of factors, including trauma from foreign objects, such as dust, dirt, or plant material, as well as scratches from other animals or even from the dog's own paws. Additionally, underlying eye conditions, such as dry eye or entropion (a condition where the eyelid rolls inward), can predispose a dog to developing corneal ulcers. Certain breeds, such as brachycephalic breeds with prominent eyes, are also more susceptible to corneal ulcers due to their eye anatomy.
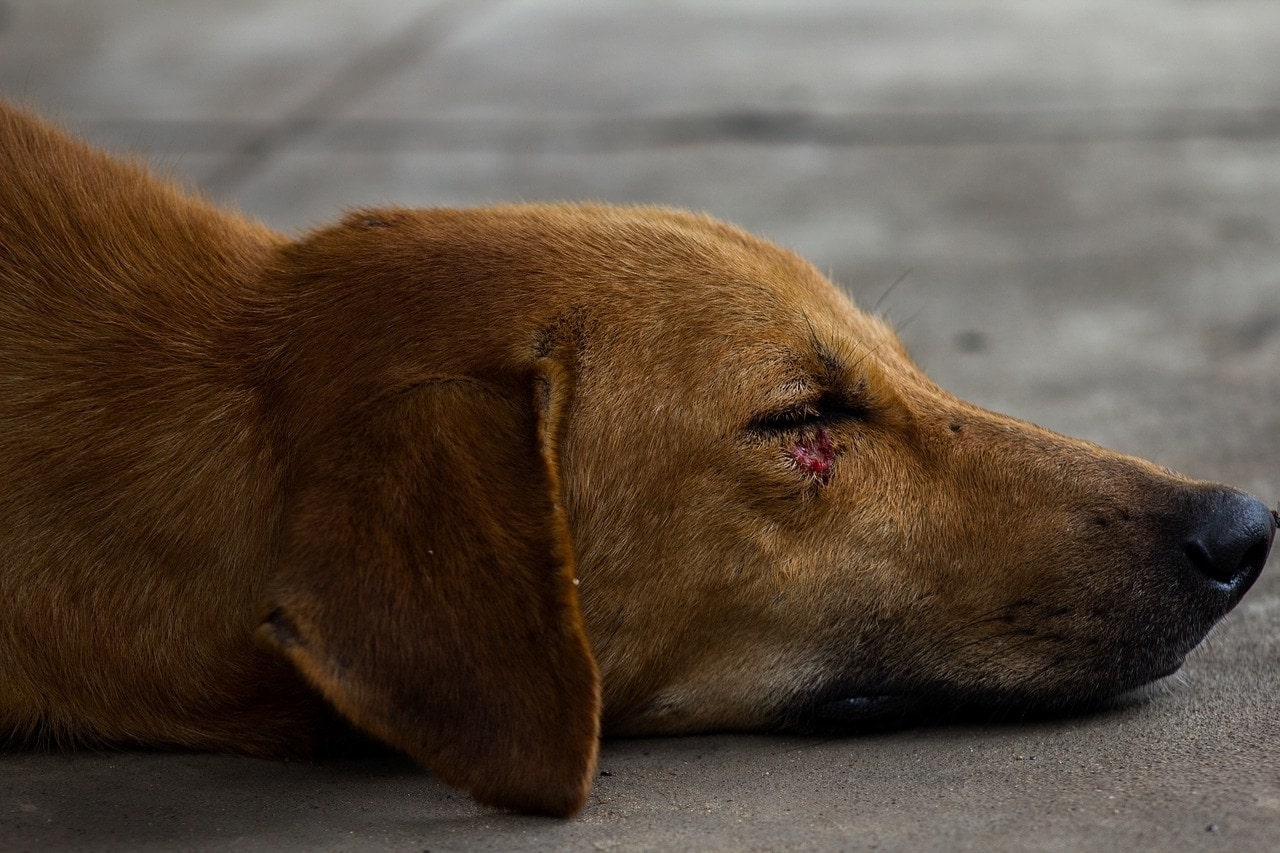
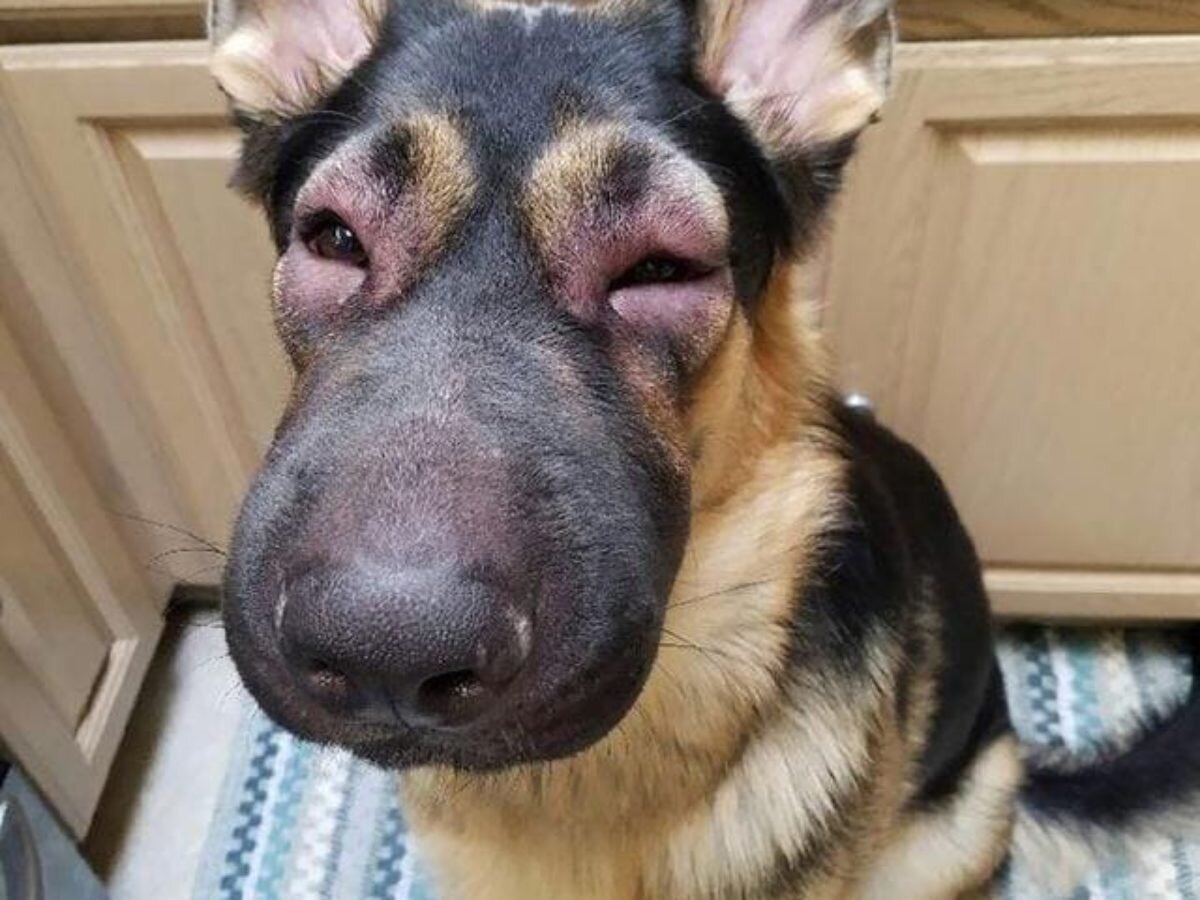
Understanding the signs and symptoms of a corneal ulcer is crucial for early detection and prompt treatment. Dogs with corneal ulcers may exhibit symptoms such as excessive blinking, squinting, redness in the eye, discharge, and increased tearing. They may also paw at or rub their eyes in an attempt to alleviate the discomfort. In some cases, the ulcer may appear as a white or grayish spot on the cornea, indicating the presence of the injury.
It's important for dog owners to be vigilant and observant of any changes in their pet's eye health, as early intervention can prevent the ulcer from worsening and causing more severe complications. Seeking prompt veterinary care is essential to accurately diagnose the ulcer and determine the underlying cause, whether it's a foreign body, infection, or an anatomical issue.
In summary, corneal ulcers in dogs are a distressing condition that can arise from various causes, leading to discomfort and potential vision impairment. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a corneal ulcer and understanding the predisposing factors can empower dog owners to take proactive measures in safeguarding their pet's eye health. Early detection and timely veterinary intervention are paramount in managing corneal ulcers and ensuring the well-being of our canine companions.
Read more: What To Do With An Infection In A Dog’s Eye
Signs and Symptoms of an Ulcer in a Dog's Eye
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of an ulcer in a dog's eye is crucial for pet owners to promptly address potential issues and seek appropriate veterinary care. Dogs, unable to verbally communicate their discomfort, rely on their human companions to observe and interpret changes in their behavior and physical well-being. Understanding the indicators of a corneal ulcer can aid in early detection and intervention, ultimately preserving the dog's ocular health.
Excessive Blinking and Squinting
One of the primary signs of a corneal ulcer in a dog's eye is excessive blinking or squinting. The dog may display a noticeable increase in the frequency of blinking, often accompanied by squinting or partial closure of the affected eye. These actions are indicative of discomfort and sensitivity to light, as the damaged cornea becomes more susceptible to irritation.
Redness and Discharge
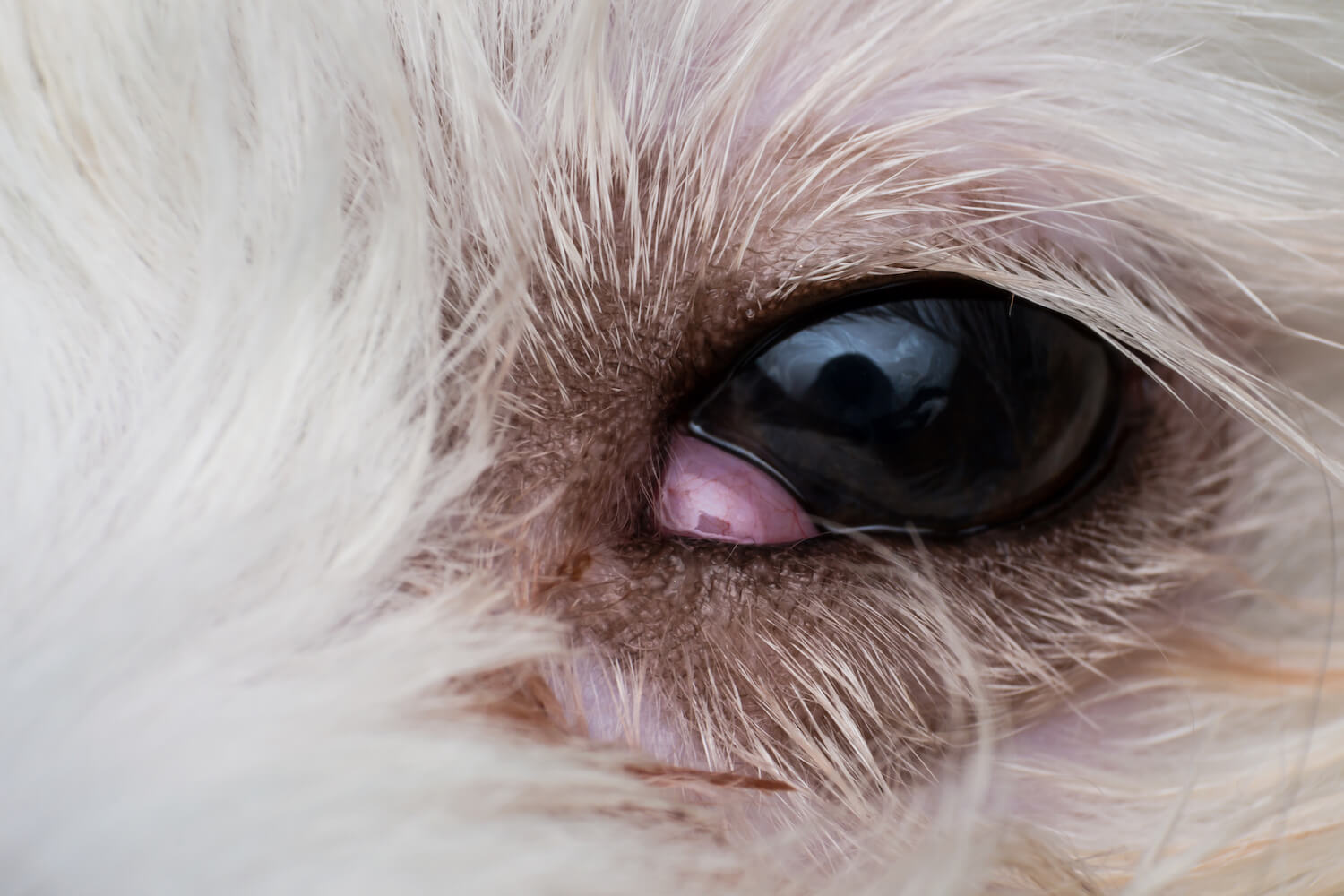
A dog with a corneal ulcer may exhibit redness in the affected eye, signaling inflammation and irritation. Additionally, there may be a presence of discharge, which can range from clear to purulent, depending on the severity of the ulcer and potential secondary infections. The combination of redness and discharge warrants immediate attention to prevent further complications.
Increased Tearing
An ulcer in a dog's eye can stimulate excessive tearing, leading to noticeable wetness around the eye. The dog may paw at the affected eye in an attempt to alleviate the discomfort caused by the increased tearing. This symptom, coupled with other indicators, should prompt pet owners to seek veterinary evaluation to address the underlying cause.
Read more: What To Do For Dog Eye Irritation
Pawing at the Eye
Dogs experiencing discomfort from a corneal ulcer may exhibit behavior such as pawing at the affected eye or rubbing their face against objects. This action is a natural response to alleviate the discomfort and may result in further trauma to the already compromised cornea. Observing such behavior should prompt immediate intervention to prevent exacerbation of the ulcer.
Visible Changes on the Cornea
In some cases, a corneal ulcer may manifest as a visible white or grayish spot on the surface of the cornea. This alteration in the appearance of the eye is a direct indication of the presence of an ulcer and warrants urgent veterinary assessment to determine the extent of the injury and initiate appropriate treatment.
By recognizing these signs and symptoms of a corneal ulcer in a dog's eye, pet owners can take proactive measures to safeguard their pet's ocular health. Early detection and timely veterinary intervention are essential in managing corneal ulcers and ensuring the well-being of our canine companions.
Seeking Veterinary Care for a Dog's Eye Ulcer
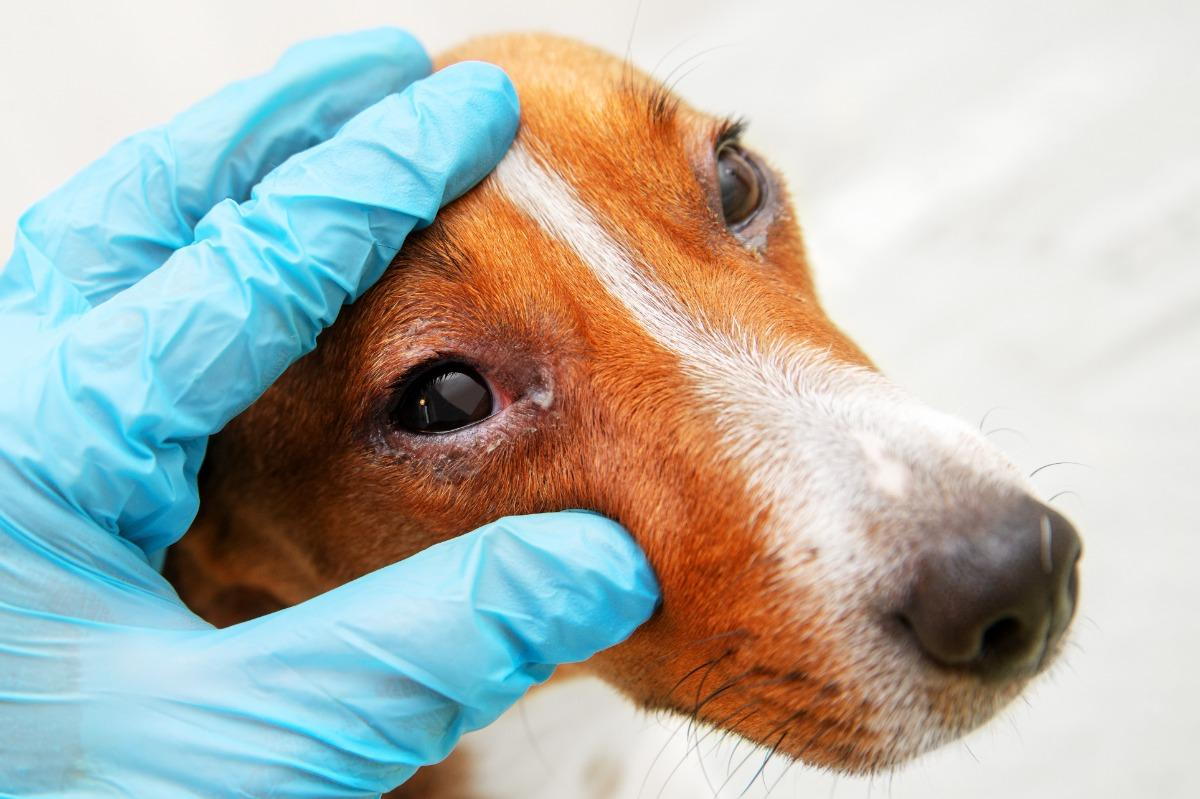
Seeking prompt veterinary care is imperative when a dog is suspected of having an eye ulcer. The expertise of a veterinarian is essential in accurately diagnosing the ulcer, determining its underlying cause, and implementing a tailored treatment plan to alleviate the dog's discomfort and prevent potential complications.
Upon observing any signs or symptoms indicative of a corneal ulcer in a dog's eye, such as excessive blinking, squinting, redness, discharge, increased tearing, or visible changes on the cornea, pet owners should prioritize scheduling a veterinary appointment without delay. Timely intervention is crucial in managing corneal ulcers and safeguarding the dog's ocular health.
During the veterinary consultation, the veterinarian will conduct a comprehensive ocular examination to assess the extent of the corneal ulcer and identify any contributing factors. This may involve the use of specialized equipment, such as a slit lamp biomicroscope, to closely examine the cornea and detect the presence of foreign bodies, abrasions, or secondary infections. Additionally, the veterinarian may perform a fluorescein stain test, where a special dye is applied to the eye to highlight the damaged areas of the cornea, aiding in the visualization and assessment of the ulcer.
Based on the findings from the examination, the veterinarian will develop a tailored treatment plan to address the dog's eye ulcer. This may include the application of ophthalmic medications, such as antibiotic or antifungal eye drops, to prevent or treat secondary infections and promote healing of the corneal ulcer. In some cases, pain management medications may also be prescribed to alleviate the dog's discomfort and minimize ocular inflammation.
Furthermore, the veterinarian will provide specific instructions for at-home care, which may involve the administration of prescribed medications, as well as guidance on monitoring the dog's eye for any changes or complications. Follow-up appointments may be scheduled to assess the progress of the ulcer and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan.
In instances where the corneal ulcer is severe or fails to respond to initial treatments, the veterinarian may consider additional interventions, such as the placement of a temporary protective contact lens or, in rare cases, surgical procedures to promote corneal healing and prevent long-term complications.
By seeking veterinary care for a dog's eye ulcer, pet owners can ensure that their canine companion receives the necessary attention and interventions to address the condition effectively. The expertise and guidance of a veterinarian are instrumental in managing corneal ulcers and promoting the overall well-being of the dog.
In summary, the prompt involvement of a veterinarian is paramount when a dog is suspected of having an eye ulcer. Through thorough ocular examinations, tailored treatment plans, and ongoing monitoring, veterinarians play a pivotal role in addressing corneal ulcers and safeguarding the ocular health of our beloved canine companions.
Home Care for a Dog's Eye Ulcer
After seeking veterinary care for a dog's eye ulcer, diligent home care is essential to support the healing process and ensure the dog's comfort. The following measures can aid in managing the ulcer and promoting ocular health:
Read more: What Do Seeing-Eye Dogs Do
Administering Prescribed Medications
Consistency in administering prescribed ophthalmic medications is crucial for the effective treatment of a dog's eye ulcer. Pet owners should carefully follow the veterinarian's instructions regarding the frequency and dosage of eye drops or ointments. It is important to gently restrain the dog and administer the medications as directed, ensuring that the solution makes direct contact with the affected eye.
Preventing Further Trauma
To prevent exacerbation of the ulcer, it is imperative to minimize the risk of further trauma to the dog's eye. This can be achieved by preventing the dog from rubbing or pawing at the affected eye. Additionally, environmental modifications, such as removing potential hazards or sharp objects from the dog's surroundings, can help create a safe space conducive to healing.
Environmental Comfort
Creating a comfortable and soothing environment for the dog can aid in the healing process. Minimizing exposure to bright lights and irritants, such as dust or smoke, can alleviate discomfort and reduce the likelihood of exacerbating the ulcer. Providing a quiet and calm space for the dog to rest can also contribute to their overall well-being during the recovery period.
Monitoring for Changes
Regular monitoring of the dog's affected eye is essential to track the progress of the ulcer and identify any changes that may require veterinary attention. Pet owners should observe the eye for signs of improvement, such as reduced redness and discharge, as well as any indications of worsening symptoms. Any unexpected changes should prompt immediate consultation with the veterinarian.
Read more: What To Do After A Dog’s Eye Is Removed
Preventing Secondary Infections
Preventing secondary infections is paramount in the management of a dog's eye ulcer. Pet owners should adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen and ensure that the dog avoids contact with potential sources of contamination. Additionally, maintaining good hygiene practices, such as keeping the dog's living area clean and free from debris, can minimize the risk of secondary complications.
By diligently implementing these home care measures, pet owners can actively contribute to the healing process and well-being of their dog during the recovery from an eye ulcer. Consistent and attentive home care, in conjunction with veterinary guidance, plays a vital role in promoting the dog's ocular health and overall quality of life.
Preventing Ulcers in a Dog's Eye
Preventing ulcers in a dog's eye is a proactive approach that focuses on minimizing potential risk factors and creating a safe environment to safeguard the ocular health of our canine companions. By implementing preventive measures, pet owners can significantly reduce the likelihood of their dogs developing corneal ulcers, thereby promoting long-term eye health and well-being.
Regular Eye Examinations
Scheduling routine eye examinations with a veterinarian is essential for proactive eye health management. Regular check-ups allow for the early detection of underlying conditions that may predispose a dog to developing corneal ulcers, such as dry eye, entropion, or other ocular abnormalities. Through comprehensive evaluations, veterinarians can identify potential concerns and provide guidance on preventive strategies tailored to the dog's specific needs.
Environmental Safety
Creating a safe and hazard-free environment for dogs is crucial in preventing eye injuries that can lead to corneal ulcers. Pet owners should carefully assess their living spaces and remove potential hazards, such as sharp objects, debris, or chemicals, that pose a risk to the dog's eyes. Additionally, ensuring that dogs are not exposed to situations where eye trauma is likely, such as interactions with aggressive animals or environments with airborne irritants, can significantly reduce the risk of corneal injuries.
Read more: What To Do If A Dog Gets Soap In Its Eye
Eye Protection During Activities
Engaging in activities that may pose a risk to the dog's eyes, such as outdoor adventures or playtime, warrants the use of protective gear. Dog goggles or protective eyewear can shield the eyes from foreign objects, dust, and UV radiation, reducing the likelihood of corneal injuries. Introducing and acclimating dogs to wearing protective eyewear during outdoor activities can provide an added layer of defense against potential eye trauma.
Regular Grooming and Hygiene
Maintaining proper grooming practices, particularly in breeds with facial folds or prominent eyes, is essential for preventing ocular issues. Regular cleaning of facial folds and ensuring that hair around the eyes is trimmed can minimize the accumulation of debris and reduce the risk of eye irritation or injury. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as keeping living areas clean and free from potential eye irritants, contributes to overall eye health.
Nutritional Support
Providing a balanced and nutritious diet that supports overall health, including ocular function, is fundamental in preventing ocular issues in dogs. Diets rich in essential nutrients, such as vitamin A, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants, can promote eye health and reduce the risk of ocular abnormalities. Consulting with a veterinarian to determine the most suitable diet for a dog's specific needs can aid in preventing potential predisposing factors for corneal ulcers.
By integrating these preventive measures into the care and management of dogs, pet owners can actively contribute to the prevention of ulcers in their canine companions' eyes. Proactive eye health management, in conjunction with regular veterinary guidance, plays a pivotal role in promoting long-term ocular health and ensuring the well-being of our beloved dogs.