Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>What Do I Do If My Dog Gets A Foxtail In Her Eye?


Eye and Ear Health
What Do I Do If My Dog Gets A Foxtail In Her Eye?
Published: February 11, 2024
Learn how to handle a foxtail in your dog's eye and prevent eye and ear health issues. Expert tips for keeping your pet safe and healthy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to our furry companions, their health and well-being are of utmost importance. As responsible pet owners, we strive to provide them with a safe and nurturing environment. However, despite our best efforts, unforeseen incidents can occur, such as the presence of foxtails. These seemingly innocuous grass-like plants can pose a serious threat to our dogs, particularly when they become lodged in their eyes.
Foxtails are prevalent in many regions, especially during the dry, warm months. Their barbed seed heads can easily attach to a dog's fur and skin, and if not promptly removed, they can work their way into sensitive areas such as the eyes. This can lead to discomfort, irritation, and potential complications if left unaddressed.
As a pet owner, it's crucial to be aware of the risks associated with foxtails and understand the necessary steps to take if your dog encounters this issue. By equipping yourself with the knowledge and preparedness to handle such situations, you can effectively safeguard your dog's ocular health and overall well-being.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of foxtails, explore the signs indicating their presence in a dog's eye, and outline the essential measures to take if your dog experiences this distressing situation. Additionally, we will discuss proactive strategies for preventing foxtail-related incidents in the future, empowering you to create a safer environment for your beloved canine companion. Let's embark on this informative journey to ensure that you are well-equipped to handle the potential threat of foxtails and protect your dog's precious eyesight.
Read more: Why Does My Dog Have A Bump By Her Eye
Understanding Foxtails
Foxtails, also known as grass awns, are a common type of weed found in various regions, particularly in dry, grassy areas. These seemingly innocuous plants can pose a significant threat to dogs due to their unique seed structure. The name "foxtail" is derived from the appearance of the seed heads, which resemble the bushy tail of a fox.
The danger lies in the barbed seed heads of foxtails, which are designed to burrow into the ground for germination. However, this natural mechanism can lead to serious issues when they come into contact with a dog's fur, skin, or, most alarmingly, their eyes. The barbs on the seeds allow them to easily attach to a dog's coat, and their pointed shape facilitates penetration into the skin or orifices.
In the context of ocular health, foxtails pose a particular risk as they can become lodged in the sensitive tissues of a dog's eye. The shape and structure of the seed heads make them prone to getting trapped in the fur around the eyes and, if not promptly addressed, they can migrate into the eye, leading to discomfort, inflammation, and potential damage to the delicate ocular structures.
It's important to note that foxtails are most prevalent during the dry, warm months when the grasses dry out and the seed heads become more prominent. Additionally, certain breeds with longer fur, such as spaniels and setters, may be more susceptible to foxtail-related issues due to the nature of their coat.
Understanding the nature of foxtails and their potential impact on a dog's well-being is crucial for pet owners. By recognizing the inherent risks associated with these seemingly innocuous plants, individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate the threat and protect their canine companions from the potential harm posed by foxtails.
By gaining insight into the characteristics and behavior of foxtails, pet owners can better appreciate the importance of preventive strategies and prompt action in the event of a foxtail-related incident. This knowledge equips them to create a safer environment for their dogs, minimizing the risk of foxtail-related complications and safeguarding their beloved pets' ocular health.
Signs of Foxtail in Dog's Eye
Identifying the signs of a foxtail lodged in your dog's eye is crucial for prompt intervention and mitigating potential complications. Dogs may exhibit various symptoms when a foxtail becomes trapped in their eye, signaling the need for immediate attention and care. Here are the key signs to watch for:
-
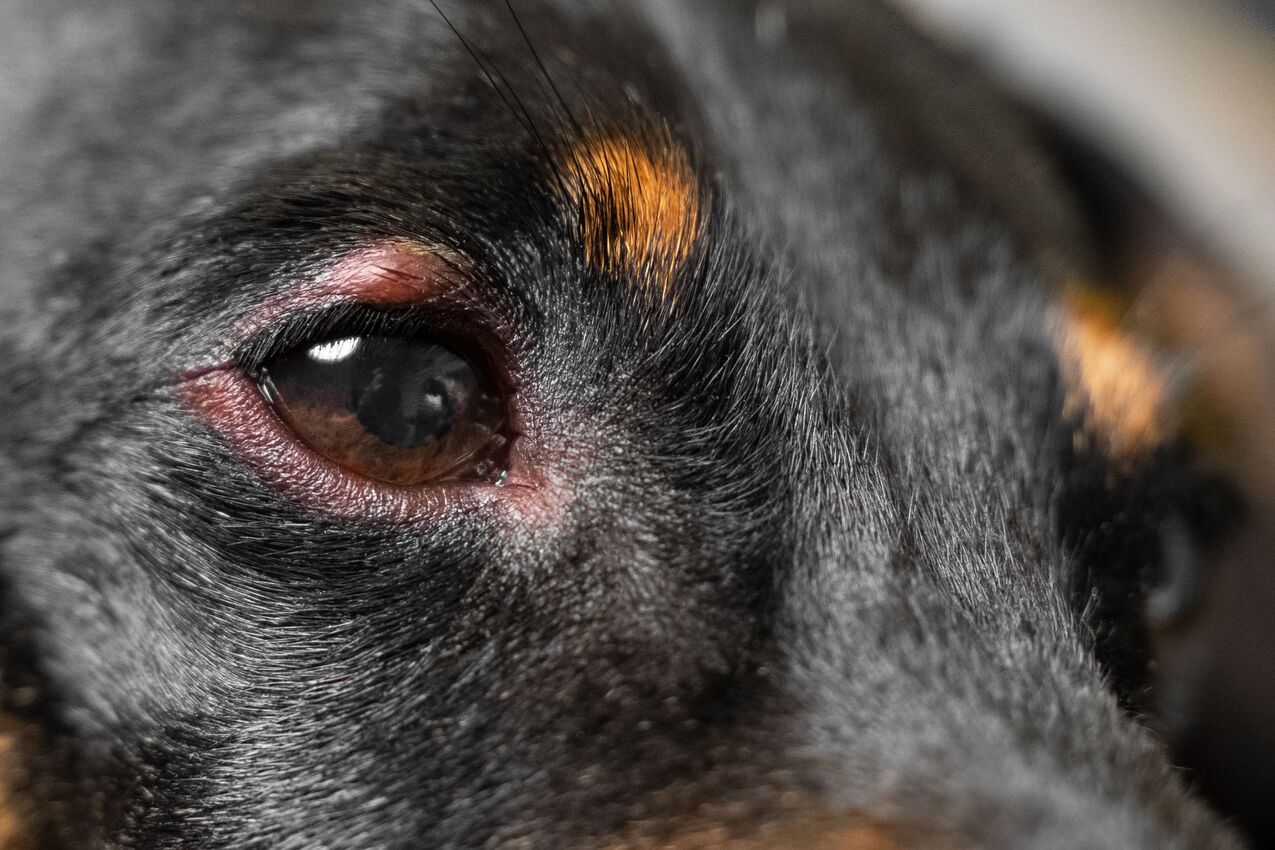
Excessive Tearing: If you notice an unusual increase in tear production from your dog's affected eye, it could indicate the presence of a foxtail. Excessive tearing is the eye's natural response to foreign objects or irritants, and it serves as a prominent indicator of ocular distress.
-
Squinting or Blinking: Dogs experiencing discomfort due to a foxtail in their eye may exhibit squinting or increased blinking. This behavior is a protective mechanism aimed at minimizing further irritation and shielding the eye from the foreign object.
-
Redness and Irritation: The affected eye may appear red, inflamed, or irritated, signaling the presence of a foreign body. This visible discomfort is a clear indication that the eye requires immediate attention to address the underlying cause.
-
Pawing at the Eye: Dogs instinctively attempt to alleviate discomfort by pawing at the affected eye. Persistent pawing or rubbing of the eye area is a strong indicator of ocular distress and warrants a thorough examination to identify and address the underlying issue.
-
Sensitivity to Light: Increased sensitivity to light, known as photophobia, can manifest when a foxtail irritates the delicate structures of the eye. Dogs may shy away from bright light or exhibit signs of discomfort when exposed to well-lit environments.
-
Visible Discharge or Tearing: The presence of discharge or excessive tearing from the affected eye, often accompanied by a cloudy or opaque appearance, can indicate the presence of a foxtail or associated inflammation.
-
Visible Foreign Object: In some cases, a foxtail may be visible on the surface of the eye or embedded in the surrounding tissues. This direct observation of the foreign object warrants immediate professional intervention to safely remove the foxtail and address any resulting complications.
By remaining vigilant and attentive to these signs, pet owners can promptly recognize the presence of a foxtail in their dog's eye and take the necessary steps to ensure their pet's ocular health and well-being. Early detection and intervention are essential in mitigating the potential risks associated with foxtails and safeguarding the delicate structures of the eye from further harm.
Steps to Take If Your Dog Gets a Foxtail in Her Eye
Discovering a foxtail in your dog's eye can be distressing, but swift and appropriate action is crucial to minimize discomfort and prevent potential complications. Here are the essential steps to take if your dog encounters this concerning situation:
-
Remain Calm: Upon noticing signs of a foxtail in your dog's eye, it's important to stay calm and composed. Your dog may be experiencing discomfort, and a calm demeanor can help reassure and soothe them during the subsequent steps.
-
Restrict Pawing: If your dog is pawing at their eye, gently restrain them from further aggravating the affected area. This can prevent additional irritation and potential injury caused by excessive rubbing.
-
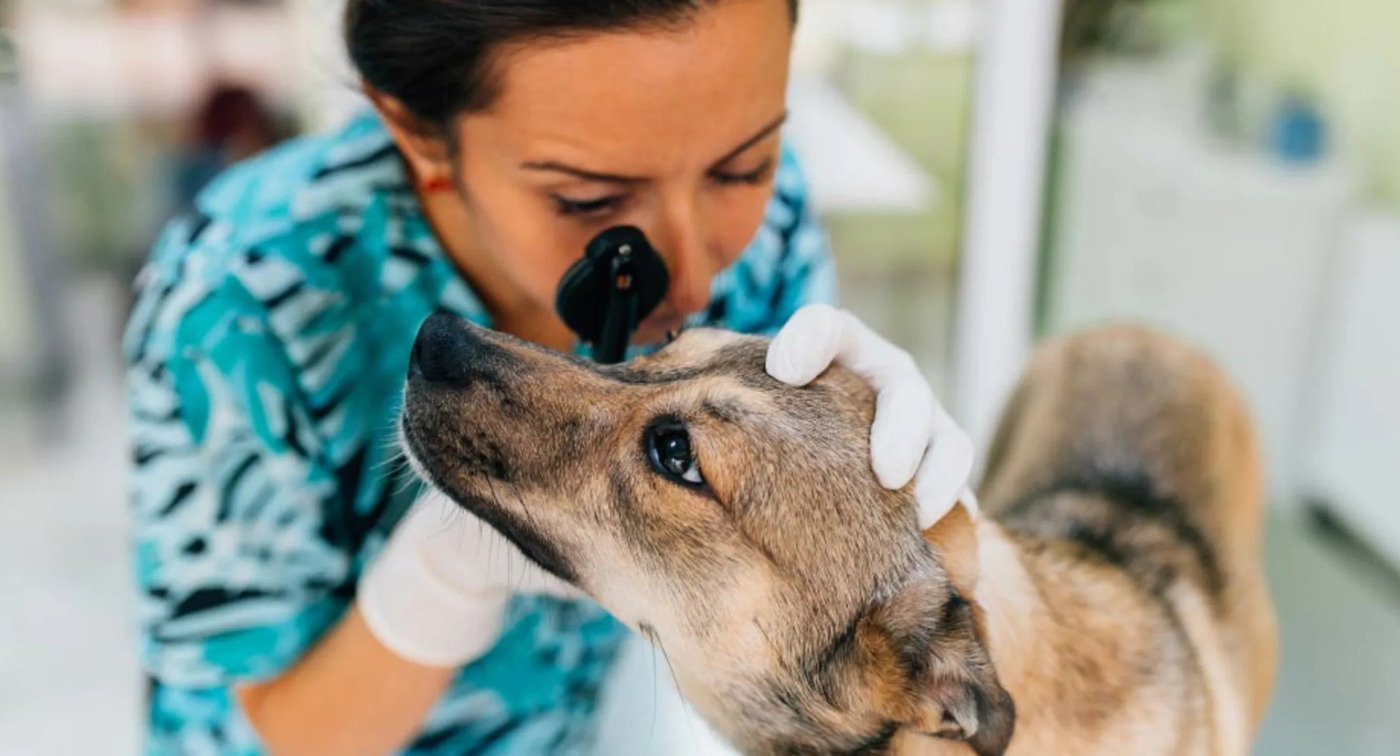
Seek Veterinary Assistance: Promptly contact your veterinarian to seek professional guidance and schedule an immediate appointment. Describe the observed symptoms and inform the veterinary staff about the potential presence of a foxtail in your dog's eye. Follow their recommendations for the next steps.
-
Minimize Handling: Refrain from attempting to remove the foxtail from your dog's eye without professional supervision. Handling the affected eye without the necessary expertise can exacerbate the situation and lead to further complications.
-
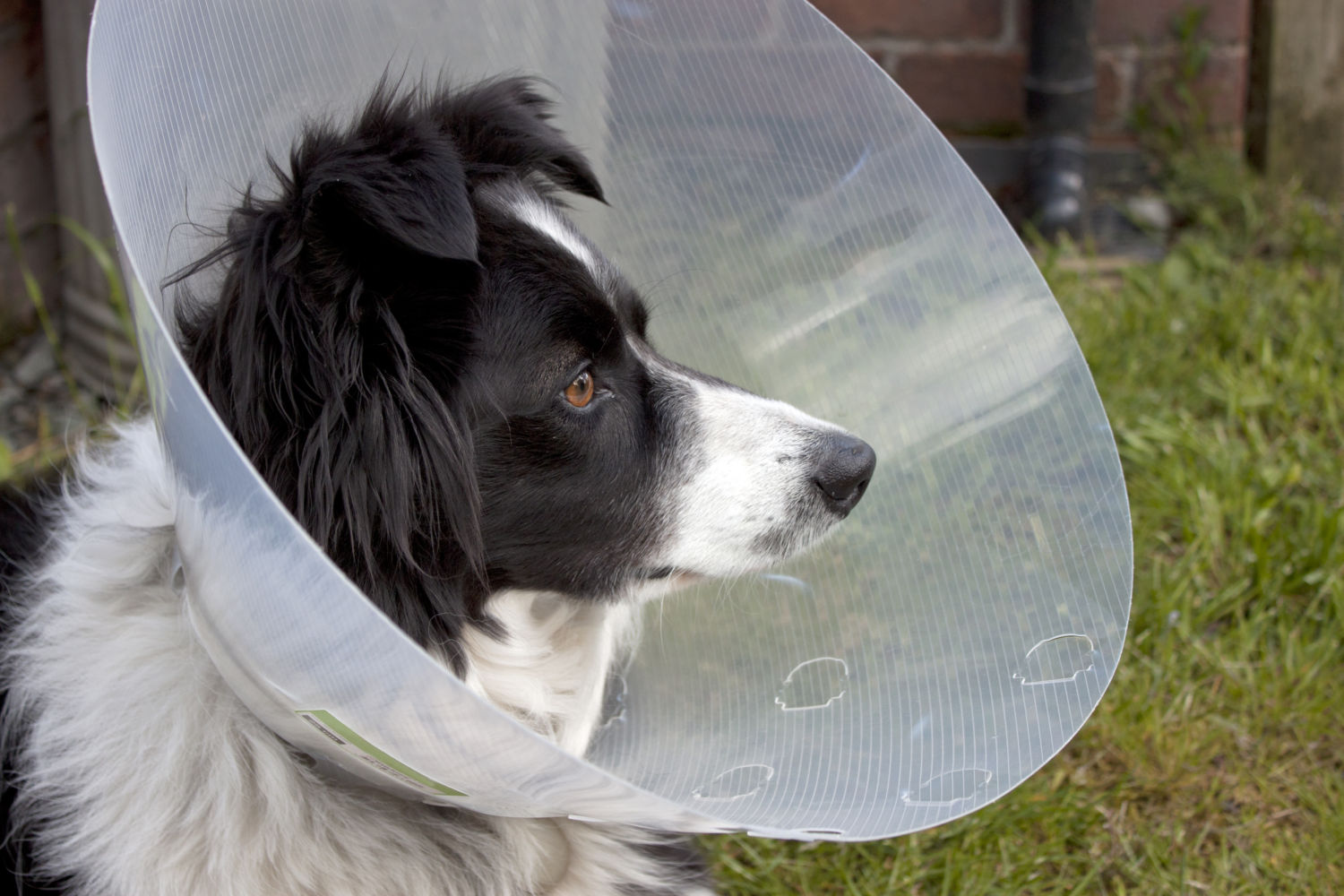
Protective Measures: If advised by your veterinarian, gently place an Elizabethan collar (cone) on your dog to prevent them from exacerbating the issue through excessive rubbing or scratching. This can safeguard the affected eye and promote healing.
-
Professional Examination: Upon reaching the veterinary clinic, your dog will undergo a thorough ocular examination to assess the extent of the foxtail's impact and any associated complications. The veterinarian will employ specialized tools and techniques to carefully examine the eye and formulate an appropriate treatment plan.
-
Sedation or Anesthesia: In cases where the foxtail is deeply embedded or causing significant discomfort, the veterinarian may recommend sedation or anesthesia to facilitate safe and precise removal of the foxtail from the eye. This ensures minimal stress and discomfort for your dog during the procedure.
-
Foxtail Removal: The veterinarian will delicately remove the foxtail from your dog's eye using specialized instruments and techniques. This meticulous process aims to eliminate the foreign object while minimizing trauma to the delicate ocular structures.
-
Post-Removal Care: Following the successful removal of the foxtail, your veterinarian will provide detailed post-removal care instructions. This may include administering prescribed eye drops or ointments, monitoring for any signs of infection or inflammation, and scheduling follow-up appointments as needed.
-
Preventive Measures: Engage in discussions with your veterinarian regarding preventive measures to minimize the risk of future foxtail-related incidents. This may involve modifying your dog's outdoor activities, grooming practices, or utilizing protective gear to mitigate the potential for foxtail exposure.
By diligently following these steps and collaborating closely with your veterinarian, you can effectively address the presence of a foxtail in your dog's eye and prioritize their ocular health and well-being. Swift and informed action is paramount in mitigating the impact of foxtails and ensuring the best possible outcome for your beloved canine companion.
Preventing Foxtails in the Future
Preventing foxtails from posing a threat to your dog's well-being involves proactive measures and vigilant management of their environment and activities. By implementing the following strategies, pet owners can significantly reduce the risk of foxtail-related incidents and create a safer outdoor experience for their canine companions.
Read more: My Cat Scratched My Dog’s Eye: What Do I Do?
1. Outdoor Activity Management
When venturing into areas where foxtails are prevalent, such as grassy fields or open landscapes, consider the timing and duration of outdoor activities. Opt for early morning or late evening walks when the ground is cooler, reducing the likelihood of foxtails becoming dry and brittle. Additionally, periodically inspect the surroundings for foxtails and promptly redirect your dog away from areas with high foxtail density.
2. Protective Gear
Outfitting your dog with protective gear, such as a well-fitted vest or coat, can serve as a physical barrier against foxtails. Look for gear specifically designed to minimize foxtail attachment and penetration, particularly in breeds with longer fur that may be more susceptible to foxtail-related issues.
3. Grooming Practices
Regular grooming plays a pivotal role in preventing foxtails from becoming embedded in your dog's coat. Brushing and combing your dog's fur after outdoor excursions can help dislodge any clinging foxtails before they have the chance to migrate to sensitive areas. Pay special attention to the paws, ears, and facial regions, as these are common entry points for foxtails.
4. Landscaping and Yard Maintenance
Maintain a well-groomed and foxtail-free yard by regularly mowing the lawn and removing any dry, overgrown grasses. Clearing debris and potential foxtail sources from your property can minimize the risk of exposure and reduce the likelihood of foxtails infiltrating your dog's outdoor space.
5. Vigilant Observation
Stay attuned to your dog's behavior and physical condition after outdoor activities. Look for any signs of foxtail attachment, such as excessive pawing, sneezing, or localized irritation. Promptly address any potential foxtail encounters to prevent further complications.
6. Veterinary Guidance
Consult your veterinarian for tailored recommendations on preventing foxtail-related issues based on your dog's breed, coat type, and environmental factors. Your veterinarian can offer valuable insights and preventive strategies to safeguard your dog from foxtail hazards.
By integrating these preventive measures into your routine care and outdoor excursions, you can significantly reduce the risk of foxtail-related incidents and create a safer environment for your dog. Proactive management and informed decision-making are essential in mitigating the potential threat of foxtails and ensuring the well-being of your beloved canine companion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, safeguarding our canine companions from the potential threat of foxtails in their eyes is a responsibility that pet owners should prioritize. The presence of these seemingly innocuous plants can lead to distressing and potentially harmful situations for dogs, particularly when they become lodged in the delicate tissues of the eye. By understanding the nature of foxtails, recognizing the signs of their presence in a dog's eye, and taking prompt and informed action, pet owners can effectively mitigate the risks and prioritize their dog's ocular health and well-being.
The signs of a foxtail in a dog's eye, including excessive tearing, squinting, redness, and sensitivity to light, serve as crucial indicators that prompt attention and intervention are necessary. By remaining vigilant and attentive to these signs, pet owners can promptly recognize the presence of a foxtail in their dog's eye and take the necessary steps to ensure their pet's ocular health and well-being. Early detection and intervention are essential in mitigating the potential risks associated with foxtails and safeguarding the delicate structures of the eye from further harm.
In the event of a foxtail-related incident, swift and appropriate action is paramount. Seeking veterinary assistance, refraining from attempting to remove the foxtail without professional supervision, and following the guidance of a veterinarian are essential steps in addressing the issue effectively. By collaborating closely with veterinary professionals, pet owners can ensure that their dog receives the necessary care and treatment to safely remove the foxtail and prevent potential complications.
Furthermore, proactive measures for preventing foxtails from posing a threat to dogs' well-being involve outdoor activity management, protective gear, grooming practices, yard maintenance, vigilant observation, and seeking veterinary guidance. By integrating these preventive measures into their routine care and outdoor excursions, pet owners can significantly reduce the risk of foxtail-related incidents and create a safer environment for their dogs.
Ultimately, by equipping themselves with knowledge, preparedness, and a proactive mindset, pet owners can effectively safeguard their canine companions from the potential threat of foxtails in their eyes. This proactive approach not only prioritizes the ocular health and well-being of dogs but also fosters a deeper bond between pet owners and their beloved companions, ensuring that they can continue to enjoy a safe and fulfilling life together.