Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Gets Ticks Off A Dog

Common Health Issues
What Gets Ticks Off A Dog
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about common health issues that can affect your dog and find out what gets ticks off a dog. Keep your furry friend healthy and happy!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
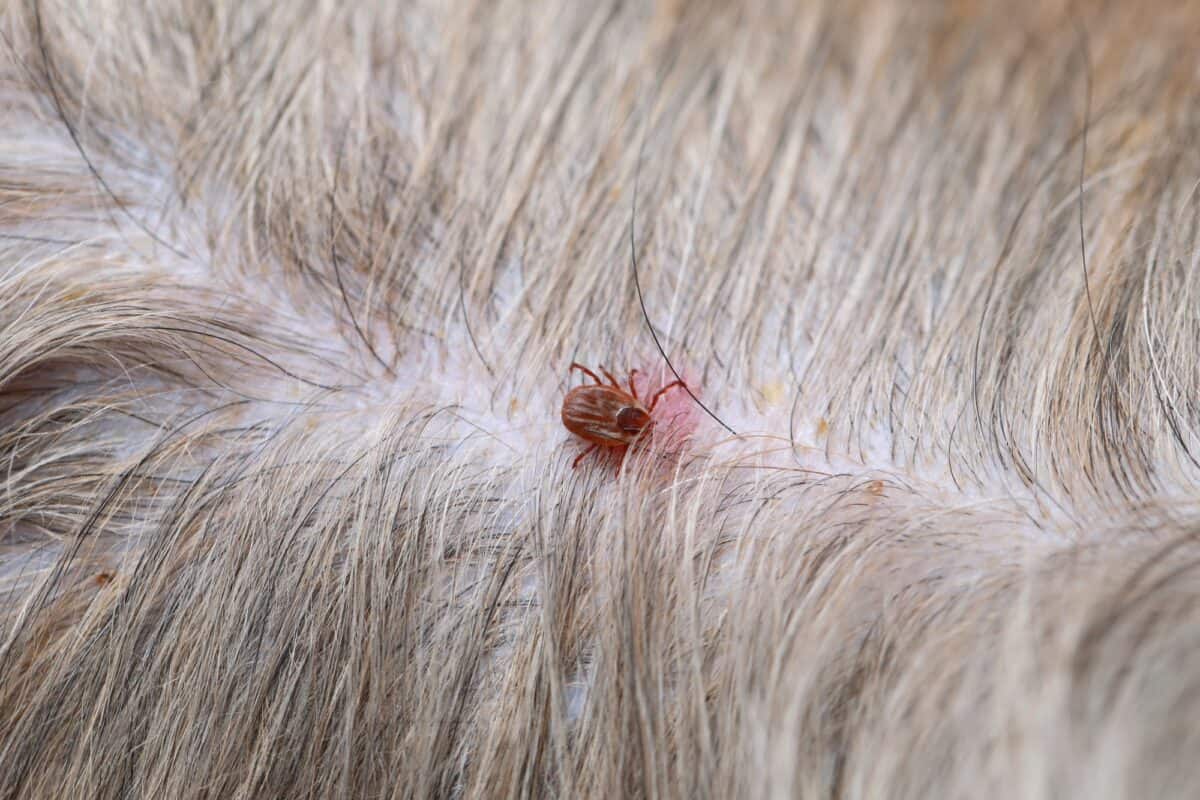
Ticks are pesky parasites that can cause a myriad of health issues for our beloved canine companions. These tiny creatures thrive in warm and humid environments, making dogs particularly susceptible to their presence. As responsible pet owners, it's crucial to understand the triggers for ticks in dogs and take proactive measures to protect our furry friends from these blood-sucking pests.
Ticks are not only a nuisance but also pose significant health risks to dogs. They can transmit various diseases, including Lyme disease, ehrlichiosis, and anaplasmosis, which can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Therefore, it's essential to be vigilant and proactive in preventing ticks from latching onto our canine companions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the common triggers for ticks in dogs, including behavioral, environmental, and health-related factors. By gaining a deeper understanding of these triggers, pet owners can take the necessary precautions to safeguard their dogs from tick infestations. Additionally, we will explore effective preventive measures to help keep our furry friends tick-free and healthy.
Understanding the triggers for ticks in dogs is the first step toward providing optimal care for our canine companions. By being informed and proactive, we can create a safe and comfortable environment for our dogs, free from the threat of tick-borne diseases. Let's embark on this journey to equip ourselves with the knowledge and tools needed to protect our furry friends from the perils of tick infestations.
Read more: How To Get A Tick Off Of My Dog’s Eye Area
Understanding the triggers for ticks in dogs
Ticks are external parasites that feed on the blood of animals, including dogs. Understanding the triggers for ticks in dogs is essential for effectively preventing infestations and minimizing the risk of tick-borne diseases. Several factors contribute to the prevalence of ticks in dogs, ranging from behavioral patterns to environmental conditions and underlying health issues.
Behavioral Triggers
Dogs that spend a significant amount of time outdoors, especially in wooded or grassy areas, are more likely to encounter ticks. Ticks thrive in warm and humid environments, making outdoor excursions an opportune time for these parasites to latch onto a dog's fur and skin. Additionally, dogs that enjoy exploring dense vegetation or tall grass are at a higher risk of coming into contact with ticks. Their curious and adventurous nature can inadvertently expose them to tick-infested areas, increasing the likelihood of tick attachment.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental factors play a significant role in the prevalence of ticks in dogs. Ticks are commonly found in areas with dense vegetation, such as forests, parks, and gardens. Moreover, ticks thrive in warm and humid climates, making certain regions more conducive to tick populations. Additionally, ticks can be prevalent during specific seasons, with spring and summer being peak times for tick activity. Understanding the environmental triggers for ticks enables pet owners to be mindful of high-risk areas and take preventive measures to minimize exposure.
Health-Related Triggers
Certain health issues can make dogs more susceptible to tick infestations. For instance, dogs with compromised immune systems may be less equipped to fend off tick-borne diseases, making them more vulnerable to the adverse effects of tick bites. Additionally, underlying health conditions that affect a dog's skin and coat, such as allergies or dermatitis, can create opportunities for ticks to attach and feed. Understanding the impact of health-related triggers empowers pet owners to prioritize their dog's overall well-being and take proactive measures to mitigate the risks associated with tick exposure.
By comprehensively understanding the triggers for ticks in dogs, pet owners can implement targeted preventive strategies to safeguard their canine companions. From behavioral modifications to environmental precautions and proactive healthcare measures, a holistic approach to tick prevention is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of dogs. With this knowledge in hand, pet owners can effectively protect their furry friends from the perils of tick infestations and ensure a safe and enjoyable environment for their beloved companions.
Common behaviors that can trigger ticks in dogs
Dogs are naturally curious and active animals, often engaging in behaviors that can inadvertently expose them to ticks. Understanding these common behaviors is essential for pet owners to recognize potential risk factors and take proactive measures to protect their furry companions.
-
Exploring Wooded and Grassland Areas: Dogs have a natural inclination to explore their surroundings, and this often leads them to wooded or grassy areas where ticks thrive. Tall grass, dense vegetation, and wooded trails provide ideal habitats for ticks, increasing the likelihood of tick encounters during outdoor excursions.
-
Roaming in Outdoor Environments: Dogs that spend a significant amount of time outdoors, whether in the backyard, parks, or hiking trails, are at a higher risk of encountering ticks. Their outdoor adventures expose them to potential tick habitats, especially in warm and humid climates where ticks are prevalent.
-
Interacting with Wildlife: Dogs may exhibit behaviors such as chasing small animals or investigating wildlife habitats, which can bring them into close proximity with ticks. Wildlife, including rodents and small mammals, can serve as hosts for ticks, increasing the likelihood of tick exposure for dogs that interact with these creatures.
-
Rolling and Playing in Vegetation: Dogs often enjoy rolling and playing in grassy or wooded areas, inadvertently coming into contact with ticks that may be lurking in the vegetation. This playful behavior can lead to tick attachment, especially in areas where ticks are abundant.
-
Exploring Moist and Shaded Areas: Dogs are drawn to moist and shaded areas, such as underbrush, shrubbery, and shaded patches, which are favored environments for ticks. Their natural curiosity may lead them to explore these areas, increasing the risk of tick encounters.
-
Frequenting Water Sources: Dogs that enjoy swimming or playing near water bodies may encounter ticks in the surrounding vegetation. Ticks can be present in areas near lakes, ponds, and streams, posing a risk to dogs that frequent these water sources.
-
Nesting and Resting in Outdoor Spaces: Dogs may seek out cozy spots for resting and nesting in outdoor environments, including areas where ticks are prevalent. Resting in tick-infested areas can lead to tick attachment and potential exposure to tick-borne diseases.
By recognizing these common behaviors that can trigger ticks in dogs, pet owners can take proactive measures to minimize the risk of tick encounters. Implementing preventive strategies, such as regular tick checks, grooming practices, and the use of tick control products, can significantly reduce the likelihood of tick infestations and protect dogs from the associated health risks. Additionally, creating awareness about these behaviors empowers pet owners to make informed decisions and provide a safe and tick-free environment for their canine companions.
Environmental factors that can trigger ticks in dogs
Environmental factors play a significant role in the prevalence of ticks in dogs. Ticks are commonly found in areas with dense vegetation, such as forests, parks, and gardens. Moreover, ticks thrive in warm and humid climates, making certain regions more conducive to tick populations. Additionally, ticks can be prevalent during specific seasons, with spring and summer being peak times for tick activity.
Dogs that frequent outdoor environments with dense vegetation are at a higher risk of encountering ticks. Ticks thrive in wooded and grassy areas, where they can easily latch onto passing animals, including dogs. Tall grass, shrubs, and leaf litter provide ideal habitats for ticks, allowing them to wait for suitable hosts to pass by.
Furthermore, ticks are more prevalent in warm and humid climates, creating favorable conditions for their survival and reproduction. Regions with mild winters and abundant vegetation provide an ideal environment for ticks to thrive, increasing the risk of tick encounters for dogs that reside or spend time in these areas.
Seasonal variations also play a crucial role in tick prevalence, with spring and summer being prime times for tick activity. During these seasons, ticks are more active and abundant, posing a heightened risk to dogs that venture into outdoor environments. Additionally, the increased outdoor activities during warmer months expose dogs to a greater likelihood of encountering ticks.
Understanding these environmental triggers empowers pet owners to be mindful of high-risk areas and take proactive measures to minimize exposure. By recognizing the environmental factors that can trigger ticks in dogs, pet owners can implement targeted preventive strategies to safeguard their canine companions. This may include avoiding heavily wooded areas during peak tick seasons, utilizing tick control products, and conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities.
By being aware of the environmental triggers for ticks, pet owners can take proactive steps to create a safer outdoor environment for their dogs. This knowledge enables them to make informed decisions about outdoor activities and implement preventive measures to minimize the risk of tick encounters. Ultimately, a proactive approach to environmental tick triggers can significantly contribute to the well-being and health of dogs, ensuring they can enjoy outdoor adventures without the threat of tick infestations.
Health issues that can trigger ticks in dogs
Certain health issues can make dogs more susceptible to tick infestations and the associated health risks. Understanding these underlying health factors is crucial for pet owners to recognize potential vulnerabilities in their canine companions and take proactive measures to mitigate the impact of tick exposure.
-
Compromised Immune System: Dogs with compromised immune systems, whether due to underlying medical conditions or certain medications, may be less equipped to fend off tick-borne diseases. A weakened immune response can make dogs more susceptible to the adverse effects of tick bites, increasing the risk of contracting tick-borne illnesses.
-
Skin and Coat Conditions: Dogs with skin and coat issues, such as allergies, dermatitis, or other inflammatory conditions, may be more prone to tick infestations. Skin abnormalities can create opportunities for ticks to attach and feed, as compromised skin barriers may make it easier for ticks to access a dog's blood supply.
-
Underlying Health Conditions: Certain underlying health issues, such as hormonal imbalances or metabolic disorders, can impact a dog's overall health and make them more vulnerable to the effects of tick-borne diseases. These conditions may compromise the dog's ability to combat tick-borne pathogens, increasing the severity of tick-related health issues.
-
Age and Health Status: Puppies, senior dogs, and those with pre-existing health concerns may be at a higher risk of experiencing complications from tick bites. Puppies with developing immune systems and senior dogs with age-related health challenges may be more susceptible to the effects of tick-borne diseases, necessitating extra vigilance in tick prevention and monitoring.
-
Previous Tick Infestations: Dogs that have experienced previous tick infestations may be more susceptible to future encounters with ticks. This is particularly relevant if the previous infestation led to the transmission of tick-borne diseases, as the dog's immune system may have been compromised or sensitized to subsequent tick bites.
By recognizing these health issues that can trigger ticks in dogs, pet owners can take proactive measures to address underlying vulnerabilities and minimize the risk of tick-related complications. This may include regular veterinary check-ups to monitor the dog's overall health, implementing preventive measures such as tick control products, and maintaining a vigilant approach to tick checks and grooming practices.
Understanding the interplay between health issues and tick susceptibility empowers pet owners to prioritize their dog's well-being and take proactive steps to mitigate the risks associated with tick exposure. By addressing underlying health concerns and implementing targeted preventive strategies, pet owners can create a safer and healthier environment for their canine companions, reducing the impact of tick-related health issues.
How to prevent ticks in dogs
Preventing ticks in dogs is a crucial aspect of responsible pet ownership, as it not only safeguards the well-being of our furry companions but also minimizes the risk of tick-borne diseases. By implementing effective preventive measures, pet owners can create a safe and tick-free environment for their dogs, allowing them to enjoy outdoor activities without the threat of tick infestations. Here are several proactive strategies to prevent ticks in dogs:
-
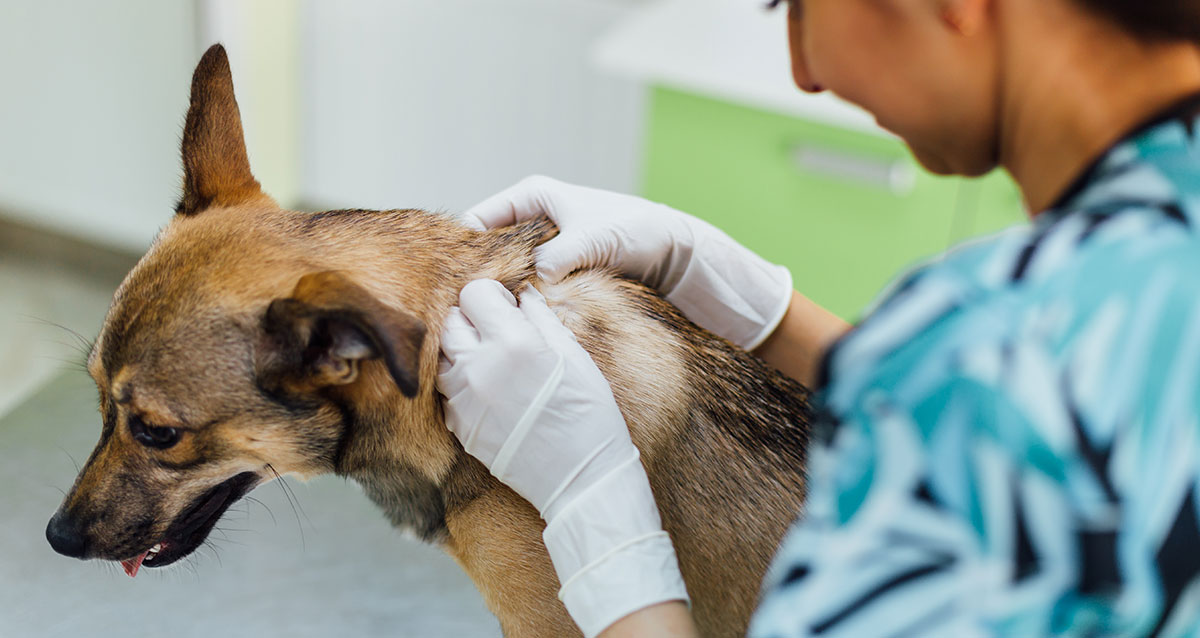
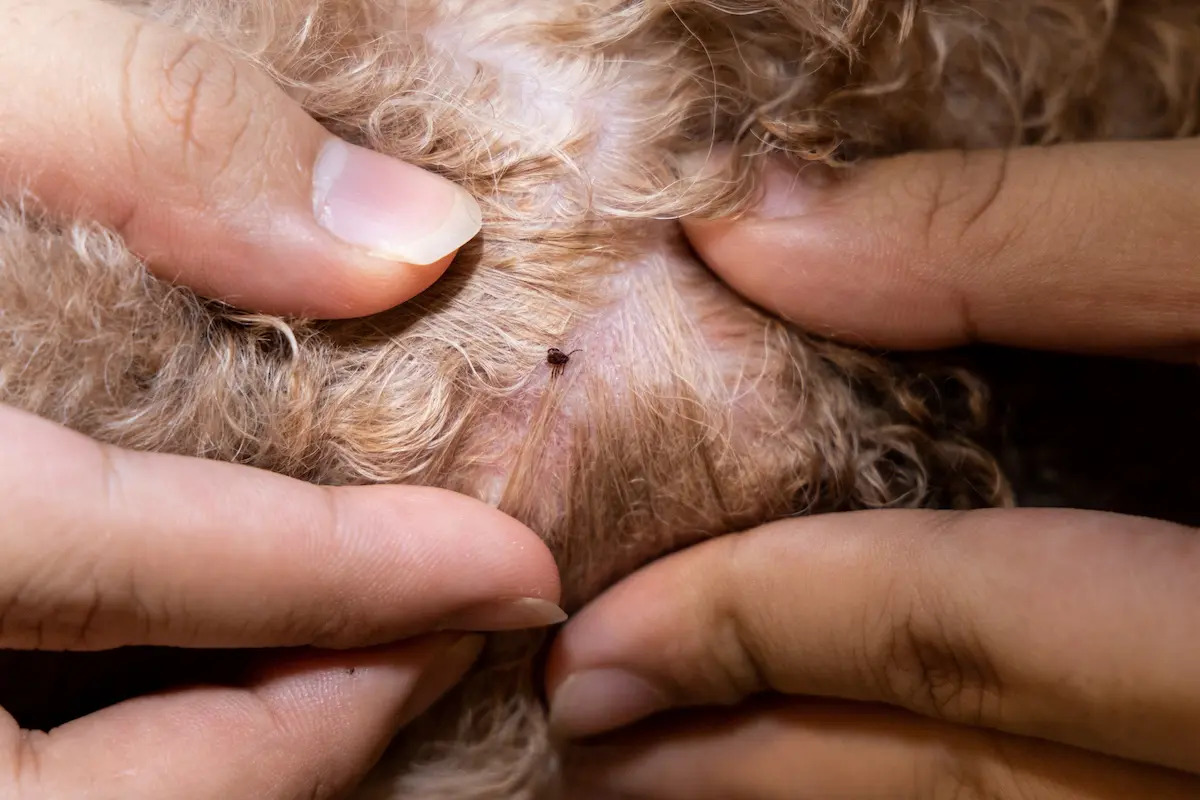
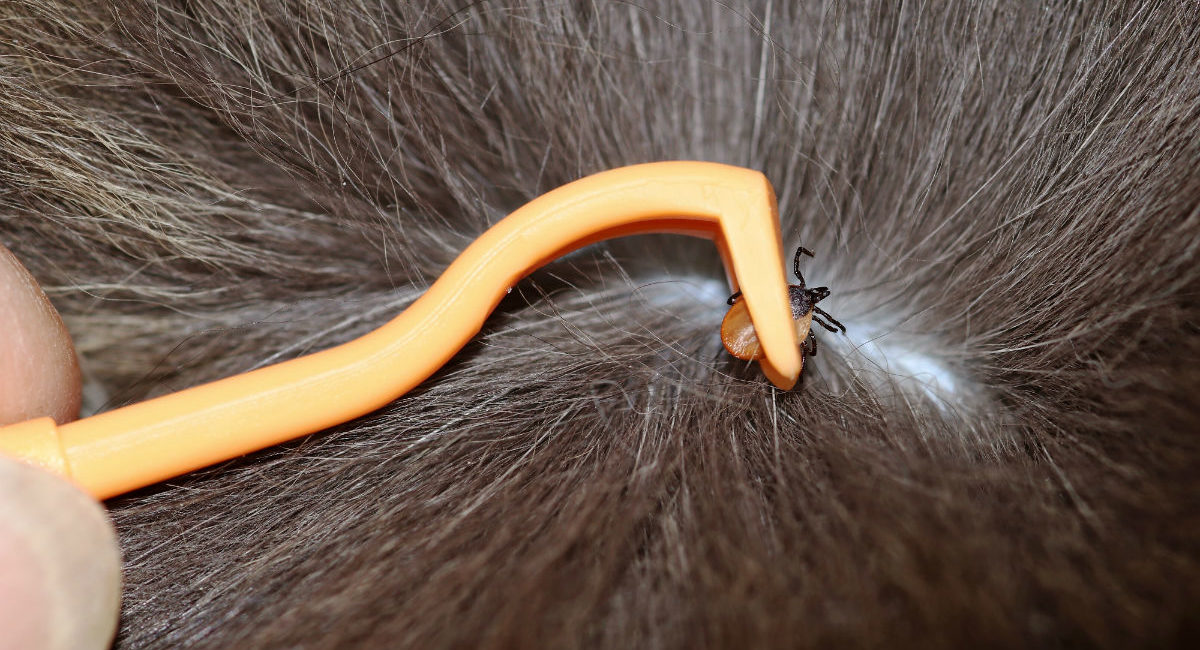
Regular Tick Checks: Conduct thorough tick checks on your dog after outdoor excursions, particularly in wooded or grassy areas. Pay close attention to areas where ticks are commonly found, such as the ears, neck, and between the toes. Promptly removing any attached ticks can prevent them from feeding and transmitting diseases.
-
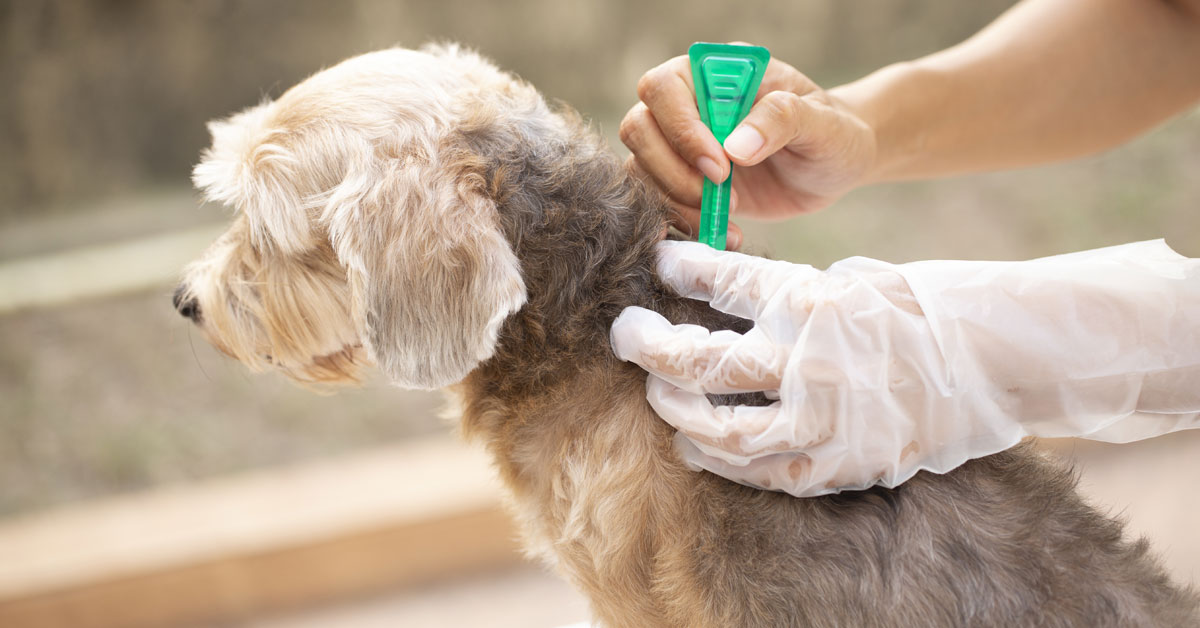
Tick Control Products: Utilize veterinarian-recommended tick control products, including spot-on treatments, collars, and oral medications. These products can effectively repel ticks and prevent infestations, providing an additional layer of protection for your dog.
-
Environmental Management: Keep your outdoor environment well-maintained by regularly mowing the lawn, trimming vegetation, and removing leaf litter. This reduces tick habitats and minimizes the likelihood of tick encounters in your dog's living spaces.
-
Tick-Resistant Landscaping: Consider incorporating tick-resistant landscaping strategies, such as using gravel or wood chips to create a barrier between wooded areas and recreational spaces. This can help deter ticks from entering areas frequented by your dog.
-
Regular Grooming: Maintain a regular grooming routine for your dog, including brushing their coat and inspecting for any signs of ticks or skin abnormalities. Keeping your dog's coat clean and well-groomed can make it easier to spot and remove ticks.
-
Indoor Living Spaces: Create a tick-free zone within your home by regularly vacuuming and cleaning indoor living spaces. This helps eliminate any ticks that may have been brought indoors on your dog's fur.
-
Consult with a Veterinarian: Schedule regular veterinary visits to discuss tick prevention strategies and ensure that your dog is up to date on tick control measures, including vaccinations and preventive medications.
-
Educate Yourself: Stay informed about the prevalence of ticks in your local area and the potential risks associated with tick-borne diseases. Understanding the seasonal variations in tick activity can help you tailor your preventive efforts accordingly.
By incorporating these preventive strategies into your dog's care routine, you can significantly reduce the risk of tick infestations and protect your canine companion from the adverse effects of tick-borne diseases. Proactive tick prevention not only contributes to your dog's overall health and well-being but also fosters a safe and enjoyable environment for them to thrive in.
Read more: What Can Be Used To Keep Ticks Off Dogs
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the triggers for ticks in dogs is paramount for pet owners to proactively protect their furry companions from the perils of tick infestations and tick-borne diseases. By delving into the behavioral, environmental, and health-related factors that can trigger ticks in dogs, we gain valuable insights into the complexities of tick prevention and the measures necessary to create a safe and tick-free environment for our canine friends.
Behavioral triggers, such as exploring wooded and grassland areas, interacting with wildlife, and frequenting outdoor environments, underscore the innate curiosity and active nature of dogs. Recognizing these behaviors empowers pet owners to implement targeted preventive strategies, including regular tick checks and the use of tick control products, to minimize the risk of tick encounters during outdoor adventures.
Environmental triggers, encompassing factors such as dense vegetation, warm and humid climates, and seasonal variations, highlight the dynamic interplay between environmental conditions and tick prevalence. By being mindful of high-risk areas and understanding the seasonal variations in tick activity, pet owners can make informed decisions about outdoor activities and implement preventive measures to safeguard their dogs from tick infestations.
Health-related triggers shed light on the vulnerabilities that certain health issues can pose for dogs in relation to tick infestations. From compromised immune systems to skin and coat conditions, recognizing these underlying health factors enables pet owners to prioritize their dog's well-being and take proactive measures to mitigate the impact of tick exposure.
Furthermore, the proactive strategies outlined for preventing ticks in dogs, including regular tick checks, tick control products, environmental management, and grooming practices, serve as actionable steps for pet owners to create a safe and tick-free environment for their dogs. By incorporating these preventive measures into their dog's care routine, pet owners can significantly reduce the risk of tick infestations and protect their canine companions from the adverse effects of tick-borne diseases.
In essence, the comprehensive understanding of tick triggers and the implementation of targeted preventive strategies are instrumental in fostering a safe and healthy environment for dogs. By equipping ourselves with the knowledge and tools needed to protect our furry friends from the perils of tick infestations, we can ensure that our canine companions can thrive and enjoy a life free from the threat of tick-borne diseases.