Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Does A Parasite In A Dog Look Like


Common Health Issues
What Does A Parasite In A Dog Look Like
Modified: March 1, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs, including what a parasite in a dog looks like. Understand the signs and symptoms to keep your furry friend healthy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Parasites are a common health concern for dogs and can have a significant impact on their well-being. These pesky organisms come in various forms, ranging from external parasites like fleas and ticks to internal parasites such as worms. Understanding the different types of parasites that can affect dogs, recognizing the signs of infestation, and knowing how to effectively treat and prevent these issues are crucial for maintaining the health and happiness of our beloved canine companions.
Parasites can cause a range of health problems for dogs, from mild irritation to severe illness. They can affect dogs of all ages and breeds, making it essential for pet owners to be vigilant and proactive in protecting their furry friends from these unwelcome intruders.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of parasites in dogs, exploring the various types of parasites, the signs of infestation, and what these parasites look like. Additionally, we will discuss treatment options and preventive measures to help dog owners safeguard their pets against these troublesome organisms.
By gaining a deeper understanding of parasites and their effects on dogs, pet owners can take proactive steps to ensure their canine companions lead healthy, parasite-free lives. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to uncover the mysteries of parasites in dogs and equip ourselves with the knowledge needed to protect our furry friends.
Read more: What Do Parasite Eggs Look Like In Dog Poop?
Types of Parasites in Dogs
Parasites that affect dogs can be broadly categorized into two main types: external parasites and internal parasites. Each type presents its own set of challenges and health risks for dogs, making it crucial for pet owners to be aware of the various parasites that can afflict their furry companions.
External Parasites
External parasites are organisms that live on the outside of a dog's body. The most common external parasites that affect dogs include:
-
Fleas: These tiny, wingless insects feed on the blood of dogs and can cause itching, skin irritation, and allergic reactions. Flea infestations can lead to dermatitis and even anemia in severe cases.
-
Ticks: Ticks are external parasites that attach themselves to a dog's skin and feed on their blood. In addition to causing skin irritation, ticks can transmit serious diseases such as Lyme disease and ehrlichiosis.
-
Mites: Ear mites, sarcoptic mange mites, and demodectic mange mites are common types of mites that can affect dogs. These microscopic parasites can cause intense itching, skin inflammation, and hair loss.
Internal Parasites
Internal parasites, as the name suggests, reside inside a dog's body. The most prevalent internal parasites in dogs include:
-
Roundworms: These are the most common intestinal parasites in dogs. Puppies can acquire roundworms from their mother's milk, while adult dogs can become infected through ingestion of contaminated soil or feces. Roundworm infestations can lead to digestive issues, malnutrition, and stunted growth.
-
Hookworms: These small, thread-like parasites attach to the lining of a dog's intestines and feed on their blood. Hookworm infestations can cause anemia, weakness, and gastrointestinal problems.
-
Tapeworms: Dogs can become infected with tapeworms by ingesting fleas or small mammals that harbor tapeworm larvae. These parasites can cause weight loss, abdominal discomfort, and irritation around the dog's anus.
-
Heartworms: Transmitted through mosquito bites, heartworms can cause serious and potentially fatal heart and lung issues in dogs. Prevention is key in protecting dogs from heartworm infestations.
Understanding the different types of parasites that can affect dogs is essential for pet owners to recognize the signs of infestation and take appropriate measures to protect their canine companions. By being informed about the various parasites and their effects, dog owners can work towards safeguarding their pets' health and well-being.
External Parasites
External parasites are organisms that live on the outside of a dog's body, causing a range of health issues and discomfort. These pesky intruders can have a significant impact on a dog's well-being, making it crucial for pet owners to be vigilant and proactive in protecting their furry companions from these unwelcome guests.
Read more: What Does A Tick Scab Look Like On A Dog?
Fleas
Fleas are among the most common external parasites that affect dogs. These tiny, wingless insects feed on the blood of dogs and can cause a myriad of problems. When a dog is infested with fleas, it can lead to intense itching, skin irritation, and allergic reactions. In severe cases, flea infestations can result in dermatitis and even anemia, especially in young or small dogs. The discomfort caused by flea bites can make dogs restless and irritable, affecting their overall quality of life.
Ticks
Ticks are another prevalent external parasite that can pose serious health risks to dogs. These arachnids attach themselves to a dog's skin and feed on their blood. In addition to causing skin irritation and discomfort, ticks can transmit dangerous diseases such as Lyme disease and ehrlichiosis. These diseases can have severe consequences for a dog's health, making tick prevention and prompt removal crucial for safeguarding a dog's well-being.
Mites
Mites are microscopic parasites that can cause significant discomfort for dogs. Ear mites, sarcoptic mange mites, and demodectic mange mites are common types of mites that can affect dogs. Ear mites can lead to intense itching and discomfort in a dog's ears, while sarcoptic and demodectic mange mites can cause skin inflammation, hair loss, and severe itching. These conditions can be distressing for dogs and may require veterinary intervention to alleviate the symptoms and eradicate the mites.
Understanding the impact of external parasites on dogs is essential for pet owners to recognize the signs of infestation and take appropriate measures to protect their canine companions. By being informed about the various external parasites and their effects, dog owners can work towards safeguarding their pets' health and well-being, ensuring they lead comfortable and parasite-free lives.
Internal Parasites
Internal parasites pose a significant threat to the health and well-being of dogs, residing inside their bodies and causing a range of health issues. These insidious organisms can have a profound impact on a dog's overall health, making it essential for pet owners to be aware of the various types of internal parasites that can afflict their furry companions.
Read more: What Does A Dog’s Eye Look Like
Roundworms
Roundworms are among the most prevalent internal parasites in dogs. These long, spaghetti-like worms reside in a dog's intestines and can cause a host of health problems. Puppies can acquire roundworms from their mother's milk, while adult dogs can become infected through ingestion of contaminated soil or feces. Roundworm infestations can lead to digestive issues, malnutrition, and stunted growth, particularly in young and developing dogs. Recognizing the signs of roundworm infestation, such as a potbellied appearance, diarrhea, vomiting, and a dull coat, is crucial for prompt intervention and treatment.
Hookworms
Hookworms are small, thread-like parasites that attach to the lining of a dog's intestines and feed on their blood. These insidious parasites can cause anemia, weakness, and gastrointestinal problems in affected dogs. Hookworm infestations are particularly concerning for puppies, as severe infestations can lead to life-threatening blood loss. Identifying the symptoms of hookworm infestation, including pale gums, weakness, and dark, tarry stools, is vital for seeking veterinary care and implementing appropriate treatment.
Tapeworms
Dogs can become infected with tapeworms through the ingestion of fleas or small mammals that harbor tapeworm larvae. These parasites can cause weight loss, abdominal discomfort, and irritation around the dog's anus. One of the telltale signs of tapeworm infestation is the presence of small, rice-like segments in a dog's feces or around the anal area. Recognizing these segments can prompt pet owners to seek veterinary guidance for effective treatment and prevention of tapeworm infestations.
Heartworms
Heartworms pose a grave threat to dogs, transmitted through mosquito bites. These parasites reside in a dog's heart and pulmonary arteries, causing severe and potentially fatal heart and lung issues. Prevention is key in protecting dogs from heartworm infestations, as treatment for advanced cases can be challenging and costly. Recognizing the signs of heartworm infestation, such as coughing, exercise intolerance, and weight loss, underscores the importance of preventive measures, including regular heartworm testing and administration of preventive medications.
Understanding the various internal parasites that can affect dogs is crucial for pet owners to recognize the signs of infestation and take proactive measures to protect their canine companions. By being informed about the impact of internal parasites and their effects, dog owners can work towards safeguarding their pets' health and well-being, ensuring they lead healthy and parasite-free lives.
Read more: What Does Cancer On A Dog’s Toe Look Like
Signs of Parasite Infestation
Recognizing the signs of parasite infestation in dogs is crucial for prompt intervention and effective treatment. The presence of parasites can cause a range of symptoms and health issues, impacting a dog's overall well-being. By being vigilant and observant, pet owners can identify potential signs of infestation and seek appropriate veterinary care to address the problem.
External Parasites
- Scratching and Biting: Dogs infested with fleas, ticks, or mites often exhibit excessive scratching, biting, and licking to alleviate the discomfort caused by these external parasites. Persistent scratching, particularly in specific areas of the body, can indicate the presence of fleas or mites.
- Skin Irritation and Redness: External parasites can cause skin irritation, redness, and inflammation. Pet owners should inspect their dog's skin for signs of red, irritated areas, as well as the presence of small black or brown specks, which could indicate flea dirt.
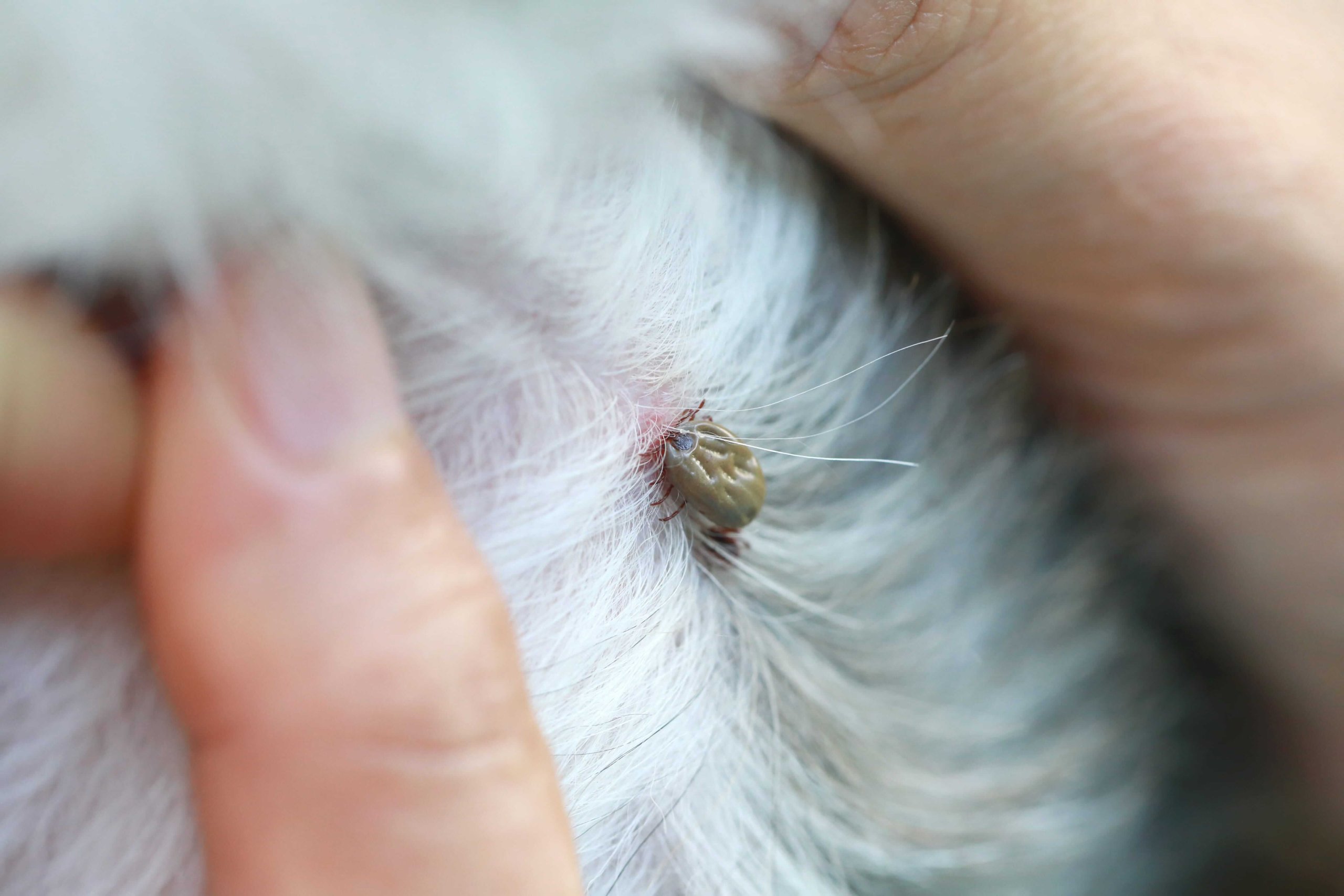
- Visible Parasites: In cases of severe infestation, external parasites such as fleas and ticks may be visible on a dog's skin or coat. Ticks can be found attached to the skin, while fleas may be visible scurrying through the fur.
Internal Parasites
- Digestive Issues: Internal parasites like roundworms and hookworms can cause digestive problems in dogs, including diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal discomfort. Changes in a dog's stool, such as the presence of blood or abnormal consistency, can be indicative of internal parasite infestation.
- Weight Loss and Poor Growth: Puppies infested with internal parasites may experience stunted growth and fail to thrive despite adequate nutrition. Additionally, adult dogs may exhibit unexplained weight loss and a lack of appetite, signaling potential internal parasite infestation.
- Lethargy and Weakness: Dogs suffering from internal parasite infestations may display signs of lethargy, weakness, and decreased activity levels. A lack of energy and enthusiasm for activities that were previously enjoyed can be indicative of underlying health issues, including parasitic infestation.
General Signs
- Anemia: Severe infestations of certain parasites, such as hookworms, can lead to anemia in dogs, characterized by pale gums, weakness, and fatigue.
- Visible Worms in Feces: In cases of intestinal parasite infestation, pet owners may observe visible worms in their dog's feces, indicating the presence of roundworms, tapeworms, or other intestinal parasites.
By remaining attentive to these signs and promptly seeking veterinary care when necessary, pet owners can ensure the early detection and effective management of parasite infestations in their beloved canine companions. Regular preventive measures, including parasite control products and veterinary check-ups, are essential for maintaining a parasite-free and healthy environment for dogs.
Read more: What Does A Tick Look Like In Dog Skin
What Do Parasites Look Like in Dogs?
Parasites that affect dogs come in various shapes and sizes, each with its own distinct appearance and characteristics. Understanding what parasites look like is essential for pet owners to identify potential infestations and take appropriate measures to protect their canine companions. Here's a closer look at the appearance of common parasites that can afflict dogs:
Read more: What Does A Tick Scab Look Like On A Dog?
Fleas
Fleas are tiny, wingless insects that are reddish-brown in color and approximately 1 to 2 millimeters in length. These agile parasites are often visible to the naked eye, especially when inspecting a dog's fur. Fleas move quickly and can be observed scurrying through the coat, particularly in areas where the fur is thinner, such as around the neck, ears, and abdomen. Additionally, flea dirt, which resembles small black or brown specks, may be present on a dog's skin or coat, indicating the presence of fleas.
Ticks
Ticks vary in size and appearance depending on their stage of development and species. These arachnids can range from the size of a pinhead to a pea and may appear flat or engorged after feeding on a dog's blood. Ticks attach themselves to a dog's skin, often in areas with less hair, such as the ears, groin, and between the toes. When inspecting a dog for ticks, pet owners should look for small, dark-colored parasites firmly attached to the skin.
Mites
Mites are microscopic parasites that are not visible to the naked eye, making their appearance elusive. However, the effects of mite infestations, such as intense itching, skin inflammation, and hair loss, can be indicative of their presence. Ear mites, for example, may cause a dark, crumbly discharge in a dog's ears, while sarcoptic and demodectic mange mites can lead to red, irritated skin and hair loss.
Roundworms and Tapeworms
Intestinal parasites such as roundworms and tapeworms are visible to the naked eye when passed in a dog's feces. Roundworms resemble spaghetti-like strands, while tapeworm segments may appear as small, white, rice-like particles around a dog's anus or in their feces. Identifying these visible signs can prompt pet owners to seek veterinary guidance for effective treatment and prevention of intestinal parasite infestations.
By familiarizing themselves with the appearance of common parasites that affect dogs, pet owners can be better equipped to detect potential infestations and take proactive measures to protect their furry companions from these unwelcome intruders. Regular grooming, thorough inspections, and preventive measures recommended by veterinarians are essential for maintaining a parasite-free environment for dogs.
Treatment and Prevention
Effective treatment and prevention strategies play a pivotal role in managing and safeguarding dogs against parasite infestations. By implementing proactive measures and seeking timely veterinary care, pet owners can ensure the well-being and comfort of their beloved canine companions.
Treatment
When a dog is diagnosed with a parasite infestation, prompt and appropriate treatment is essential to alleviate discomfort and eradicate the parasites. Treatment options may vary depending on the type of parasite and the severity of the infestation. Veterinary guidance is crucial for determining the most effective treatment approach, which may include:
-
Prescription Medications: Veterinarians may prescribe oral or topical medications to eliminate parasites such as fleas, ticks, and intestinal worms. These medications are designed to target and eradicate the specific parasites affecting the dog, providing relief and preventing further infestations.
-
Medicated Baths and Dips: In cases of severe flea or tick infestations, veterinarians may recommend medicated baths or dips to help eliminate parasites and soothe irritated skin. These treatments can provide immediate relief and aid in the eradication of external parasites.
-
Injections and Preventive Medications: For certain parasites, such as heartworms, preventive medications in the form of injections or oral tablets are available. These medications are administered regularly to protect dogs from heartworm infestations and other internal parasites.
Prevention
Preventive measures are key to maintaining a parasite-free environment for dogs and minimizing the risk of infestations. Pet owners can take proactive steps to prevent parasites from affecting their furry companions, including:
-
Regular Parasite Control Products: Utilizing veterinarian-recommended flea and tick control products, such as spot-on treatments, collars, and oral medications, can help prevent external parasite infestations. These products are designed to repel and eliminate parasites, reducing the likelihood of infestations.
-
Year-Round Heartworm Prevention: Administering year-round heartworm preventive medications is essential for protecting dogs from potentially fatal heartworm infestations. These medications are available in various forms, including chewable tablets and topical treatments, and should be administered as directed by a veterinarian.
-
Routine Veterinary Examinations: Regular veterinary check-ups enable early detection of parasite infestations and allow veterinarians to recommend appropriate preventive measures and treatments. Veterinary examinations also provide an opportunity to discuss parasite control strategies tailored to the specific needs of the dog.
-
Environmental Management: Maintaining a clean and hygienic living environment for dogs can help minimize the risk of parasite infestations. Regular cleaning of bedding, grooming tools, and living areas can reduce the presence of parasites and their eggs.
By prioritizing preventive measures and promptly addressing parasite infestations through effective treatment, pet owners can create a safe and comfortable environment for their dogs. Collaborating with veterinarians to develop a comprehensive parasite control plan tailored to the specific needs of each dog is essential for promoting their overall health and well-being.
Read more: What Does Arthritis Look Like In A Dog?
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the impact of parasites on dogs and the measures to prevent and treat infestations is crucial for ensuring the health and well-being of our beloved canine companions. Parasites, whether external or internal, can pose significant health risks and discomfort for dogs, ranging from skin irritation and itching to severe illnesses and life-threatening conditions.
By familiarizing themselves with the appearance of common parasites such as fleas, ticks, mites, roundworms, and tapeworms, pet owners can be better equipped to detect potential infestations and take proactive measures to protect their furry companions from these unwelcome intruders. Regular grooming, thorough inspections, and preventive measures recommended by veterinarians are essential for maintaining a parasite-free environment for dogs.
Recognizing the signs of parasite infestation, such as excessive scratching, skin irritation, digestive issues, and lethargy, empowers pet owners to seek timely veterinary care and implement appropriate treatment. Additionally, preventive measures, including the use of parasite control products, year-round heartworm prevention, routine veterinary examinations, and environmental management, play a pivotal role in minimizing the risk of infestations and creating a safe and comfortable living environment for dogs.
Effective treatment options, including prescription medications, medicated baths, and preventive medications, are essential for eradicating parasites and alleviating discomfort in affected dogs. Collaborating with veterinarians to develop a comprehensive parasite control plan tailored to the specific needs of each dog is essential for promoting their overall health and well-being.
By prioritizing preventive measures and promptly addressing parasite infestations through effective treatment, pet owners can ensure the well-being and comfort of their beloved canine companions. Through vigilance, education, and proactive care, we can create a safe and parasite-free environment for our dogs, allowing them to lead healthy, happy, and fulfilling lives as cherished members of our families.