Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>What Does A Dog’s Eye With Cataracts Look Like?
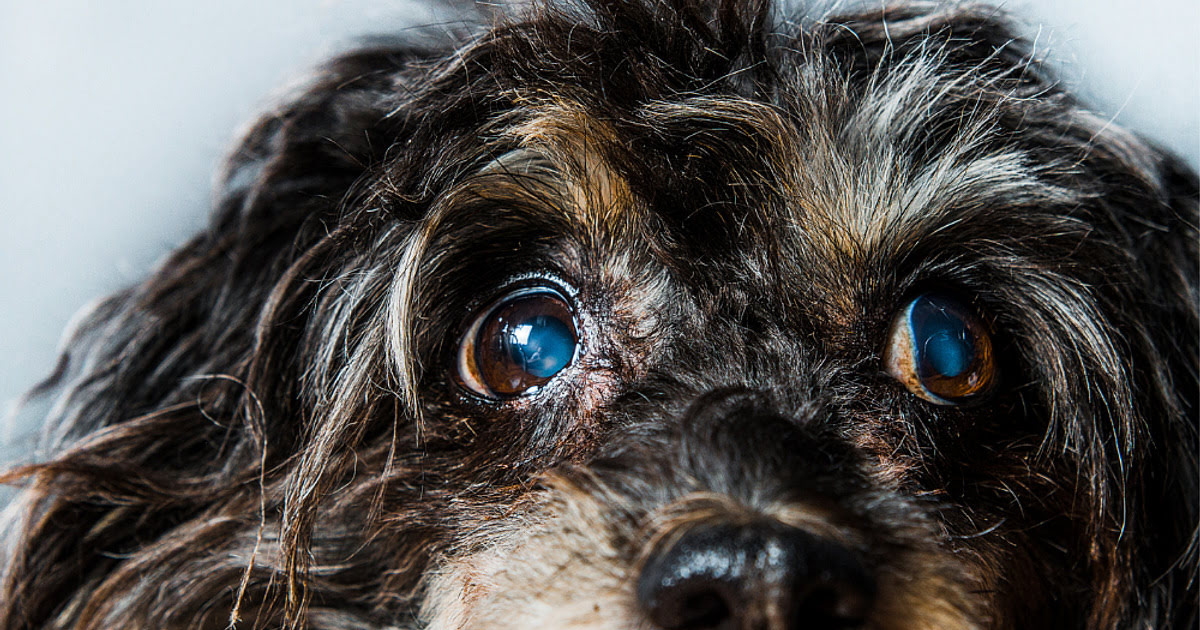


Eye and Ear Health
What Does A Dog’s Eye With Cataracts Look Like?
Published: February 11, 2024
Discover what a dog's eye with cataracts looks like and learn about eye and ear health. Find out how to recognize and address these issues.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Cataracts are a common eye condition that can affect dogs of all breeds and ages. Just like in humans, cataracts in dogs can cause a clouding of the eye's lens, leading to impaired vision and, in severe cases, blindness. As a pet owner, it's essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms of cataracts in dogs, as early detection and intervention can significantly impact the outcome for your furry companion.
Understanding the impact of cataracts on a dog's vision and overall well-being is crucial for providing the best possible care. In this article, we will delve into the world of canine cataracts, exploring the symptoms, effects on a dog's eyes, and available treatment options. By gaining a deeper understanding of this condition, you can be better equipped to recognize potential issues with your dog's eyes and take proactive steps to ensure their ocular health.
Cataracts can have a profound impact on a dog's quality of life, affecting their ability to navigate their surroundings, engage in play, and maintain their independence. By shedding light on this topic, we aim to empower pet owners with the knowledge and insight needed to advocate for their dog's eye health and seek appropriate veterinary care when necessary.
Throughout this article, we will provide valuable information on what cataracts look like in a dog's eye, how they manifest, and the available options for managing this condition. Whether you're a seasoned pet owner or a new puppy parent, understanding cataracts in dogs is an essential aspect of responsible pet care. Let's embark on this journey to uncover the nuances of cataracts in dogs and equip ourselves with the knowledge to support our canine companions through any ocular challenges they may face.
Read more: What Does A Dog’s Eye Look Like
Understanding Cataracts in Dogs
Cataracts in dogs are a prevalent ocular condition characterized by the clouding of the eye's lens, leading to impaired vision. This condition can affect dogs of all breeds and ages, and while it is more commonly associated with older canines, cataracts can also develop in younger dogs due to genetic predisposition, diabetes, or trauma to the eye.
The lens of the eye plays a crucial role in focusing light onto the retina, enabling clear vision. When cataracts form, the normally transparent lens becomes cloudy, obstructing the passage of light and causing visual disturbances for the affected dog. This clouding can range from minor opacity to complete coverage of the lens, resulting in varying degrees of vision impairment.
Understanding the underlying causes of cataracts in dogs is essential for pet owners and veterinary professionals alike. While age-related cataracts are common, other factors such as genetics, diabetes mellitus, ocular trauma, and nutritional deficiencies can also contribute to the development of cataracts in dogs. Genetic predisposition to cataracts is particularly prevalent in certain breeds, highlighting the importance of responsible breeding practices and genetic screening to minimize the incidence of hereditary cataracts.
As cataracts progress, they can significantly impact a dog's quality of life, hindering their ability to see clearly and navigate their environment with confidence. This can lead to behavioral changes, reluctance to engage in physical activities, and potential safety concerns for the affected dog. Therefore, recognizing the signs of cataracts and seeking timely veterinary evaluation is crucial for ensuring the well-being of our canine companions.
By gaining a deeper understanding of cataracts in dogs, pet owners can proactively monitor their dog's ocular health and seek professional guidance if any concerning symptoms arise. Through education and awareness, we can work towards promoting early detection, intervention, and appropriate management of cataracts in dogs, ultimately enhancing the overall ocular health and quality of life for our beloved canine friends.
Symptoms of Cataracts in Dogs
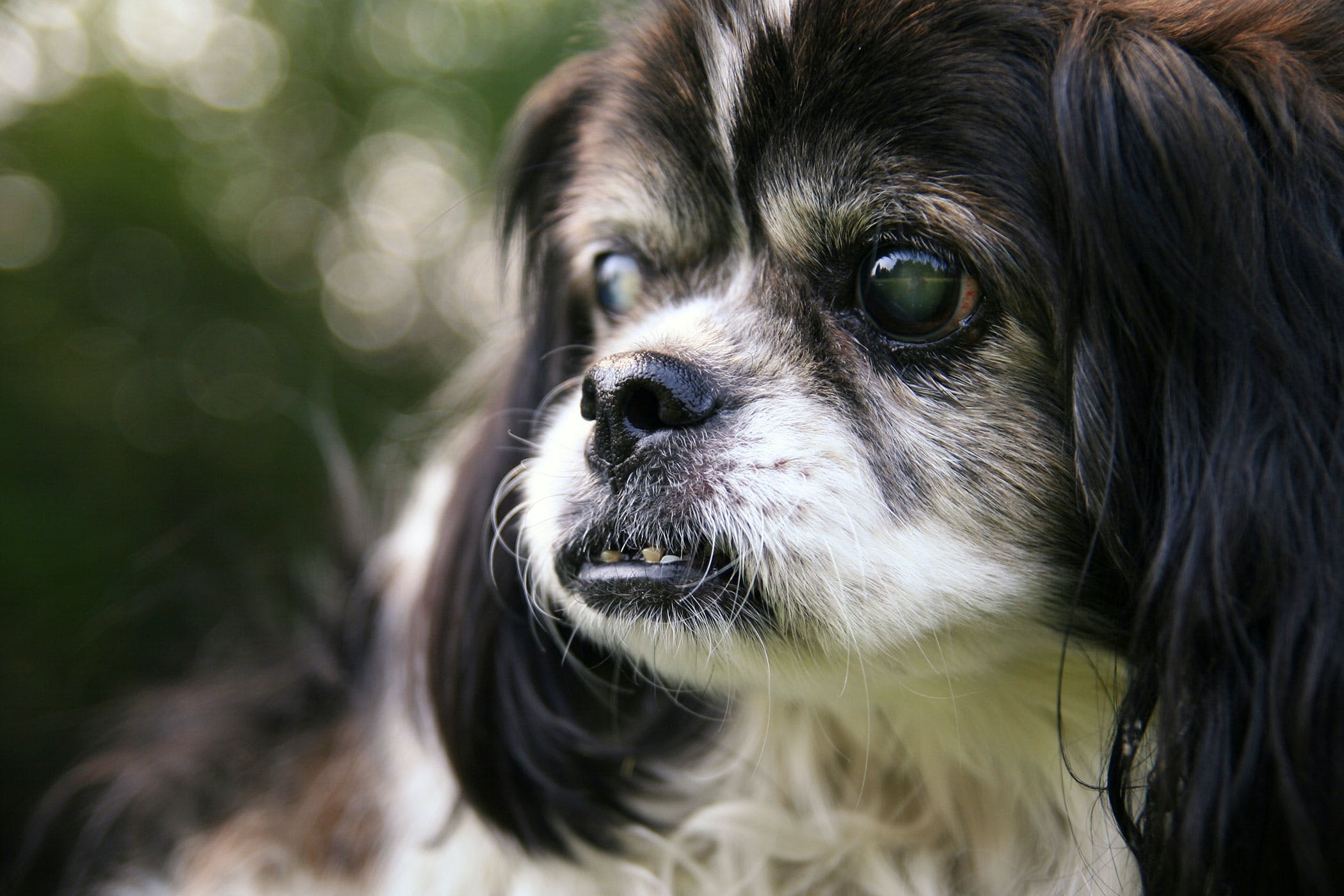
Identifying the symptoms of cataracts in dogs is crucial for early detection and intervention. While cataracts can manifest differently in each dog, there are several common signs that pet owners should be mindful of. One of the most noticeable symptoms is a change in the dog's eye appearance. As cataracts develop, the affected eye may appear cloudy or opaque, obscuring the natural clarity of the lens. This cloudiness can vary in intensity, ranging from subtle haziness to a more pronounced white or bluish discoloration within the eye.
In addition to changes in eye appearance, dogs with cataracts may exhibit alterations in their behavior and visual capabilities. Pet owners may observe their dog displaying signs of visual impairment, such as bumping into objects, hesitancy when navigating familiar spaces, or difficulty locating items. Dogs with cataracts may also demonstrate an increased sensitivity to light, leading to squinting or avoiding bright environments.
Furthermore, cataracts can impact a dog's overall demeanor and activity level. Pet owners may notice their dog becoming more hesitant to engage in activities that require visual acuity, such as playing fetch or navigating stairs. Additionally, dogs with cataracts may display changes in their interaction with their human companions, potentially becoming more reliant on auditory cues and physical touch due to compromised vision.
It's important to note that the progression of cataracts can vary, and early-stage cataracts may not always present obvious symptoms. Therefore, regular observation of your dog's behavior and eye health is essential for detecting any subtle changes that may indicate the presence of cataracts.
As responsible pet owners, being attuned to these potential symptoms and seeking prompt veterinary evaluation can make a significant difference in managing cataracts and preserving a dog's visual function. By recognizing the signs of cataracts and taking proactive measures, pet owners can advocate for their dog's ocular health and well-being, ultimately enhancing their quality of life.
Understanding the symptoms of cataracts in dogs empowers pet owners to be proactive in seeking professional guidance and appropriate care for their furry companions. By remaining vigilant and responsive to any changes in their dog's eye health and behavior, pet owners can play a pivotal role in supporting their dog through potential ocular challenges.
How Cataracts Affect a Dog's Eyes
Cataracts can have a profound impact on a dog's eyes, leading to significant changes in visual acuity and overall ocular health. As cataracts progress, the clouding of the eye's lens obstructs the passage of light, resulting in impaired vision for the affected dog. This impairment can manifest in various ways, influencing the dog's ability to perceive and interact with their environment.
The presence of cataracts can cause a noticeable reduction in a dog's visual clarity, leading to difficulties in discerning objects, people, or other animals. The clouded lens hinders the transmission of clear visual signals to the retina, resulting in blurred or distorted vision for the affected dog. This can impact their spatial awareness, making it challenging for them to navigate their surroundings with confidence.
Furthermore, cataracts can affect a dog's sensitivity to light, leading to increased discomfort in bright environments. Dogs with cataracts may exhibit signs of photophobia, such as squinting, pawing at their eyes, or avoiding well-lit areas. This heightened sensitivity to light can contribute to their overall visual discomfort and may lead to behavioral changes as they seek relief from the glare.
In addition to visual disturbances, cataracts can impact a dog's overall ocular health and well-being. The clouding of the lens can create an environment conducive to inflammation and secondary complications, potentially leading to discomfort, redness, and irritation in the affected eye. Moreover, the presence of cataracts may increase the risk of developing other ocular conditions, emphasizing the importance of proactive management and veterinary care.
As cataracts progress, they can significantly alter a dog's perception of the world, influencing their confidence, independence, and overall quality of life. The visual impairment caused by cataracts can lead to behavioral adjustments, as affected dogs may become more reliant on auditory and olfactory cues to compensate for their compromised vision.
Understanding how cataracts affect a dog's eyes is essential for pet owners, as it underscores the significance of early detection, intervention, and appropriate management. By recognizing the impact of cataracts on a dog's visual function and overall ocular health, pet owners can advocate for their furry companions and seek timely veterinary evaluation to address any potential concerns.
By gaining insight into the effects of cataracts on a dog's eyes, pet owners can take proactive measures to support their dog's ocular health and well-being, ultimately enhancing their quality of life and ensuring that they receive the care and attention they deserve.
What to Look for in a Dog's Eye with Cataracts
When observing a dog's eye for potential cataracts, several key indicators can provide valuable insights into the presence and progression of this ocular condition. Understanding what to look for in a dog's eye with cataracts empowers pet owners to be proactive in monitoring their canine companion's ocular health and seeking timely veterinary evaluation when necessary.
-
Cloudy or Opaque Appearance: One of the most prominent signs of cataracts in a dog's eye is the presence of cloudiness or opacity within the lens. This clouded appearance may vary in intensity, ranging from subtle haziness to a more pronounced white or bluish discoloration. Observing any deviation from the eye's natural clarity can prompt further investigation.
-
Changes in Visual Behavior: Dogs with cataracts may exhibit alterations in their visual behavior, such as bumping into objects, hesitancy when navigating familiar spaces, or difficulty locating items. Pet owners should pay attention to any shifts in their dog's visual acuity and confidence in their surroundings.
-
Increased Sensitivity to Light: Cataracts can lead to heightened sensitivity to light, resulting in behaviors such as squinting, pawing at the eyes, or avoiding well-lit areas. Observing how a dog responds to varying light conditions can offer valuable clues regarding their ocular comfort and potential visual disturbances.
-
Behavioral Changes: Dogs with cataracts may demonstrate changes in their overall demeanor and activity level. Pet owners should be attentive to any reluctance to engage in activities that require visual acuity, as well as alterations in their interaction with human companions, potentially indicating visual discomfort or impairment.
-
Regular Eye Examinations: Scheduling routine eye examinations for dogs, especially as they age, can aid in the early detection of cataracts and other ocular conditions. Veterinary professionals can conduct comprehensive assessments to evaluate a dog's eye health and identify any potential signs of cataracts.
By being mindful of these indicators and actively monitoring a dog's eye health, pet owners can play a pivotal role in advocating for their furry companion's ocular well-being. Early detection of cataracts allows for timely intervention and appropriate management, ultimately contributing to the preservation of a dog's visual function and overall quality of life.
Read more: What Does A Tick Scab Look Like On A Dog?
Treatment Options for Cataracts in Dogs
When it comes to addressing cataracts in dogs, pet owners may wonder about the available treatment options to support their furry companions' ocular health. While cataracts in dogs can pose significant challenges, there are several approaches to consider, each with its own considerations and potential benefits.
-
Surgical Intervention: In cases where cataracts significantly impair a dog's vision and quality of life, surgical removal of the affected lens, known as phacoemulsification, may be recommended. This procedure involves the delicate extraction of the clouded lens and its replacement with an artificial intraocular lens (IOL) to restore clear vision. Surgical intervention for cataracts in dogs requires specialized expertise and post-operative care to ensure optimal outcomes.
-
Medical Management: In instances where surgical intervention may not be feasible or immediately necessary, medical management focused on addressing underlying conditions contributing to cataract development, such as diabetes mellitus, can be a crucial aspect of treatment. Controlling systemic factors that contribute to cataract formation can help mitigate the progression of the condition and support overall ocular health.
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Support: Regardless of the chosen treatment approach, ongoing monitoring of a dog's ocular health is essential. Regular veterinary examinations, including comprehensive eye assessments, can aid in tracking the progression of cataracts and identifying any potential complications. Additionally, providing a supportive environment for a dog with cataracts, including minimizing environmental hazards and ensuring their comfort, is integral to their well-being.
-
Nutritional Support: Proper nutrition plays a vital role in supporting a dog's overall health, including their ocular function. Diets rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and essential nutrients can contribute to ocular health and may have a supportive role in managing cataracts. Consulting with a veterinarian to determine an appropriate diet tailored to a dog's specific needs is essential.
-
Holistic Care and Complementary Therapies: Complementary approaches, such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, and supportive therapies, may be considered as part of a holistic care plan for dogs with cataracts. While these modalities should be approached with caution and under the guidance of a qualified veterinary professional, they can potentially complement traditional treatment strategies and contribute to a dog's overall well-being.
Understanding the available treatment options for cataracts in dogs empowers pet owners to make informed decisions regarding their canine companion's ocular health. Each dog's unique circumstances, including their age, overall health, and the extent of cataract progression, should be carefully considered when determining the most suitable approach. By working closely with veterinary professionals and prioritizing the well-being of their furry companions, pet owners can navigate the complexities of managing cataracts in dogs and provide the support and care their dogs need to thrive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cataracts in dogs represent a significant ocular concern that can impact a dog's visual function, overall well-being, and quality of life. Understanding the nuances of this condition is essential for pet owners, as it empowers them to recognize potential signs of cataracts and take proactive measures to support their furry companions' ocular health.
By gaining insight into the symptoms and effects of cataracts on a dog's eyes, pet owners can play a pivotal role in advocating for their canine companions and seeking timely veterinary evaluation when necessary. The clouding of the eye's lens, changes in visual behavior, increased sensitivity to light, and potential behavioral adjustments serve as valuable indicators for pet owners to monitor when assessing their dog's ocular health.
Moreover, being aware of the available treatment options for cataracts in dogs allows pet owners to make informed decisions regarding their dog's care. From surgical intervention to medical management, ongoing monitoring, nutritional support, and holistic care, there are diverse approaches to consider, each tailored to a dog's unique circumstances and well-being.
Ultimately, the well-being of dogs with cataracts hinges on early detection, intervention, and ongoing support from veterinary professionals and pet owners alike. By fostering a collaborative relationship with veterinary experts and prioritizing the ocular health of their furry companions, pet owners can navigate the complexities of managing cataracts in dogs and provide the care and attention their dogs need to thrive.
As responsible pet owners, it is crucial to remain vigilant and responsive to any changes in a dog's eye health and behavior, seeking professional guidance at the earliest signs of concern. Through education, awareness, and proactive advocacy, pet owners can make a meaningful difference in supporting their dogs through potential ocular challenges, ultimately enhancing their quality of life and ensuring that they receive the care they deserve.
In essence, the journey of understanding cataracts in dogs is a testament to the unwavering bond between pet owners and their furry companions. By equipping ourselves with knowledge, compassion, and a commitment to proactive care, we can navigate the complexities of cataracts in dogs and provide the support and attention necessary to safeguard their ocular health and overall well-being.