Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>How To Get A Worm Out Of A Dog’s Eye

Eye and Ear Health
How To Get A Worm Out Of A Dog’s Eye
Published: February 12, 2024
Learn effective ways to remove a worm from your dog's eye and maintain their eye and ear health. Expert tips and guidance for pet owners.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Discovering a worm in your dog's eye can be a distressing experience for any pet owner. It's a situation that requires immediate attention and careful handling to ensure the well-being of your furry friend. While it may seem alarming, it's essential to approach the situation calmly and with a clear understanding of the necessary steps to address the issue effectively.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of dealing with a worm in a dog's eye, providing you with valuable insights on identifying the problem, safely removing the worm, and implementing preventive measures to safeguard your dog's ocular health. By gaining a deeper understanding of this issue, you'll be better equipped to handle such situations with confidence and ensure the optimal eye health of your beloved canine companion.
Understanding the nuances of this delicate matter is crucial, as it empowers you to take proactive measures to protect your dog's eyes from potential harm. With the right knowledge and approach, you can effectively address the presence of a worm in your dog's eye, minimize the risk of recurrence, and provide your pet with the care and attention they deserve.
Join us as we embark on this insightful journey, equipping you with the knowledge and expertise to navigate the challenge of dealing with a worm in your dog's eye. Let's delve into the intricacies of this issue and empower you to become a vigilant and proactive guardian of your dog's ocular health.
Read more: How To Get Sand Out Of Dog’s Eye
Understanding the problem
The presence of a worm in a dog's eye can pose significant health risks and discomfort for the affected canine. This issue typically arises due to the infestation of a parasitic worm, such as a roundworm or a filarial worm, in the ocular region. These worms can infiltrate the eye through various means, including contact with contaminated soil, ingestion of infected prey, or transmission by vectors such as mosquitoes.
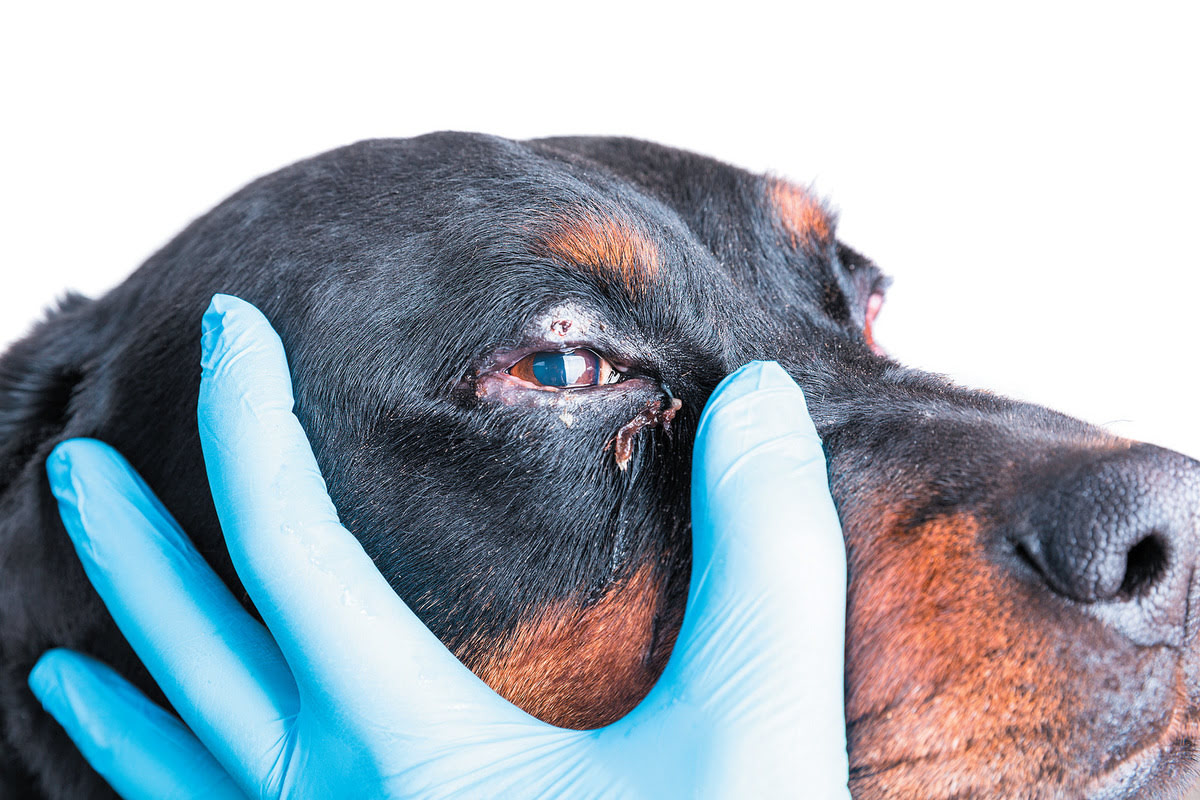
When a worm takes residence in a dog's eye, it can lead to a range of adverse effects, including irritation, inflammation, and potential damage to the ocular tissues. The presence of the worm may trigger excessive tearing, redness, and visible discomfort in the affected eye. Additionally, the dog may exhibit behaviors such as pawing at the eye, rubbing it against surfaces, or displaying signs of distress and agitation.
Understanding the problem entails recognizing the potential sources of worm infestation and comprehending the implications it can have on the dog's ocular health. It's crucial to acknowledge that the presence of a worm in the eye is not only a physical discomfort for the dog but also a concerning health issue that requires prompt and appropriate intervention.
By gaining a deeper understanding of the problem, pet owners can proactively monitor their dog's ocular health, minimize the risk of worm infestation, and swiftly address any signs of discomfort or abnormality in the eye. This proactive approach empowers pet owners to safeguard their dog's well-being and ensure that their ocular health remains uncompromised.
In the subsequent sections, we will explore the signs that indicate the presence of a worm in a dog's eye, the steps to safely remove the worm, preventive measures to mitigate the risk of infestation, and the importance of seeking veterinary assistance when necessary. By delving into these aspects, we aim to equip pet owners with the knowledge and guidance needed to navigate this challenging situation with confidence and competence.
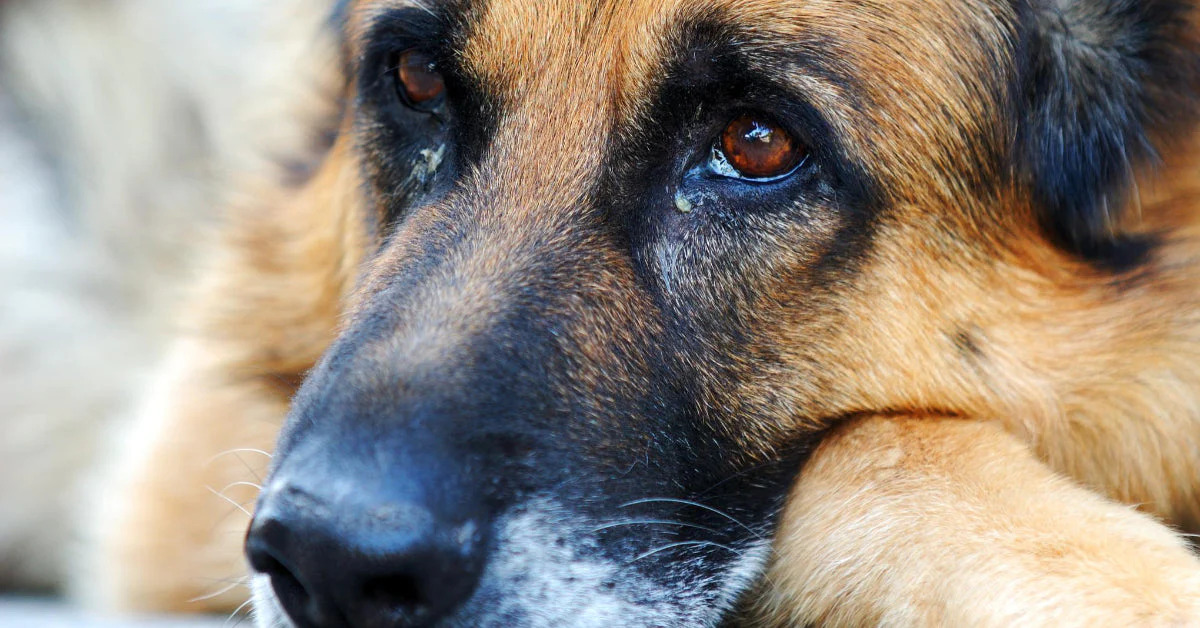
Signs of a worm in a dog's eye
Identifying the presence of a worm in a dog's eye requires keen observation and an understanding of the telltale signs that may manifest in the affected canine. These signs serve as crucial indicators of a potential ocular infestation, prompting pet owners to take swift and decisive action to address the issue. By recognizing these signs early on, pet owners can mitigate the impact of the infestation and provide timely intervention to alleviate the dog's discomfort and safeguard its ocular health.
-
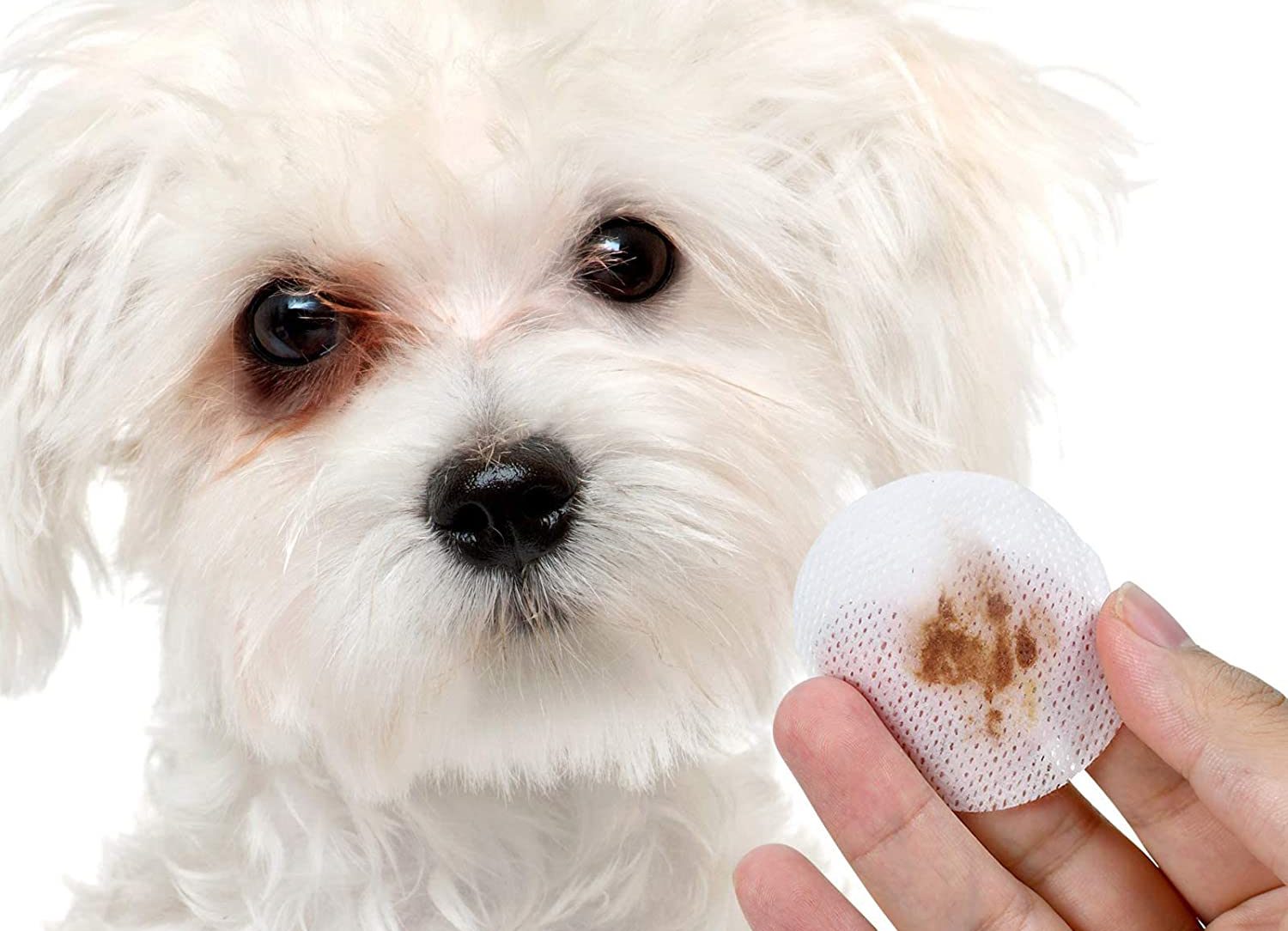
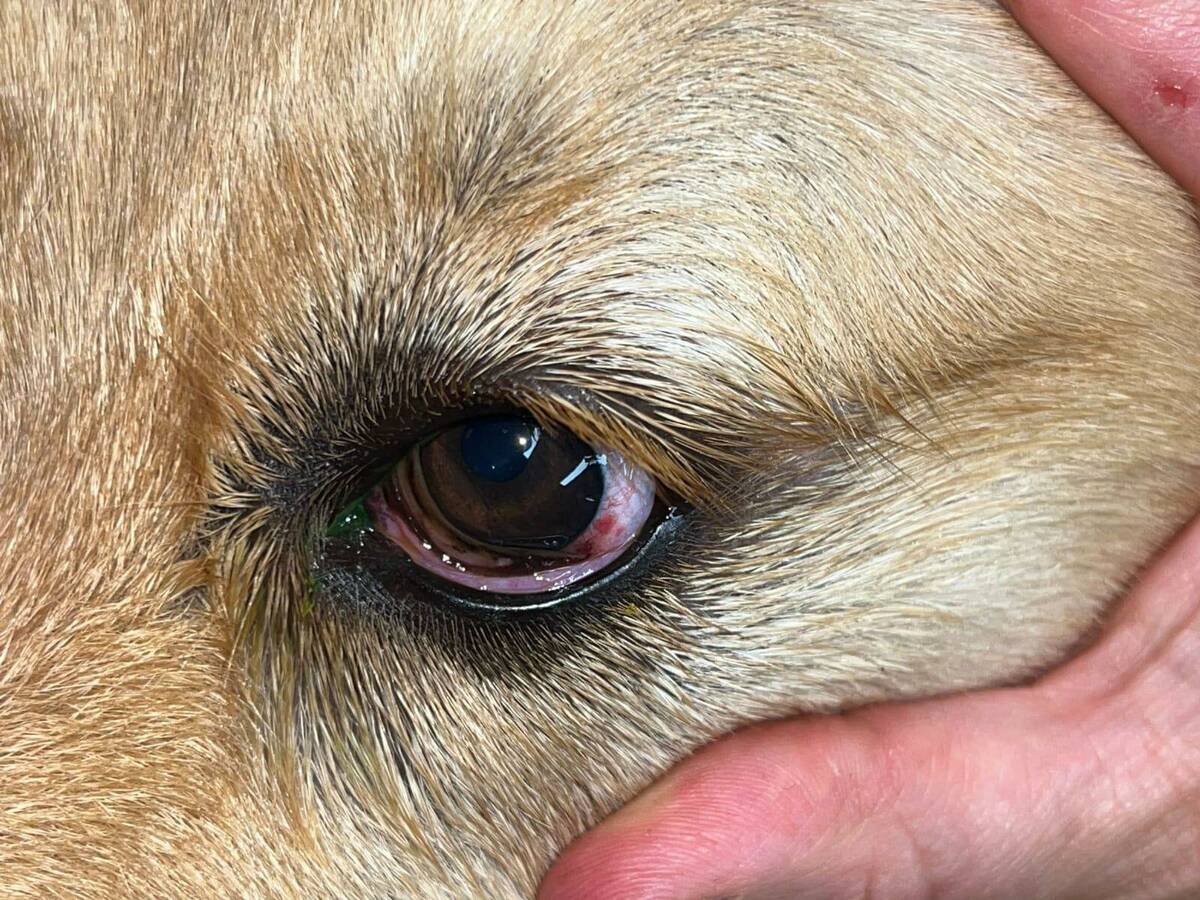
Excessive Tearing: One of the primary signs of a worm in a dog's eye is excessive tearing or ocular discharge. The affected eye may exhibit a noticeable increase in tear production, leading to damp fur around the eye and visible signs of moisture or discharge.
-
Redness and Irritation: The presence of a worm in the eye can trigger inflammation and irritation, causing the affected eye to appear red and potentially swollen. The dog may exhibit signs of discomfort, such as frequent blinking or squinting, indicative of the ocular distress caused by the infestation.
-
Rubbing or Pawing at the Eye: Dogs experiencing discomfort due to a worm in their eye may engage in behaviors such as rubbing the affected eye against surfaces or pawing at it in an attempt to alleviate the irritation. This persistent behavior serves as a clear indication of ocular discomfort and the need for intervention.
-
Visible Worm or Foreign Object: In some cases, the presence of a worm in the eye may be visibly apparent, especially if the infestation has progressed to a noticeable extent. Pet owners may observe the presence of a worm or a foreign object in the dog's eye, signaling the urgent need for intervention to address the infestation.
-
Sensitivity to Light: Dogs with a worm in their eye may display heightened sensitivity to light, leading them to avoid well-lit areas or exhibit signs of discomfort when exposed to bright light. This sensitivity serves as a notable indicator of ocular distress and the potential presence of a worm in the eye.
By remaining vigilant and attuned to these signs, pet owners can promptly identify the presence of a worm in their dog's eye and take the necessary steps to address the issue effectively. Swift recognition of these signs enables pet owners to provide their canine companions with the care and attention needed to alleviate discomfort, mitigate the impact of the infestation, and safeguard their ocular health.
Steps to safely remove a worm from a dog's eye
When faced with the presence of a worm in a dog's eye, it is crucial to approach the situation with care and precision to ensure the safe and effective removal of the parasite. The following steps outline a systematic approach to addressing this delicate issue, prioritizing the well-being and comfort of the affected canine.
-
Seek Veterinary Guidance: Before attempting to remove the worm from the dog's eye, it is advisable to seek professional veterinary guidance. A veterinarian can provide valuable insights and specific instructions tailored to the unique circumstances of the infestation. Their expertise ensures that the removal process is conducted with the utmost consideration for the dog's ocular health and overall well-being.
-
Restraint and Calming: Prior to the removal procedure, it is essential to restrain the dog gently to prevent excessive movement that may exacerbate the situation. Calming the dog through soothing verbal reassurance and gentle petting can help minimize stress and facilitate a more controlled environment for the removal process.
-
Irrigation and Lubrication: The affected eye should be irrigated with a sterile saline solution to flush out any debris or foreign particles surrounding the worm. This irrigation process serves to cleanse the eye and create a more favorable environment for the subsequent removal steps. Additionally, the application of a lubricating eye ointment can help ease the movement of the worm and reduce potential friction during the removal process.
-
Precise Extraction: Using specialized ophthalmic instruments under the guidance of a veterinarian, the worm is carefully extracted from the dog's eye with precision and delicacy. This step demands meticulous attention to detail and a steady hand to ensure the complete removal of the parasite without causing undue trauma to the ocular tissues.
-
Post-Removal Care: Following the successful extraction of the worm, the dog's eye is thoroughly examined to assess any potential damage or residual irritants. The application of a soothing eye wash or prescribed ophthalmic medication may be recommended to alleviate any lingering discomfort and promote the healing process.
-
Monitoring and Follow-Up: After the removal procedure, diligent monitoring of the dog's ocular health is essential to ensure that no complications arise. Any signs of persistent irritation, redness, or abnormal discharge should be promptly reported to the veterinarian for further evaluation and follow-up care.
By adhering to these systematic steps and prioritizing the expertise of a veterinary professional, pet owners can navigate the process of safely removing a worm from a dog's eye with diligence and care. This approach safeguards the dog's ocular health and minimizes the potential for complications, ultimately fostering a swift and effective resolution to the challenging situation.
Preventing worms in a dog's eye
Preventing worms in a dog's eye is a proactive endeavor that revolves around implementing strategic measures to minimize the risk of ocular infestations and safeguard the overall well-being of canine companions. By adopting a comprehensive approach to preventive care, pet owners can create a protective environment that mitigates the likelihood of worms infiltrating their dog's eyes. Here are essential strategies to prevent worms in a dog's eye:
Read more: How Do I Get A Hair Out Of My Dog’s Eye
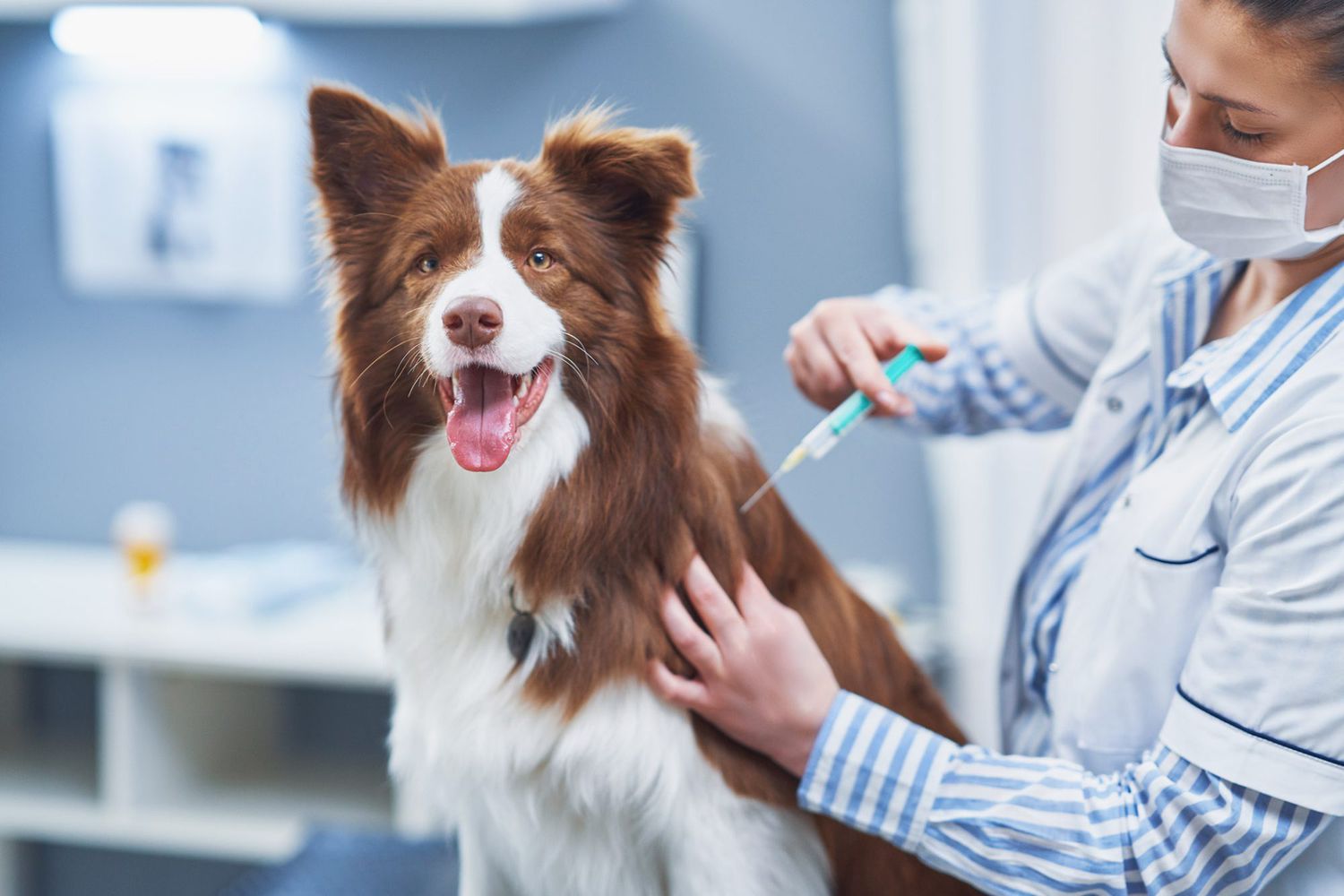
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Scheduling routine veterinary check-ups is a fundamental aspect of preventive care for a dog's ocular health. During these examinations, veterinarians can assess the dog's overall well-being, including ocular health, and provide guidance on preventive measures tailored to the specific needs of the canine. By maintaining regular veterinary visits, pet owners can stay informed about potential risk factors and receive professional recommendations to safeguard their dog's ocular health.
Parasite Control and Preventive Medication
Implementing a robust parasite control regimen, including the use of preventive medications prescribed by a veterinarian, is instrumental in minimizing the risk of ocular worm infestations. These medications, such as monthly heartworm preventives that also target other parasites, serve as a proactive defense against potential ocular parasites. By adhering to a veterinarian-recommended parasite control protocol, pet owners can effectively mitigate the risk of worms infiltrating their dog's eyes.
Environmental Management
Maintaining a clean and hygienic living environment for the dog plays a pivotal role in preventing ocular worm infestations. Regularly cleaning and sanitizing the dog's living spaces, including bedding, toys, and outdoor areas, helps minimize the presence of potential worm-carrying vectors. Additionally, exercising caution in areas known for high parasite prevalence, such as wooded or marshy regions, can reduce the dog's exposure to ocular parasites.
Preventative Measures Against Vectors
Taking proactive measures to protect the dog from common parasite-carrying vectors, such as mosquitoes and flies, is essential in preventing ocular worm infestations. Utilizing vet-approved insect repellents and ensuring the dog's living areas are equipped with protective barriers, such as screens and netting, can significantly reduce the risk of vector-borne ocular parasites. By minimizing the dog's exposure to these vectors, pet owners can fortify their preventive efforts against ocular worm infestations.
Read more: What Are The Worms Dogs Get From Fleas?
Ocular Hygiene and Care
Maintaining optimal ocular hygiene for the dog is paramount in preventing ocular worm infestations. Regularly cleaning the dog's eyes with veterinarian-recommended eye wash solutions helps remove potential irritants and minimizes the risk of ocular parasites gaining a foothold. Additionally, promptly addressing any signs of ocular discomfort or abnormality can prevent the progression of potential infestations, underscoring the importance of proactive ocular care.
By integrating these preventive strategies into their canine care routines, pet owners can fortify their dog's defenses against ocular worm infestations and cultivate a protective environment that prioritizes ocular health. This proactive approach empowers pet owners to take decisive measures to prevent ocular parasites, ensuring the well-being and comfort of their beloved canine companions.
When to seek veterinary help
Recognizing the appropriate circumstances that warrant veterinary intervention is crucial in ensuring the optimal ocular health of a dog facing a worm infestation. While pet owners can take proactive measures to address certain aspects of the issue, there are specific scenarios where seeking professional veterinary help is imperative.
-
Persistent Ocular Discomfort: If the dog continues to exhibit signs of ocular discomfort, such as excessive tearing, redness, or visible distress, despite initial home care measures, it is essential to seek veterinary assistance. Persistent discomfort may indicate underlying complications or the presence of residual irritants that require professional evaluation and targeted treatment.
-
Incomplete Worm Removal: In cases where the worm extraction process is incomplete or poses challenges due to the worm's location or the dog's reaction, veterinary assistance is warranted. Veterinarians possess the expertise and specialized equipment necessary to navigate complex removal scenarios, ensuring the thorough extraction of the worm without compromising the dog's ocular health.
-
Signs of Ocular Inflammation: If the affected eye displays persistent signs of inflammation, including swelling, discharge, or pronounced redness, veterinary evaluation is essential. Ocular inflammation may signify secondary complications or the presence of underlying infections that necessitate professional assessment and tailored therapeutic interventions.
-
Unexplained Behavioral Changes: Dogs experiencing ocular discomfort due to a worm infestation may exhibit unexplained behavioral changes, such as reluctance to engage in regular activities or heightened agitation. These behavioral shifts may indicate escalating discomfort or complications, prompting the need for veterinary evaluation to address the underlying issues effectively.
-
Recurrent Ocular Symptoms: In instances where ocular symptoms associated with the worm infestation recur or fail to resolve despite initial intervention, seeking veterinary help is paramount. Recurrent symptoms may signify unresolved issues or the presence of additional ocular parasites, necessitating professional assessment and targeted management strategies.
By remaining attentive to these indicators and promptly seeking veterinary assistance when warranted, pet owners can ensure that their dog receives timely and comprehensive care to address the complexities of a worm infestation in the eye. Veterinary expertise plays a pivotal role in navigating challenging scenarios, safeguarding the dog's ocular health, and fostering a swift resolution to the issue.