Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Many Fleas Does A Dog Have
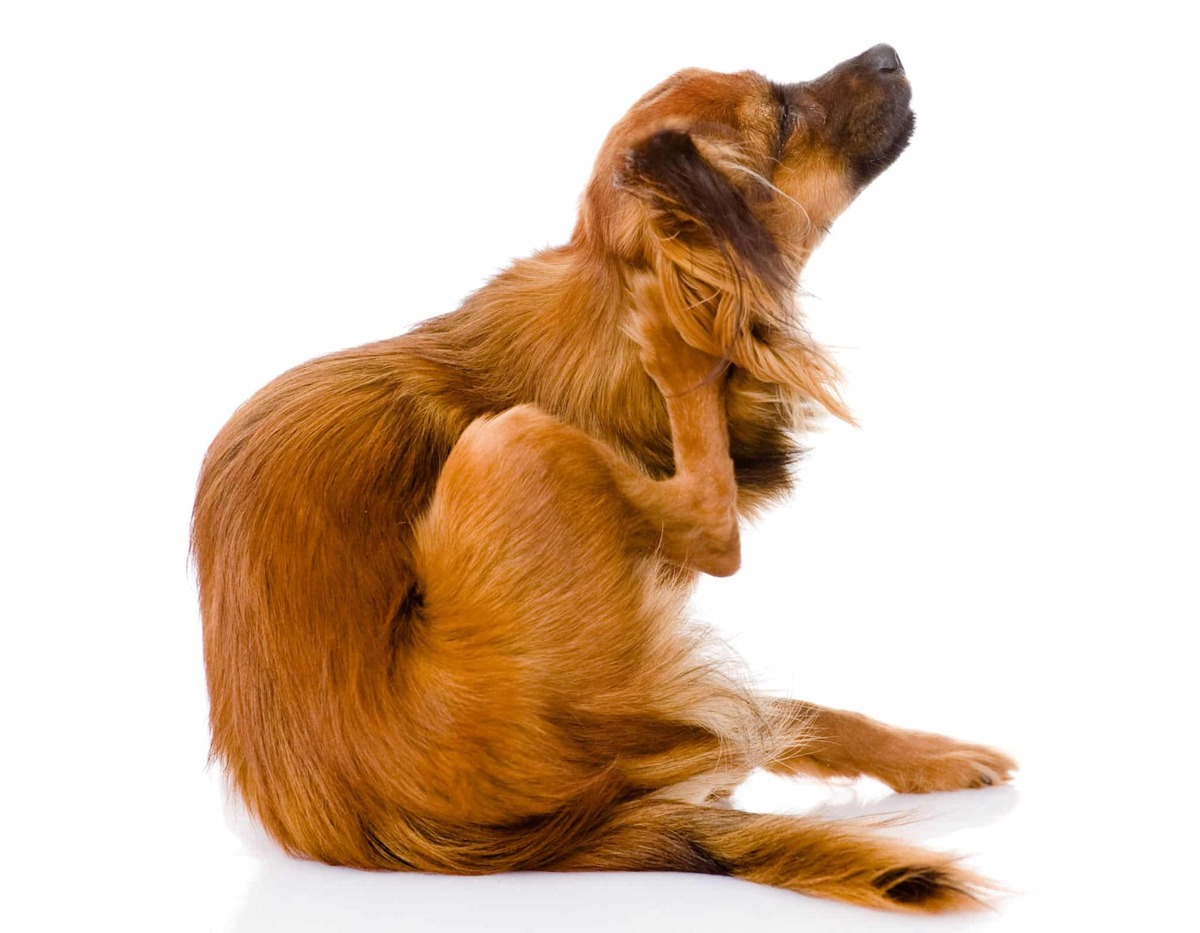


Common Health Issues
How Many Fleas Does A Dog Have
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs, including the number of fleas a dog can have. Understand the impact of fleas on your dog's health and how to prevent infestations.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Fleas are a common nuisance for dogs and their owners. These tiny, wingless parasites can cause a range of health issues for our furry friends, making it essential for pet owners to understand the impact of flea infestations and how to prevent and treat them effectively.
Flea infestations can lead to discomfort, itching, and skin irritation in dogs, often resulting in excessive scratching and potential hair loss. In severe cases, fleas can even transmit diseases and cause anemia, particularly in young or small dogs. Therefore, it's crucial for dog owners to be proactive in managing and preventing flea infestations to safeguard their pet's well-being.
Understanding the behavior and life cycle of fleas is key to addressing this issue effectively. By gaining insight into the factors that contribute to flea infestations and learning how to identify and treat them, dog owners can take proactive measures to protect their pets from the discomfort and health risks associated with fleas.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of fleas and their impact on dogs, exploring the factors that contribute to flea infestations, how to identify fleas on your dog, and the best practices for preventing and treating flea infestations. By the end of this article, you will have the knowledge and tools to ensure that your beloved canine companion remains free from the grasp of these pesky parasites.
Read more: How Many Dogs In The US Have Heartworm
Understanding Fleas and Their Impact on Dogs
Fleas are ectoparasites that belong to the order Siphonaptera, and they are a common nuisance for dogs. These tiny, wingless insects have specialized mouthparts that allow them to feed on the blood of their hosts, including dogs. Fleas are equipped with powerful hind legs that enable them to jump impressive distances, making it easy for them to move between hosts and infest new environments.
The impact of flea infestations on dogs can be significant. When fleas feed on a dog's blood, they can cause a range of health issues, including skin irritation, itching, and discomfort. Dogs suffering from flea infestations often exhibit symptoms such as excessive scratching, biting, and licking, which can lead to skin damage and hair loss. In severe cases, flea bites can trigger allergic reactions in dogs, resulting in dermatitis and further exacerbating their discomfort.
Beyond the immediate physical effects, fleas can also transmit diseases to dogs. One of the most concerning diseases spread by fleas is murine typhus, which can cause fever, headache, and muscle pain in dogs. Additionally, fleas can serve as intermediate hosts for tapeworms, leading to intestinal infestations in dogs. Furthermore, severe flea infestations can result in anemia, particularly in young or small dogs, due to the loss of blood from repeated flea bites.
Understanding the life cycle of fleas is crucial in addressing infestations effectively. Fleas undergo complete metamorphosis, progressing through egg, larval, pupal, and adult stages. The entire life cycle can take as little as two to three weeks under optimal conditions, allowing flea populations to multiply rapidly. This rapid reproduction contributes to the resilience of flea infestations, making it essential for dog owners to take proactive measures to prevent and treat these parasites.
In summary, fleas pose a significant threat to the well-being of dogs, causing discomfort, skin irritation, and potential health complications. By gaining a deeper understanding of the impact of flea infestations on dogs and the behavior of these parasites, dog owners can take proactive steps to protect their pets from the adverse effects of flea infestations.
Factors Affecting Flea Infestation in Dogs
Several factors contribute to the likelihood and severity of flea infestations in dogs. Understanding these factors is crucial for implementing effective prevention and treatment strategies. Here are the key elements that influence flea infestations in dogs:
Environmental Conditions
The environment plays a significant role in the prevalence of fleas. Fleas thrive in warm, humid conditions, making certain geographic locations more prone to infestations. Additionally, indoor environments with central heating or warm climates can create ideal conditions for fleas to breed and survive. Areas with dense vegetation, such as gardens and parks, can also harbor fleas, increasing the risk of infestation for dogs that frequent these spaces.
Seasonal Variation
Flea infestations often peak during warmer months, as the conducive environmental conditions support rapid flea reproduction. Spring and summer provide the ideal combination of warmth and humidity for fleas to thrive, leading to heightened infestation risks for dogs during these seasons. However, in regions with milder climates, fleas can pose a year-round threat, necessitating consistent preventive measures.
Read more: How Many Dogs Have Arthritis
Pet Lifestyle and Behavior
The lifestyle and behavior of dogs can influence their susceptibility to flea infestations. Dogs that spend significant time outdoors, especially in areas with dense vegetation or wildlife, are at a higher risk of encountering fleas. Additionally, interactions with other animals, such as stray dogs or wildlife, can increase the likelihood of flea transmission. Dogs that frequent communal spaces, such as dog parks or pet-friendly areas, may also face elevated exposure to fleas.
Hygiene and Grooming Practices
Maintaining proper hygiene and grooming practices for dogs is essential in preventing flea infestations. Regular bathing and grooming help to remove adult fleas and their eggs, reducing the likelihood of infestation. Dogs with long or dense coats may be more susceptible to flea infestations, as fleas can easily conceal themselves within the fur. Furthermore, neglecting to clean and vacuum indoor spaces can contribute to the persistence of flea eggs and larvae, perpetuating infestation risks.
Preexisting Infestations
If a dog has been previously exposed to fleas or resides in an environment with a history of infestations, the risk of recurring flea problems is heightened. Flea eggs and pupae can remain dormant in the environment for extended periods, reemerging as adult fleas when conditions are favorable. Therefore, addressing preexisting infestations and implementing ongoing preventive measures is crucial for breaking the cycle of infestation.
By considering these factors, dog owners can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of flea infestations and tailor their preventive efforts accordingly. Proactive management of environmental conditions, seasonal variations, pet lifestyle, hygiene practices, and preexisting infestations can significantly reduce the risk of flea infestations in dogs, promoting their overall well-being and comfort.
How to Identify Fleas on Your Dog
Identifying fleas on your dog is crucial for prompt intervention and effective flea control. While fleas are small and agile, making them adept at evading detection, there are several key indicators that can help dog owners identify the presence of these pesky parasites.
Read more: How Many Calories Does A Senior Dog Need
1. Scratching and Irritation
One of the most common signs of flea infestation in dogs is excessive scratching, biting, or licking. If your dog displays persistent itching, particularly around the base of the tail, abdomen, or hindquarters, it may indicate the presence of fleas. Additionally, visible signs of skin irritation, such as redness, inflammation, or small bumps, can signal flea bites.
2. Flea Dirt and Eggs
Flea dirt, which appears as tiny black specks resembling ground pepper, is a telltale sign of flea infestation. This excrement consists of digested blood excreted by fleas and is often found on the dog's skin, fur, or bedding. Furthermore, the presence of flea eggs, which are small, white ovals, can indicate an active infestation.
3. Visible Fleas
While adult fleas are adept at evading detection, careful observation may reveal their presence. Inspect your dog's fur, particularly in areas where fleas tend to congregate, such as the neck, back, and tail. Adult fleas are small, dark brown insects with flattened bodies, and they may be visible to the naked eye, especially when the fur is parted.
4. Allergic Reactions
Some dogs may exhibit allergic reactions to flea saliva, leading to a condition known as flea allergy dermatitis (FAD). Symptoms of FAD include intense itching, hair loss, and inflamed skin, often concentrated in the lower back, tail base, and hind legs. Identifying these allergic reactions can indicate the presence of fleas and the need for immediate intervention.
Read more: Why Does My Dog Have Fleas After Treatment?
5. Behavioral Changes
Flea infestations can cause discomfort and distress in dogs, leading to changes in behavior. If your dog appears restless, agitated, or exhibits unusual grooming habits, it may be a sign of flea-related discomfort. Additionally, dogs with severe flea infestations may become lethargic or exhibit signs of discomfort during physical activities.
By remaining vigilant and attentive to these indicators, dog owners can effectively identify fleas on their pets and take proactive measures to address infestations. Early detection enables prompt intervention, reducing the impact of flea infestations on dogs and promoting their overall well-being.
Preventing and Treating Flea Infestations in Dogs
Preventing and treating flea infestations in dogs is essential for maintaining their health and well-being. By implementing proactive measures and utilizing effective treatment options, dog owners can safeguard their pets from the discomfort and health risks associated with fleas.
Prevention Strategies
-
Regular Grooming: Establish a routine grooming schedule for your dog, including regular baths and thorough combing or brushing to remove adult fleas and their eggs. Pay special attention to areas where fleas tend to congregate, such as the neck and base of the tail.
-
Environmental Management: Keep indoor and outdoor environments clean and well-maintained. Regularly vacuuming carpets, upholstery, and pet bedding can help eliminate flea eggs and larvae. Additionally, outdoor areas frequented by dogs should be kept free of debris and maintained to reduce flea habitats.
-
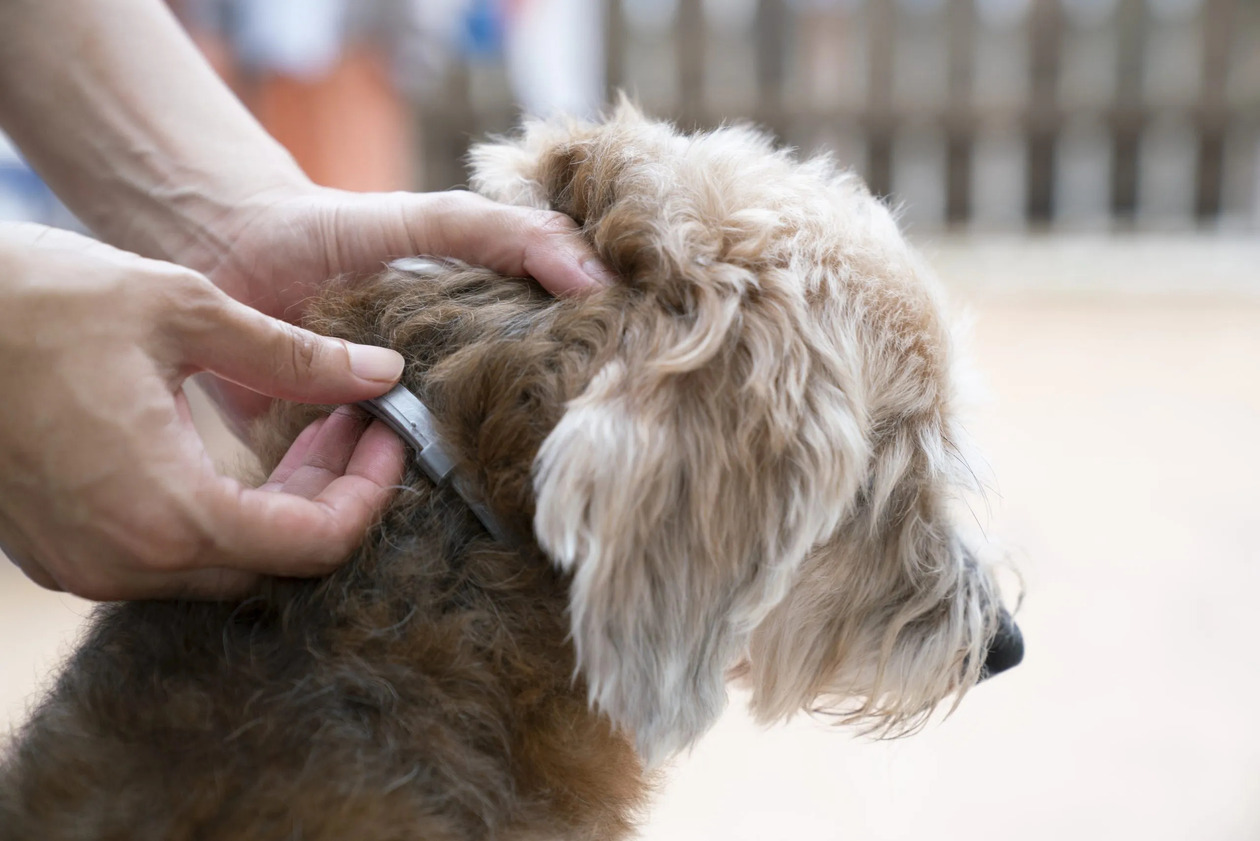
Use of Preventive Products: Consult with your veterinarian to select and administer appropriate flea preventive products for your dog. Options may include topical treatments, oral medications, or flea collars designed to repel and kill fleas. Consistent use of these products can provide long-term protection against infestations.
-
Regular Veterinary Check-ups: Schedule regular veterinary examinations for your dog to monitor their overall health and detect early signs of flea infestations. Veterinarians can provide guidance on preventive measures and recommend suitable flea control products based on your dog's specific needs.
Treatment Approaches
-
Topical Treatments: Topical flea treatments, applied directly to the dog's skin, are effective in killing adult fleas and preventing reinfestation. These treatments often provide long-lasting protection and may also target other parasites, such as ticks.
-
Oral Medications: Oral flea medications, available in chewable or tablet forms, offer systemic protection by targeting fleas throughout the dog's body. These medications can kill adult fleas and disrupt their life cycle, preventing the development of new fleas.
-
Flea Collars: Flea collars release active ingredients that repel and kill fleas, providing continuous protection for dogs. When selecting a flea collar, ensure that it is designed to effectively control fleas without causing discomfort or skin irritation for your dog.
-
Environmental Treatments: In cases of severe infestations, environmental treatments may be necessary to eliminate flea populations in the dog's living spaces. This may involve the use of insecticidal sprays, foggers, or professional pest control services to eradicate fleas from indoor environments.
-
Comprehensive Approach: Combining preventive measures with targeted treatments can enhance the effectiveness of flea control. By addressing both the dog and its environment, dog owners can achieve comprehensive flea management and reduce the risk of reinfestation.
By integrating these preventive and treatment strategies, dog owners can effectively protect their pets from flea infestations and ensure their continued comfort and well-being. Consistent vigilance and proactive management are key to mitigating the impact of fleas on dogs and fostering a healthy living environment for our beloved canine companions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, flea infestations pose significant challenges for dogs and their owners, impacting the pets' comfort, health, and overall well-being. Understanding the behavior of fleas, the factors contributing to infestations, and the methods for identifying and addressing these parasites is crucial for effective flea control.
By gaining insight into the impact of flea infestations on dogs, it becomes evident that these tiny parasites can cause a range of health issues, from skin irritation and itching to the transmission of diseases and potential anemia. The rapid life cycle of fleas, coupled with their resilience in various environments, underscores the importance of proactive flea management.
Factors such as environmental conditions, seasonal variations, pet lifestyle, hygiene practices, and preexisting infestations play pivotal roles in influencing the likelihood and severity of flea infestations in dogs. By considering these factors, dog owners can tailor their preventive efforts to mitigate the risk of infestations and create a healthier living environment for their pets.
Identifying fleas on dogs requires vigilance and attentiveness to key indicators, including scratching, flea dirt and eggs, visible fleas, allergic reactions, and behavioral changes. Early detection enables prompt intervention, reducing the impact of flea infestations and promoting the well-being of dogs.
Preventing and treating flea infestations involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing regular grooming, environmental management, the use of preventive products, and veterinary guidance. Additionally, treatment options such as topical treatments, oral medications, flea collars, and environmental treatments offer effective means of addressing existing infestations and preventing reoccurrences.
By integrating these strategies, dog owners can create a comprehensive flea management plan that safeguards their pets from the discomfort and health risks associated with fleas. Consistent vigilance and proactive management are essential for mitigating the impact of fleas on dogs and fostering a healthy living environment for our beloved canine companions.
In essence, by understanding the dynamics of flea infestations and implementing proactive measures, dog owners can ensure that their pets remain free from the grasp of these pesky parasites, allowing them to thrive in a comfortable and flea-free environment.