Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Where Do Fleas Like To Be On Dogs


Common Health Issues
Where Do Fleas Like To Be On Dogs
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about common health issues for dogs, including where fleas like to be on dogs. Discover how to keep your furry friend healthy and happy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Fleas are a common nuisance for dogs and their owners. These tiny, blood-sucking parasites can cause discomfort and health issues for our furry friends. Understanding where fleas like to be on dogs and how to prevent and treat infestations is crucial for maintaining our pets' well-being.
Fleas are not just a seasonal problem; they can thrive in warm, humid environments and can infest dogs at any time of the year. These pesky insects can quickly multiply and spread, making it essential for dog owners to be proactive in preventing and addressing flea infestations.
In this article, we will delve into the world of fleas and explore where they like to reside on dogs. We will also discuss the signs of flea infestations, preventive measures, and effective treatments to keep our canine companions free from these bothersome pests. Understanding the behavior of fleas and their impact on dogs is the first step in ensuring the health and happiness of our beloved pets.
Read more: What Do Ticks And Fleas Look Like On Dogs
Understanding Fleas
Fleas are small, wingless insects that belong to the order Siphonaptera. These pesky parasites are notorious for their ability to infest dogs and cause a range of health issues. The most common type of flea that affects dogs is the Ctenocephalides felis, also known as the cat flea, which can infest both cats and dogs.
Fleas have a remarkable ability to jump, thanks to their powerful hind legs. In fact, they can jump up to 150 times their own body length, allowing them to easily move between hosts and within the environment. These agile insects are equipped with specialized mouthparts that are adapted for piercing the skin and sucking blood. When fleas bite dogs to feed on their blood, it can lead to irritation, itching, and discomfort for the affected animals.
Fleas undergo a complete metamorphosis, progressing through four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. Understanding these stages is crucial for effectively combating flea infestations. Flea eggs are typically laid on the host animal but can also fall off onto bedding, carpets, and other areas where the dog spends time. Once the eggs hatch, they give rise to larvae that feed on organic debris and flea feces in the environment. The larvae then spin cocoons and enter the pupal stage, where they develop into adult fleas. This entire life cycle can occur in as little as two to three weeks under ideal conditions, allowing flea populations to rapidly multiply.
Fleas thrive in warm, humid environments, making them particularly prevalent during the spring and summer months. However, they can also survive indoors during the winter, especially in centrally heated homes. Understanding the environmental conditions that favor flea development is essential for implementing effective preventive measures.
In addition to causing discomfort for dogs, fleas can transmit diseases and parasites, such as tapeworms, to their hosts. This further underscores the importance of preventing and treating flea infestations to safeguard the health of dogs.
By gaining a deeper understanding of the behavior and life cycle of fleas, dog owners can take proactive steps to protect their pets from these persistent pests. From regular grooming and environmental management to the use of preventive medications, there are various strategies for combating fleas and ensuring the well-being of canine companions.
Where Do Fleas Like to Be on Dogs
Fleas are opportunistic parasites that seek out warm-blooded hosts, such as dogs, for their blood meals. When it comes to infesting dogs, fleas tend to congregate in specific areas on the canine's body. Understanding these preferred locations is crucial for detecting and addressing flea infestations effectively.
-
Around the Neck and Head: Fleas often target the neck and head areas of dogs. These regions provide easy access to the dog's blood supply and offer warmth and protection for the fleas. The fur around the neck and head provides an ideal environment for fleas to hide and reproduce, making regular inspection and preventive measures essential.
-
Along the Back and Tail: The back and tail are common hotspots for flea infestations. Dogs with thick or long fur may provide ample hiding places for fleas along their backs and at the base of their tails. Fleas can easily maneuver through the fur, making it challenging to detect their presence without close examination.
-
Under the Legs and Around the Groin: Fleas may also gravitate toward the areas under the dog's legs and around the groin. These regions offer a warm and sheltered environment, making them attractive to fleas seeking a blood meal. Dogs may exhibit increased scratching and discomfort in these areas when infested with fleas.
-
Between the Toes and Paw Pads: Fleas can hide between a dog's toes and paw pads, especially in breeds with long hair or furry feet. These areas provide protection and warmth for the fleas while remaining relatively inconspicuous. Checking between the toes and paw pads is crucial for detecting and addressing flea infestations in dogs.
-
Under the Tail: The underside of a dog's tail can also be a favored location for fleas. Dogs may exhibit signs of discomfort, such as excessive licking or biting at the base of their tails, when fleas are present in this area.
Understanding where fleas like to be on dogs enables pet owners to conduct thorough inspections and take targeted preventive measures. Regular grooming, including combing and inspecting these specific areas, can aid in early detection and prompt action against flea infestations. Additionally, using veterinarian-recommended flea prevention products and maintaining a clean living environment can help minimize the risk of fleas infesting dogs.
By being vigilant and proactive, dog owners can effectively protect their furry companions from the discomfort and health risks associated with flea infestations.
Signs of Fleas on Dogs
Detecting the presence of fleas on dogs is crucial for timely intervention and effective flea control. Understanding the signs of flea infestations can help pet owners identify and address the problem before it escalates. Here are the common signs that indicate the presence of fleas on dogs:
-
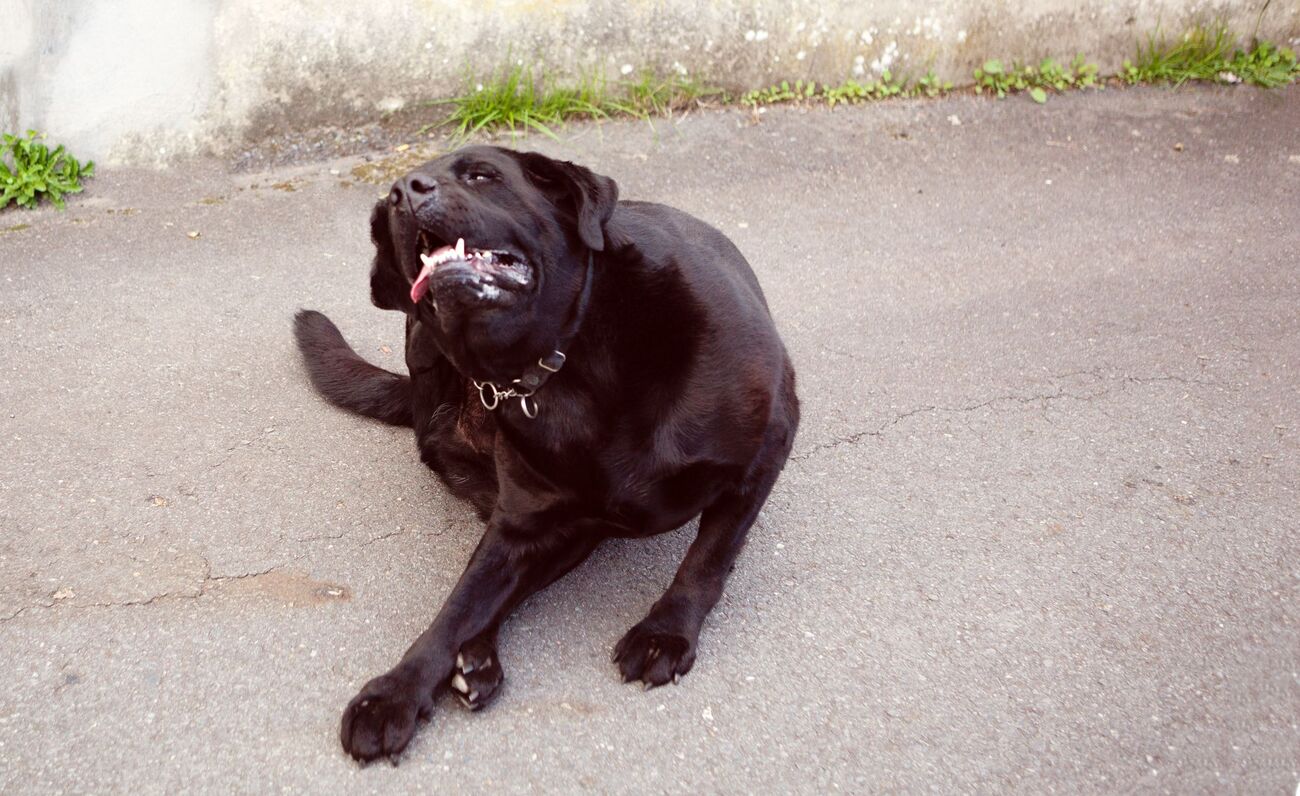
Excessive Scratching and Biting: Dogs infested with fleas often exhibit increased scratching and biting, particularly in areas where fleas tend to congregate. Persistent scratching, biting, or licking, especially around the neck, head, and base of the tail, may indicate the presence of fleas.
-
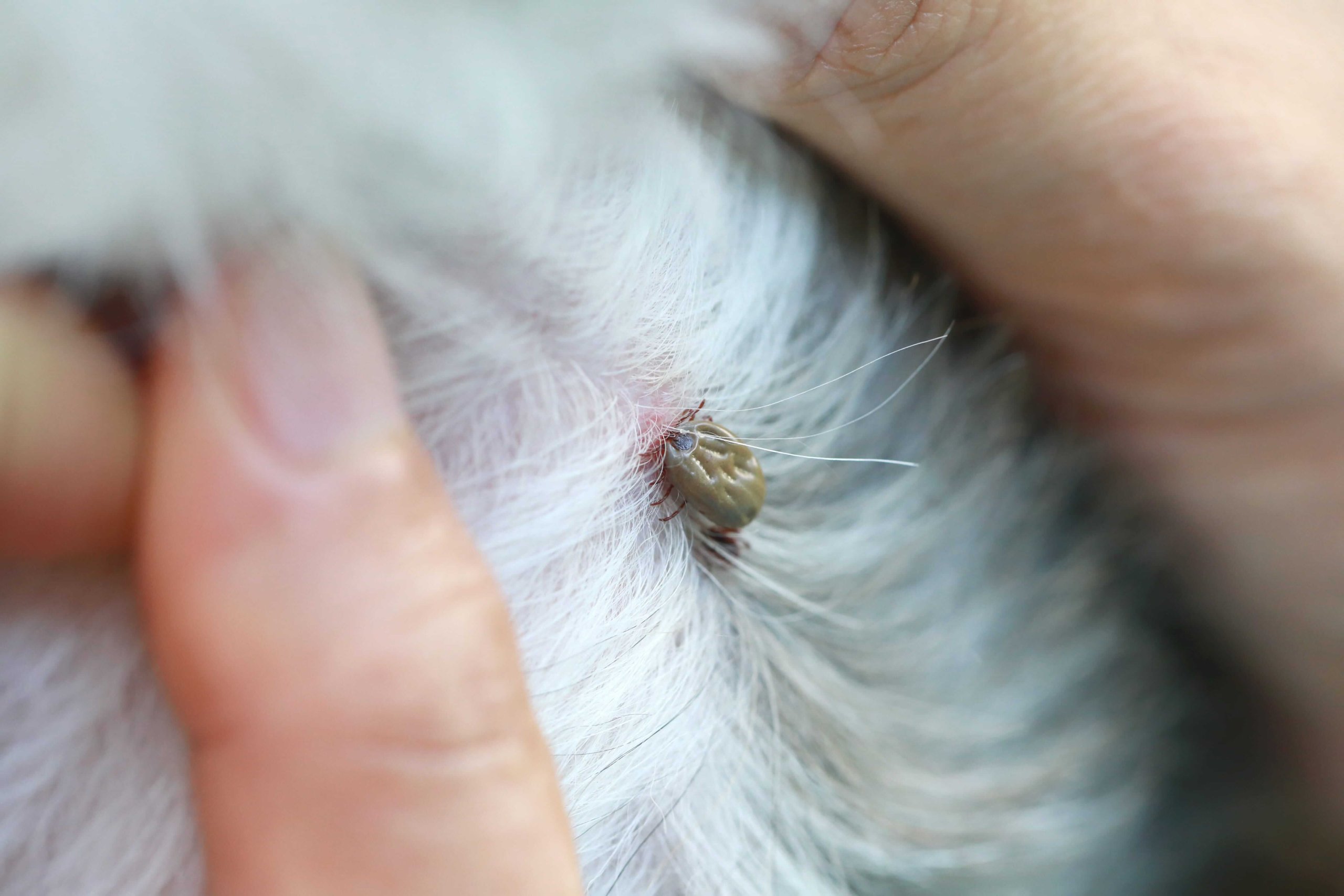
Visible Fleas or Flea Dirt: Flea dirt, which appears as small black specks resembling ground pepper, may be noticeable on the dog's skin and fur. This is actually flea feces and is a telltale sign of flea infestation. Additionally, in severe cases, live fleas may be visible on the dog's coat, especially when parting the fur and inspecting closely.
-
Hair Loss and Skin Irritation: Flea bites can cause allergic reactions in some dogs, leading to hair loss, redness, and skin irritation. Dogs may develop hot spots, also known as acute moist dermatitis, as a result of flea bites, leading to further discomfort and skin inflammation.
-
Restlessness and Agitation: Infested dogs may display signs of restlessness, agitation, and general discomfort. They may exhibit unusual behavior, such as pacing, restlessly shifting positions, or struggling to find relief from the itching and irritation caused by flea bites.
-
Pale Gums and Anemia: In severe cases of flea infestations, dogs may experience blood loss due to persistent flea feeding. This can lead to anemia, characterized by symptoms such as pale gums, weakness, and lethargy. Anemic dogs may appear fatigued and exhibit reduced energy levels.
-
Visible Skin Lesions: Flea bites can result in visible skin lesions, including small red bumps or scabs, particularly in areas where fleas have fed. These lesions may be accompanied by secondary bacterial infections, further exacerbating the dog's discomfort and skin issues.
-
Allergic Dermatitis: Some dogs may develop flea allergy dermatitis, an allergic reaction to flea saliva. This condition can cause intense itching, hair loss, and inflamed skin, leading to significant discomfort and distress for affected dogs.
By recognizing these signs of flea infestations, dog owners can take prompt action to address the problem and provide relief for their pets. Implementing thorough flea control measures, including regular grooming, environmental management, and the use of veterinarian-recommended flea prevention products, is essential for safeguarding the well-being of dogs and preventing the adverse effects of flea infestations.
Preventing Fleas on Dogs
Preventing fleas on dogs is a proactive approach that involves implementing various strategies to minimize the risk of flea infestations and safeguard the well-being of our canine companions. By taking preventive measures, dog owners can create an environment that is less hospitable to fleas, reducing the likelihood of infestations and the associated discomfort for their pets.
Read more: Where Do Dogs Get Ticks?
Regular Grooming and Inspection
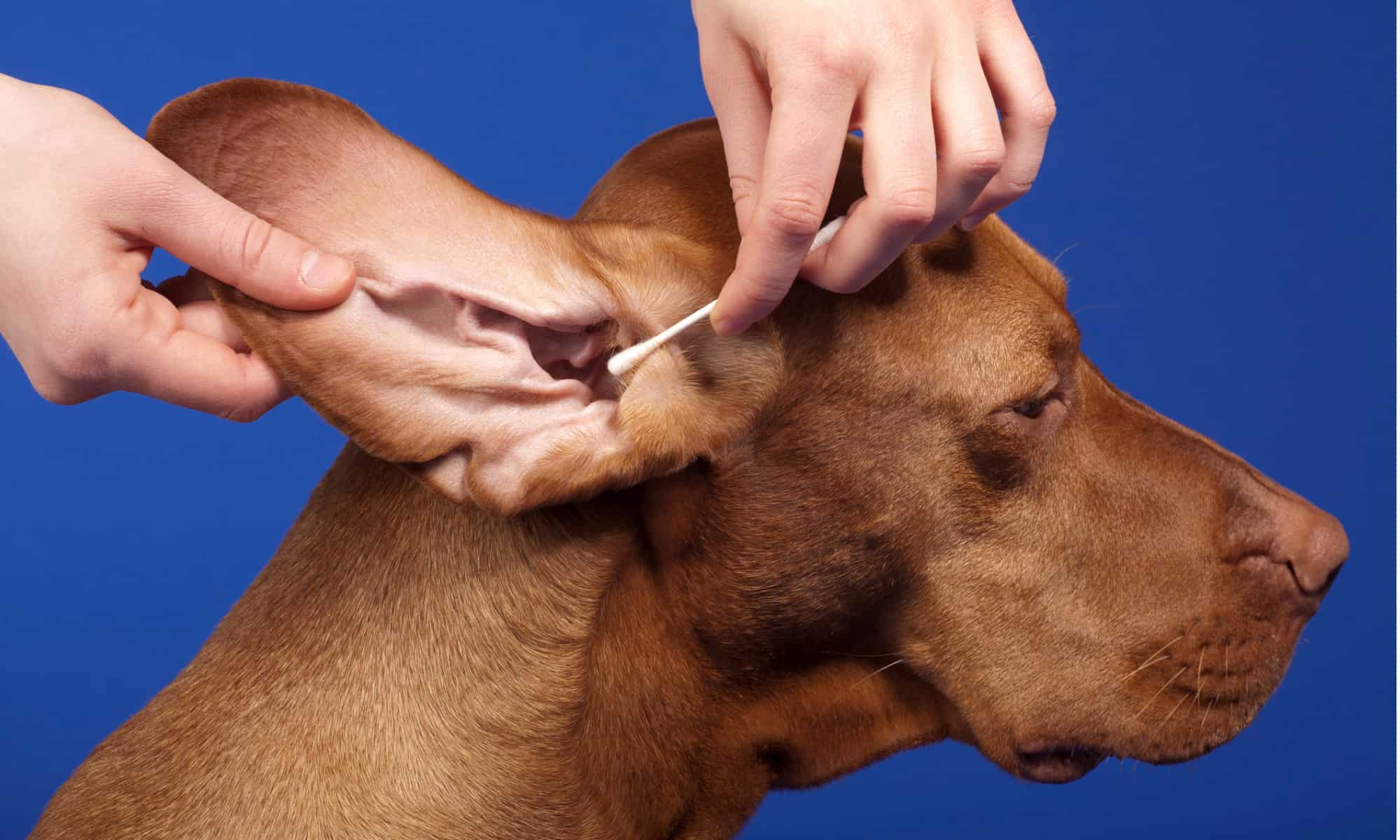
Regular grooming plays a pivotal role in preventing fleas on dogs. Thoroughly combing the dog's coat with a fine-toothed flea comb can help detect the presence of fleas and flea dirt. Additionally, inspecting specific areas where fleas tend to congregate, such as around the neck, head, and base of the tail, enables early detection and intervention. Keeping the dog's coat clean and well-maintained can also discourage flea infestations.
Environmental Management
Maintaining a clean living environment is essential for preventing fleas on dogs. Regular vacuuming of carpets, rugs, and upholstered furniture can help remove flea eggs, larvae, and pupae from the environment. Washing the dog's bedding and frequently cleaning areas where the dog spends time, such as pet crates and resting areas, can also contribute to flea prevention. Additionally, outdoor areas frequented by the dog should be kept tidy to minimize flea habitats.
Use of Preventive Medications
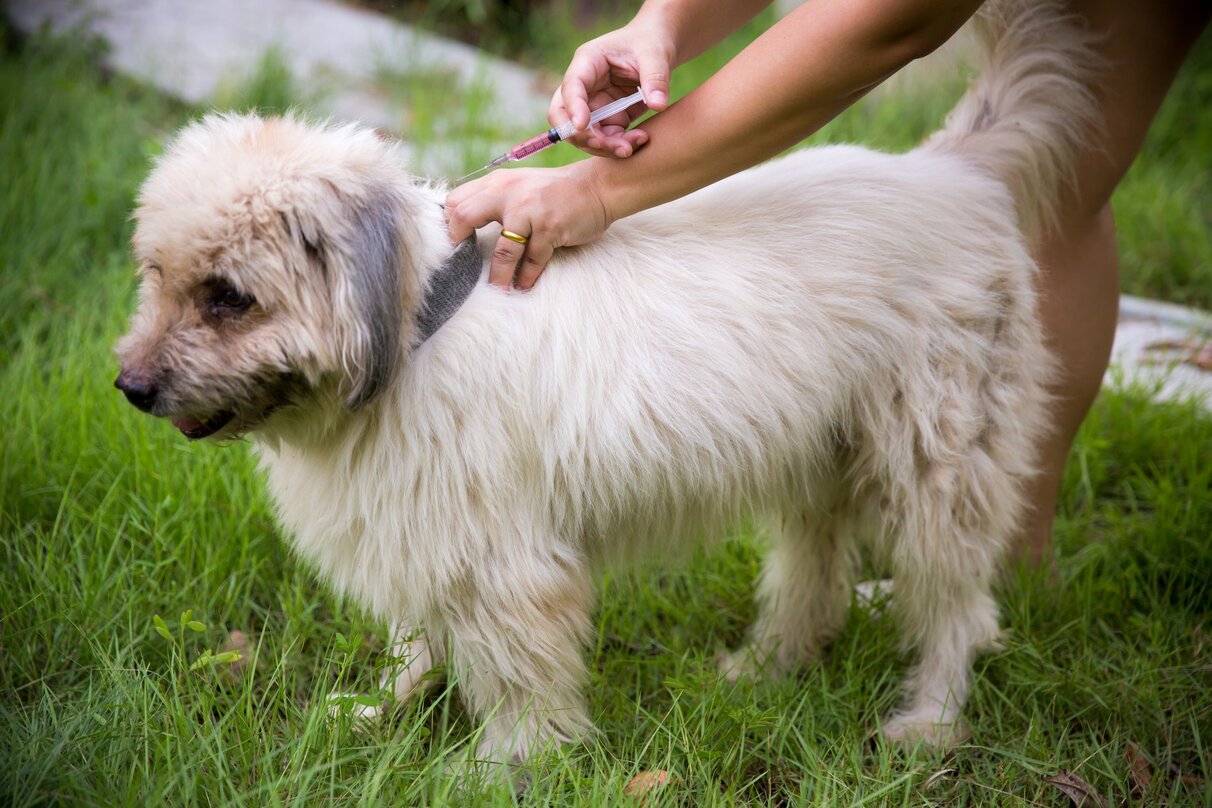
Veterinarian-recommended flea prevention products, such as topical treatments, oral medications, and flea collars, can be instrumental in preventing fleas on dogs. These products are designed to repel fleas, disrupt their life cycle, or kill adult fleas, providing long-lasting protection for dogs. It is essential to follow the veterinarian's recommendations regarding the selection and application of flea prevention products to ensure their effectiveness and safety for the dog.
Regular Veterinary Care
Regular veterinary check-ups enable early detection of potential flea infestations and allow for timely intervention. Veterinarians can provide guidance on flea prevention and recommend suitable products based on the dog's specific needs and health status. Additionally, veterinarians can conduct flea screenings and address any underlying health issues that may make the dog more susceptible to flea infestations.
Read more: What Do Fleas Look Like On My Dog?
Integrated Approach
Implementing an integrated approach to flea prevention, which combines grooming, environmental management, and the use of preventive medications, can significantly reduce the risk of fleas on dogs. By incorporating multiple preventive strategies, dog owners can create a comprehensive defense against flea infestations and ensure the comfort and well-being of their pets.
By being proactive and diligent in implementing preventive measures, dog owners can effectively protect their furry companions from the nuisance and potential health risks associated with flea infestations. Creating a flea-free environment not only benefits the dogs but also contributes to a harmonious and enjoyable coexistence between pets and their owners.
Treating Fleas on Dogs
When a dog is found to have fleas, prompt and effective treatment is essential to alleviate the discomfort and health risks associated with flea infestations. Treating fleas on dogs involves a multi-faceted approach aimed at eradicating adult fleas, interrupting the flea life cycle, and addressing any secondary issues caused by the infestation.
Use of Veterinary-Approved Flea Treatments
Veterinarian-recommended flea treatments, such as spot-on solutions, oral medications, and flea collars, are commonly used to treat fleas on dogs. These products are designed to kill adult fleas, disrupt the flea life cycle, or repel fleas from infesting the dog. It is crucial to follow the veterinarian's instructions regarding the selection, application, and frequency of flea treatments to ensure their effectiveness and safety for the dog.
Environmental Control Measures
In addition to treating the dog, environmental control measures are vital for eliminating fleas from the living environment. Vacuuming carpets, rugs, and upholstery, followed by thorough cleaning and washing of the dog's bedding and resting areas, can help remove flea eggs, larvae, and pupae. Regular cleaning of the indoor and outdoor spaces frequented by the dog can contribute to breaking the flea life cycle and preventing re-infestations.
Flea Baths and Grooming
Flea baths and grooming play a crucial role in treating fleas on dogs. Specialized flea shampoos and dips can be used to kill adult fleas and soothe the dog's skin. Thoroughly combing the dog's coat with a fine-toothed flea comb can help remove adult fleas and flea dirt, aiding in the treatment process. Regular grooming can also help monitor the dog's progress and detect any lingering signs of flea infestations.
Addressing Secondary Health Issues
Flea infestations can lead to secondary health issues, such as allergic dermatitis, skin irritation, and bacterial infections. Treating these secondary issues may involve the use of medicated shampoos, topical treatments, or oral medications to alleviate skin inflammation, itching, and discomfort. In severe cases, veterinary intervention may be necessary to address complications arising from flea infestations.
Follow-Up and Prevention
After initiating flea treatment, it is essential to follow up with the veterinarian's recommendations and monitor the dog for any signs of re-infestation or adverse reactions to the treatment. Implementing preventive measures, such as regular grooming, environmental management, and the use of flea prevention products, is crucial for preventing future flea infestations and maintaining the dog's well-being.
By employing a comprehensive approach to treating fleas on dogs, pet owners can effectively eliminate fleas from their pets and living spaces, providing relief and comfort for their canine companions. Timely and thorough treatment not only addresses the immediate issue of flea infestations but also contributes to the long-term health and happiness of dogs.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding where fleas like to reside on dogs and how to prevent and treat infestations is crucial for maintaining the health and well-being of our beloved pets. Fleas, as persistent parasites, tend to congregate in specific areas on a dog's body, including around the neck and head, along the back and tail, under the legs and around the groin, between the toes and paw pads, and under the tail. By being aware of these preferred locations, pet owners can conduct thorough inspections and take targeted preventive measures to combat flea infestations effectively.
Recognizing the signs of flea infestations, such as excessive scratching, visible fleas or flea dirt, hair loss, restlessness, and pale gums, is essential for early detection and intervention. By promptly addressing flea infestations, pet owners can alleviate the discomfort and potential health risks associated with these pesky parasites. Implementing preventive measures, including regular grooming, environmental management, the use of preventive medications, and regular veterinary care, is instrumental in creating a flea-free environment for dogs.
When it comes to treating flea infestations, a multi-faceted approach is necessary. Utilizing veterinarian-approved flea treatments, implementing environmental control measures, conducting flea baths and grooming, and addressing any secondary health issues caused by the infestation are crucial steps in eradicating fleas from dogs and their living spaces. Following up with preventive measures is equally important to prevent future infestations and maintain the dog's well-being.
By being proactive and diligent in preventing and treating fleas on dogs, pet owners can ensure the comfort, health, and happiness of their furry companions. Creating a flea-free environment not only benefits the dogs but also fosters a harmonious and enjoyable coexistence between pets and their owners. With a comprehensive understanding of flea behavior, preventive measures, and effective treatments, pet owners can confidently protect their dogs from the nuisance and potential health risks posed by flea infestations.