Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Heart Health>How Many Dogs In The US Have Heartworm


Heart Health
How Many Dogs In The US Have Heartworm
Published: February 7, 2024
Learn about heart health for dogs in the US and find out how many are affected by heartworm. Protect your pet with the right preventive measures.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Heartworm disease is a serious and potentially fatal condition that can affect dogs across the United States. It is caused by the parasitic worm Dirofilaria immitis, which is transmitted through the bite of an infected mosquito. Once inside a dog's body, these worms can grow and multiply, leading to severe damage to the heart, lungs, and blood vessels.
Understanding the impact of heartworm disease is crucial for dog owners and veterinarians alike. By recognizing the risks and taking proactive measures, it is possible to protect our furry companions from this debilitating illness. In this article, we will delve into the prevalence of heartworm in the US, the factors that contribute to its spread, and the available prevention and treatment options. By gaining a deeper understanding of this disease, we can work together to safeguard the well-being of our beloved canine friends.
Read more: How Many Fleas Does A Dog Have
Understanding Heartworm Disease
Heartworm disease is a potentially life-threatening condition that primarily affects dogs but can also occur in other mammal species, including cats and ferrets. The disease is caused by the parasitic worm Dirofilaria immitis, which is transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes. Once a mosquito carrying heartworm larvae bites a dog, the larvae enter the dog's bloodstream and begin their journey to the heart and lungs, where they mature into adult worms.
As the adult worms grow and multiply, they can cause severe damage to the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. The presence of these worms can lead to a range of health issues, including lung disease, heart failure, and organ damage. If left untreated, heartworm disease can be fatal for dogs.
The lifecycle of the heartworm begins when an infected mosquito bites a host, transmitting the microscopic heartworm larvae into the animal's bloodstream. Over the course of several months, these larvae develop into mature adult worms, with the potential to grow up to 12 inches in length. Once mature, the worms reside in the heart and pulmonary arteries, where they can cause significant damage to the cardiovascular system.
The severity of heartworm disease can vary depending on factors such as the number of worms present, the duration of the infection, and the dog's overall health. In some cases, dogs may show minimal or no symptoms in the early stages of the disease, making it challenging to detect without proper testing. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms such as coughing, fatigue, difficulty breathing, and weight loss may become apparent.
Understanding the lifecycle and potential impact of heartworm disease is essential for pet owners and veterinarians. By recognizing the risks associated with heartworm infection, individuals can take proactive measures to protect their pets and minimize the spread of this debilitating illness. Through education, regular testing, and preventative measures, we can work towards reducing the prevalence of heartworm disease and ensuring the well-being of our canine companions.
Prevalence of Heartworm in the US
Heartworm disease is a significant concern for dogs across the United States, with prevalence varying by region. The American Heartworm Society conducts annual surveys to assess the impact of heartworm infection, providing valuable insights into the distribution and prevalence of this disease.
According to the latest data from the American Heartworm Society, heartworm disease has been diagnosed in all 50 states, highlighting the widespread nature of this condition. While certain regions may have a higher incidence of heartworm infection due to environmental factors and mosquito populations, it is essential for dog owners nationwide to be aware of the potential risks.
The prevalence of heartworm in the US is influenced by various factors, including climate, temperature, and mosquito activity. Warmer and more humid regions tend to have a higher prevalence of heartworm disease, as these conditions are conducive to mosquito breeding and the transmission of heartworm larvae. However, it is important to note that heartworm infection can occur in any state, making it a relevant concern for dogs throughout the country.
In addition to geographical factors, the prevalence of heartworm disease is also impacted by human behavior and pet care practices. Dogs that are not consistently administered heartworm preventatives are at a higher risk of infection, regardless of their location. Furthermore, the movement of infected animals from one region to another can contribute to the spread of heartworm disease, emphasizing the need for comprehensive prevention strategies at a national level.
The prevalence of heartworm in the US serves as a reminder of the importance of proactive measures to protect dogs from this potentially life-threatening disease. Regular testing, year-round preventative medication, and mosquito control efforts are crucial components of a comprehensive approach to minimizing the impact of heartworm infection. By understanding the prevalence of heartworm disease and its implications, dog owners and veterinarians can work together to safeguard the well-being of canine companions across the nation.
The prevalence of heartworm disease in the US underscores the significance of proactive measures to protect dogs from this potentially life-threatening condition. By understanding the distribution and impact of heartworm infection, pet owners and veterinary professionals can collaborate to implement effective prevention and treatment strategies, ultimately reducing the prevalence of heartworm disease and ensuring the health and longevity of dogs nationwide.
Risk Factors for Heartworm Infection
Several factors contribute to the risk of heartworm infection in dogs, highlighting the importance of understanding these elements to effectively mitigate the spread of this debilitating disease.
-
Climate and Environmental Conditions: Warmer, humid climates create favorable conditions for mosquito breeding and the transmission of heartworm larvae. Regions with a higher prevalence of mosquitoes pose an increased risk of heartworm infection for dogs. Additionally, areas with standing water, such as ponds, marshes, and wetlands, provide breeding grounds for mosquitoes, further elevating the risk of heartworm transmission.
-
Lack of Preventative Measures: Dogs that are not consistently administered heartworm preventatives are at a heightened risk of infection. Failure to provide year-round preventative medication leaves dogs vulnerable to heartworm disease, especially in regions with a high prevalence of infected mosquitoes. Regular administration of preventatives, as recommended by veterinarians, is essential for protecting dogs from heartworm infection.
-
Travel and Movement: Dogs that travel or are relocated from regions with a high incidence of heartworm disease to areas with lower prevalence can introduce the infection to new environments. Additionally, the movement of infected animals from one location to another can contribute to the spread of heartworm disease, emphasizing the need for comprehensive prevention strategies at a national and international level.
-
Mosquito Exposure: Dogs that spend a significant amount of time outdoors, particularly during peak mosquito activity, are at an increased risk of heartworm infection. Mosquito bites are the primary mode of heartworm transmission, and dogs that have frequent exposure to mosquitoes face a higher likelihood of contracting the disease. This risk factor underscores the importance of implementing mosquito control measures and minimizing outdoor exposure during peak mosquito activity periods.
-
Lack of Testing and Monitoring: Failure to conduct regular heartworm testing and monitoring can result in undetected infections, allowing the disease to progress unchecked. Routine testing enables early detection of heartworm infection, facilitating timely intervention and treatment. Without regular screening, infected dogs may not display noticeable symptoms until the disease has advanced, making it challenging to address effectively.
Understanding the risk factors for heartworm infection is crucial for pet owners and veterinary professionals. By recognizing these contributing elements, individuals can take proactive measures to protect dogs from this potentially life-threatening disease. Through education, preventative measures, and comprehensive testing protocols, the impact of heartworm infection can be minimized, ultimately safeguarding the well-being of canine companions.
Prevention and Treatment Options
Preventing heartworm infection and effectively managing the disease are essential components of ensuring the health and well-being of dogs. By implementing comprehensive prevention strategies and exploring available treatment options, pet owners and veterinary professionals can work together to protect dogs from the devastating impact of heartworm disease.
Read more: How Many Dogs Have Arthritis
Prevention
Year-Round Preventative Medication
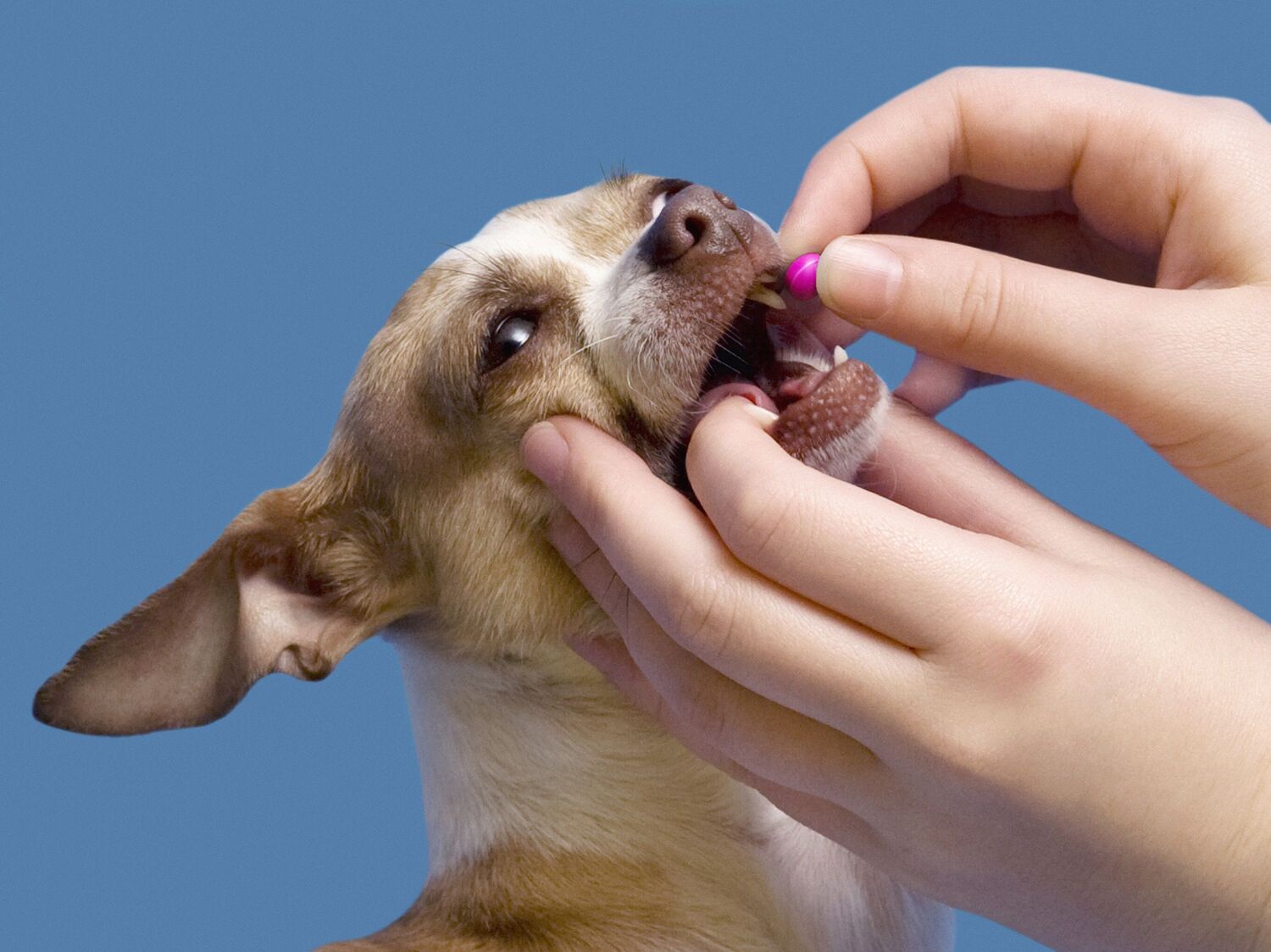
Year-round administration of heartworm preventatives, as recommended by veterinarians, is a fundamental aspect of protecting dogs from heartworm infection. These medications are available in various forms, including chewable tablets, topical treatments, and injectable formulations. By consistently providing preventatives, dog owners can significantly reduce the risk of heartworm disease and safeguard their pets' health.
Regular Veterinary Care and Testing
Routine veterinary visits enable comprehensive health assessments, including heartworm testing. Annual heartworm tests are recommended for all dogs, regardless of their preventative medication status. These tests help detect the presence of heartworm infection at an early stage, allowing for prompt intervention and treatment. Additionally, regular check-ups provide opportunities for veterinarians to assess overall health and discuss preventative measures with pet owners.
Mosquito Control
Implementing mosquito control measures in and around the home environment can help minimize the risk of heartworm transmission. This includes eliminating standing water, using mosquito repellents, and utilizing mosquito control products as recommended by veterinarians. By reducing mosquito exposure, pet owners can further protect their dogs from potential infection.
Treatment
Diagnosing Heartworm Disease
In the event of a positive heartworm test result, further diagnostic procedures, such as blood tests, chest X-rays, and ultrasound examinations, may be conducted to assess the extent of the infection and its impact on the dog's health. These diagnostic measures provide valuable insights for developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment Protocols
The treatment of heartworm disease typically involves a multi-step protocol aimed at eliminating the adult worms from the dog's body. This process may include the administration of medications to kill the adult worms, as well as supportive care to manage potential complications associated with the treatment. It is essential for pet owners to closely follow their veterinarian's guidance throughout the treatment process to ensure the best possible outcome for their dog.
Post-Treatment Care and Monitoring
Following treatment, dogs require careful post-treatment care and monitoring to assess their recovery and overall well-being. This may involve restricted activity, medication administration, and regular veterinary check-ups to evaluate the dog's response to treatment and address any lingering effects of the disease.
By prioritizing preventative measures and exploring available treatment options, pet owners and veterinary professionals can collaborate to protect dogs from heartworm infection and provide effective care for those affected by the disease. Through proactive management and comprehensive support, the impact of heartworm disease can be minimized, ultimately contributing to the health and longevity of canine companions nationwide.
Conclusion
In conclusion, heartworm disease poses a significant threat to the well-being of dogs across the United States. The prevalence of this potentially life-threatening condition underscores the importance of proactive measures to protect canine companions from the devastating impact of heartworm infection. By understanding the risk factors, prevalence, and available prevention and treatment options, pet owners and veterinary professionals can work together to safeguard the health and longevity of dogs nationwide.
The widespread nature of heartworm disease serves as a reminder of the need for comprehensive prevention strategies. Climate and environmental conditions, lack of preventative measures, travel and movement, mosquito exposure, and the absence of regular testing and monitoring all contribute to the risk of heartworm infection. By recognizing these factors, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize the spread of this debilitating disease, ultimately protecting their pets from its harmful effects.
Year-round preventative medication, regular veterinary care and testing, and mosquito control efforts are fundamental components of an effective prevention approach. By consistently administering heartworm preventatives, conducting routine testing, and implementing mosquito control measures, pet owners can significantly reduce the risk of heartworm infection for their dogs. Additionally, early detection through regular testing enables prompt intervention and treatment, contributing to better outcomes for affected animals.
In the event of a positive heartworm diagnosis, exploring available treatment options is essential for effectively managing the disease. Diagnosing heartworm disease, implementing treatment protocols, and providing post-treatment care and monitoring are crucial steps in supporting the recovery and well-being of affected dogs. By closely following veterinary guidance and prioritizing comprehensive care, pet owners can contribute to the successful treatment of heartworm disease in their pets.
Overall, the prevalence of heartworm disease in the US highlights the importance of education, proactive measures, and collaborative efforts to protect dogs from this debilitating condition. By raising awareness, implementing preventative strategies, and prioritizing the health of canine companions, individuals can work towards reducing the impact of heartworm disease and ensuring the well-being of dogs nationwide. Through a collective commitment to proactive management and comprehensive support, the prevalence of heartworm disease can be minimized, ultimately contributing to the health and longevity of our beloved canine friends.