Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Disease Does The American Dog Tick Carry


Common Health Issues
What Disease Does The American Dog Tick Carry
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about the common health issues associated with the American dog tick and how to protect your pet from potential diseases. Understand the risks and preventive measures.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The American dog tick, scientifically known as Dermacentor variabilis, is a common ectoparasite found in North America. This tick species is notorious for transmitting various diseases to both animals and humans, making it a significant concern for public health and veterinary medicine. Understanding the potential health risks associated with the American dog tick is crucial for implementing effective preventive measures and ensuring timely treatment in case of exposure.
The prevalence of the American dog tick in outdoor environments, including grassy areas, wooded regions, and even urban parks, underscores the importance of raising awareness about the diseases it carries. As pet owners, outdoor enthusiasts, and individuals residing in tick-prone areas, being informed about the potential health implications of American dog tick bites is essential for safeguarding both human and animal well-being.
In the following sections, we will delve into the diseases carried by the American dog tick, explore the symptoms and treatment options for these illnesses, and discuss preventive measures to mitigate the risk of tick-borne diseases. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the American dog tick and the associated health concerns, individuals can make informed decisions to protect themselves, their pets, and their families from potential tick-borne threats.
Read more: Where Are American Dog Ticks Found?
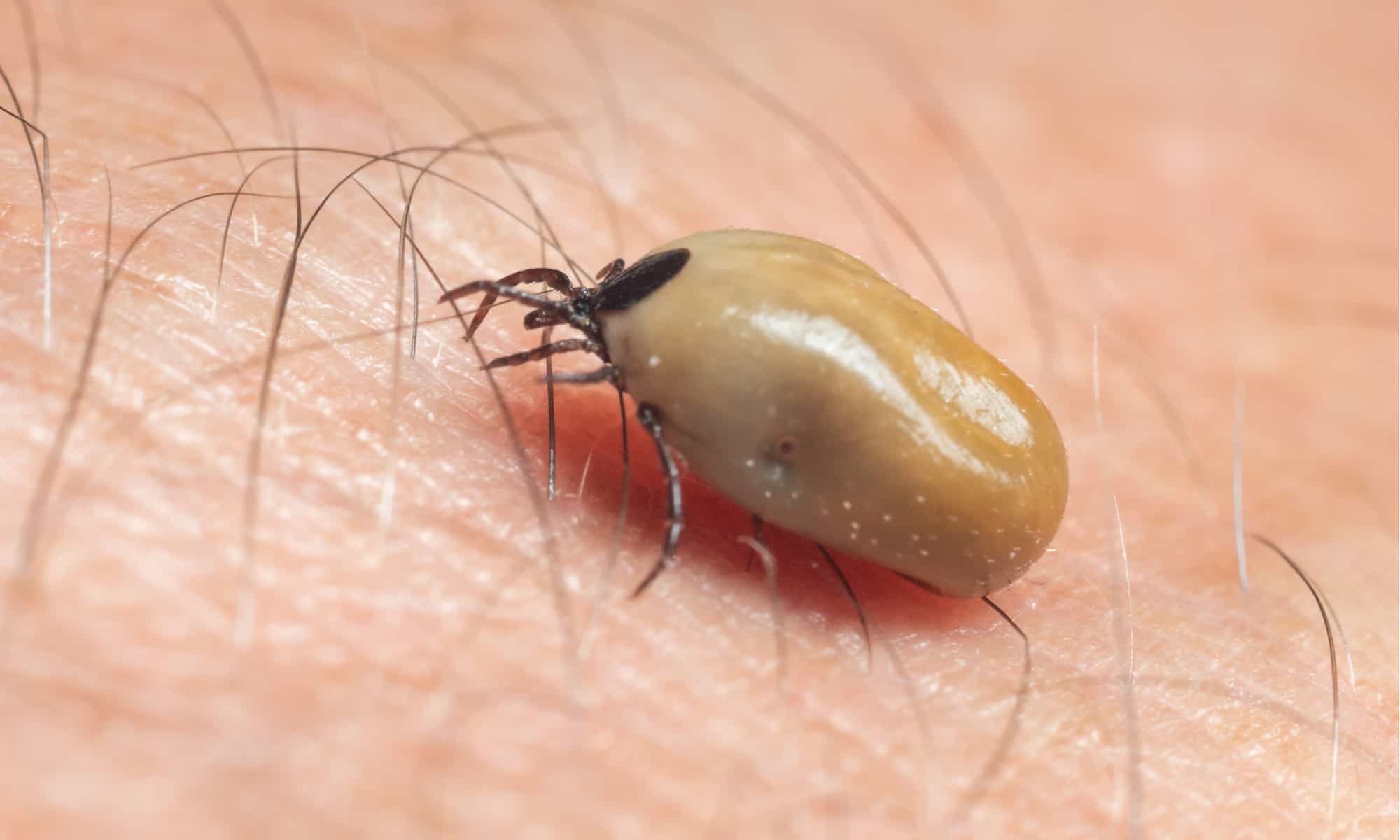
The American Dog Tick
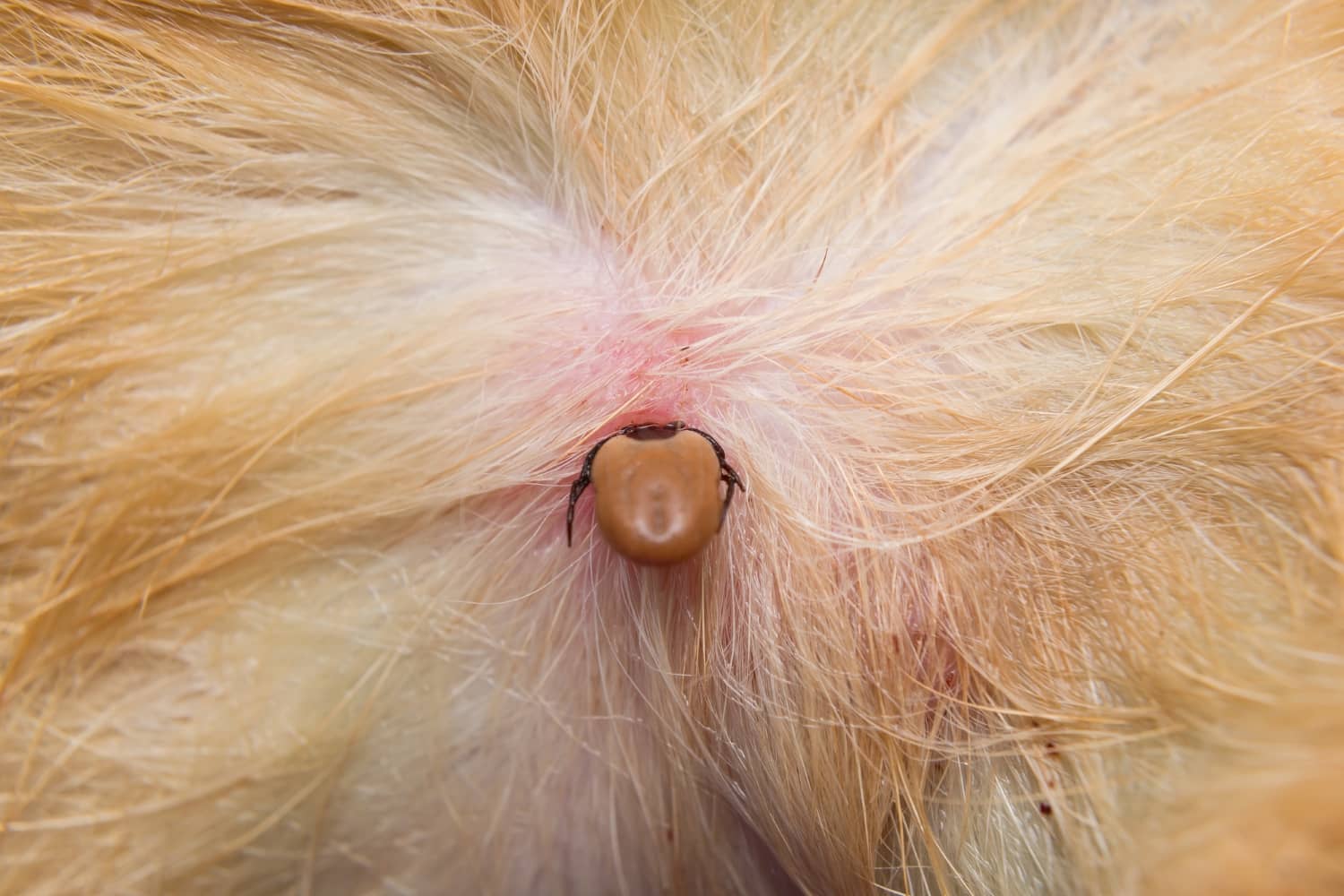
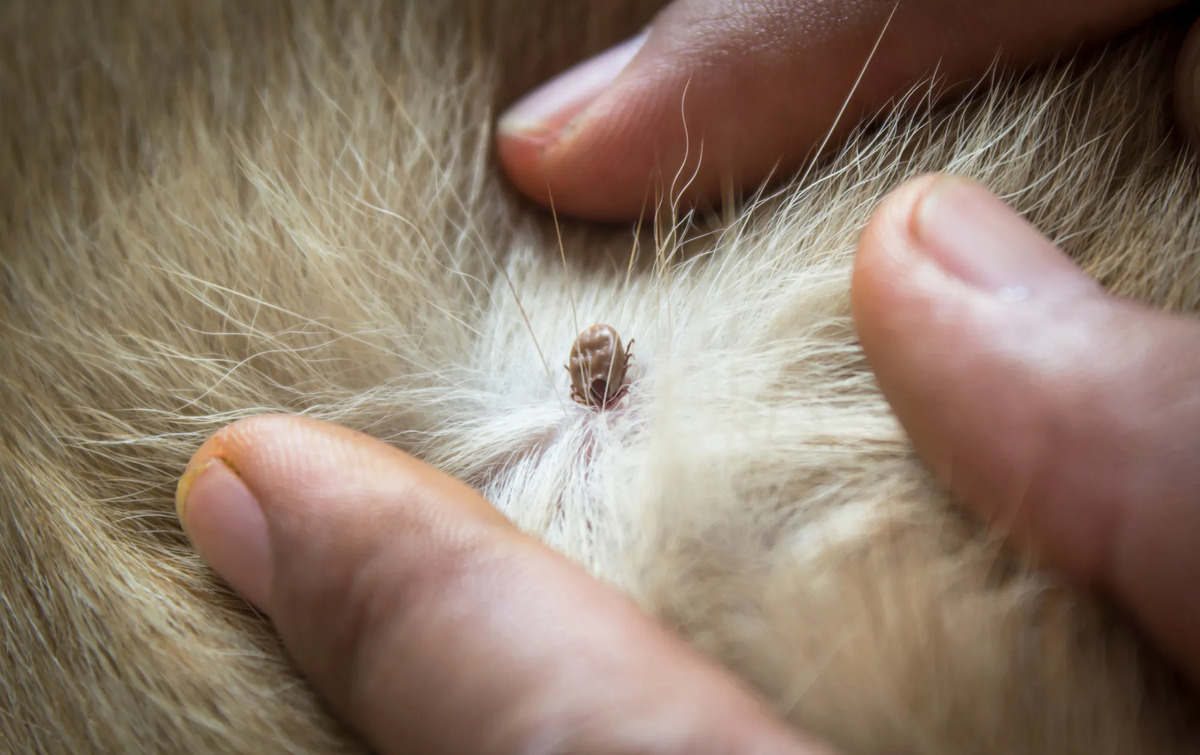
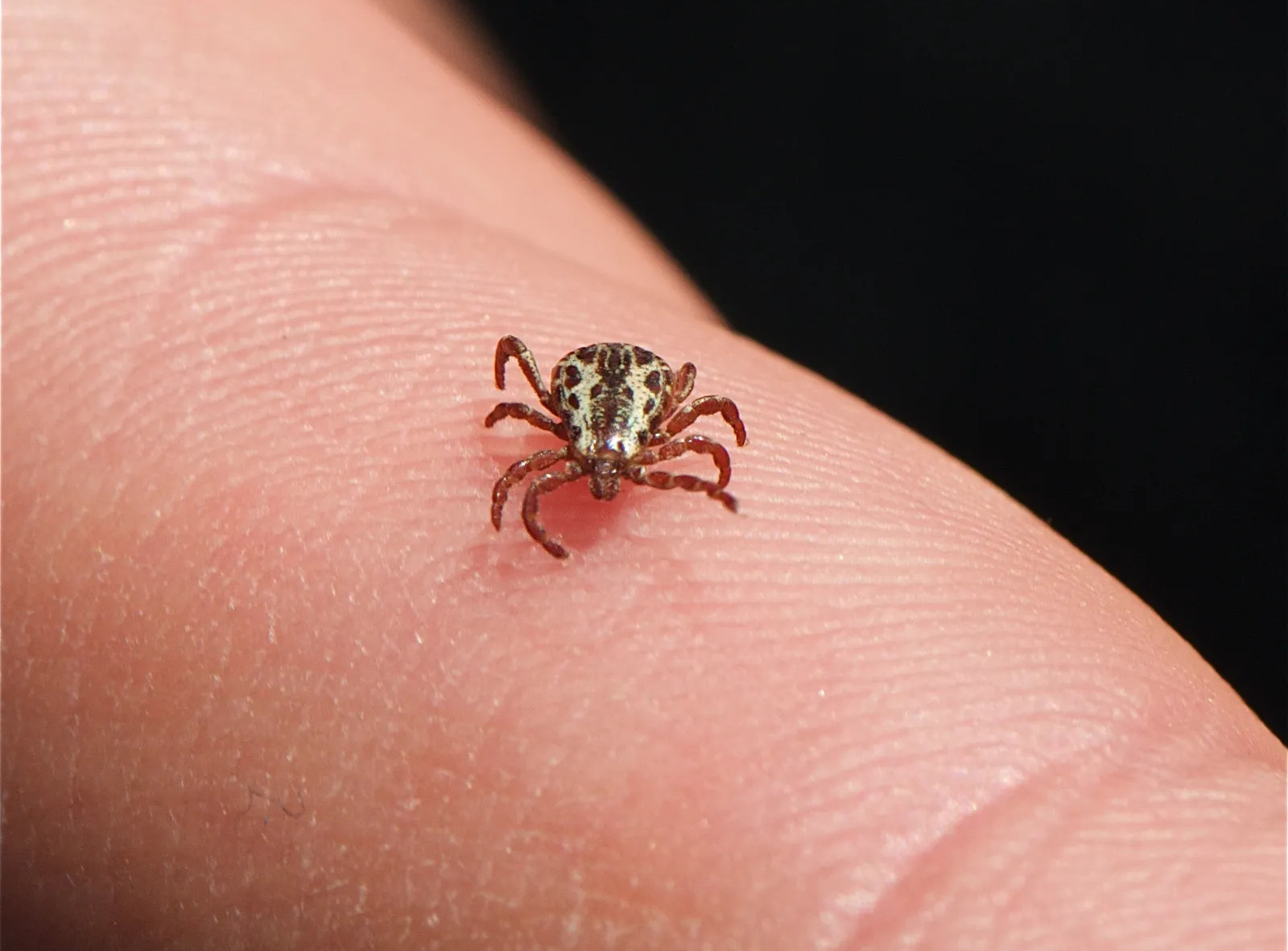
The American dog tick, scientifically known as Dermacentor variabilis, is a prevalent ectoparasite found in various regions across North America. This species of tick is recognized for its distinctive appearance, characterized by a reddish-brown body and prominent mouthparts. The American dog tick is commonly encountered in outdoor environments, including grassy areas, wooded regions, and even urban parks, where it exhibits a propensity for latching onto passing hosts in search of a blood meal.
One of the distinguishing features of the American dog tick is its broad host range, as it readily feeds on a variety of animals, including dogs, rodents, deer, and occasionally humans. This adaptability contributes to the widespread distribution of the American dog tick and its potential to pose health risks to both animals and humans.
In terms of life cycle, the American dog tick undergoes four developmental stages: egg, larva, nymph, and adult. Throughout its life cycle, this tick species relies on blood meals to progress from one stage to the next. Notably, the American dog tick is known to transmit various pathogens during its feeding process, making it a vector for several diseases that can impact both animals and humans.
Understanding the behavior and habitat preferences of the American dog tick is crucial for implementing effective preventive measures to minimize the risk of tick encounters. Additionally, recognizing the physical characteristics of this tick species can aid in prompt identification and removal, thereby reducing the likelihood of disease transmission.
Given the potential health implications associated with the American dog tick, it is essential for individuals, particularly pet owners and outdoor enthusiasts, to familiarize themselves with the appearance, habits, and potential risks posed by this tick species. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the American dog tick, individuals can proactively take steps to mitigate the threat of tick-borne diseases and safeguard the well-being of themselves and their pets.
Diseases Carried by the American Dog Tick
The American dog tick is a vector for several diseases that can have significant implications for both animal and human health. Understanding the potential illnesses transmitted by this tick species is crucial for recognizing the associated symptoms, seeking timely treatment, and implementing preventive measures to mitigate the risk of exposure.
One of the most well-known diseases carried by the American dog tick is Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF). This potentially severe illness is caused by the bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii, which can be transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick. RMSF is characterized by symptoms such as fever, headache, rash, and muscle aches, and if left untreated, it can lead to serious complications, including organ damage and even death. Prompt recognition of the symptoms and appropriate medical intervention are essential for managing RMSF effectively.
Another notable disease associated with the American dog tick is tularemia, caused by the bacterium Francisella tularensis. While tularemia can be transmitted through various routes, including tick bites, the American dog tick has been identified as a potential vector for this pathogen. Symptoms of tularemia may include fever, skin ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, and respiratory issues. Timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial for addressing tularemia and preventing its potential complications.
Additionally, the American dog tick is implicated in the transmission of Ehrlichiosis, a bacterial illness that can affect both dogs and humans. Ehrlichiosis is caused by various species of the Ehrlichia bacterium and can manifest with symptoms such as fever, fatigue, joint pain, and in severe cases, bleeding disorders. Early detection and appropriate antibiotic treatment are essential for managing Ehrlichiosis effectively.
Furthermore, the American dog tick has been associated with the transmission of Babesiosis, a parasitic disease caused by Babesia microti and other Babesia species. This illness can lead to symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue, and anemia, posing particular risks to individuals with compromised immune systems. Timely diagnosis and targeted medical intervention are crucial for addressing Babesiosis and preventing its potential complications.
By understanding the diseases carried by the American dog tick and recognizing the associated symptoms, individuals can take proactive measures to minimize the risk of exposure and seek timely medical attention if necessary. Additionally, implementing preventive strategies to reduce tick encounters and conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities can contribute to mitigating the impact of these tick-borne illnesses on both animal and human health.
Symptoms and Treatment of Diseases Carried by the American Dog Tick
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF)
Symptoms of RMSF typically appear within two weeks of a tick bite and may include fever, headache, rash, muscle aches, and nausea. In severe cases, RMSF can lead to complications such as organ damage and neurological issues. Prompt medical attention is crucial for diagnosing RMSF, and treatment often involves the administration of antibiotics, such as doxycycline, to effectively combat the infection. Early recognition of symptoms and timely intervention are essential for managing RMSF and preventing its potential complications.
Read more: What Diseases Do Dogs Get From Ticks
Tularemia
Tularemia can manifest with symptoms such as fever, skin ulcers at the site of the tick bite, swollen lymph nodes, and respiratory problems. In some cases, tularemia can lead to severe illness and complications. Treatment for tularemia typically involves the use of antibiotics, such as gentamicin or doxycycline, to address the infection. Timely diagnosis and targeted medical intervention are essential for managing tularemia effectively and preventing its potential complications.
Ehrlichiosis
Symptoms of Ehrlichiosis may include fever, fatigue, muscle aches, joint pain, and in severe cases, bleeding disorders. Timely diagnosis and appropriate antibiotic treatment, often with doxycycline, are essential for managing Ehrlichiosis effectively and preventing its progression to severe illness. Early recognition of symptoms and prompt medical intervention are crucial for addressing Ehrlichiosis and minimizing its impact on both animal and human health.
Babesiosis
Babesiosis can lead to symptoms such as fever, chills, fatigue, and anemia, particularly posing risks to individuals with compromised immune systems. Treatment for Babesiosis often involves the use of specific medications, such as atovaquone and azithromycin, to combat the parasitic infection. Timely diagnosis and targeted medical intervention are crucial for addressing Babesiosis effectively and preventing its potential complications.
By recognizing the symptoms associated with diseases carried by the American dog tick and seeking prompt medical attention, individuals can effectively address these illnesses and minimize their impact on both animal and human health. Additionally, implementing preventive measures to reduce tick encounters and conducting thorough tick checks after outdoor activities can contribute to mitigating the risk of exposure to these tick-borne diseases.
Prevention and Control of American Dog Tick Diseases
Preventing and controlling diseases carried by the American dog tick is paramount for safeguarding the well-being of both animals and humans. Implementing proactive measures to minimize the risk of tick encounters and effectively managing potential exposure are essential components of comprehensive tick-borne disease control strategies.
Read more: What Is Sunken Eye Disease In Dogs?
Environmental Modifications
Modifying the outdoor environment to reduce tick habitats can significantly contribute to disease prevention. This includes maintaining well-groomed yards, minimizing overgrown vegetation, and creating physical barriers, such as gravel or wood chips, to separate recreational areas from tick-prone habitats. By creating less favorable environments for ticks, individuals can mitigate the risk of exposure to the American dog tick and reduce the likelihood of disease transmission.
Tick Control Products
Utilizing tick control products, such as acaricides and tick repellents, can aid in reducing tick populations and preventing bites. Pet owners can consider using veterinarian-recommended tick prevention products for their animals, including topical treatments, collars, and oral medications designed to repel and eliminate ticks. Additionally, individuals can use tick repellents containing DEET or permethrin on clothing and exposed skin when venturing into tick-infested areas, thereby reducing the risk of tick bites.
Regular Tick Checks
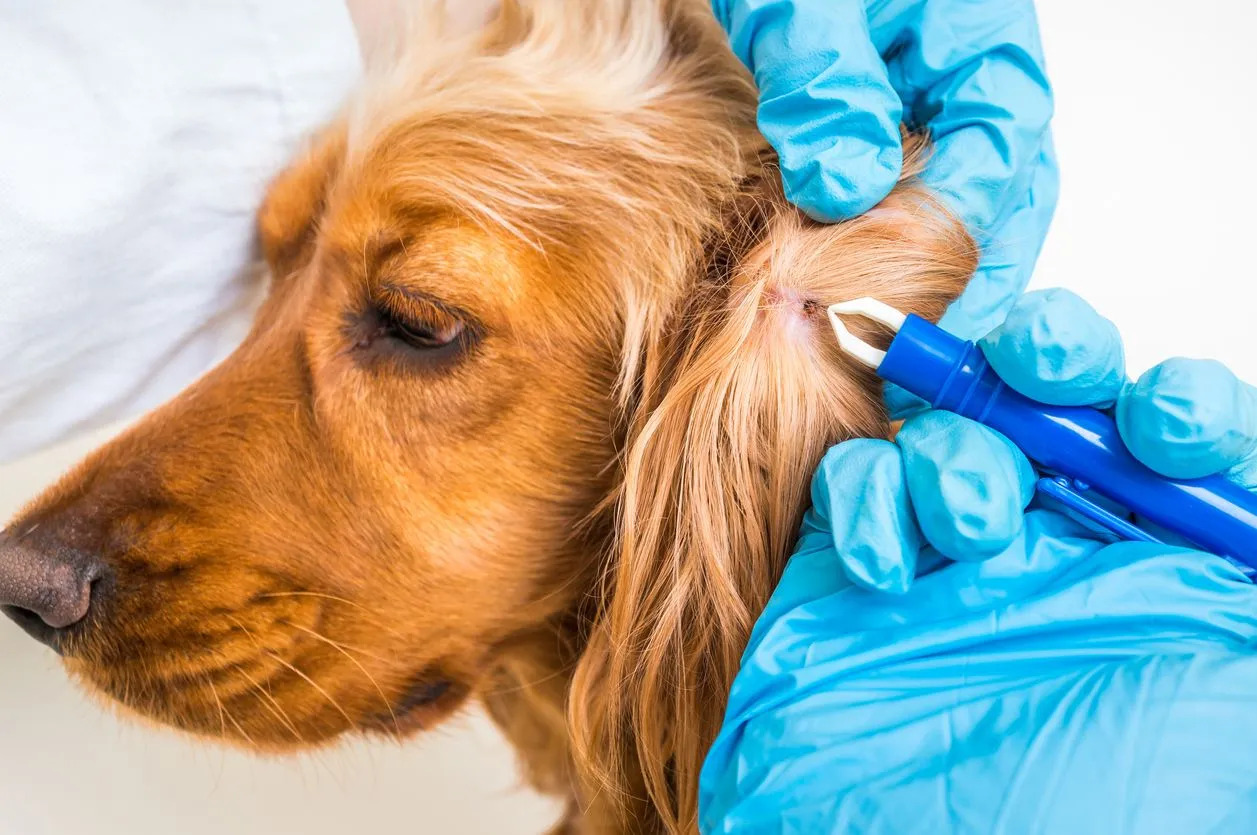
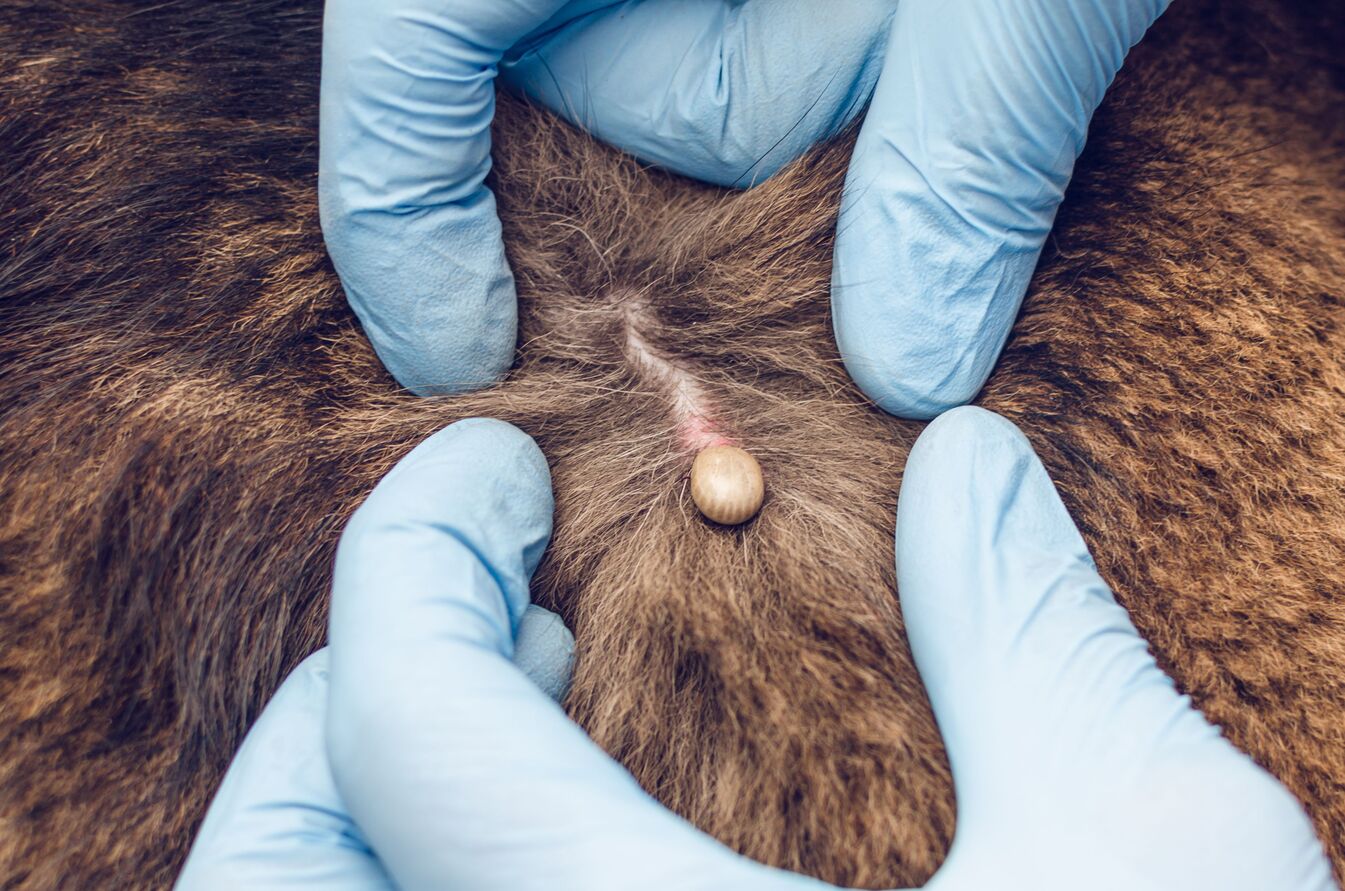
Conducting thorough tick checks after spending time outdoors is crucial for promptly identifying and removing any attached ticks. Individuals should carefully inspect themselves, their children, and their pets for ticks, paying close attention to areas such as the scalp, behind the ears, along the hairline, and within body folds. Prompt tick removal can help prevent the transmission of tick-borne pathogens and reduce the likelihood of disease transmission.
Personal Protective Measures
Implementing personal protective measures, such as wearing long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and closed-toe shoes, can serve as physical barriers to prevent tick bites. Tucking pants into socks and using insect repellents can further enhance protection against tick encounters. Additionally, showering promptly after outdoor activities and laundering clothing at high temperatures can help remove any ticks that may have been picked up during outdoor excursions.
Read more: What Is Dental Disease In Dogs?
Education and Awareness
Raising awareness about the risks associated with the American dog tick and the diseases it carries is essential for empowering individuals to take proactive measures. Providing education about tick-borne diseases, including their symptoms, preventive strategies, and the importance of timely medical attention, can equip individuals with the knowledge needed to protect themselves and their pets from potential tick-borne threats.
By integrating these preventive and control measures into everyday practices, individuals can effectively reduce the risk of exposure to diseases carried by the American dog tick. Proactive tick management, coupled with informed decision-making and timely intervention, plays a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of tick-borne illnesses on both animal and human health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the American dog tick poses significant health risks due to its potential to transmit various diseases to both animals and humans. Understanding the diseases carried by this tick species, including Rocky Mountain spotted fever, tularemia, ehrlichiosis, and babesiosis, is crucial for recognizing the associated symptoms, seeking timely treatment, and implementing preventive measures to mitigate the risk of exposure.
By familiarizing themselves with the appearance, habits, and potential risks posed by the American dog tick, individuals can proactively take steps to safeguard their well-being and that of their pets. Recognizing the symptoms of tick-borne diseases and seeking prompt medical attention are essential for effectively addressing these illnesses and preventing potential complications.
Furthermore, implementing environmental modifications, utilizing tick control products, conducting regular tick checks, and adopting personal protective measures are integral components of comprehensive tick-borne disease prevention and control strategies. By integrating these measures into everyday practices, individuals can effectively reduce the risk of exposure to diseases carried by the American dog tick.
Raising awareness about the risks associated with the American dog tick and providing education about tick-borne diseases are essential for empowering individuals to make informed decisions and take proactive measures to protect themselves and their pets from potential tick-borne threats.
Ultimately, by prioritizing preventive strategies, prompt recognition of symptoms, and timely medical intervention, individuals can minimize the impact of tick-borne illnesses on both animal and human health. Through a combination of knowledge, vigilance, and proactive measures, the potential risks associated with the American dog tick can be effectively mitigated, contributing to the well-being of individuals and their animal companions.