Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Diseases Do Dogs Get From Ticks


Common Health Issues
What Diseases Do Dogs Get From Ticks
Published: February 5, 2024
Learn about the common health issues dogs can get from ticks and how to protect your furry friend. Understand the diseases and their symptoms.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Ticks are tiny, blood-sucking parasites that pose a significant health risk to dogs. These pesky creatures are not only a nuisance but also carriers of various diseases that can severely impact a dog's well-being. As a responsible pet owner, it's crucial to understand the potential dangers associated with tick bites and the diseases they can transmit to your furry companion.
Tick-borne diseases are a growing concern for dog owners worldwide, as these ailments can lead to serious health complications if left untreated. From Lyme disease to Ehrlichiosis, the range of illnesses transmitted by ticks underscores the importance of proactive prevention and timely intervention.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of ticks and the diseases they can transmit to dogs. By gaining a deeper understanding of these common health threats, you'll be better equipped to safeguard your canine companion's health and well-being. Let's explore the intricacies of tick-borne diseases and empower ourselves with the knowledge needed to protect our beloved pets from these pervasive health risks.
Read more: How Do You Get Rid Of Seed Ticks From Dogs
Understanding Ticks and Their Diseases
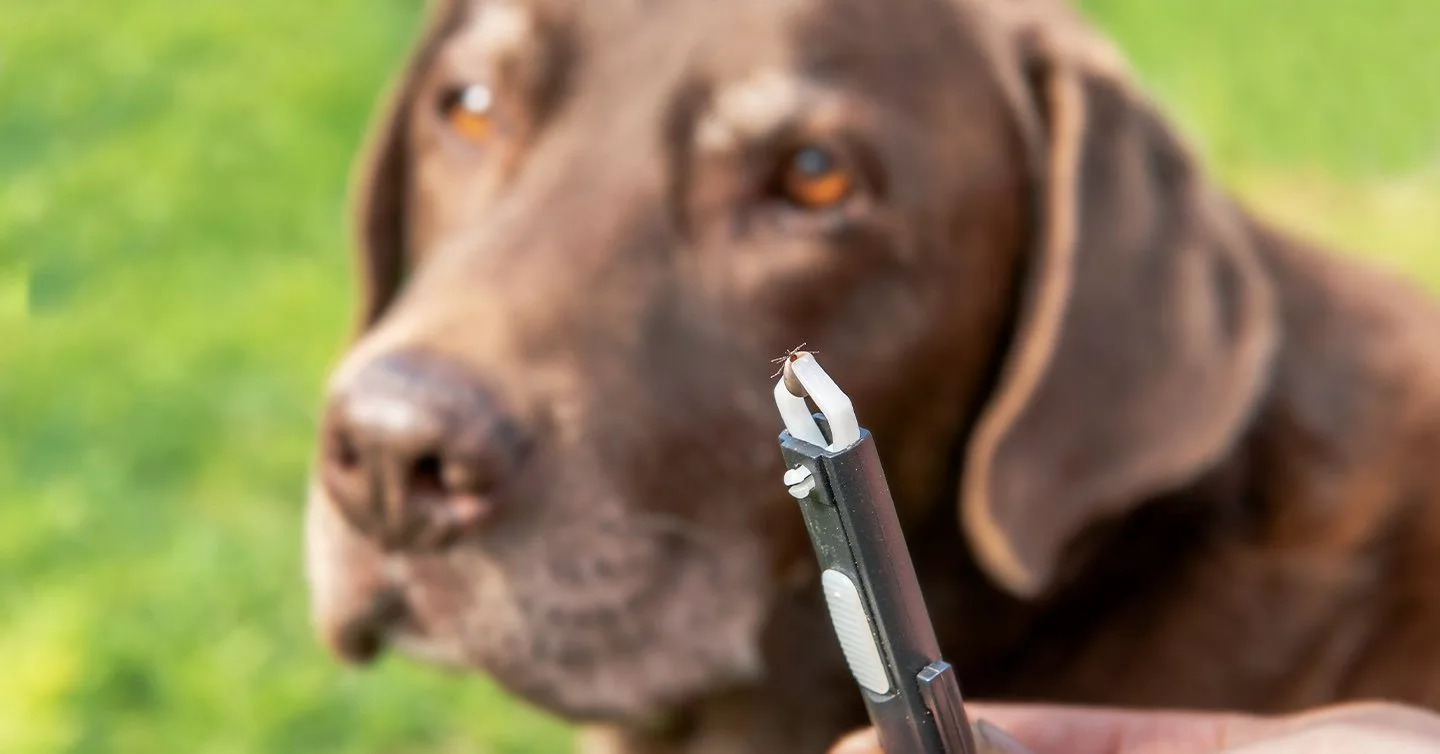
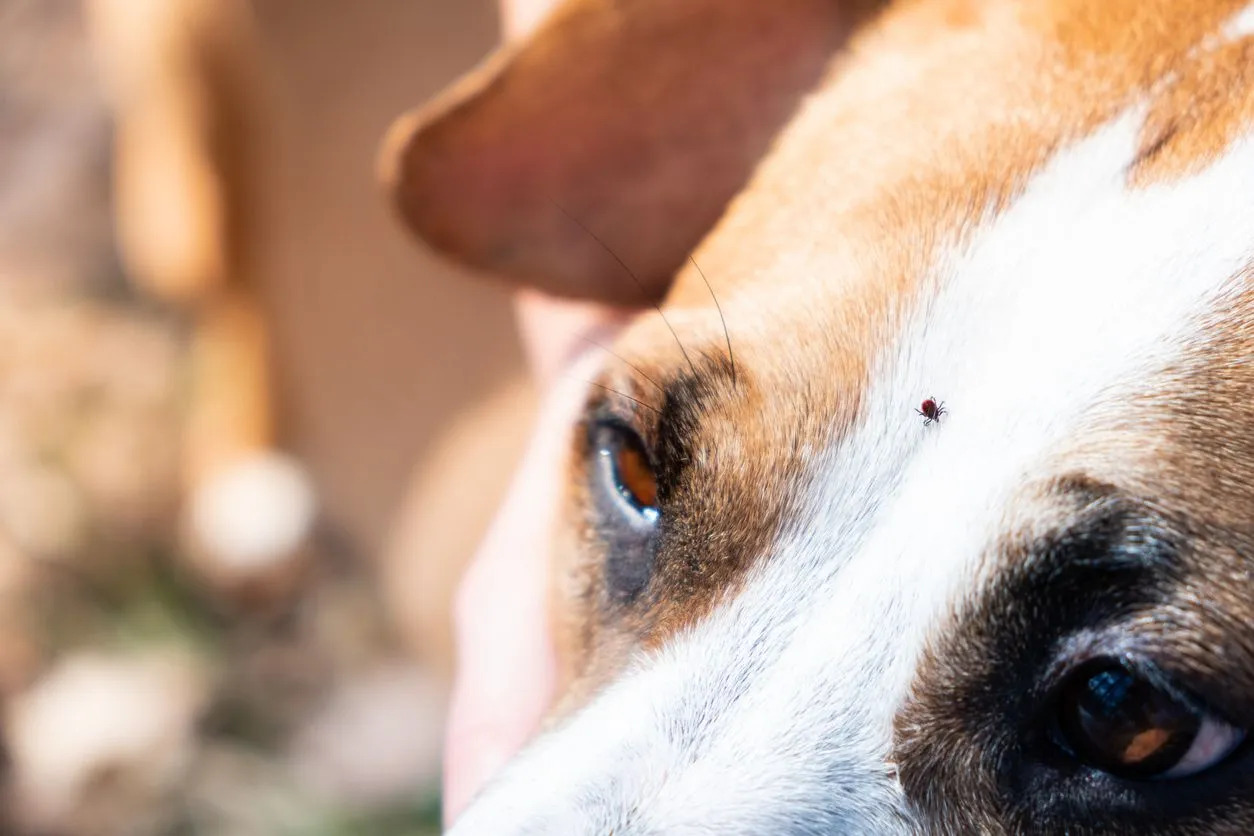
Ticks are arachnids belonging to the order Parasitiformes, and they thrive in diverse environments, including wooded areas, grasslands, and even urban settings. These blood-feeding parasites have a remarkable ability to latch onto hosts, including dogs, and feed on their blood. Ticks are not only adept at finding their hosts but also possess the capability to transmit a range of diseases during the feeding process.
One of the most concerning aspects of ticks is their potential to transmit various pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, and protozoa, which can lead to debilitating diseases in dogs. These pathogens are often harbored within the tick's salivary glands, and when the tick attaches itself to a host, it can transmit these disease-causing agents into the host's bloodstream.
The diseases transmitted by ticks can vary depending on the species of tick and the geographical region. Common tick-borne diseases in dogs include Lyme disease, Ehrlichiosis, Anaplasmosis, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and Babesiosis, among others. Each of these diseases is caused by different pathogens and can result in a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe illness.
Understanding the life cycle of ticks is crucial in comprehending their role as disease vectors. Ticks progress through various life stages, including larva, nymph, and adult, with each stage requiring a blood meal to advance to the next. During each feeding stage, ticks have the potential to transmit diseases to their hosts, making them a persistent threat to the health of dogs.
It's important to recognize that ticks are not just a seasonal concern; they can be active year-round in certain regions. Therefore, consistent vigilance and preventive measures are essential to minimize the risk of tick infestation and disease transmission to dogs.
By gaining a deeper understanding of ticks and the diseases they can transmit, dog owners can take proactive steps to protect their pets from these pervasive health risks. Through effective prevention, regular tick checks, and prompt removal of any attached ticks, pet owners can significantly reduce the likelihood of tick-borne diseases affecting their canine companions.
Common Tick-Borne Diseases in Dogs
Tick-borne diseases pose a significant threat to the health and well-being of dogs, with a range of ailments that can result from tick bites. Understanding these common diseases is crucial for dog owners to recognize the symptoms and seek timely veterinary care. Here are some of the most prevalent tick-borne diseases in dogs:
1. Lyme Disease
Lyme disease, caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, is transmitted through the bite of an infected black-legged tick, also known as the deer tick. This disease can lead to joint pain, lameness, fever, and lethargy in dogs. In severe cases, Lyme disease can cause kidney damage and other serious health complications.
2. Ehrlichiosis
Ehrlichiosis is caused by several species of the Ehrlichia bacteria, which are transmitted through the bites of infected brown dog ticks, lone star ticks, and other tick species. This disease can manifest in acute, subclinical, and chronic phases, with symptoms including fever, lethargy, anemia, and bleeding disorders.
3. Anaplasmosis
Anaplasmosis is caused by the bacterium Anaplasma phagocytophilum, which is transmitted through the bites of infected ticks, including the black-legged tick and the western black-legged tick. Dogs with anaplasmosis may experience lameness, joint pain, fever, lethargy, and decreased appetite.
4. Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Rocky Mountain spotted fever is caused by the bacterium Rickettsia rickettsii, transmitted primarily by the American dog tick, the Rocky Mountain wood tick, and the brown dog tick. Symptoms of this disease in dogs include fever, joint pain, neurological abnormalities, and potentially life-threatening complications if left untreated.
5. Babesiosis
Babesiosis is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Babesia, which are transmitted through the bites of infected ticks, such as the brown dog tick and the American dog tick. This disease can lead to symptoms such as fever, pale gums, weakness, and in severe cases, organ failure.
6. Hepatozoonosis
Hepatozoonosis is caused by the protozoan parasite Hepatozoon, which is transmitted through the ingestion of infected ticks. This disease can result in muscle pain, fever, and potentially severe muscle and bone damage in dogs.
These common tick-borne diseases underscore the importance of proactive prevention, regular tick checks, and prompt removal of any attached ticks to minimize the risk of disease transmission to dogs. By staying informed about these prevalent diseases, dog owners can take proactive measures to protect their beloved pets from the potentially devastating effects of tick-borne illnesses.
Symptoms and Treatment of Tick-Borne Diseases
Tick-borne diseases can manifest a wide array of symptoms in dogs, ranging from mild discomfort to severe illness. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early intervention and prompt veterinary care. Common symptoms of tick-borne diseases in dogs include fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, joint pain, lameness, swollen lymph nodes, and in severe cases, neurological abnormalities and organ damage. Additionally, some dogs may experience anemia, bleeding disorders, and pale gums as a result of certain tick-borne illnesses.
Upon observing any of these symptoms, it is imperative for dog owners to seek immediate veterinary attention. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential in managing tick-borne diseases and preventing potential complications. Veterinary professionals may conduct blood tests to identify the specific pathogens causing the illness and tailor the treatment accordingly.
The treatment of tick-borne diseases in dogs typically involves the administration of antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, and supportive care to alleviate symptoms and combat the underlying infection. In cases of severe illness, hospitalization and intensive care may be necessary to stabilize the dog's condition and facilitate recovery.
Furthermore, proactive measures such as tick removal, parasite control, and vaccination against specific tick-borne diseases can play a pivotal role in preventing these illnesses in dogs. Tick prevention products, including topical treatments, oral medications, and tick collars, can help repel and eliminate ticks, reducing the risk of disease transmission.
In addition to veterinary intervention, providing a comfortable and stress-free environment for the affected dog is essential for their recovery. Adequate rest, a balanced diet, and close monitoring of the dog's condition are integral components of the treatment process.
As responsible pet owners, staying vigilant for any signs of tick-borne diseases and promptly seeking veterinary care are paramount in safeguarding the health and well-being of our canine companions. By understanding the symptoms and pursuing appropriate treatment, we can mitigate the impact of tick-borne diseases and ensure the best possible outcome for our beloved dogs.
Prevention and Control of Tick-Borne Diseases in Dogs
Preventing and controlling tick-borne diseases in dogs is paramount in safeguarding their health and well-being. Implementing proactive measures to minimize the risk of tick infestation and disease transmission is crucial for pet owners. Here are essential strategies for preventing and controlling tick-borne diseases in dogs:
1. Tick Prevention Products
Utilizing tick prevention products such as topical treatments, oral medications, and tick collars can effectively repel and eliminate ticks. These products are designed to disrupt the tick's life cycle and prevent infestation, reducing the likelihood of disease transmission to dogs.
2. Regular Tick Checks
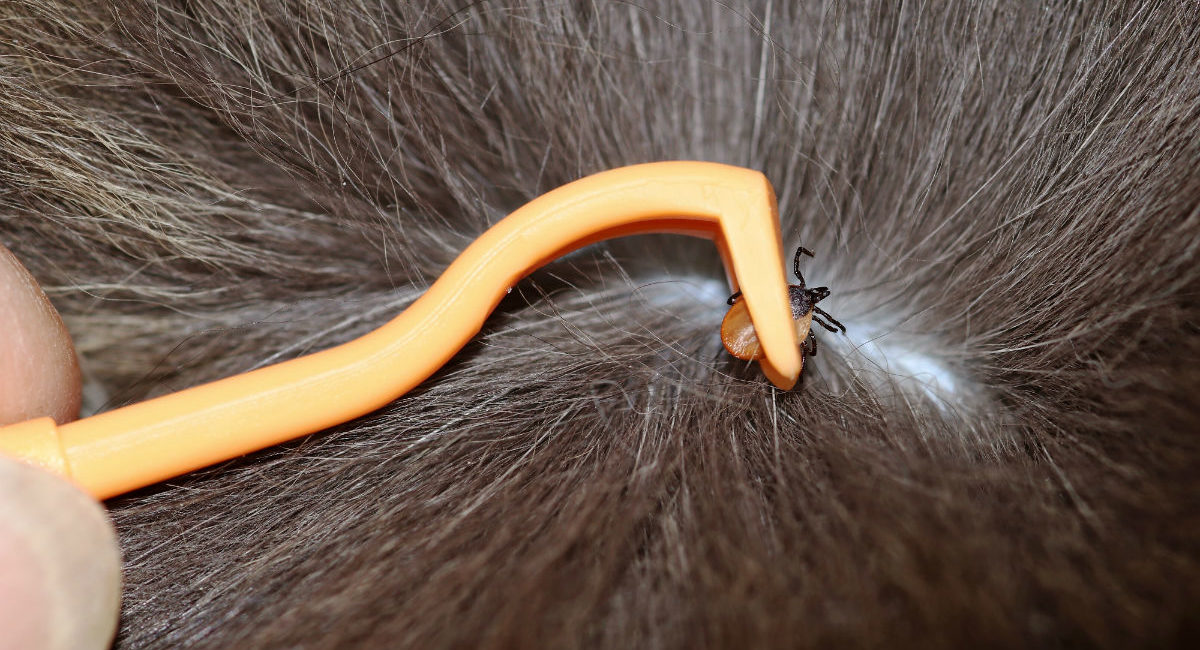
Performing thorough tick checks on dogs after outdoor activities is essential for early detection and removal of any attached ticks. Paying close attention to areas such as the ears, neck, and between the toes can help identify and promptly remove ticks before they have a chance to transmit diseases.
Read more: What Parasite Do You Get From Dog Kisses?
3. Environmental Management
Maintaining a well-groomed and tick-free environment in and around the home can significantly reduce the risk of tick exposure for dogs. Keeping lawns mowed, removing leaf litter, and minimizing areas of tall grass and brush can help create a less hospitable environment for ticks.
4. Vaccination
In regions where specific tick-borne diseases are prevalent, vaccination against these illnesses can provide an additional layer of protection for dogs. Consultation with a veterinarian regarding the appropriate vaccinations based on the dog's lifestyle and geographical location is crucial for effective disease prevention.
5. Professional Pest Control
Engaging professional pest control services to address tick infestations in the outdoor environment can help mitigate the risk of tick-borne diseases. Pest control experts can employ targeted strategies to reduce tick populations and create a safer outdoor environment for dogs.
6. Education and Awareness
Educating oneself about the prevalence of tick-borne diseases in specific regions and staying informed about the latest preventive measures is essential for effective disease control. Raising awareness among fellow pet owners about the importance of tick prevention and control can contribute to a collective effort in safeguarding canine health.
By integrating these preventive strategies into a comprehensive tick-borne disease control plan, dog owners can significantly reduce the risk of their pets contracting these potentially debilitating illnesses. Consistent vigilance, proactive measures, and regular veterinary consultations are integral components of an effective approach to tick-borne disease prevention and control in dogs.
Read more: What Time Of Year Do Dogs Get Ticks
Conclusion
In conclusion, the threat of tick-borne diseases looms large for our canine companions, necessitating a proactive and informed approach to safeguard their health. The intricate interplay between ticks and the diseases they transmit underscores the importance of understanding, preventing, and managing these pervasive health risks.
By delving into the world of ticks and their associated diseases, we have gained valuable insights into the potential dangers that these blood-feeding parasites pose to dogs. From Lyme disease to Ehrlichiosis, the spectrum of tick-borne illnesses highlights the need for heightened awareness and preventive measures.
Recognizing the common symptoms and understanding the treatment options for tick-borne diseases is pivotal in ensuring timely intervention and optimal care for affected dogs. Early diagnosis, veterinary consultation, and tailored treatment regimens play a crucial role in mitigating the impact of these illnesses and facilitating the recovery of our beloved pets.
Moreover, the proactive prevention and control strategies discussed provide a comprehensive framework for minimizing the risk of tick infestation and disease transmission. From tick prevention products to regular tick checks and environmental management, each strategy contributes to a multi-faceted approach aimed at protecting dogs from the perils of tick-borne diseases.
As responsible pet owners, it is incumbent upon us to remain vigilant, stay informed, and take proactive steps to shield our canine companions from the potential harm posed by ticks and the diseases they carry. By integrating these insights into our daily routines and prioritizing preventive measures, we can create a safer and healthier environment for our beloved dogs.
In essence, the journey through the realm of tick-borne diseases has equipped us with the knowledge and tools needed to navigate this complex landscape and ensure the well-being of our furry friends. By fostering a proactive and informed mindset, we can fortify our efforts in protecting our dogs from the pervasive threats posed by ticks and their associated diseases.
In closing, let us embark on this collective endeavor to champion the health and happiness of our canine companions, arming ourselves with knowledge, vigilance, and a steadfast commitment to their well-being in the face of tick-borne diseases.