Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Can One Tell If A Female Dog Has Breast Cancer

Common Health Issues
How Can One Tell If A Female Dog Has Breast Cancer
Published: February 4, 2024
Learn about common health issues in female dogs, including how to recognize signs of breast cancer and when to seek veterinary care. Understand the importance of early detection and treatment.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Breast cancer is a concerning health issue that affects not only humans but also our beloved canine companions. Female dogs, like their human counterparts, can develop breast cancer, also known as mammary gland tumors. This condition is a significant health concern for female dogs, and understanding its signs, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options is crucial for ensuring the well-being of our furry friends.
As responsible pet owners, it's essential to be aware of the potential risks and health challenges that our female dogs may face. By familiarizing ourselves with the nuances of breast cancer in female dogs, we can take proactive steps to monitor their health and seek timely veterinary care if any concerning symptoms arise.
In the following sections, we will delve into the intricacies of breast cancer in female dogs, exploring the signs and symptoms that pet owners should watch for, the diagnostic methods used by veterinarians to identify this condition, and the available treatment options. Additionally, we will discuss preventive measures and compassionate care strategies for female dogs diagnosed with breast cancer.
Understanding breast cancer in female dogs is a vital aspect of responsible pet ownership, and by gaining insights into this health issue, we can better support the well-being of our furry companions. Let's embark on this informative journey to learn more about breast cancer in female dogs and how we can effectively address this common health concern.
Understanding Breast Cancer in Female Dogs
Breast cancer, also known as mammary gland tumors, is a prevalent health issue in female dogs. The mammary glands, responsible for producing milk, are susceptible to developing tumors, which can be benign or malignant. Understanding the nature of breast cancer in female dogs is crucial for pet owners to recognize the potential risks and take proactive measures to safeguard their pets' health.
Female dogs have mammary glands arranged in two rows along their abdomen, typically consisting of five pairs. These glands are hormonally responsive, making female dogs more prone to developing mammary tumors, especially if they have not been spayed. The risk of developing mammary tumors increases with age, with unspayed female dogs being at a higher risk compared to those that have been spayed before their first heat cycle.
Mammary tumors in female dogs can be classified as benign or malignant. Benign tumors are non-cancerous and tend to grow slowly, often remaining localized in one area. On the other hand, malignant tumors are cancerous and have the potential to spread to other parts of the body, posing a more significant health threat to the affected dog.
Understanding the characteristics of mammary tumors, including their potential for malignancy and metastasis, is essential for pet owners to comprehend the severity of this condition. Additionally, being aware of the risk factors, such as age, hormonal influences, and spaying status, empowers pet owners to make informed decisions regarding their female dogs' health and well-being.
By gaining a comprehensive understanding of breast cancer in female dogs, pet owners can be better equipped to recognize any abnormal changes in their pets' mammary glands and seek prompt veterinary attention. This knowledge also underscores the importance of preventive measures, such as spaying at an early age, to mitigate the risk of mammary tumors in female dogs.
In essence, understanding breast cancer in female dogs involves recognizing the anatomical and physiological factors that contribute to the development of mammary tumors, as well as the distinction between benign and malignant growths. This knowledge serves as a cornerstone for proactive pet care and empowers pet owners to advocate for the health of their female canine companions.
Signs and Symptoms of Breast Cancer in Female Dogs
Identifying the signs and symptoms of breast cancer in female dogs is paramount for early detection and timely intervention. While mammary tumors may initially go unnoticed, vigilant pet owners can observe subtle changes that may indicate the presence of this condition. Here are the key signs and symptoms to watch for:
-
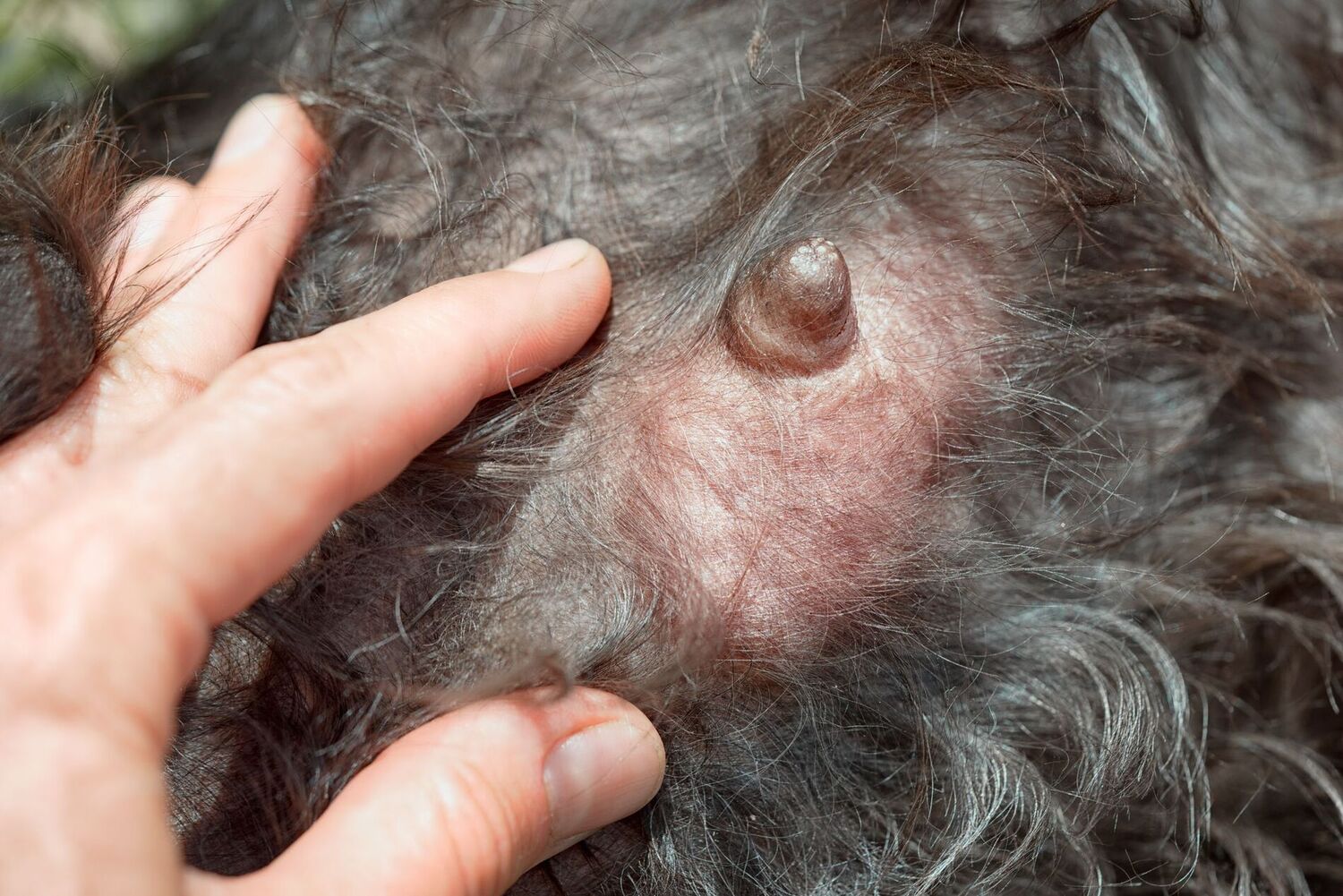
Lump Formation: The most common indicator of mammary tumors in female dogs is the presence of lumps or masses within the mammary glands. These lumps may vary in size and can be detected through palpation during regular grooming or petting sessions. It's essential to monitor the size, texture, and mobility of these lumps and promptly report any new developments to a veterinarian.
-
Swelling and Enlargement: Unexplained swelling or enlargement of the mammary glands, particularly in one or more glands, can be indicative of underlying health issues, including mammary tumors. Pet owners should pay attention to any asymmetry or abnormal growth in the mammary area and seek veterinary evaluation if such changes are observed.
-
Discharge from Nipples: Abnormal discharge, such as blood or pus, from the nipples of a female dog warrants immediate attention. Discharge may be accompanied by inflammation or ulceration around the affected nipples, signaling potential malignancy in the mammary glands.
-
Changes in Skin and Nipple Color: Changes in the color or texture of the skin surrounding the mammary glands, as well as alterations in the nipple appearance, should not be overlooked. Discoloration, ulceration, or the presence of crusty areas on the skin may indicate an underlying health issue, including mammary tumors.
-
Behavioral Changes: Female dogs affected by breast cancer may exhibit behavioral changes, such as increased sensitivity or discomfort when the affected mammary glands are touched. Additionally, signs of pain, restlessness, or reluctance to engage in physical activities may be indicative of underlying health concerns.
-
Lethargy and Weight Loss: Advanced stages of breast cancer in female dogs can lead to systemic effects, including lethargy, decreased appetite, and unexplained weight loss. These nonspecific symptoms may accompany the progression of mammary tumors and should prompt a comprehensive veterinary assessment.
Recognizing these signs and symptoms of breast cancer in female dogs empowers pet owners to take proactive measures in safeguarding their pets' health. Regular monitoring of the mammary glands, coupled with prompt veterinary consultation upon observing any concerning changes, is instrumental in ensuring early detection and effective management of mammary tumors in female dogs.
Diagnosing Breast Cancer in Female Dogs
Diagnosing breast cancer in female dogs involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses clinical evaluation, diagnostic imaging, and laboratory tests. Veterinary professionals employ a combination of techniques to accurately assess the presence of mammary tumors and determine their nature, whether benign or malignant. The diagnostic process is crucial for guiding treatment decisions and formulating a tailored care plan for affected female dogs.
Clinical Examination
The diagnostic journey begins with a thorough clinical examination conducted by a veterinarian. During this assessment, the vet carefully palpates the mammary glands to identify any lumps, masses, or abnormalities. The size, texture, and mobility of the detected growths are meticulously evaluated to gauge their potential for malignancy. Additionally, the presence of swelling, discharge, or changes in skin and nipple appearance is noted during the clinical examination.
Read more: How To Tell If A Dog Is Blind In One Eye
Diagnostic Imaging
Diagnostic imaging techniques, such as radiography (X-rays) and ultrasonography, play a pivotal role in the evaluation of mammary tumors in female dogs. X-rays provide valuable insights into the internal structure of the mammary glands and aid in identifying the extent of tumor involvement. Ultrasonography, on the other hand, enables detailed visualization of the mammary tissue, facilitating the detection of abnormalities that may not be palpable during physical examination.
Fine Needle Aspiration
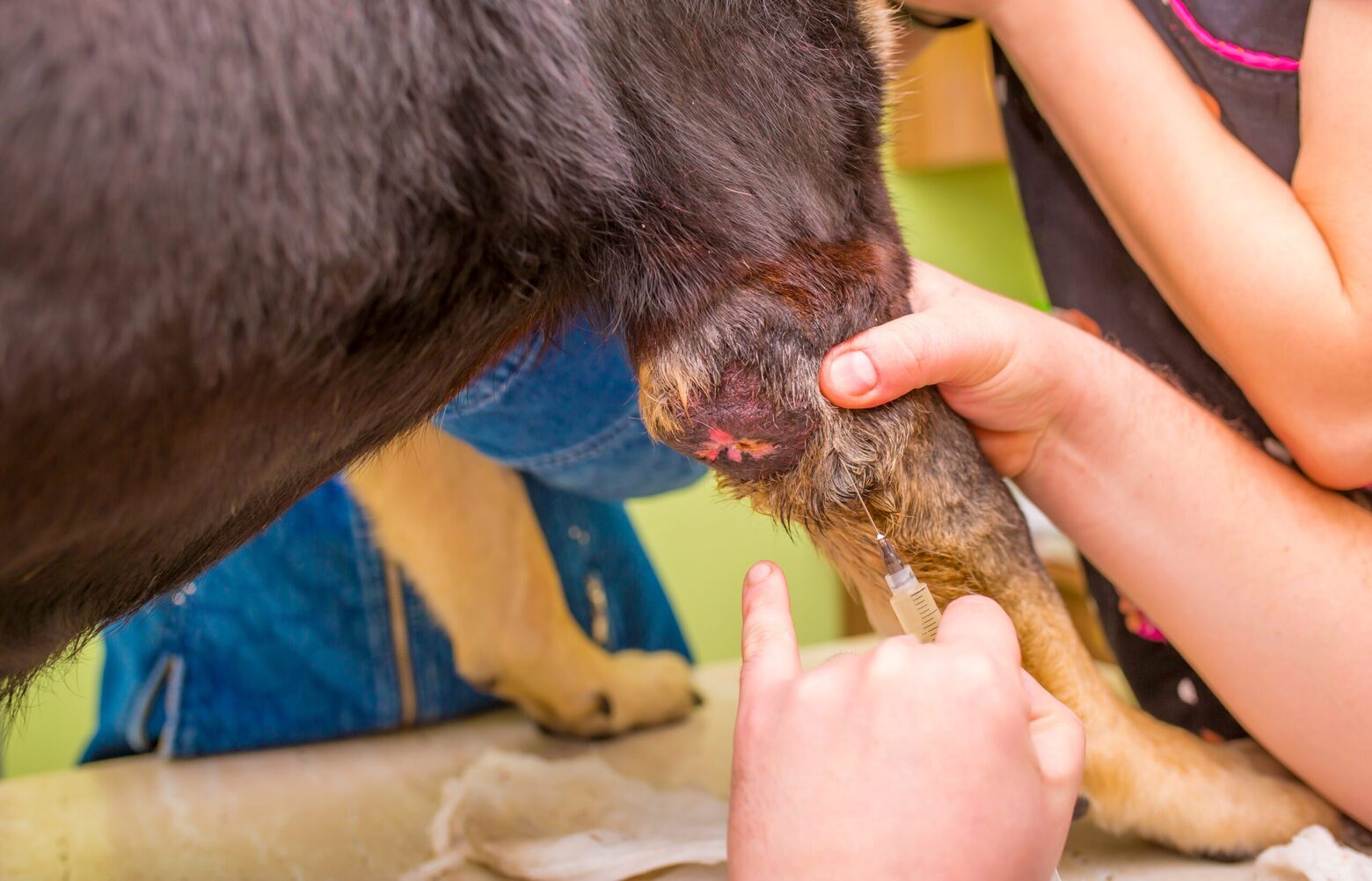
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) is a minimally invasive procedure used to obtain cellular samples from mammary masses for cytological evaluation. A fine needle is inserted into the tumor, and a small sample of cells is aspirated for microscopic examination. FNA allows veterinarians to assess the cellular characteristics of the tumor, distinguishing between benign and malignant growths based on the presence of abnormal cell types and features.
Biopsy
In cases where a definitive diagnosis is required, a biopsy may be recommended to obtain tissue samples from the mammary tumors. The collected tissue is then analyzed histologically to determine the nature of the growth and assess its potential for malignancy. Biopsy results provide crucial information that guides treatment decisions and helps veterinarians formulate an appropriate management strategy for female dogs with breast cancer.
Laboratory Tests
Laboratory tests, including blood work and biochemical analyses, are often conducted to assess the overall health status of the affected female dogs. These tests aid in identifying any systemic effects of mammary tumors, such as anemia or alterations in organ function, and provide valuable insights into the dog's overall well-being. Additionally, hormonal assays may be performed to evaluate the influence of hormonal factors on the development and progression of mammary tumors.
In summary, diagnosing breast cancer in female dogs involves a multifaceted approach that integrates clinical evaluation, diagnostic imaging, cytological and histological analyses, and comprehensive laboratory assessments. This comprehensive diagnostic process enables veterinarians to accurately characterize mammary tumors, determine their potential for malignancy, and devise tailored treatment plans to address this common health issue in female dogs.
Treatment Options for Breast Cancer in Female Dogs
The treatment of breast cancer in female dogs is multifaceted, aiming to address the specific characteristics of mammary tumors and the overall health status of the affected dogs. Upon diagnosis, veterinarians collaborate with pet owners to formulate a tailored treatment plan that may encompass surgical intervention, adjunctive therapies, and supportive care measures. The selection of treatment options is guided by the nature of the mammary tumors, their stage of progression, and the individual needs of the affected female dogs.
Surgical Excision
Surgical removal of mammary tumors is a primary treatment modality for female dogs diagnosed with breast cancer. The extent of surgical excision depends on the size, location, and number of tumors, as well as the potential for malignancy. In cases of benign tumors, complete excision of the growths may offer curative outcomes, while malignant tumors may necessitate more extensive surgical procedures to achieve optimal tumor removal and minimize the risk of recurrence.
Mastectomy
In instances where multiple mammary tumors are present or when malignancy is confirmed, mastectomy, the surgical removal of one or more mammary glands, may be recommended. Mastectomy aims to eliminate the affected glands to prevent further tumor progression and reduce the likelihood of metastasis. This procedure may be combined with tumor excision to comprehensively address the presence of mammary tumors in female dogs.
Chemotherapy
Adjuvant chemotherapy may be employed to complement surgical intervention in cases of malignant mammary tumors. Chemotherapeutic agents are administered to impede the growth and spread of cancer cells, thereby reducing the risk of metastasis and enhancing the overall treatment outcomes. Chemotherapy regimens are tailored to the specific needs of the affected dogs and are designed to minimize adverse effects while effectively targeting cancerous cells.
Read more: How To Tell If Your Senior Dog Has Tumors
Radiation Therapy
In certain instances, radiation therapy may be utilized to target residual cancer cells following surgical excision of mammary tumors. This localized treatment modality aims to destroy cancerous cells and minimize the risk of local recurrence. Radiation therapy may be recommended based on the characteristics of the mammary tumors and the overall health status of the affected female dogs.
Palliative Care
For cases where mammary tumors are advanced or metastatic, palliative care measures are implemented to alleviate discomfort and enhance the quality of life for affected female dogs. Pain management, nutritional support, and attentive nursing care are integral components of palliative care, aiming to provide comfort and support for dogs with advanced-stage breast cancer.
Supportive Therapies
Complementary supportive therapies, such as nutritional supplementation, immune-modulating agents, and pain management strategies, are integrated into the treatment plan to address the holistic needs of female dogs with breast cancer. These supportive measures aim to bolster the overall well-being of the affected dogs and mitigate the potential side effects of primary treatment modalities.
In essence, the treatment options for breast cancer in female dogs are tailored to the specific characteristics of mammary tumors, encompassing surgical intervention, adjunctive therapies, and compassionate care measures. By leveraging a comprehensive approach that addresses the individual needs of affected dogs, veterinarians strive to optimize treatment outcomes and enhance the well-being of female dogs diagnosed with this common health concern.
Prevention and Care for Female Dogs with Breast Cancer
Preventing and caring for female dogs with breast cancer involves a proactive approach that encompasses preventive measures, attentive monitoring, and holistic support to safeguard the health and well-being of our furry companions. By prioritizing preventive strategies and implementing compassionate care, pet owners can play a pivotal role in mitigating the risk of breast cancer in female dogs and advocating for their overall health.
Read more: How To Tell If A Lump In A Dog Is Cancer
Spaying at an Early Age
Spaying female dogs at an early age, ideally before their first heat cycle, is a fundamental preventive measure for reducing the risk of mammary tumors. Research indicates that spaying significantly decreases the likelihood of developing mammary cancer, particularly when performed before the onset of reproductive maturity. By opting for timely spaying, pet owners can effectively minimize the hormonal influences that predispose female dogs to mammary tumors, thereby promoting their long-term health.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Routine veterinary check-ups are essential for monitoring the health of female dogs and detecting any potential abnormalities in the mammary glands. Pet owners should prioritize regular physical examinations conducted by veterinarians, who can assess the condition of the mammary glands, palpate for lumps or masses, and provide guidance on preventive care. Early detection of mammary tumors through proactive veterinary monitoring enables timely intervention and enhances the prospects for successful treatment outcomes.
Healthy Lifestyle and Nutrition
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet, coupled with regular exercise, is integral to promoting the overall health and immune function of female dogs. A wholesome diet rich in essential nutrients, coupled with adequate hydration, supports the body's natural defense mechanisms and contributes to optimal well-being. Additionally, maintaining a healthy body weight and preventing obesity through portion control and regular physical activity may help mitigate the risk of certain health conditions, including mammary tumors.
Environmental and Behavioral Considerations
Creating a safe and enriching environment for female dogs, free from potential carcinogens and harmful substances, is crucial for their long-term health. Pet owners should be mindful of environmental factors that may pose health risks, such as exposure to tobacco smoke, pesticides, and other toxins. Furthermore, promoting mental and emotional well-being through positive reinforcement, mental stimulation, and social interaction contributes to a holistic approach to canine care, potentially influencing overall health outcomes.
Compassionate Support and Monitoring
In addition to preventive measures, providing compassionate support and attentive monitoring for female dogs is paramount. This entails regular observation of the mammary glands for any changes, such as lumps, swelling, or discharge, and promptly seeking veterinary attention if any abnormalities are noted. Furthermore, fostering a nurturing and supportive environment that prioritizes the physical and emotional needs of female dogs contributes to their overall well-being and resilience.
By embracing a comprehensive approach that integrates preventive strategies, attentive monitoring, and compassionate care, pet owners can champion the health and vitality of their female dogs. Proactive measures, coupled with a nurturing and supportive environment, serve as cornerstones for promoting the well-being of female dogs and mitigating the risk of breast cancer, ultimately fostering a fulfilling and healthy life for our beloved canine companions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, breast cancer in female dogs is a significant health concern that demands attention and proactive measures from pet owners and veterinary professionals alike. Understanding the nuances of this condition, including its signs, symptoms, diagnostic approaches, treatment modalities, and preventive strategies, is pivotal for advocating the well-being of our furry companions.
By recognizing the potential risk factors and being vigilant in observing the signs of mammary tumors, pet owners can play a crucial role in early detection and timely intervention. Regular veterinary check-ups, coupled with a nurturing and supportive environment, contribute to the holistic care of female dogs and enhance their resilience against this common health issue.
Furthermore, the integration of preventive measures, such as early spaying, healthy lifestyle practices, and attentive monitoring, empowers pet owners to mitigate the risk of breast cancer in their female dogs. Proactive veterinary care, compassionate support, and a balanced approach to canine well-being collectively contribute to fostering a fulfilling and healthy life for our beloved furry companions.
In essence, the journey of addressing breast cancer in female dogs encompasses knowledge, vigilance, and compassionate care. By embracing a comprehensive understanding of this condition and prioritizing preventive strategies and supportive measures, pet owners can champion the health and vitality of their female dogs, ultimately fostering a fulfilling and healthy life for our beloved canine companions.