Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Dogs Can Sniff Out Diabetes And Cancer


Common Health Issues
How Dogs Can Sniff Out Diabetes And Cancer
Published: January 30, 2024
Learn how dogs can detect diabetes and cancer, two common health issues, through their incredible sense of smell. Discover the amazing ways dogs are helping in early detection and treatment.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Dogs have long been recognized as man's best friend, offering companionship, loyalty, and unwavering support. However, their remarkable olfactory abilities have also positioned them as invaluable allies in the realm of healthcare. Canine scent detection, a fascinating field of study, explores the extraordinary capacity of dogs to sniff out various health conditions, including diabetes and cancer. This remarkable ability has sparked widespread interest and ongoing research, shedding light on the potential for dogs to contribute to early disease detection and medical diagnosis.
The olfactory system of dogs is truly remarkable, with an estimated 300 million scent receptors compared to a human's mere 5 to 6 million. This heightened sense of smell enables dogs to detect minute scent molecules, making them adept at identifying subtle changes in the body's chemistry. As a result, dogs have been trained to detect specific odors associated with various health conditions, paving the way for innovative applications in the field of healthcare.
In this article, we will delve into the captivating world of canine scent detection, exploring the science behind this phenomenon and shedding light on how dogs can detect diabetes and cancer. Additionally, we will uncover the intricate process of training dogs for scent detection, as well as the current and future applications of this remarkable ability in the realm of healthcare. Join us on this enlightening journey as we unravel the extraordinary capabilities of our canine companions and their potential to revolutionize the landscape of medical diagnostics.
Read more: When Can My Dog Go Out After Vaccinations
The Science Behind Canine Scent Detection
The olfactory prowess of dogs is a marvel of nature, rooted in their intricate and highly specialized olfactory system. At the core of this remarkable ability lies the canine nose, which is equipped with an extraordinary number of scent receptors, estimated to be around 300 million. In comparison, the human olfactory system pales in comparison, with a mere 5 to 6 million scent receptors. This stark contrast underscores the unparalleled sensitivity and acuity of a dog's sense of smell, allowing them to perceive odors at concentrations as low as parts per trillion.
The olfactory receptors in a dog's nose are intricately linked to the olfactory bulb in the brain, forming a complex network that processes and interprets scent information. When a dog inhales, scent molecules are captured by the olfactory receptors and transmitted to the olfactory bulb, where they are meticulously analyzed. This process enables dogs to discern an extensive array of scents, distinguishing between subtle variations and identifying specific odors with remarkable precision.
Moreover, the vomeronasal organ, also known as Jacobson's organ, further amplifies a dog's olfactory capabilities. This specialized organ is dedicated to detecting pheromones, chemical signals that convey vital information about an individual's health, reproductive status, and emotional state. By integrating information from both the olfactory receptors and the vomeronasal organ, dogs can perceive an intricate tapestry of scents, providing them with a comprehensive understanding of their olfactory environment.
The brain of a dog plays a pivotal role in processing and interpreting scent information, with specialized neural pathways dedicated to olfactory processing. This intricate neural architecture enables dogs to not only detect a diverse range of scents but also to associate specific odors with distinct outcomes or conditions. Through associative learning, dogs can link a particular scent with a specific action or response, a fundamental aspect of their remarkable scent detection abilities.
In essence, the science behind canine scent detection is a testament to the extraordinary biological adaptations that equip dogs with an unparalleled sense of smell. Their intricate olfactory system, coupled with specialized neural processing, endows them with the remarkable ability to detect subtle changes in scent, paving the way for their invaluable contributions to the realm of healthcare.
How Dogs Can Detect Diabetes
Dogs possess an astonishing ability to detect the subtle biochemical changes that occur in individuals with diabetes. This remarkable capability stems from their keen sense of smell and their aptitude for discerning specific odors associated with the condition. In individuals with diabetes, the body undergoes metabolic shifts that result in the production of distinct volatile organic compounds, which are emitted through breath, sweat, and urine. These unique scent molecules serve as telltale indicators of the presence of diabetes, and dogs have been trained to recognize and alert to these specific odors.
The scent associated with diabetes is attributed to the presence of compounds such as isoprene, acetone, and other volatile organic compounds that are elevated in individuals with the condition. These compounds emit a distinct odor that is imperceptible to humans but discernible to the highly sensitive olfactory receptors of dogs. Through rigorous training, dogs can learn to differentiate these scent molecules from the myriad of odors in their environment, enabling them to identify individuals with diabetes based on their unique scent profile.
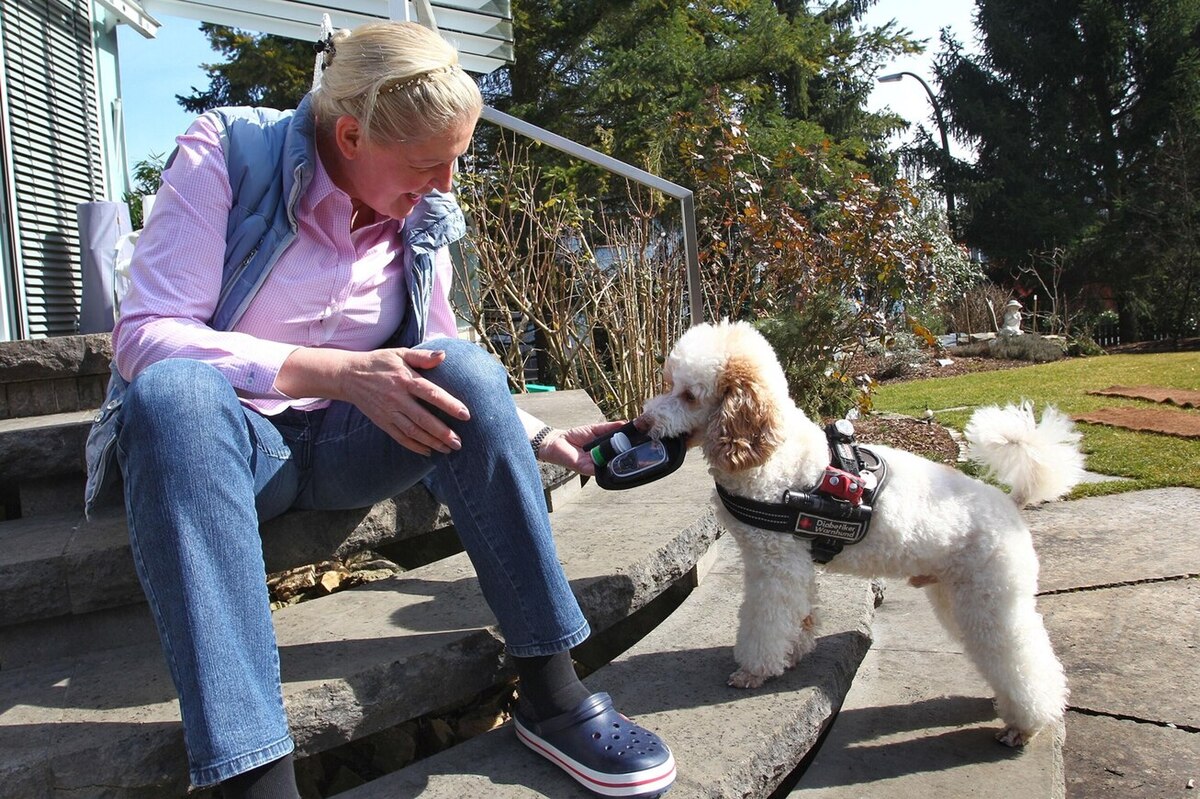
The process of training dogs for diabetes detection involves exposing them to scent samples from individuals with diabetes, allowing them to familiarize themselves with the characteristic odor associated with the condition. Through positive reinforcement and reward-based training methods, dogs learn to associate the scent of diabetes with a specific response, such as alerting their handler or exhibiting a trained behavior. This meticulous training equips dogs with the ability to reliably detect the scent of diabetes, paving the way for their invaluable role in alerting individuals to potential fluctuations in their blood sugar levels.
The potential applications of canine diabetes detection are far-reaching, offering a non-invasive and proactive approach to monitoring blood sugar levels. Dogs trained in diabetes detection can provide early alerts to individuals with diabetes, signaling fluctuations in their blood glucose levels before they reach critical thresholds. This early warning system empowers individuals to take timely measures to manage their condition, potentially averting medical emergencies and enhancing their overall well-being.
In essence, the ability of dogs to detect diabetes exemplifies the profound impact of their olfactory prowess in the realm of healthcare. Their remarkable sensitivity to scent enables them to serve as vigilant allies in the management of diabetes, offering a unique and invaluable contribution to the well-being of individuals living with this condition.
How Dogs Can Detect Cancer
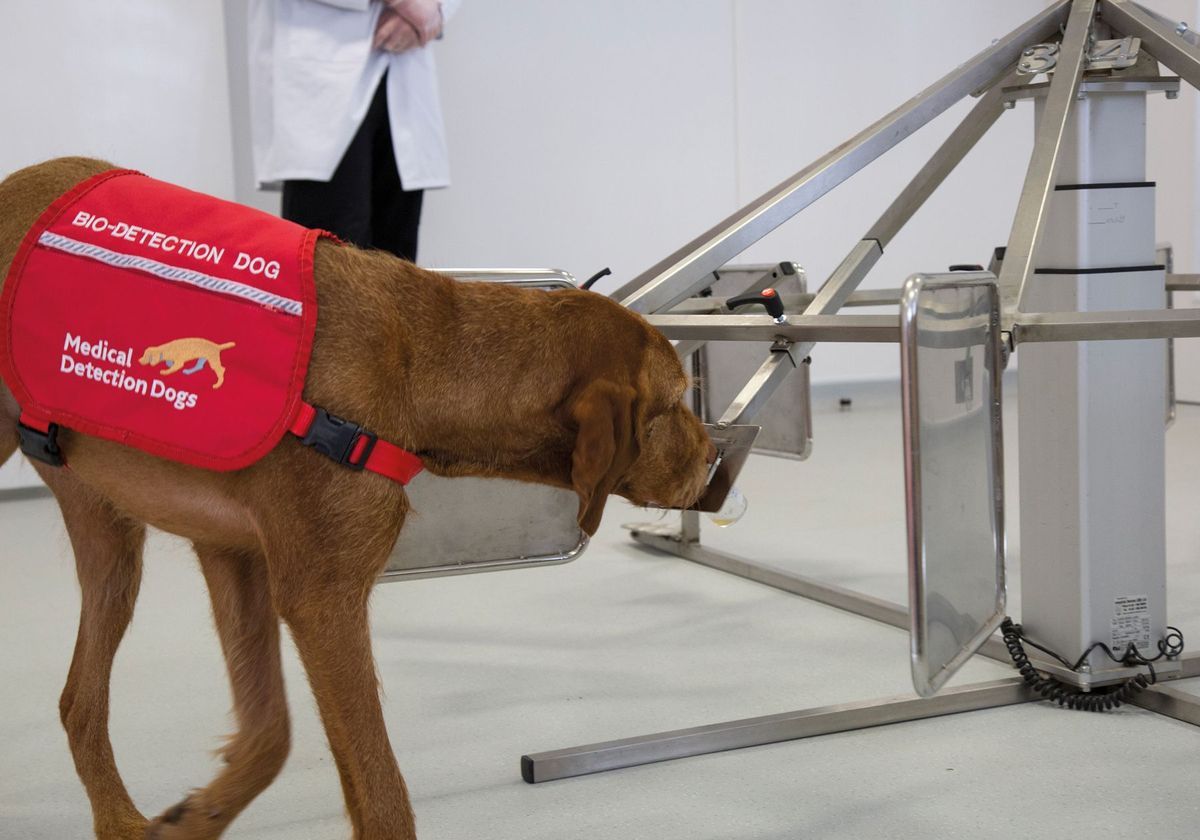
The remarkable olfactory abilities of dogs extend beyond diabetes detection, encompassing their extraordinary capacity to sniff out various types of cancer. This groundbreaking capability has sparked widespread interest and ongoing research, shedding light on the potential for dogs to contribute to early cancer detection and medical diagnosis.
Cancer cells emit unique volatile organic compounds that impart a distinct odor, undetectable to the human nose but discernible to the highly sensitive olfactory receptors of dogs. Through rigorous training and exposure to scent samples from individuals with cancer, dogs can learn to recognize and differentiate these specific odors from the myriad of scents in their environment. The process of training dogs for cancer detection involves positive reinforcement and reward-based methods, allowing them to associate the scent of cancer with a specific response, such as alerting their handler or exhibiting a trained behavior.
The scent associated with cancer varies depending on the type and stage of the disease, with different types of cancer emitting distinct odor profiles. Research has demonstrated that dogs can effectively detect various types of cancer, including lung, breast, prostate, colorectal, and skin cancer, among others. Their ability to discern these subtle scent differences underscores the remarkable precision of their olfactory capabilities and the potential for early cancer detection.
The implications of canine cancer detection are profound, offering a non-invasive and potentially cost-effective approach to cancer screening. Dogs trained in cancer detection have demonstrated the ability to identify cancerous samples with impressive accuracy, raising the prospect of their integration into cancer screening programs. Their role in providing early alerts to the presence of cancerous odors holds significant promise for enhancing early diagnosis and improving treatment outcomes for individuals affected by cancer.
Furthermore, the potential applications of canine cancer detection extend to areas where traditional diagnostic methods may be limited or inaccessible. In settings where advanced medical facilities are scarce, dogs trained in cancer detection could serve as invaluable allies in identifying potential cases of cancer, particularly in communities with limited access to conventional diagnostic technologies.
In essence, the ability of dogs to detect cancer exemplifies the transformative potential of their olfactory prowess in the realm of healthcare. Their remarkable sensitivity to scent positions them as invaluable allies in the early detection of cancer, offering a unique and promising avenue for improving cancer diagnosis and ultimately, the well-being of individuals affected by this complex disease.
Training Dogs for Scent Detection
Training dogs for scent detection is a meticulous and intricate process that harnesses their innate olfactory abilities to recognize specific odors associated with various health conditions. This specialized training equips dogs with the capability to detect subtle scent changes, paving the way for their invaluable contributions to healthcare, including the detection of diabetes and cancer.
The training process begins with exposing dogs to scent samples relevant to the targeted health condition, such as breath, sweat, or urine samples from individuals with diabetes or cancer. Through controlled exposure to these scent sources, dogs become familiar with the distinct odors associated with the respective conditions. Positive reinforcement and reward-based methods are integral to the training process, as dogs learn to associate the targeted scent with a specific response, such as alerting their handler or exhibiting a trained behavior.
Consistency and repetition play a crucial role in reinforcing the association between the targeted scent and the desired response. Training sessions are structured to gradually increase the complexity and specificity of the scent detection tasks, allowing dogs to refine their olfactory discrimination skills. As dogs demonstrate proficiency in identifying the targeted scent, they are rewarded, reinforcing their ability to recognize and alert to the specific odor.
Moreover, the training process incorporates rigorous scent discrimination exercises, where dogs learn to differentiate the targeted scent from a range of distractor odors. This aspect of training enhances the precision and reliability of their scent detection abilities, ensuring that they can discern the relevant odor amidst varying environmental scents.
Handlers and trainers play a pivotal role in guiding and shaping the dogs' scent detection capabilities, providing consistent cues and reinforcement to reinforce the desired behaviors. The bond between the dog and its handler is a critical component of the training process, fostering trust, communication, and collaboration essential for effective scent detection work.
The culmination of the training process is the deployment of dogs in real-world scenarios, where they apply their scent detection skills to identify individuals with diabetes or cancer based on their unique odor profiles. The ongoing refinement of their abilities through regular training and exposure to diverse scent sources further enhances their proficiency in detecting the targeted odors.
In essence, the training of dogs for scent detection represents a harmonious fusion of their innate olfactory prowess with structured learning and reinforcement, culminating in their remarkable ability to contribute to the early detection and management of various health conditions. This specialized training underscores the transformative potential of canine scent detection in the realm of healthcare, offering a non-invasive and proactive approach to disease detection and diagnosis.
Read more: What Can I Do For A Diabetic Dog
Current and Future Applications of Canine Scent Detection
The current and future applications of canine scent detection span a diverse array of healthcare domains, offering innovative solutions for early disease detection, medical diagnostics, and therapeutic support. The remarkable olfactory abilities of dogs have paved the way for their integration into various facets of healthcare, with ongoing research and exploration of their potential applications.
In the realm of disease detection, dogs trained in scent detection have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in identifying individuals with diabetes and various types of cancer based on their unique odor profiles. This capability holds significant promise for enhancing early diagnosis, enabling proactive interventions, and potentially improving treatment outcomes for individuals affected by these conditions. The non-invasive nature of canine scent detection positions it as a valuable complement to traditional diagnostic methods, offering a cost-effective and accessible approach to disease screening.
Furthermore, the potential applications of canine scent detection extend to areas such as public health surveillance, where dogs could be deployed to identify individuals infected with specific pathogens or diseases. Their ability to discern subtle changes in scent could contribute to the early detection of infectious diseases, potentially aiding in the containment and management of public health threats.
In the context of therapeutic support, dogs trained in scent detection have the potential to provide invaluable assistance to individuals managing chronic health conditions. Their ability to alert to fluctuations in blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes can serve as a proactive warning system, empowering individuals to take timely measures to manage their condition. Moreover, the emotional support and companionship offered by scent detection dogs can have a profound impact on the well-being of individuals navigating the complexities of chronic illness.
Looking ahead, the future applications of canine scent detection hold immense promise for advancing personalized medicine and precision healthcare. The integration of dogs into medical settings, diagnostic laboratories, and community health initiatives could revolutionize disease screening and early intervention strategies. Additionally, ongoing research endeavors seek to unravel the full potential of canine scent detection in identifying a broader spectrum of health conditions, including neurological disorders, infectious diseases, and metabolic imbalances.
The evolving landscape of canine scent detection is characterized by ongoing innovation, collaboration between researchers, healthcare professionals, and canine handlers, and a steadfast commitment to harnessing the remarkable capabilities of dogs for the betterment of human health. As research continues to unveil the multifaceted applications of canine scent detection, the potential for transformative impact in healthcare remains a compelling and promising frontier.
In essence, the current and future applications of canine scent detection represent a paradigm shift in healthcare, offering a harmonious convergence of cutting-edge science, compassionate support, and the unwavering loyalty of our canine companions. This remarkable synergy holds the potential to redefine disease detection, diagnosis, and therapeutic care, ushering in a new era of proactive and personalized healthcare interventions.