Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Long Can A Dog Live With Skin Cancer


Common Health Issues
How Long Can A Dog Live With Skin Cancer
Published: February 4, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs, including skin cancer. Discover how long a dog can live with skin cancer and how to manage this condition. Gain insights into prevention and treatment options.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Skin cancer is a concerning health issue that can affect our beloved canine companions. Just like humans, dogs are susceptible to developing various forms of cancer, including skin cancer. As responsible pet owners, it's crucial to be aware of the signs, treatment options, and prognosis associated with this condition. By understanding the nature of skin cancer in dogs, we can take proactive measures to ensure the well-being of our furry friends.
Skin cancer in dogs can manifest in different ways, ranging from benign growths to malignant tumors. While certain breeds may be predisposed to developing skin cancer, it's important to note that any dog, regardless of breed or age, can be affected. Therefore, staying informed about the potential risks and symptoms of skin cancer is essential for early detection and intervention.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of skin cancer in dogs, including its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis. Additionally, we will explore preventive measures that can help minimize the risk of skin cancer in our canine companions. By gaining a deeper understanding of this common health issue, we can equip ourselves with the knowledge needed to provide the best possible care for our furry friends.
Understanding the nuances of skin cancer in dogs is not only beneficial for identifying potential warning signs but also for promoting a proactive approach to their overall health. With the right information and awareness, we can take meaningful steps to safeguard our dogs against the impact of skin cancer and ensure that they lead happy, healthy lives.
Read more: How Long Can A Dog Live With Kidney Cancer
Understanding Skin Cancer in Dogs
Skin cancer in dogs encompasses a spectrum of conditions that affect the skin and underlying tissues. Just like in humans, skin cancer in dogs can arise from various factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Understanding the different types of skin cancer that can affect dogs is essential for recognizing potential warning signs and seeking timely veterinary care.
Types of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer in dogs can manifest in several forms, with some of the most common types including:
- Mast Cell Tumors: These are one of the most prevalent forms of skin cancer in dogs, often appearing as raised lumps on the skin. Mast cell tumors can vary in severity, and their behavior ranges from benign to aggressive.
- Melanoma: Similar to humans, dogs can develop melanoma, which originates from the pigment-producing cells in the skin. Melanomas can be benign or malignant and may occur in areas with little or no hair, such as the mouth, lips, and nail beds.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This type of skin cancer typically arises from the outer layer of the skin and is commonly associated with sun exposure. It can present as raised, crusty, or bleeding lesions, often found on areas with sparse hair coverage, such as the abdomen and groin.
Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of skin cancer in dogs. Breeds with light-colored or thin coats, as well as those with exposed skin areas, are more susceptible to the harmful effects of UV radiation. Additionally, prolonged sun exposure, especially in regions with intense sunlight, can increase the risk of skin cancer in dogs. Furthermore, genetic predisposition and immune system deficiencies can also play a role in the development of this condition.
Environmental Influences
Environmental factors, such as exposure to carcinogens and toxic substances, can also contribute to the onset of skin cancer in dogs. Contact with certain chemicals, including those found in herbicides, pesticides, and environmental pollutants, may elevate the risk of developing skin tumors. Moreover, chronic irritation or inflammation of the skin due to allergies or infections can potentially predispose dogs to the development of skin cancer.
By understanding the diverse nature of skin cancer in dogs, including its types, risk factors, and environmental influences, pet owners can become more attuned to the potential threats to their canine companions' skin health. This knowledge serves as a foundation for recognizing early signs of skin cancer and taking proactive measures to mitigate its impact on dogs' well-being.
Read more: How Long Does A Dog Live With Cancer
Symptoms of Skin Cancer in Dogs
Identifying the symptoms of skin cancer in dogs is crucial for early detection and prompt intervention. While the specific signs may vary depending on the type and location of the cancer, there are common indicators that pet owners should be vigilant about. By recognizing these symptoms, pet owners can seek veterinary care and explore appropriate treatment options to address the condition effectively.
Visible Skin Abnormalities
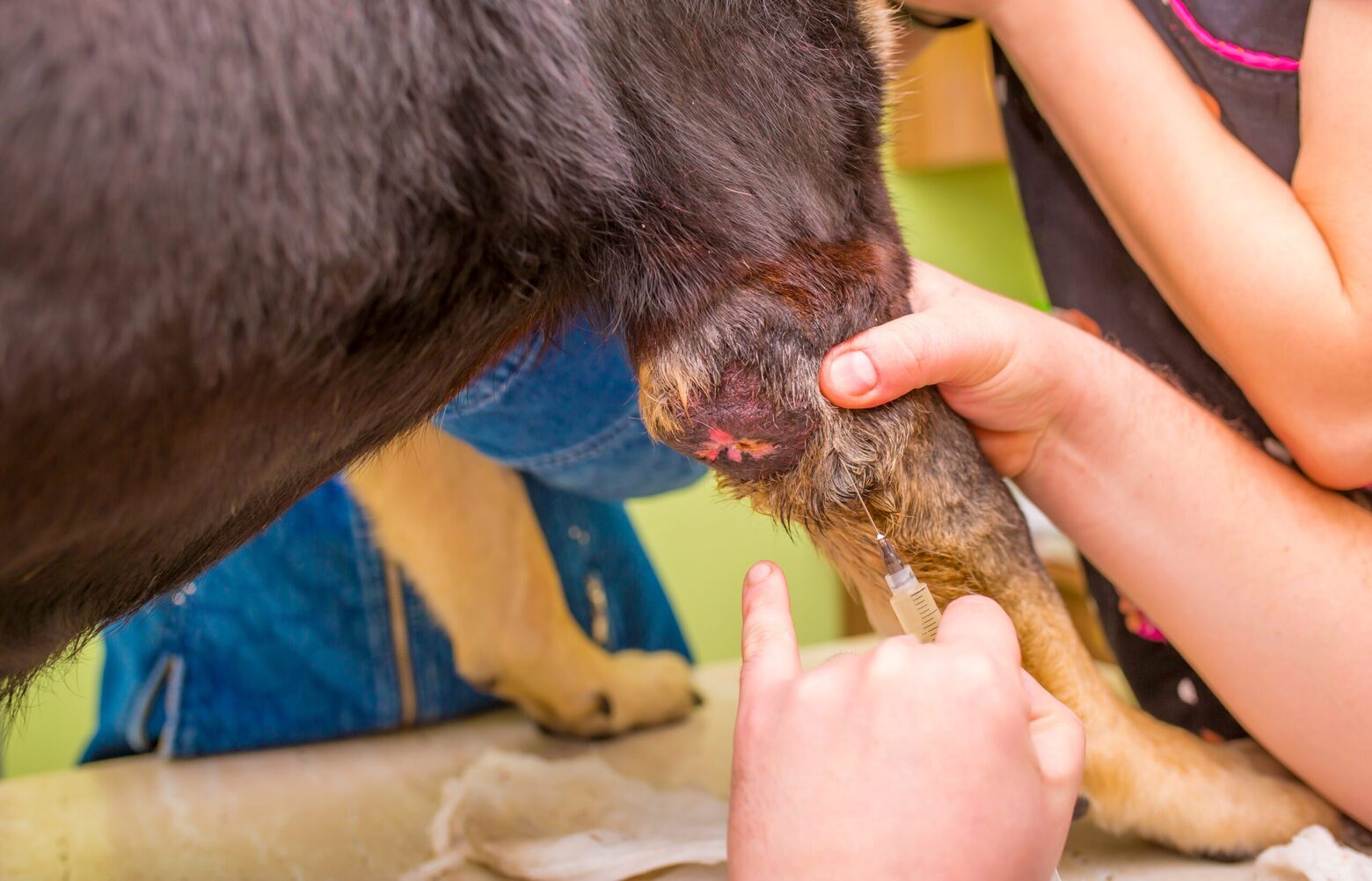
One of the primary symptoms of skin cancer in dogs is the presence of visible skin abnormalities. These may include lumps, bumps, or sores that do not heal or continue to grow. These abnormal growths can appear as raised or ulcerated lesions, and they may vary in size and color. Additionally, any changes in the color or texture of the skin, such as darkening or thickening, should be closely monitored as potential signs of skin cancer.
Skin Lesions and Irritation
Dogs with skin cancer may exhibit persistent irritation or discomfort in specific areas. This can manifest as excessive itching, licking, or biting at a particular spot on the skin. Skin lesions that appear inflamed, crusty, or prone to bleeding should be regarded as potential indicators of skin cancer. Furthermore, the presence of non-healing wounds or sores, especially in areas exposed to sunlight, warrants immediate attention from a veterinarian.
Hair Loss and Skin Discoloration
Unexplained hair loss or changes in the pigmentation of the skin can also signal the presence of skin cancer in dogs. Areas of the skin that lose hair or exhibit unusual discoloration, such as darkening or depigmentation, may indicate underlying malignancies. Pet owners should carefully monitor their dog's skin for any irregularities in hair growth patterns and color changes, as these can provide valuable insights into the presence of skin cancer.
Read more: How Long Can A Dog Live With Arthritis
Behavioral Changes
In some cases, dogs with skin cancer may display behavioral changes that reflect their discomfort or distress. This can include increased sensitivity or pain when specific areas of the skin are touched. Additionally, dogs may exhibit signs of lethargy, reluctance to move, or changes in their overall demeanor. These behavioral shifts can serve as subtle yet significant cues for pet owners to investigate potential skin cancer in their canine companions.
Systemic Symptoms
In advanced stages of skin cancer, dogs may experience systemic symptoms that extend beyond the skin. These can include weight loss, loss of appetite, and overall decline in health. It's essential for pet owners to be attentive to any changes in their dog's overall well-being, as these systemic symptoms can indicate the progression of skin cancer and its impact on the dog's health.
By being attuned to these symptoms of skin cancer in dogs, pet owners can actively monitor their canine companions' skin health and take proactive measures to address any concerning signs. Early detection and timely veterinary intervention are pivotal in managing skin cancer effectively and improving the prognosis for affected dogs.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing skin cancer in dogs involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses clinical evaluation, diagnostic tests, and histopathological examination. Upon observing potential symptoms of skin cancer in their canine companions, pet owners should promptly seek veterinary care to initiate the diagnostic process. Veterinarians employ various methods to confirm the presence of skin cancer and determine the most suitable treatment options for affected dogs.
Diagnostic Procedures
-
Physical Examination: The initial step in diagnosing skin cancer involves a thorough physical examination of the dog's skin. Veterinarians assess the size, location, and characteristics of any abnormal growths or lesions, and may also palpate the regional lymph nodes to evaluate for signs of metastasis.
-
Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA): To obtain a definitive diagnosis, veterinarians may perform FNA, a minimally invasive procedure that involves extracting cells from suspicious skin masses using a fine needle. These cells are then examined under a microscope to identify cancerous changes.
-
Biopsy: In cases where FNA results are inconclusive or further characterization of the tumor is required, a biopsy may be recommended. This involves surgically removing a sample of the abnormal tissue for histopathological analysis, which provides detailed insights into the type and aggressiveness of the cancer.
Treatment Modalities
-
Surgical Excision: For localized skin cancer, surgical excision is a common treatment approach. This involves removing the cancerous growth along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete eradication of the tumor. The extent of surgical excision depends on the type and stage of the skin cancer.
-
Radiation Therapy: In instances where surgical removal is challenging or when cancer cells have spread, radiation therapy may be employed. This targeted treatment modality aims to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors using high-energy radiation beams, while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
-
Chemotherapy: Certain types of skin cancer in dogs may necessitate chemotherapy, which involves administering anti-cancer medications to impede the growth and spread of malignant cells. Chemotherapy can be used as a primary treatment or in conjunction with surgery and radiation therapy, depending on the specific characteristics of the cancer.
-
Immunotherapy: Emerging as a promising avenue for treating skin cancer in dogs, immunotherapy harnesses the dog's immune system to recognize and combat cancer cells. This approach aims to bolster the immune response against cancer, potentially enhancing treatment outcomes and reducing the risk of recurrence.
-
Palliative Care: In cases where skin cancer is advanced and aggressive, palliative care focuses on alleviating pain and improving the dog's quality of life. This may involve pain management, wound care, and supportive measures to enhance comfort and well-being.
Multidisciplinary Approach
The diagnosis and treatment of skin cancer in dogs often involve a multidisciplinary approach, with collaboration between veterinarians, oncologists, and pathologists. This collaborative effort ensures that the most effective treatment strategies are tailored to the individual needs of each dog, taking into account factors such as the type of cancer, its stage, and the dog's overall health.
By leveraging a combination of diagnostic techniques and treatment modalities, veterinarians strive to provide comprehensive care for dogs affected by skin cancer. This integrated approach aims to optimize treatment outcomes, minimize the impact of the disease, and enhance the overall well-being of canine patients.
Prognosis and Life Expectancy
The prognosis for dogs diagnosed with skin cancer is influenced by various factors, including the type of cancer, its stage at the time of diagnosis, the effectiveness of treatment, and the overall health of the dog. Understanding the prognosis and potential life expectancy for dogs with skin cancer is essential for pet owners to make informed decisions regarding their canine companions' care and well-being.
The prognosis for skin cancer in dogs can vary widely based on the specific type of cancer and its behavior. Benign tumors, such as certain mast cell tumors, may have a favorable prognosis if they are identified and treated early. Conversely, malignant forms of skin cancer, including aggressive melanomas and squamous cell carcinomas, may present greater challenges in terms of prognosis and treatment outcomes.
In cases where skin cancer is detected in its early stages and promptly addressed through surgical excision or other targeted treatments, the prognosis for affected dogs may be relatively positive. By effectively removing the cancerous growth and preventing its spread, veterinarians can significantly improve the long-term outlook for these canine patients. Additionally, advancements in treatment modalities, such as radiation therapy and immunotherapy, have contributed to enhanced prognoses for certain types of skin cancer in dogs.
However, for more advanced or aggressive forms of skin cancer that have metastasized or infiltrated vital structures, the prognosis may be guarded. Metastatic skin cancer, characterized by the spread of cancer cells to distant organs or lymph nodes, poses significant challenges in terms of treatment and long-term prognosis. In such cases, the focus may shift towards palliative care aimed at maintaining the dog's comfort and quality of life.
The life expectancy of dogs diagnosed with skin cancer is intricately linked to the prognosis and the effectiveness of treatment. Dogs with benign or early-stage skin cancer that undergo successful treatment may continue to lead fulfilling lives with a near-normal life expectancy. Conversely, dogs with advanced or aggressive forms of skin cancer may experience a more guarded prognosis, with potential implications for their life expectancy.
It's important to note that each case of skin cancer in dogs is unique, and the prognosis should be evaluated in the context of the individual dog's health status and response to treatment. Regular monitoring, follow-up care, and proactive management are essential for optimizing the prognosis and enhancing the quality of life for dogs affected by skin cancer.
By gaining insights into the prognosis and potential life expectancy associated with skin cancer in dogs, pet owners can collaborate closely with veterinarians to develop tailored care plans that prioritize the well-being and longevity of their beloved canine companions. This proactive approach aims to maximize the positive outcomes and quality of life for dogs facing the challenges of skin cancer.
Tips for Preventing Skin Cancer in Dogs
Preventing skin cancer in dogs involves proactive measures aimed at minimizing their exposure to potential risk factors and promoting skin health. By implementing preventive strategies, pet owners can significantly reduce the likelihood of their canine companions developing skin cancer. Here are essential tips for preventing skin cancer in dogs:
-
Limit Sun Exposure: Minimize your dog's exposure to direct sunlight, especially during peak hours when UV radiation is most intense. Provide shaded areas and avoid prolonged outdoor activities, particularly for breeds with light-colored or thin coats that are more susceptible to sun damage.
-
Sunscreen for Dogs: Consider using pet-safe sunscreen on areas of your dog's skin that are prone to sun exposure, such as the nose, ears, and belly. Choose a sunscreen specifically formulated for dogs to protect their skin from harmful UV rays.
-
Regular Skin Checks: Conduct routine skin checks on your dog to monitor for any changes, lumps, or abnormalities. Early detection of skin irregularities can facilitate prompt veterinary evaluation and intervention, potentially preventing the progression of pre-cancerous or cancerous skin lesions.
-
Provide Adequate Shelter: Ensure that your dog has access to sheltered and shaded areas, especially during sunny weather. This helps minimize direct sun exposure and reduces the risk of sunburn and related skin damage.
-
Maintain a Healthy Diet: A balanced and nutritious diet plays a crucial role in supporting your dog's overall health, including their skin. Opt for high-quality dog food that provides essential nutrients, vitamins, and antioxidants to promote skin resilience and immune function.
-
Environmental Awareness: Be mindful of potential environmental carcinogens and toxins that your dog may encounter. Minimize their exposure to harmful chemicals, such as herbicides, pesticides, and pollutants, to reduce the risk of skin cancer development.
-
Regular Veterinary Visits: Schedule regular check-ups with your veterinarian to assess your dog's overall health, including their skin condition. Veterinarians can provide valuable guidance on skin care and recommend preventive measures tailored to your dog's specific needs.
-
Protective Clothing: Consider using protective clothing, such as lightweight dog shirts or vests, to shield your dog's skin from direct sunlight, especially during outdoor activities. This can be particularly beneficial for dogs with light-colored or thin coats.
-
Hydration and Cooling: Ensure that your dog stays well-hydrated and has access to fresh water, especially in warm weather. Additionally, provide cooling options, such as shaded areas and water sources, to prevent overheating and sun-related skin issues.
-
Breed-Specific Considerations: Be mindful of breed-specific vulnerabilities to skin cancer. Certain breeds, such as Dalmatians and Bull Terriers, may have a higher predisposition to specific types of skin cancer, necessitating tailored preventive measures and vigilance.
By incorporating these preventive tips into your dog's care routine, you can actively mitigate the risk of skin cancer and promote their skin health and overall well-being. Proactive measures, environmental awareness, and regular veterinary involvement are key components of a comprehensive approach to preventing skin cancer in dogs.
Read more: How Long Will A Dog Live With Heartworm?
Conclusion
In conclusion, skin cancer in dogs is a significant health concern that demands attention and proactive measures from pet owners. By understanding the diverse nature of skin cancer, including its types, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive strategies, pet owners can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their canine companions' skin health. The recognition of visible skin abnormalities, behavioral changes, and systemic symptoms serves as a crucial foundation for early detection and timely intervention.
The diagnostic process for skin cancer in dogs involves a multifaceted approach, encompassing physical examinations, diagnostic tests, and histopathological analysis. This comprehensive evaluation enables veterinarians to formulate tailored treatment plans that address the specific type and stage of the cancer, optimizing the prospects for successful outcomes. From surgical excision and radiation therapy to emerging modalities such as immunotherapy, the treatment landscape for skin cancer in dogs continues to evolve, offering new avenues for managing this condition effectively.
Understanding the prognosis and potential life expectancy associated with skin cancer in dogs empowers pet owners to make informed decisions regarding their canine companions' care. While early detection and targeted treatments can yield positive prognoses, advanced or aggressive forms of skin cancer may necessitate palliative care focused on enhancing the dog's comfort and quality of life.
Furthermore, preventive measures, such as limiting sun exposure, conducting regular skin checks, and providing adequate shelter, are instrumental in minimizing the risk of skin cancer in dogs. By integrating these preventive strategies into their daily routines, pet owners can proactively promote their dogs' skin health and reduce the likelihood of skin cancer development.
Ultimately, the well-being of dogs affected by skin cancer hinges on the collaborative efforts of pet owners and veterinary professionals. Regular veterinary visits, environmental awareness, and breed-specific considerations contribute to a holistic approach to skin cancer prevention and management. By prioritizing skin health and staying attuned to potential warning signs, pet owners can champion the proactive care and well-being of their beloved canine companions, ensuring that they lead fulfilling and healthy lives free from the burden of skin cancer.