Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Why Would A Dog Get Liver Cancer

Common Health Issues
Why Would A Dog Get Liver Cancer
Published: February 4, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs, including liver cancer. Discover the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Liver cancer, also known as hepatic neoplasia, is a concerning health issue that can affect our beloved canine companions. This condition occurs when abnormal cells within the liver multiply uncontrollably, leading to the formation of tumors. While the exact cause of liver cancer in dogs is not always clear, several factors can contribute to its development. Understanding the potential causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures is crucial for pet owners to ensure the well-being of their furry friends.
Liver cancer can be a distressing diagnosis for dog owners, as the liver plays a vital role in the body's metabolic processes, including detoxification, digestion, and nutrient storage. When cancerous cells invade this essential organ, it can disrupt its normal functions and pose serious health risks for the affected dog.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the various aspects of liver cancer in dogs, shedding light on the potential causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and preventive measures. By gaining a deeper understanding of this condition, pet owners can be better equipped to recognize the signs, seek timely veterinary care, and make informed decisions regarding their dog's health.
Throughout this article, we will explore the complexities of liver cancer in dogs, aiming to provide valuable insights that empower pet owners to navigate this challenging health issue with knowledge and confidence. From recognizing the subtle signs of liver cancer to exploring the available treatment options, our goal is to equip readers with the information they need to support their canine companions through this difficult journey.
As we embark on this exploration of liver cancer in dogs, it is important to approach the topic with empathy, awareness, and a commitment to promoting the well-being of our furry friends. By fostering a deeper understanding of this condition, we can work towards enhancing the quality of life for dogs affected by liver cancer and supporting their human companions through this challenging experience.
Causes of Liver Cancer in Dogs
Liver cancer in dogs can arise from various factors, although the precise cause of this condition is not always straightforward. Understanding the potential triggers for hepatic neoplasia is essential for pet owners seeking to safeguard their canine companions' health. While the exact origins of liver cancer in dogs may vary, several common factors have been identified as potential contributors to the development of this serious condition.
-
Genetic Predisposition: Certain breeds may have a genetic predisposition to liver cancer. While any dog can develop this condition, certain breeds, such as the Labrador Retriever, Cocker Spaniel, and Doberman Pinscher, may have a higher susceptibility to hepatic neoplasia.
-
Environmental Toxins: Exposure to environmental toxins and carcinogens can pose a significant risk to a dog's liver health. Substances such as pesticides, herbicides, and industrial chemicals may contribute to the development of liver cancer in dogs, emphasizing the importance of minimizing a dog's exposure to harmful environmental agents.
-
Chronic Inflammation: Persistent inflammation within the liver, often resulting from conditions such as chronic hepatitis or long-term exposure to certain toxins, can increase the likelihood of cancerous growths. Chronic inflammation creates an environment conducive to the proliferation of abnormal cells, potentially leading to the formation of tumors within the liver.
-
Infectious Agents: Certain infectious agents, such as the canine hepatitis virus, have been associated with an increased risk of liver cancer in dogs. These pathogens can instigate chronic liver inflammation, paving the way for the development of cancerous lesions over time.
-
Age and Hormonal Factors: As dogs age, their susceptibility to various health conditions, including liver cancer, may increase. Additionally, hormonal imbalances or disruptions can impact the liver's cellular environment, potentially contributing to the development of cancerous growths.
-
Diet and Nutrition: While the direct link between diet and liver cancer in dogs is not fully elucidated, poor nutrition and dietary imbalances can impact overall health, potentially influencing the risk of developing hepatic neoplasia.
By recognizing these potential causes of liver cancer in dogs, pet owners can take proactive measures to minimize risk factors and prioritize their canine companions' liver health. Through a combination of responsible breeding practices, environmental awareness, preventive healthcare, and attentive monitoring, pet owners can play a pivotal role in mitigating the potential causes of liver cancer in their beloved dogs.
Symptoms of Liver Cancer in Dogs
Identifying the symptoms of liver cancer in dogs is crucial for timely intervention and effective management of this serious health condition. While the signs of liver cancer can initially be subtle, vigilant pet owners can play a pivotal role in recognizing potential indicators of hepatic neoplasia. Understanding the manifestations of liver cancer in dogs empowers pet owners to seek prompt veterinary care, facilitating early diagnosis and tailored treatment plans to support their canine companions' well-being.
The symptoms of liver cancer in dogs can manifest in various ways, reflecting the impact of cancerous growths on the liver's functions and the overall health of the affected dog. These signs may include:
-
Jaundice: One of the hallmark symptoms of liver cancer in dogs is jaundice, characterized by a yellowing of the skin, gums, and whites of the eyes. This discoloration occurs due to the buildup of bilirubin, a pigment produced by the liver, and can serve as a visible indicator of liver dysfunction.
-
Lethargy and Weakness: Dogs with liver cancer may exhibit increased lethargy, weakness, and a reluctance to engage in physical activities. The presence of cancerous growths can disrupt the liver's ability to maintain energy levels, leading to a noticeable decline in the affected dog's overall vitality.
-
Loss of Appetite and Weight Loss: Liver cancer can impact a dog's appetite, resulting in a decreased interest in food and subsequent weight loss. Changes in eating habits, accompanied by unexplained weight loss, can signal underlying health issues, including liver cancer.
-
Abdominal Distension: As liver tumors grow, they can cause abdominal distension or swelling. This physical manifestation may be observable through a visibly enlarged abdomen, signaling the presence of cancerous growths within the liver.
-
Vomiting and Diarrhea: Dogs with liver cancer may experience gastrointestinal disturbances, such as recurrent vomiting and diarrhea. These symptoms can stem from the liver's compromised ability to regulate digestive processes, leading to digestive discomfort and irregularities.
-
Increased Thirst and Urination: Liver cancer can affect a dog's urinary habits, resulting in increased thirst and urination. These changes may indicate the impact of liver dysfunction on the body's fluid balance and metabolic processes.
-
Behavioral Changes: Dogs with liver cancer may exhibit alterations in behavior, such as irritability, restlessness, or disorientation. These changes can stem from the physiological effects of liver cancer on the dog's overall well-being and neurological function.
Recognizing these symptoms of liver cancer in dogs empowers pet owners to promptly seek veterinary evaluation and diagnostic testing. By remaining attentive to their dog's well-being and promptly addressing concerning symptoms, pet owners can facilitate early detection and intervention, optimizing the prospects for effective treatment and supportive care for their beloved canine companions.
Diagnosing Liver Cancer in Dogs
Diagnosing liver cancer in dogs requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses clinical evaluation, diagnostic testing, and imaging studies to ascertain the presence of cancerous growths within the liver. Given the subtle nature of early symptoms and the intricate nature of hepatic neoplasia, veterinary professionals employ a range of diagnostic modalities to achieve an accurate assessment and formulate tailored treatment plans for affected dogs.
Diagnostic Procedures
Blood Tests
Blood tests, including liver function panels and complete blood counts, provide valuable insights into the dog's overall health and the liver's functional status. Abnormalities in liver enzymes, such as elevated levels of alkaline phosphatase and alanine transaminase, can indicate liver dysfunction and raise suspicion of underlying pathology, including liver cancer.
Imaging Studies
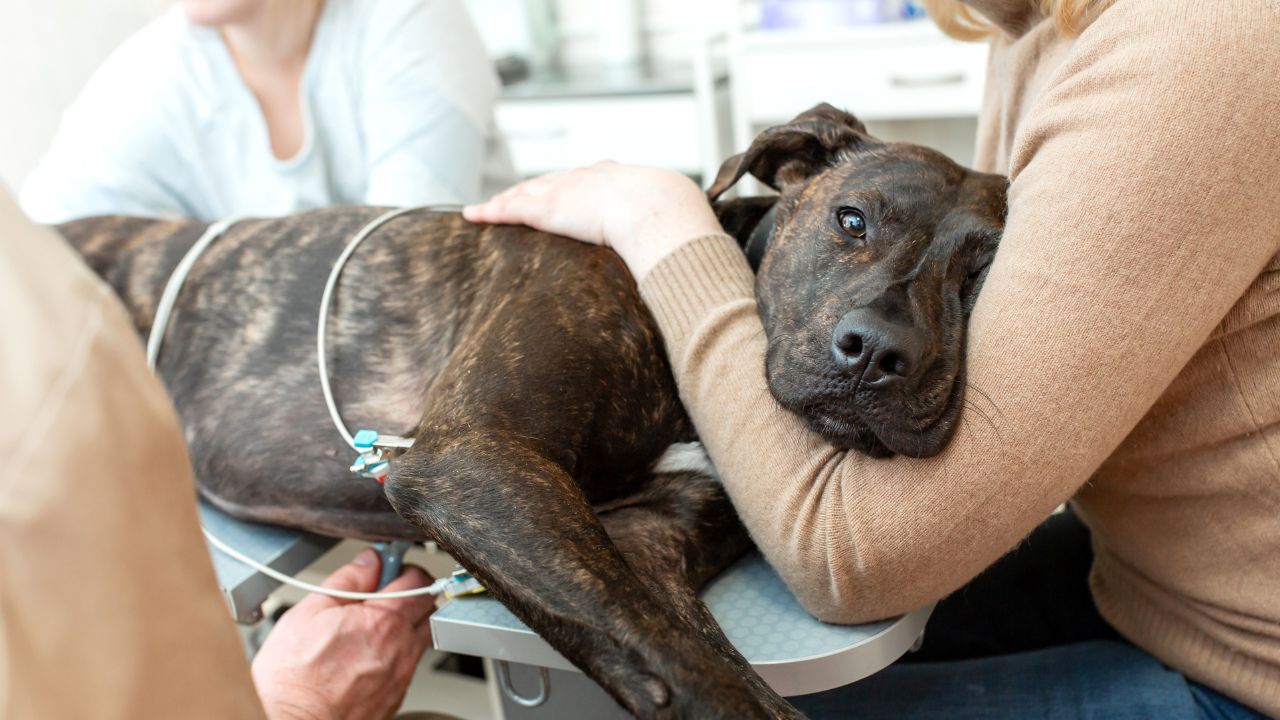
Imaging techniques, such as ultrasound, radiography, and advanced modalities like computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), play a pivotal role in visualizing the liver and detecting potential tumors. These non-invasive methods enable veterinarians to assess the size, location, and characteristics of liver masses, facilitating the diagnostic process and guiding subsequent interventions.
Fine Needle Aspiration
Fine needle aspiration involves the collection of tissue samples from liver masses using a thin needle, allowing for microscopic examination of the cells. This procedure, often guided by ultrasound or CT imaging, aids in confirming the presence of cancerous cells within the liver and determining the nature of the tumors, contributing to an accurate diagnosis.
Biopsy
In cases where fine needle aspiration yields inconclusive results, a liver biopsy may be recommended to obtain larger tissue samples for histopathological analysis. This invasive procedure involves the surgical extraction of liver tissue for detailed examination, providing crucial insights into the nature and extent of the liver lesions.
Read more: My Dog Has Cancer: What CBD Oil Would Help
Differential Diagnoses
Given the diverse range of liver conditions that can manifest with similar symptoms, differential diagnoses are essential to rule out other potential causes of the observed clinical signs. Conditions such as hepatitis, hepatic lipidosis, and benign liver tumors may present overlapping symptoms, emphasizing the need for thorough diagnostic evaluation to differentiate liver cancer from other liver-related disorders.
Veterinary Consultation
The process of diagnosing liver cancer in dogs necessitates close collaboration between pet owners and veterinary professionals. Through open communication and a shared commitment to the dog's well-being, pet owners can actively participate in the diagnostic process, providing valuable insights into the dog's medical history, observed symptoms, and overall health status, thereby contributing to a comprehensive diagnostic approach.
By employing a multifaceted diagnostic strategy that integrates clinical assessment, laboratory tests, imaging studies, and histopathological analyses, veterinary professionals can effectively diagnose liver cancer in dogs, laying the foundation for tailored treatment plans and supportive care to address this challenging health condition. Early and accurate diagnosis is pivotal in initiating timely interventions and optimizing the prospects for managing liver cancer in affected dogs, underscoring the significance of a thorough and meticulous diagnostic approach.
Treatment Options for Liver Cancer in Dogs
The treatment of liver cancer in dogs necessitates a comprehensive and individualized approach, tailored to the specific characteristics of the cancerous growths, the dog's overall health, and the extent of the disease. While the management of liver cancer in dogs can present challenges, various treatment modalities and supportive measures are available to address this complex health condition and optimize the well-being of affected canine companions.
Surgical Intervention
Surgical resection, aimed at removing cancerous tumors from the liver, represents a primary treatment option for localized liver cancer in dogs. In cases where the tumors are confined to specific regions of the liver and have not metastasized, surgical removal can offer the potential for disease control and prolonged survival. However, the feasibility of surgical intervention depends on factors such as the size, location, and number of liver tumors, as well as the dog's overall health status.
Read more: How Dogs Get Brain Cancer
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy, either as a standalone treatment or in conjunction with surgical resection, may be employed to target cancerous cells within the liver and mitigate the progression of the disease. While chemotherapy in dogs aims to minimize adverse effects and enhance quality of life, it can play a valuable role in managing liver cancer by impeding the growth of cancerous tumors and addressing potential metastatic spread.
Palliative Care
In cases where curative treatment options are not feasible or where the cancer has advanced significantly, palliative care focuses on alleviating symptoms, enhancing comfort, and maintaining the dog's quality of life. Palliative measures, including pain management, nutritional support, and supportive therapies, aim to mitigate discomfort and optimize the well-being of dogs affected by advanced liver cancer.
Interventional Radiology
Interventional radiology techniques, such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) or radiofrequency ablation (RFA), may be considered as adjunctive treatments for liver cancer in dogs. These minimally invasive procedures target cancerous lesions within the liver, offering localized therapy to manage the disease while minimizing the impact on the surrounding healthy liver tissue.
Supportive Therapies
Supportive care, encompassing measures such as dietary management, nutritional support, and pain alleviation, plays a crucial role in enhancing the overall well-being of dogs undergoing treatment for liver cancer. By addressing the dog's nutritional needs, managing potential side effects of treatment, and promoting physical comfort, supportive therapies contribute to a holistic approach to managing liver cancer in dogs.
Read more: Why Do Most Dogs Die Of Cancer
Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-Up
Following the initiation of treatment, ongoing monitoring and follow-up evaluations are essential to assess the dog's response to therapy, monitor disease progression, and adjust treatment plans as necessary. Regular veterinary consultations, imaging studies, and laboratory tests enable veterinarians to track the dog's health status and make informed decisions regarding the management of liver cancer.
By integrating these treatment options and supportive measures, veterinary professionals strive to address liver cancer in dogs with a comprehensive and compassionate approach, aiming to optimize the well-being and quality of life of affected canine companions. Through a combination of targeted therapies, palliative care, and ongoing support, the management of liver cancer in dogs seeks to mitigate the impact of this challenging health condition and promote the best possible outcomes for dogs and their human companions.
Prevention of Liver Cancer in Dogs
Preventing liver cancer in dogs encompasses proactive measures aimed at minimizing potential risk factors and promoting overall liver health. While the development of liver cancer can be influenced by various factors, including genetic predisposition and environmental exposures, pet owners can play a pivotal role in mitigating these risks and safeguarding their canine companions' well-being. By prioritizing preventive strategies and fostering a liver-friendly environment, pet owners can contribute to reducing the likelihood of liver cancer in dogs.
Responsible Breeding Practices
Responsible breeding practices, including genetic screening and selection, can help mitigate the risk of inherited predispositions to liver cancer in certain dog breeds. By working with reputable breeders and prioritizing genetic health in breeding programs, pet owners can contribute to reducing the prevalence of genetic factors associated with liver cancer.
Environmental Awareness
Minimizing a dog's exposure to environmental toxins and carcinogens is essential for liver cancer prevention. This includes avoiding contact with potentially harmful substances such as pesticides, herbicides, and industrial chemicals. Creating a safe and toxin-free living environment for dogs can significantly reduce the risk of liver cancer associated with environmental exposures.
Read more: Why Hypercalcemia Indicates Cancer In Dogs
Nutritional Support
Providing a balanced and nutritious diet is fundamental to supporting overall liver health in dogs. High-quality, well-balanced meals tailored to a dog's specific nutritional needs can contribute to optimal liver function and bolster the body's natural defenses against potential health challenges, including liver cancer.
Regular Veterinary Care
Routine veterinary check-ups and preventive care play a crucial role in monitoring a dog's overall health, including liver function. By adhering to recommended vaccination schedules, parasite control, and wellness examinations, pet owners can proactively address potential health concerns and detect early signs of liver abnormalities, contributing to timely intervention and disease prevention.
Exercise and Weight Management
Regular exercise and weight management are integral components of maintaining a dog's overall health and well-being. Obesity and sedentary lifestyles can impact liver function and contribute to various health issues, including liver cancer. By promoting physical activity and managing a healthy weight, pet owners can support their dogs' liver health and reduce the risk of associated complications.
Health Monitoring
Vigilant monitoring of a dog's health, including the prompt recognition of potential symptoms and behavioral changes, enables pet owners to seek timely veterinary care and diagnostic evaluation. By staying attuned to their dog's well-being and promptly addressing any concerning signs, pet owners can facilitate early detection and intervention, potentially mitigating the progression of liver cancer.
By embracing these preventive strategies and prioritizing proactive measures, pet owners can contribute to fostering a liver-friendly environment for their canine companions, reducing potential risk factors, and promoting overall liver health. Through a proactive and attentive approach to preventive care, pet owners can work towards minimizing the likelihood of liver cancer in dogs and supporting their beloved companions' long-term well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the complexities of liver cancer in dogs underscore the significance of proactive awareness, early detection, and comprehensive care to support the well-being of our beloved canine companions. From understanding the potential causes and symptoms to navigating the diagnostic process and exploring treatment options, the journey of addressing liver cancer in dogs demands a multifaceted approach rooted in empathy, knowledge, and a commitment to promoting the best possible outcomes for affected dogs.
As pet owners, our dedication to fostering a liver-friendly environment, prioritizing preventive measures, and remaining vigilant to potential signs of liver cancer empowers us to play a pivotal role in safeguarding our dogs' health. By embracing responsible breeding practices, environmental awareness, and nutritional support, we can contribute to mitigating potential risk factors and promoting optimal liver function in our canine companions.
The recognition of symptoms such as jaundice, lethargy, and changes in appetite serves as a crucial foundation for seeking timely veterinary care and diagnostic evaluation. Through open communication and collaboration with veterinary professionals, we can navigate the diagnostic process, enabling early detection and tailored treatment plans to address liver cancer in dogs with diligence and compassion.
The treatment journey for liver cancer in dogs encompasses a spectrum of options, including surgical intervention, chemotherapy, palliative care, and ongoing monitoring, each aimed at optimizing the well-being and quality of life of affected dogs. By embracing these treatment modalities and supportive measures, we strive to mitigate the impact of liver cancer and provide compassionate care for our canine companions throughout their journey.
Furthermore, the proactive integration of preventive strategies, including regular veterinary care, exercise, and weight management, contributes to fostering a liver-friendly environment for our dogs, reducing potential risk factors, and promoting overall liver health. Through these proactive measures, we work towards minimizing the likelihood of liver cancer and supporting the long-term well-being of our beloved companions.
In essence, the journey of addressing liver cancer in dogs is one that calls for empathy, awareness, and a steadfast commitment to promoting the best possible outcomes for our furry friends. By embracing a holistic approach rooted in preventive care, early detection, and comprehensive treatment, we can navigate the complexities of liver cancer in dogs with dedication and compassion, striving to enhance the quality of life for our canine companions and support them through this challenging experience.










