Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Muscular and Joint Health>What Is The Injectable Drug For Dogs With Arthritis?


Muscular and Joint Health
What Is The Injectable Drug For Dogs With Arthritis?
Modified: February 21, 2024
Discover the best injectable drug for dogs with arthritis to support their muscular and joint health. Learn about effective treatments for canine arthritis.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Arthritis is a common condition that affects dogs of all ages and breeds. It is characterized by inflammation and stiffness in the joints, leading to pain and discomfort for our beloved canine companions. As pet owners, witnessing our furry friends struggle with mobility issues can be heart-wrenching. Fortunately, advancements in veterinary medicine have led to the development of injectable drugs that can provide relief and improve the quality of life for dogs suffering from arthritis.
In this article, we will delve into the world of injectable drugs for dogs with arthritis, exploring the various options available, their benefits, potential side effects, and the proper administration of these medications. By gaining a deeper understanding of these injectable drugs, pet owners can make informed decisions in collaboration with their veterinarians to ensure the well-being of their canine companions.
Armed with this knowledge, you will be better equipped to navigate the journey of managing arthritis in dogs, offering them the care and support they need to lead happy, active lives. Let's embark on this enlightening exploration of injectable drugs for arthritis in dogs, uncovering the valuable insights that will empower you as a responsible and caring pet owner.
Understanding Arthritis in Dogs
Arthritis, also known as osteoarthritis or degenerative joint disease, is a prevalent condition that affects dogs, particularly as they age. This debilitating ailment can also manifest in younger dogs due to genetic predispositions, joint injuries, or developmental issues. The hallmark of arthritis is the progressive degeneration of the cartilage within the joints, leading to inflammation, pain, and reduced mobility.
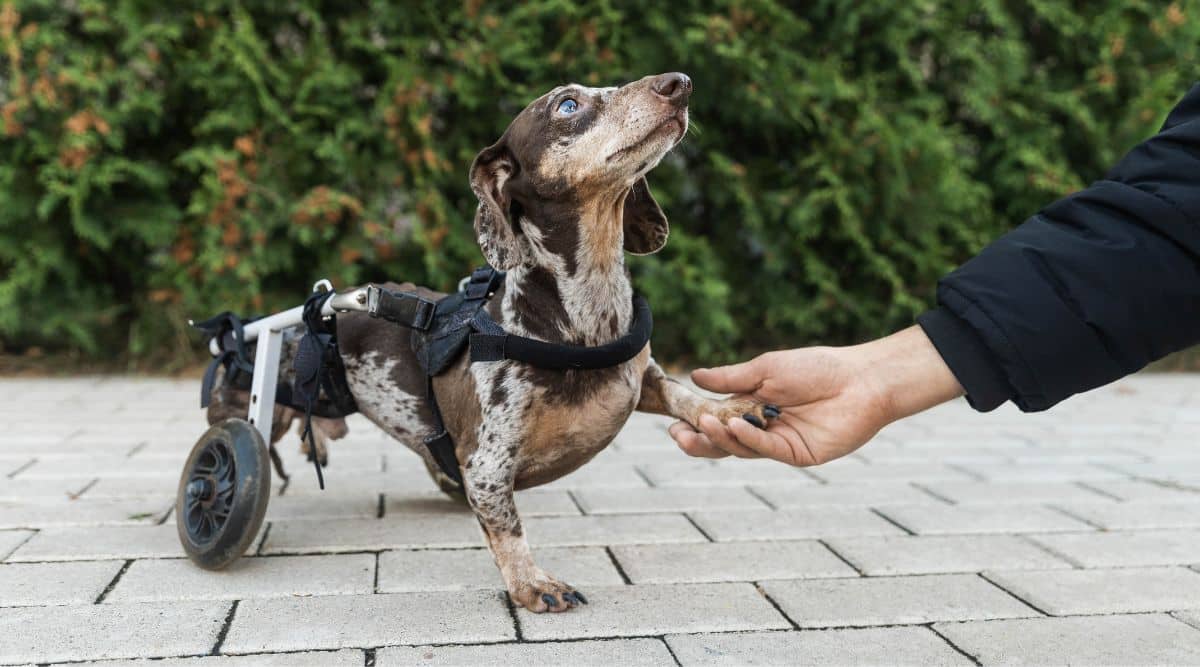
The most commonly affected joints in dogs with arthritis include the hips, elbows, knees, and shoulders. As the cartilage deteriorates, the bones within the joint may begin to rub against each other, causing discomfort and limiting the dog's ability to move freely. This can result in stiffness, lameness, and difficulty performing everyday activities such as walking, running, and climbing stairs.
Recognizing the signs of arthritis in dogs is crucial for early intervention and effective management. Common symptoms include reluctance to engage in physical activities, limping, stiffness after rest, decreased muscle mass, and behavioral changes such as irritability or withdrawal. Additionally, some dogs may exhibit signs of pain when their affected joints are touched or manipulated.
It's important to note that arthritis can significantly impact a dog's overall well-being, affecting not only their physical health but also their emotional and mental state. The chronic pain and discomfort associated with arthritis can lead to a diminished quality of life, potentially causing frustration and anxiety for the affected dogs.
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of arthritis in dogs empowers pet owners to proactively seek appropriate treatment and support for their furry companions. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of arthritis, pet owners can collaborate with veterinarians to implement comprehensive care plans tailored to their dog's specific needs. This may involve a combination of medication, lifestyle modifications, weight management, and physical therapy to alleviate pain and improve joint function.
In the next sections, we will explore the injectable drug options available for managing arthritis in dogs, shedding light on their benefits, potential side effects, and proper administration. This comprehensive understanding will equip pet owners with the knowledge to make informed decisions and provide the best possible care for their canine companions.
Injectable Drug Options for Arthritis in Dogs
When it comes to managing arthritis in dogs, injectable drugs offer a valuable treatment option that can significantly alleviate pain and improve joint function. These medications are designed to target the underlying inflammation and provide relief for dogs suffering from arthritis. Let's explore some of the commonly used injectable drug options for arthritis in dogs:
1. Adequan:
Adequan, also known as polysulfated glycosaminoglycan, is a popular injectable medication used to treat arthritis in dogs. It works by promoting the repair of damaged cartilage and inhibiting the enzymes responsible for cartilage breakdown. Adequan is administered as a series of injections, typically given twice weekly for a period of four to eight weeks, followed by maintenance injections as prescribed by the veterinarian. This medication has been shown to improve joint lubrication and reduce inflammation, leading to enhanced mobility and reduced pain in arthritic dogs.
2. Legend:
Legend, or hyaluronate sodium, is another injectable drug that has been beneficial in managing arthritis in dogs. It functions by supplementing the natural synovial fluid within the joints, thereby enhancing joint lubrication and reducing friction between the cartilage surfaces. Legend injections are administered directly into the affected joint, providing targeted relief and promoting improved joint mobility. This medication is often recommended for dogs with degenerative joint disease and has been found to alleviate discomfort and support joint health.
Read more: What To Do For Dog’s Hip Arthritis
3. Corticosteroids:
Corticosteroids, such as methylprednisolone or triamcinolone, are potent anti-inflammatory drugs that can be administered via injection to alleviate the symptoms of arthritis in dogs. These medications work by suppressing the inflammatory response within the joints, thereby reducing swelling and pain. While corticosteroid injections can provide rapid relief for arthritic dogs, they are typically used judiciously due to the potential for side effects with long-term use. Veterinarians carefully assess the individual needs of each dog before recommending corticosteroid injections as part of their arthritis management plan.
4. Polysulfated Glycosaminoglycans (PSGAGs):
Polysulfated glycosaminoglycans, similar to Adequan, are injectable drugs that target the underlying mechanisms of arthritis in dogs. These medications work by promoting cartilage repair and reducing inflammation within the joints. PSGAG injections have been shown to enhance joint lubrication and slow down the progression of arthritis, offering long-term benefits for dogs struggling with joint pain and stiffness.
5. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy:
Platelet-rich plasma therapy involves the extraction and concentration of platelets from the dog's own blood, which are then injected into the affected joints. This innovative approach harnesses the regenerative properties of platelets to promote tissue repair and reduce inflammation within the arthritic joints. PRP therapy has gained attention for its potential in supporting joint health and improving mobility in dogs with arthritis.
These injectable drug options represent a diverse range of treatments that can be tailored to meet the specific needs of dogs with arthritis. By working closely with veterinarians, pet owners can explore the most suitable injectable drug options for their canine companions, taking into account factors such as the dog's age, overall health, and the severity of arthritis. With the right treatment approach, injectable drugs can play a pivotal role in enhancing the well-being of dogs struggling with arthritis, allowing them to enjoy a more comfortable and active lifestyle.
Benefits of Injectable Drugs for Arthritis in Dogs
Injectable drugs for arthritis in dogs offer a multitude of benefits that contribute to the overall well-being and quality of life of our canine companions. These medications are specifically formulated to target the underlying causes of arthritis and provide targeted relief, addressing the pain, inflammation, and mobility issues associated with this debilitating condition.
One of the primary advantages of injectable drugs is their ability to directly deliver therapeutic agents to the affected joints, ensuring localized treatment and minimizing systemic side effects. By administering these medications via injection, veterinarians can precisely target the inflamed or degenerated joints, maximizing the efficacy of the treatment while minimizing the potential impact on other bodily systems.
Furthermore, injectable drugs for arthritis in dogs have been shown to promote cartilage repair and enhance joint lubrication, leading to improved mobility and reduced discomfort. These medications work to mitigate the progressive degeneration of the cartilage within the joints, thereby slowing down the advancement of arthritis and supporting joint health over the long term.
In addition to their therapeutic effects, injectable drugs offer convenience and ease of administration for pet owners and veterinarians alike. The controlled delivery of medication through injections allows for precise dosing and scheduling, ensuring that the dog receives the necessary treatment at the appropriate intervals. This streamlined approach to medication administration simplifies the management of arthritis in dogs, providing a structured and consistent treatment regimen.
Moreover, many injectable drugs for arthritis in dogs have demonstrated a favorable safety profile when used as directed by veterinarians. With proper monitoring and adherence to prescribed protocols, these medications can offer relief without compromising the overall health of the dog. This balance between efficacy and safety is a crucial consideration in the selection of treatment options for arthritic dogs, providing reassurance for pet owners and veterinarians alike.
Another notable benefit of injectable drugs is their potential to complement other components of a comprehensive arthritis management plan. When integrated with strategies such as weight management, physical therapy, and dietary supplements, injectable medications can contribute to a holistic approach to supporting joint health and alleviating the symptoms of arthritis in dogs.
By harnessing the therapeutic benefits of injectable drugs, pet owners can play a proactive role in enhancing the comfort and mobility of their arthritic dogs. These medications offer a valuable tool in the arsenal of treatments available for managing arthritis, empowering pet owners to provide the best possible care for their beloved canine companions.
In the next sections, we will delve into the potential side effects of injectable drugs for arthritis in dogs and explore the proper administration of these medications, equipping pet owners with comprehensive knowledge to make informed decisions in collaboration with their veterinarians.
Potential Side Effects of Injectable Drugs for Arthritis in Dogs
While injectable drugs for arthritis in dogs offer valuable therapeutic benefits, it is essential for pet owners to be aware of the potential side effects associated with these medications. Understanding the possible adverse reactions can empower pet owners to monitor their dogs closely and collaborate effectively with veterinarians to ensure the safe and effective use of injectable drugs for arthritis.
-
Injection Site Reactions: One of the most common side effects of injectable drugs is the possibility of localized reactions at the site of injection. This may include redness, swelling, or discomfort at the injection site. Pet owners should carefully observe the injection sites following administration and promptly report any unusual reactions to their veterinarians.
-
Gastrointestinal Upset: Some injectable medications, particularly non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may pose a risk of gastrointestinal disturbances in dogs. This can manifest as vomiting, diarrhea, or decreased appetite. Monitoring the dog's digestive health and reporting any signs of gastrointestinal upset to the veterinarian is crucial for timely intervention.
-
Allergic Reactions: Dogs may exhibit allergic reactions to certain injectable drugs, presenting symptoms such as itching, hives, facial swelling, or difficulty breathing. While allergic reactions are relatively rare, pet owners should be vigilant and seek immediate veterinary attention if their dogs display any signs of an allergic response.
-
Liver or Kidney Effects: Some injectable medications, particularly those that are metabolized by the liver or excreted by the kidneys, may pose a risk of adverse effects on these vital organs. Regular monitoring of liver and kidney function through blood tests is essential to detect any potential complications early on.
-
Systemic Effects: In some cases, injectable drugs may exert systemic effects beyond the targeted joints, impacting other physiological systems in the dog's body. This underscores the importance of close monitoring by veterinarians to assess the overall well-being of the dog during the course of treatment.
It is important to emphasize that the likelihood and severity of side effects can vary depending on the specific medication, the dog's individual health status, and the adherence to prescribed protocols. Veterinarians play a crucial role in evaluating the overall risk-benefit profile of injectable drugs and guiding pet owners in mitigating potential side effects.
By remaining vigilant and proactive, pet owners can collaborate with veterinarians to minimize the risk of adverse reactions and ensure the safe and effective use of injectable drugs for managing arthritis in dogs. This partnership fosters a comprehensive approach to caring for arthritic dogs, prioritizing their comfort and well-being while mitigating potential treatment-related complications.
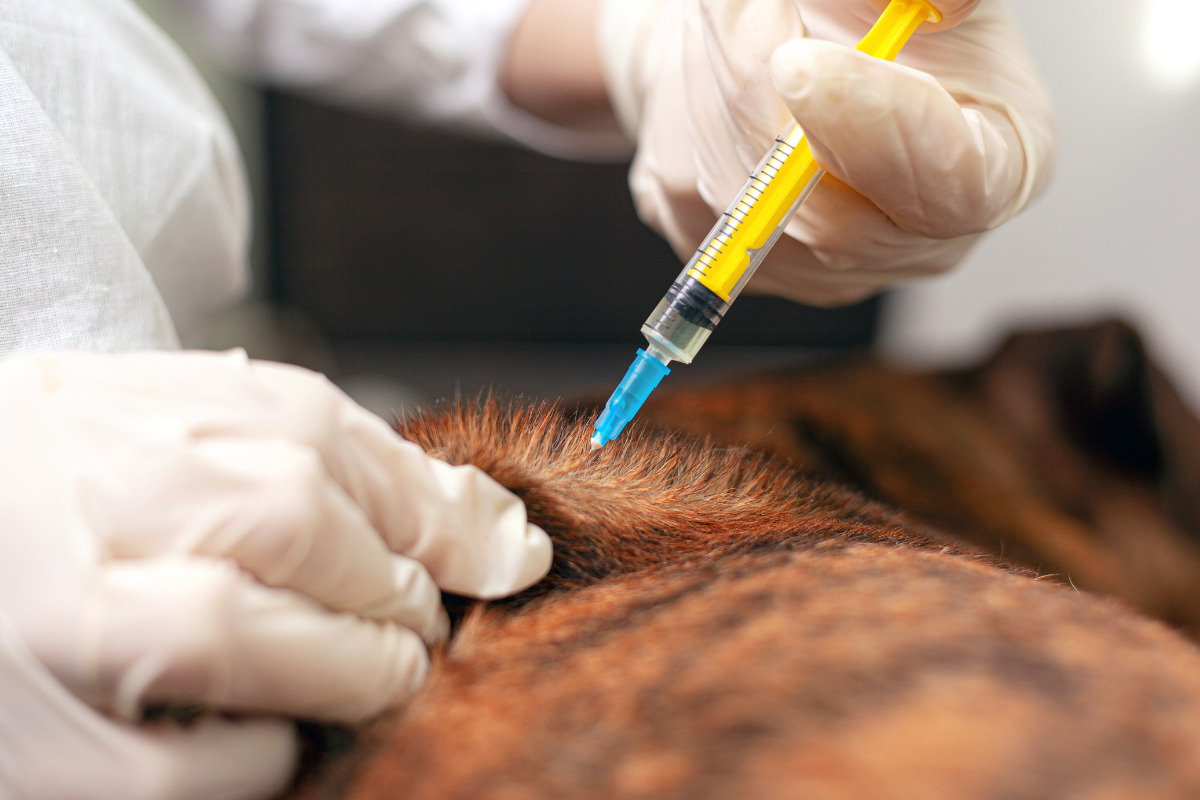
How to Administer Injectable Drugs to Dogs with Arthritis
Administering injectable drugs to dogs with arthritis requires careful attention to detail and a compassionate approach to ensure the well-being of our canine companions. Proper administration of these medications is essential to maximize their therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential discomfort for the dogs. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to administer injectable drugs to dogs with arthritis:
-
Consultation with Veterinarian: Before initiating any injectable drug therapy for arthritis in dogs, it is imperative to consult with a veterinarian. The veterinarian will conduct a thorough assessment of the dog's condition, including joint mobility, pain levels, and overall health status. Based on this evaluation, the veterinarian will recommend the most suitable injectable drug and establish a customized treatment plan tailored to the dog's specific needs.
-
Injection Technique: Injectable drugs for arthritis in dogs are typically administered via subcutaneous or intramuscular injections. Pet owners should receive detailed instructions from the veterinarian on the proper injection technique, including the precise location for subcutaneous injections and the appropriate depth for intramuscular injections. It is essential to adhere to the recommended injection sites and techniques to ensure the safe and effective delivery of the medication.
-
Scheduling and Dosage: Pet owners must adhere to the prescribed dosing schedule and dosage of the injectable drug as outlined by the veterinarian. This may involve a series of initial loading doses followed by maintenance injections at specified intervals. Accurate dosing and adherence to the treatment schedule are crucial to optimize the therapeutic effects of the medication and support the dog's joint health.
-
Environment and Restraint: Creating a calm and comfortable environment for administering injectable drugs is essential to minimize stress for the dog. Pet owners should choose a quiet area free from distractions and provide gentle restraint to ensure the dog remains still during the injection process. Using positive reinforcement and offering treats or praise can help alleviate any anxiety or apprehension the dog may experience.
-
Monitoring and Observation: Following the administration of injectable drugs, pet owners should monitor the dog for any immediate reactions or discomfort. Observing the injection site for signs of swelling, redness, or irritation is important, as is keeping a record of the dog's response to the medication. Any unexpected reactions or changes in the dog's behavior should be promptly reported to the veterinarian for further evaluation.
-
Collaboration with Veterinarian: Throughout the course of injectable drug therapy, ongoing collaboration with the veterinarian is essential. This includes regular follow-up appointments to assess the dog's response to the medication, monitor joint function, and make any necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Open communication with the veterinarian allows for proactive management of the dog's arthritis and ensures that any concerns or questions are addressed promptly.
By following these guidelines and working closely with veterinarians, pet owners can administer injectable drugs to dogs with arthritis in a safe, effective, and compassionate manner. This collaborative approach prioritizes the well-being of arthritic dogs, empowering pet owners to play an active role in supporting their canine companions through the challenges of arthritis management.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the management of arthritis in dogs through the use of injectable drugs represents a significant advancement in veterinary medicine, offering targeted relief and improved joint function for our beloved canine companions. The diverse range of injectable drug options, including Adequan, Legend, corticosteroids, polysulfated glycosaminoglycans, and platelet-rich plasma therapy, provides veterinarians and pet owners with valuable tools to address the multifaceted challenges of arthritis in dogs.
By understanding the underlying mechanisms of arthritis and recognizing the signs and symptoms of this condition, pet owners can proactively collaborate with veterinarians to implement comprehensive care plans tailored to their dog's specific needs. Injectable drugs play a pivotal role in this approach, offering benefits such as promoting cartilage repair, enhancing joint lubrication, and minimizing discomfort for arthritic dogs.
While injectable drugs for arthritis in dogs offer numerous therapeutic advantages, it is essential for pet owners to be mindful of the potential side effects associated with these medications. By remaining vigilant and proactive, pet owners can collaborate with veterinarians to minimize the risk of adverse reactions and ensure the safe and effective use of injectable drugs for managing arthritis in dogs.
The proper administration of injectable drugs to dogs with arthritis requires careful attention to detail and a compassionate approach to ensure the well-being of our canine companions. Through consultation with veterinarians, adherence to prescribed dosing schedules, and ongoing collaboration, pet owners can play an active role in supporting their arthritic dogs through the challenges of arthritis management.
In essence, the comprehensive understanding of injectable drugs for arthritis in dogs empowers pet owners to make informed decisions and provide the best possible care for their canine companions. By leveraging the therapeutic benefits of injectable drugs and embracing a collaborative approach with veterinarians, pet owners can enhance the comfort, mobility, and overall quality of life for their dogs struggling with arthritis. This partnership fosters a holistic and compassionate approach to caring for arthritic dogs, prioritizing their well-being and ensuring that they can continue to enjoy active and fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by arthritis.