Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>What Happens If A Dog Licks Your Eye


Eye and Ear Health
What Happens If A Dog Licks Your Eye
Published: February 11, 2024
Learn about the potential risks and consequences if a dog licks your eye, and how it can impact your eye and ear health. Understand the importance of protecting your eyes and ears from potential infections.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
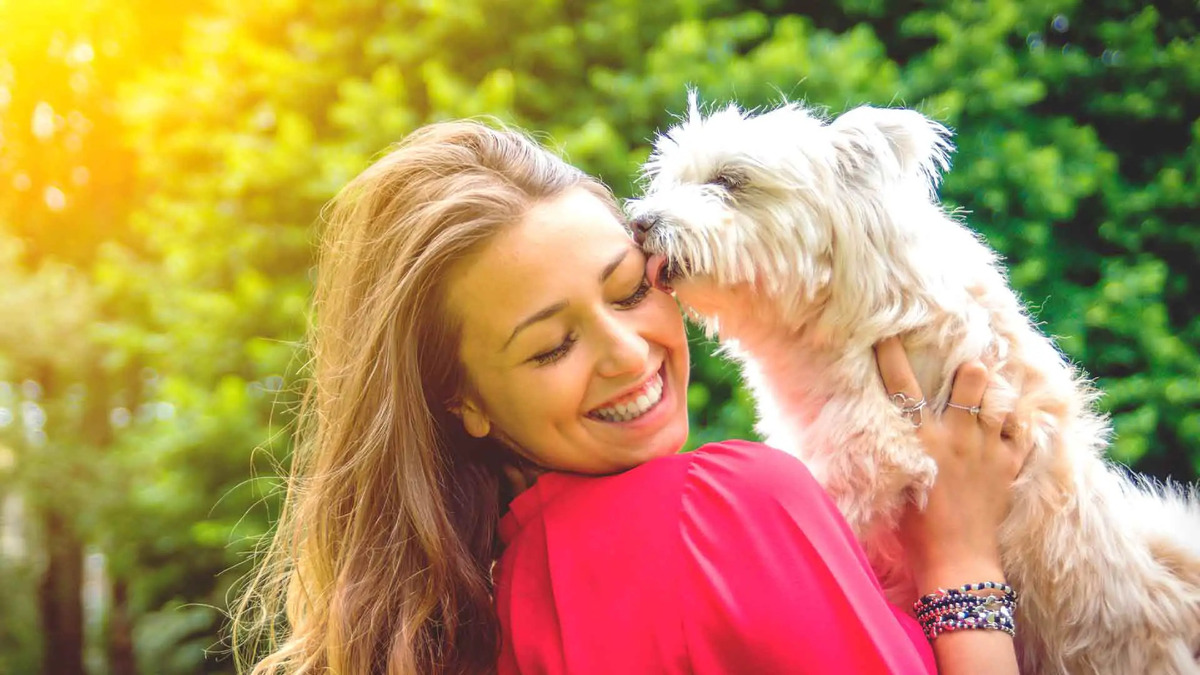
Have you ever wondered what would happen if a dog were to lick your eye? It's a curious thought, and one that may have crossed your mind if you're a dog owner or simply an animal lover. Dogs are known for their affectionate nature, and licking is one of the ways they express their love and bond with their human companions. While it may seem endearing, the act of a dog licking your eye raises questions about potential risks and health implications.
In this article, we'll delve into the intriguing topic of what happens if a dog licks your eye. We'll explore the reasons behind a dog's licking behavior, the potential risks associated with this action, and the measures you can take to safeguard your eye health. Whether you're a dog owner or simply curious about the interaction between dogs and humans, this article aims to shed light on this unique and thought-provoking scenario. So, let's embark on this fascinating journey to uncover the mysteries of canine affection and its impact on our eye health.
Why do dogs lick?
Dogs have a natural inclination to lick, and this behavior serves various purposes rooted in their instincts and social dynamics. Understanding the reasons behind a dog's licking behavior can provide valuable insights into their communication and emotional expression.
-
Affection and Bonding: Licking is a fundamental way for dogs to show affection and strengthen their bond with humans. It is a form of social interaction that mimics the nurturing behavior exhibited by mother dogs towards their puppies. When a dog licks a person, it signifies trust, comfort, and a desire for closeness.
-
Exploration and Communication: Dogs rely heavily on their sense of taste and smell to explore and understand their environment. Licking allows them to gather information about the objects, surfaces, and individuals they encounter. It serves as a means of communication, enabling dogs to convey their curiosity, recognition, and emotional state.
-
Grooming and Care: Licking is an integral part of a dog's grooming routine. They use their tongues to clean themselves and maintain hygiene. When dogs lick their human companions, it can be a display of caregiving behavior, akin to how they groom their fellow pack members.
-
Stress Relief and Soothing: Licking can be a self-soothing mechanism for dogs, especially in stressful or anxious situations. It provides them with a sense of comfort and security, similar to how humans may engage in soothing activities when feeling distressed.
-
Taste and Salt Cravings: Dog saliva contains enzymes and minerals, and licking can be driven by the taste and salt content of human skin. This natural inclination may be linked to their dietary preferences and the instinctual drive to seek out essential nutrients.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of a dog's licking behavior underscores the depth of their emotional connection with humans and their environment. It is a complex form of communication and expression that reflects the intricate bond between dogs and their human companions.
Risks of a dog licking your eye
The act of a dog licking your eye may seem harmless or even endearing, but it poses potential risks to your eye health. While dogs are beloved companions, their saliva contains a diverse array of bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms that can lead to various health concerns when in contact with the delicate tissues of the eye. Understanding these risks is crucial for safeguarding your ocular well-being and taking proactive measures to mitigate potential harm.
-
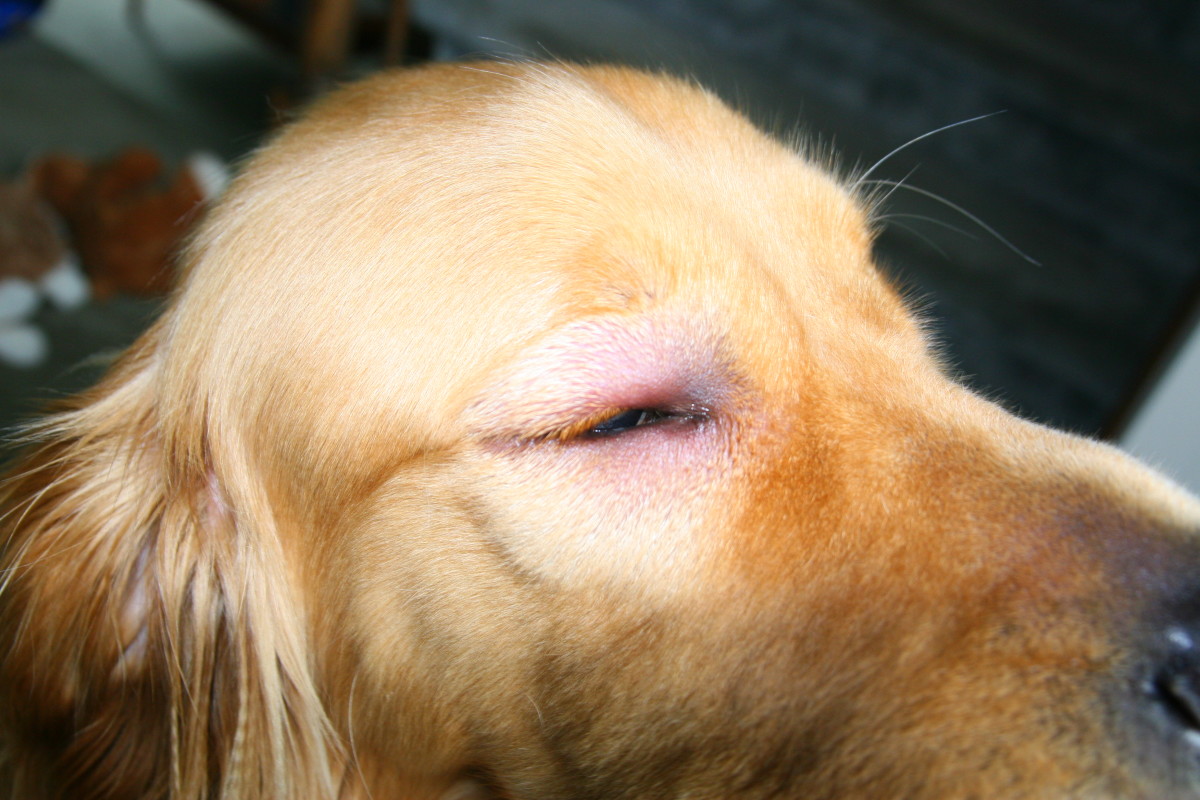
Bacterial Infections: Dog saliva harbors a multitude of bacteria, including species such as Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Pasteurella. When a dog licks your eye, these bacteria can be transferred, increasing the risk of bacterial conjunctivitis (commonly known as pink eye) or other bacterial infections. The moist and warm environment of the eye provides an ideal breeding ground for bacteria, potentially leading to redness, swelling, and discomfort.
-
Viral Infections: In addition to bacteria, dogs can carry viruses such as herpesvirus and papillomavirus in their saliva. Direct contact between dog saliva and the eye can facilitate the transmission of these viruses, potentially causing viral conjunctivitis or other viral infections. These conditions can manifest as inflammation, discharge, and sensitivity to light, necessitating prompt medical attention.
-
Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be allergic to components present in dog saliva, leading to allergic conjunctivitis upon contact with the eye. Allergic reactions can result in itching, redness, and excessive tearing, contributing to discomfort and visual disturbances.
-
Foreign Particles and Irritants: Apart from microorganisms, a dog's tongue may carry foreign particles, dirt, or irritants that can inadvertently enter the eye during licking. This can trigger irritation, corneal abrasions, or foreign body sensation, potentially compromising the eye's integrity and visual acuity.
-
Imbalance of Eye Microbiota: The introduction of foreign microorganisms from dog saliva can disrupt the delicate balance of the eye's natural microbiota, which plays a crucial role in maintaining ocular health and immunity. Imbalances in the ocular microbiota can predispose the eye to infections and inflammatory conditions, necessitating interventions to restore equilibrium.
Understanding the potential risks associated with a dog licking your eye underscores the importance of exercising caution and implementing preventive measures. While dogs provide companionship and affection, it is essential to prioritize eye safety and hygiene, especially when interacting closely with our furry friends. By being mindful of these risks, you can take proactive steps to protect your eye health and enjoy the enriching bond with your canine companion.
Potential infections from dog saliva
When a dog licks your eye, there is a potential risk of various infections stemming from the microorganisms present in their saliva. Dog saliva contains a diverse array of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens that can pose significant health concerns when they come into contact with the delicate tissues of the eye. Understanding the potential infections that can arise from dog saliva is crucial for recognizing the associated risks and taking proactive measures to safeguard ocular health.
Bacterial Infections
Dog saliva harbors a multitude of bacteria, including Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, and Pasteurella species. These bacteria can be transferred to the eye through licking, increasing the risk of bacterial conjunctivitis, commonly known as pink eye. Bacterial conjunctivitis manifests as redness, swelling, and discomfort, potentially leading to vision disturbances if left untreated. The warm and moist environment of the eye provides an ideal breeding ground for bacteria, underscoring the potential severity of bacterial infections resulting from dog saliva contact.
Read more: Why Does My Dog Lick My Other Dog’s Eye
Viral Infections
In addition to bacteria, dogs can carry viruses such as herpesvirus and papillomavirus in their saliva. Direct contact between dog saliva and the eye can facilitate the transmission of these viruses, potentially causing viral conjunctivitis or other viral infections. Viral conjunctivitis presents with inflammation, discharge, and sensitivity to light, necessitating prompt medical attention to mitigate the impact on ocular health. The potential transmission of viral infections through dog saliva underscores the need for vigilance and preventive measures when dogs interact closely with human eyes.
Allergic Reactions
Some individuals may exhibit allergic reactions to components present in dog saliva, leading to allergic conjunctivitis upon contact with the eye. Allergic conjunctivitis can result in itching, redness, and excessive tearing, contributing to discomfort and visual disturbances. The allergic response triggered by dog saliva highlights the diverse range of potential reactions that can occur, emphasizing the importance of understanding individual susceptibility to allergens present in canine saliva.
Foreign Particles and Irritants
Apart from microorganisms, a dog's tongue may carry foreign particles, dirt, or irritants that can inadvertently enter the eye during licking. This can trigger irritation, corneal abrasions, or foreign body sensation, potentially compromising the eye's integrity and visual acuity. The introduction of foreign particles and irritants from dog saliva underscores the multifaceted nature of the risks associated with canine licking behavior, necessitating vigilance and prompt attention to mitigate potential ocular complications.
Imbalance of Eye Microbiota
The introduction of foreign microorganisms from dog saliva can disrupt the delicate balance of the eye's natural microbiota, which plays a crucial role in maintaining ocular health and immunity. Imbalances in the ocular microbiota can predispose the eye to infections and inflammatory conditions, necessitating interventions to restore equilibrium and mitigate the impact of microbial disruptions. The potential imbalance of eye microbiota resulting from dog saliva contact underscores the intricate interplay between external factors and ocular health maintenance.
Understanding the potential infections that can arise from dog saliva contact highlights the need for proactive measures to safeguard eye health when interacting with dogs. By recognizing the diverse range of risks associated with canine licking behavior, individuals can prioritize preventive strategies and seek prompt medical attention if concerns arise. This awareness empowers individuals to enjoy the companionship of dogs while maintaining a vigilant approach to ocular health protection.
What to do if a dog licks your eye
If a dog licks your eye, it's essential to take prompt and proactive measures to mitigate potential risks and safeguard your ocular health. While the act of a dog licking your eye may occur spontaneously or inadvertently, being prepared to address this situation can significantly reduce the likelihood of adverse health effects. Here are the recommended steps to follow if a dog licks your eye:
-
Rinse Your Eye Thoroughly: Immediately flush your eye with clean, lukewarm water for several minutes. This helps to wash away any potential contaminants present in the dog's saliva, reducing the risk of infection or irritation. Gently hold your eyelids open while allowing the water to flow over your eye, ensuring comprehensive rinsing.
-
Avoid Rubbing Your Eye: Refrain from rubbing or touching your eye with your hands or fingers after a dog licks it. Rubbing can exacerbate any irritation or introduce additional contaminants to the eye. Instead, maintain a hands-off approach and focus on thorough rinsing to minimize potential harm.
-
Seek Medical Evaluation: Contact an eye care professional or healthcare provider for further assessment and guidance. Even if immediate symptoms are not apparent, it is advisable to seek professional evaluation to ensure comprehensive ocular health monitoring. The healthcare provider can assess the risk of potential infections, provide appropriate treatment if necessary, and offer personalized recommendations based on the specific circumstances.
-
Monitor for Symptoms: Be vigilant for any unusual symptoms or changes in your eye following the dog's licking incident. These may include redness, swelling, excessive tearing, discomfort, or changes in vision. If any concerning symptoms manifest, promptly seek medical attention to address potential complications and receive tailored care.
-
Maintain Ocular Hygiene: Emphasize diligent ocular hygiene practices following the dog's licking incident. Avoid touching or rubbing your eyes with unwashed hands, and consider using sterile eye drops or artificial tears to maintain ocular moisture and cleanliness. Adhering to stringent hygiene measures can help mitigate the risk of secondary complications.
-
Educate Others: If you are in a shared environment or community setting, such as a household with multiple individuals or a public space, consider educating others about the potential risks associated with dog saliva and eye contact. By raising awareness, you can contribute to a proactive approach to eye health protection and promote informed decision-making in similar situations.
By promptly implementing these proactive measures and seeking professional evaluation when necessary, individuals can effectively address the aftermath of a dog licking their eye and minimize potential health risks. This proactive approach underscores the importance of prioritizing ocular health and taking decisive steps to mitigate the impact of canine saliva contact on eye well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the interaction between dogs and humans, particularly the scenario of a dog licking a person's eye, encompasses a complex interplay of affection, communication, and potential health risks. While dogs express their love and bonding through licking, it is essential to recognize the potential implications for eye health and take proactive measures to mitigate associated risks.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of a dog's licking behavior provides valuable insights into the depth of the human-canine bond. Dogs use licking as a means of expressing affection, exploring their environment, and engaging in caregiving behaviors. This unique form of communication underscores the emotional connection and social dynamics between dogs and their human companions, enriching the bond that transcends verbal interaction.
However, the act of a dog licking a person's eye poses potential risks to ocular health, including bacterial and viral infections, allergic reactions, and the introduction of foreign particles. The diverse array of microorganisms present in dog saliva underscores the need for vigilance and proactive measures to safeguard eye health when interacting closely with dogs.
By promptly rinsing the eye, seeking medical evaluation, and maintaining stringent ocular hygiene, individuals can effectively address the aftermath of a dog licking their eye and minimize potential health risks. This proactive approach empowers individuals to enjoy the companionship of dogs while prioritizing ocular health protection.
Furthermore, raising awareness about the potential risks associated with dog saliva and eye contact can contribute to informed decision-making and proactive eye health management in shared environments or community settings. Educating others about the importance of ocular hygiene and prompt response to potential exposures fosters a collective commitment to eye health protection in diverse social contexts.
In essence, the interaction between dogs and humans, including the act of a dog licking a person's eye, encapsulates a blend of emotional connection, communication, and the imperative of maintaining ocular health. By embracing the joys of canine companionship while being mindful of potential risks, individuals can cultivate a harmonious and health-conscious relationship with their furry friends, fostering a balance between affection and well-being.