Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>What Was Your Dog’s Eye Pressure In Glaucoma?


Eye and Ear Health
What Was Your Dog’s Eye Pressure In Glaucoma?
Published: February 11, 2024
Monitor your dog's eye pressure for glaucoma with our expert tips on eye and ear health. Learn how to keep your pet's vision in check.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Welcome to the world of canine eye health! As a loving pet owner, you understand the importance of ensuring your furry friend's well-being. One crucial aspect of your dog's health is their eye pressure, especially when it comes to the risk of glaucoma. Glaucoma, a condition characterized by increased intraocular pressure, can lead to irreversible vision loss if left untreated. Therefore, monitoring your dog's eye pressure is paramount in safeguarding their ocular health.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of glaucoma in dogs, the significance of monitoring eye pressure, various methods for measuring eye pressure, factors influencing eye pressure, and how to interpret the results. By the end of this article, you will have a deeper understanding of the importance of maintaining optimal eye pressure in your canine companion and the measures you can take to ensure their ocular well-being.
Let's embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the mysteries of canine eye health and equip ourselves with the knowledge to protect our furry friends from the potential risks associated with glaucoma.
Read more: What Eye Drops Are Good For Glaucoma In Dogs
Understanding Glaucoma in Dogs
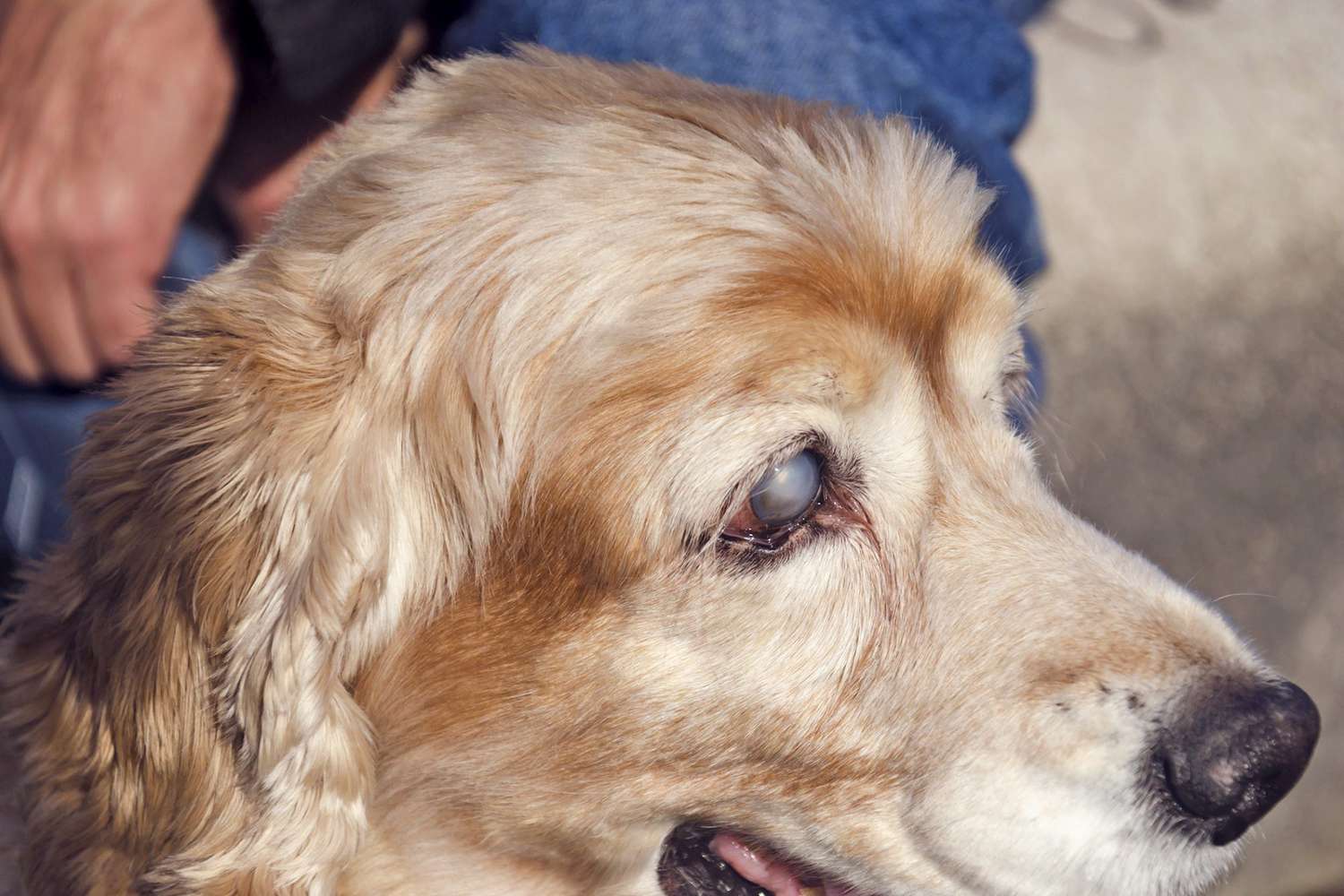
Glaucoma, a serious and potentially blinding eye condition, affects dogs much like it does humans. It is characterized by increased intraocular pressure, which can lead to damage of the optic nerve and irreversible vision loss if left untreated. The eye functions like a camera, with a clear fluid called aqueous humor constantly circulating to maintain its shape and nourish the surrounding tissues. In a healthy eye, the production and drainage of this fluid are balanced, maintaining a normal intraocular pressure. However, in glaucoma, this delicate balance is disrupted, resulting in elevated pressure within the eye.
There are two primary types of glaucoma in dogs: primary and secondary. Primary glaucoma is hereditary and typically affects specific breeds, such as Cocker Spaniels, Basset Hounds, and Siberian Huskies. On the other hand, secondary glaucoma occurs as a result of other ocular conditions, such as uveitis or lens luxation, leading to increased intraocular pressure.
The onset of glaucoma can be insidious, often with subtle or intermittent symptoms that may go unnoticed by pet owners. However, as the condition progresses, affected dogs may exhibit signs such as redness in the whites of the eyes, cloudiness within the cornea, dilated pupils, and vision impairment. It's crucial for pet owners to remain vigilant and seek prompt veterinary attention if any of these symptoms are observed.
Understanding the nuances of glaucoma in dogs empowers pet owners to recognize potential warning signs and take proactive measures to safeguard their canine companions' ocular health. By staying informed about this condition, pet owners can work in tandem with veterinary professionals to ensure early detection and effective management of glaucoma, ultimately preserving their dog's precious eyesight.
Importance of Monitoring Eye Pressure
Monitoring your dog's eye pressure is a critical aspect of proactive eye care, especially when it comes to the early detection and management of glaucoma. As a responsible pet owner, understanding the significance of regular eye pressure assessments for your canine companion is paramount in safeguarding their ocular health.
Glaucoma, a stealthy and potentially devastating eye condition, often progresses silently, with symptoms manifesting only in the advanced stages. By monitoring your dog's eye pressure, you can detect subtle changes indicative of elevated intraocular pressure, allowing for timely intervention and treatment. Early detection is key in preventing irreversible damage to the optic nerve and preserving your dog's vision.
Regular eye pressure monitoring is particularly crucial for certain dog breeds predisposed to primary glaucoma, such as Cocker Spaniels, Basset Hounds, and Siberian Huskies. By proactively tracking their eye pressure, you can identify any deviations from the normal range and take preemptive measures to mitigate the risk of glaucoma development.
Furthermore, for dogs diagnosed with glaucoma, consistent monitoring of their eye pressure is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of treatment and disease progression. By closely tracking changes in intraocular pressure, veterinarians can tailor treatment plans to effectively manage the condition and minimize the risk of vision loss.
In addition to aiding in the diagnosis and management of glaucoma, regular eye pressure assessments also contribute to overall preventive care for your dog's eyes. By monitoring their eye pressure as part of routine veterinary check-ups, potential issues can be identified early, allowing for prompt intervention and reducing the likelihood of ocular complications.
By prioritizing the monitoring of your dog's eye pressure, you demonstrate a commitment to their well-being and take proactive steps to preserve their ocular health. This proactive approach not only enhances the quality of life for your furry friend but also strengthens the bond between pet and owner, fostering a nurturing environment that prioritizes their health and happiness.
In essence, the importance of monitoring eye pressure for dogs cannot be overstated. It serves as a cornerstone of preventive care, early detection, and effective management of glaucoma, ultimately contributing to the long-term well-being and visual health of your beloved canine companion.
Methods for Measuring Dog's Eye Pressure
When it comes to assessing a dog's eye pressure, veterinary professionals employ various methods to obtain accurate and reliable measurements. These techniques are instrumental in evaluating intraocular pressure, a crucial indicator in the diagnosis and management of ocular conditions, particularly glaucoma. Let's explore the primary methods utilized for measuring a dog's eye pressure:
-
Tonometry: Tonometry is the gold standard for measuring intraocular pressure in dogs. The two main types of tonometry used in veterinary practice are applanation tonometry and rebound tonometry. Applanation tonometry involves gently flattening a small area of the cornea with a specialized instrument to determine the amount of force required, providing an accurate measurement of intraocular pressure. On the other hand, rebound tonometry utilizes a small probe that makes brief contact with the cornea, emitting a gentle air puff to assess intraocular pressure. Both methods offer precise and reliable measurements, aiding in the early detection and monitoring of elevated eye pressure.
-
Tono-Pen: The Tono-Pen is a handheld device commonly used in veterinary clinics to measure intraocular pressure in dogs. This portable instrument allows for quick and efficient assessments, making it particularly useful for dogs who may not tolerate traditional tonometry methods. The Tono-Pen gently touches the cornea to obtain pressure readings, providing valuable data for assessing ocular health and detecting potential abnormalities.
-
Diaton Transpalpebral Tonometer: The Diaton tonometer offers a non-invasive approach to measuring intraocular pressure in dogs. Unlike traditional tonometry methods that require direct contact with the cornea, the Diaton tonometer measures eye pressure through the eyelid, making it a suitable option for dogs with sensitive eyes or those exhibiting signs of ocular discomfort. This innovative technique provides accurate readings while minimizing stress for the canine patient.
-
Pneumotonometry: Pneumotonometry, also known as pneumatic tonometry, utilizes a gentle stream of air to assess intraocular pressure in dogs. This non-invasive method offers a comfortable and stress-free experience for the dog, making it an ideal choice for those who may be apprehensive about traditional tonometry techniques. Pneumotonometry provides valuable insights into the dog's eye pressure, facilitating comprehensive ocular evaluations.
By employing these advanced methods for measuring a dog's eye pressure, veterinary professionals can obtain precise and reliable data essential for diagnosing ocular conditions, monitoring treatment efficacy, and preserving the visual health of canine patients. These techniques underscore the commitment to delivering exceptional care and ensuring the well-being of our beloved four-legged companions.
Factors Affecting Dog's Eye Pressure
The delicate balance of intraocular pressure in a dog's eyes is influenced by various factors, each playing a crucial role in maintaining ocular health. Understanding these factors is essential for pet owners and veterinary professionals alike, as they can impact the risk of developing glaucoma and other ocular conditions. Let's delve into the key factors that can affect a dog's eye pressure:
-
Breed Predisposition: Certain dog breeds exhibit a genetic predisposition to primary glaucoma, placing them at a higher risk of elevated intraocular pressure. Breeds such as Cocker Spaniels, Basset Hounds, and Siberian Huskies are particularly susceptible to primary glaucoma, underscoring the importance of proactive eye pressure monitoring in these canine companions.
-
Age: Advancing age can influence a dog's susceptibility to changes in eye pressure. As dogs grow older, the dynamics of aqueous humor production and drainage may undergo alterations, potentially leading to fluctuations in intraocular pressure. Aging dogs may require more frequent eye pressure assessments to detect age-related changes and mitigate the risk of ocular complications.
-
Ocular Trauma or Injury: Traumatic incidents, such as blunt force trauma or penetrating injuries to the eye, can disrupt the delicate mechanisms regulating intraocular pressure. These traumatic events may result in acute increases in eye pressure, necessitating immediate veterinary attention to assess and address the impact on ocular health.
-
Ocular Anatomy and Structure: Variations in the anatomical structure of a dog's eyes can influence the dynamics of intraocular pressure. Anomalies such as narrow drainage angles or anatomical abnormalities within the eye can impede the proper outflow of aqueous humor, leading to elevated eye pressure and an increased risk of glaucoma development.
-
Systemic Health Conditions: Underlying systemic health issues, such as hypertension or endocrine disorders, can exert indirect effects on a dog's eye pressure. Systemic conditions that impact vascular health and fluid dynamics within the body may contribute to fluctuations in intraocular pressure, highlighting the interconnected nature of overall health and ocular well-being.
-
Medications and Anesthesia: Certain medications and anesthetic agents can influence a dog's intraocular pressure, particularly during surgical procedures or medical treatments. It is essential for veterinary professionals to consider the potential impact of medications on eye pressure and take appropriate measures to mitigate any adverse effects during the course of treatment.
By recognizing and understanding the multifaceted factors that can affect a dog's eye pressure, pet owners and veterinary professionals can proactively address potential risk factors, implement targeted monitoring strategies, and tailor preventive measures to safeguard ocular health. This comprehensive approach underscores the commitment to preserving the visual well-being of our canine companions and mitigating the impact of factors that may predispose them to ocular conditions such as glaucoma.
Read more: What Happens If A Dog Licks Your Eye
Interpreting Eye Pressure Results
Interpreting eye pressure results is a pivotal aspect of canine ocular health assessment, providing valuable insights into the status of intraocular pressure and its implications for the dog's overall eye health. When evaluating eye pressure measurements, veterinary professionals consider various factors to accurately interpret the results and make informed decisions regarding diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing monitoring.
The interpretation of eye pressure results involves comparing the obtained measurements to established reference ranges for normal intraocular pressure in dogs. These reference ranges serve as benchmarks for assessing the dog's eye pressure and identifying any deviations that may indicate potential ocular abnormalities. Additionally, the interpretation takes into account the specific method used for measuring eye pressure, as different tonometry techniques may yield slightly varying results.
In cases where the eye pressure measurements fall within the normal reference range, it indicates that the dog's intraocular pressure is within the expected parameters, signifying healthy ocular function. This outcome provides reassurance regarding the absence of elevated eye pressure, reducing the immediate concern for conditions such as glaucoma.
Conversely, if the eye pressure measurements exceed the normal reference range, it raises red flags regarding elevated intraocular pressure, warranting further investigation and potential diagnostic assessments for ocular conditions such as glaucoma. Elevated eye pressure measurements prompt veterinary professionals to conduct a comprehensive ocular examination, including assessing the optic nerve, evaluating the drainage angles, and examining the overall ocular health to ascertain the underlying cause of the increased intraocular pressure.
Furthermore, the interpretation of eye pressure results considers the dog's medical history, breed predisposition to glaucoma, and any concurrent ocular or systemic conditions. These contextual factors provide a comprehensive understanding of the dog's ocular health status, enabling veterinary professionals to tailor their approach to diagnosis, treatment, and ongoing management based on the individualized needs of the canine patient.
In cases where a dog has been diagnosed with glaucoma, the interpretation of eye pressure results becomes integral in monitoring the effectiveness of treatment interventions. Regular assessments of eye pressure allow veterinary professionals to gauge the response to treatment, adjust therapeutic strategies as needed, and mitigate the risk of progressive vision loss associated with glaucoma.
By meticulously interpreting eye pressure results, veterinary professionals can make informed clinical decisions, provide targeted interventions, and collaborate with pet owners to optimize the ocular health and well-being of their canine companions. This proactive approach underscores the commitment to preserving vision and enhancing the quality of life for dogs at risk of ocular conditions such as glaucoma.
Conclusion
In the realm of canine eye health, the significance of monitoring eye pressure cannot be overstated. As responsible pet owners, prioritizing regular eye pressure assessments for our beloved canine companions is a proactive step towards safeguarding their ocular well-being. The journey through the intricacies of glaucoma in dogs, the methods for measuring eye pressure, and the factors influencing intraocular pressure has equipped us with valuable insights into the critical role of eye pressure monitoring in preserving our dogs' vision.
By understanding the nuances of glaucoma in dogs, we have gained a deeper appreciation for the stealthy nature of this condition and the imperative of early detection. Recognizing the subtle signs and symptoms of glaucoma empowers us to remain vigilant and seek prompt veterinary attention, ensuring timely intervention and effective management to protect our dogs from irreversible vision loss.
Exploring the diverse methods for measuring a dog's eye pressure has shed light on the advanced techniques employed by veterinary professionals to obtain precise and reliable measurements. From tonometry to innovative non-invasive tonometry options, these methods underscore the commitment to delivering exceptional care and ensuring accurate assessments for our canine companions.
The multifaceted factors influencing a dog's eye pressure have provided us with a comprehensive understanding of the interconnected elements that impact ocular health. By recognizing breed predispositions, age-related changes, ocular trauma, and systemic health influences, we are better equipped to address potential risk factors and implement targeted monitoring strategies to safeguard our dogs' vision.
Interpreting eye pressure results serves as the cornerstone of ocular health assessment, guiding veterinary professionals in making informed clinical decisions and tailoring individualized treatment plans. The ability to discern normal and elevated eye pressure measurements empowers us to collaborate with veterinary professionals in the ongoing management of ocular conditions, particularly glaucoma, and optimize the visual health of our canine companions.
In essence, the journey through the intricacies of canine eye pressure monitoring culminates in a profound commitment to the well-being of our furry friends. By prioritizing regular eye pressure assessments, we demonstrate a dedication to preserving their vision, enhancing their quality of life, and fostering a nurturing environment that prioritizes their ocular health. Together, we embark on a journey of proactive care, unwavering vigilance, and a shared commitment to safeguarding the precious gift of sight for our beloved canine companions.