Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>What Causes Droopy Eye In Dogs


Eye and Ear Health
What Causes Droopy Eye In Dogs
Published: February 12, 2024
Learn about the causes of droopy eye in dogs and how to maintain their eye and ear health. Keep your furry friend happy and healthy with our expert tips.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
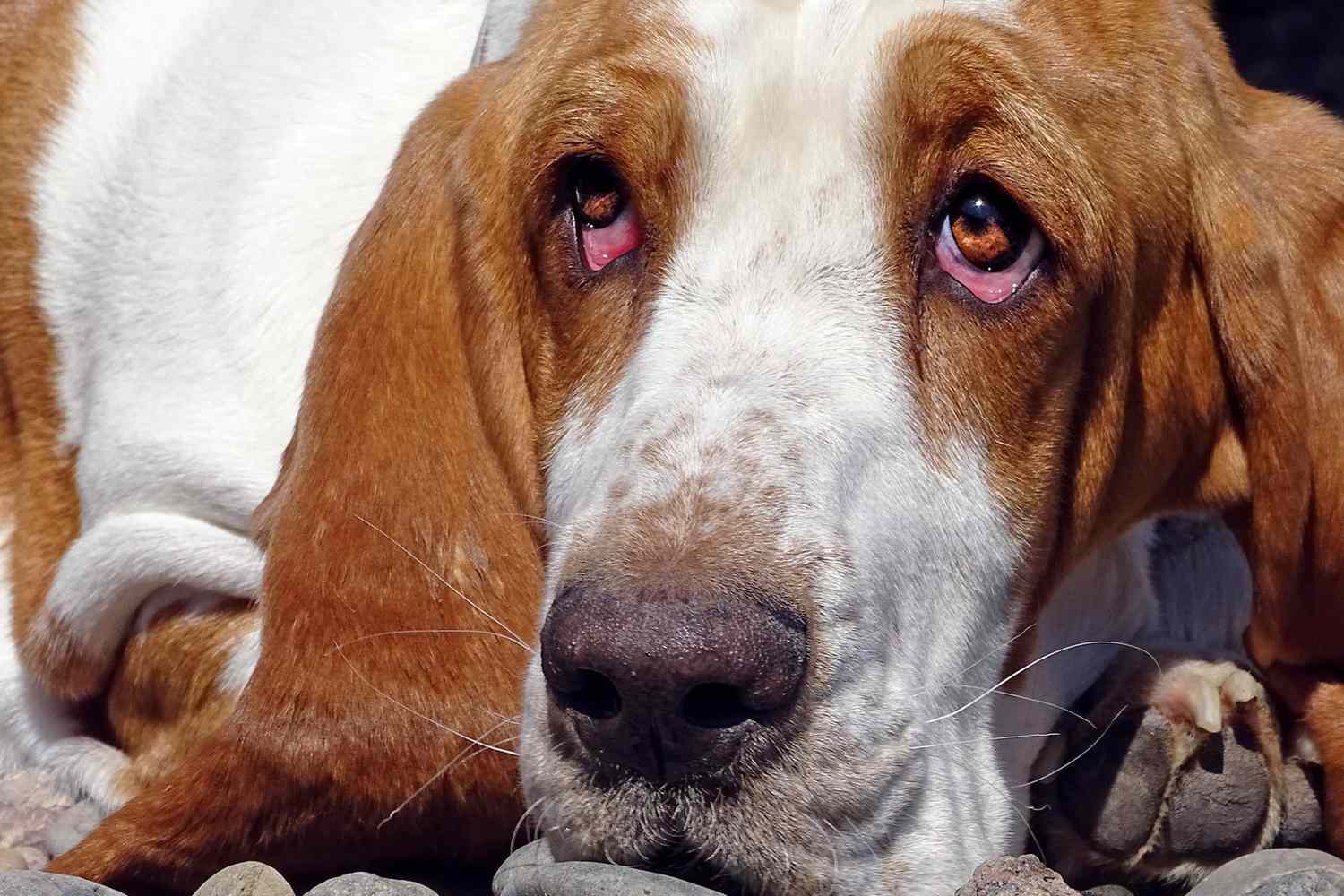
Droopy eye, also known as ptosis, is a condition that can affect dogs, causing one or both of their eyelids to sag or droop. This condition can be concerning for pet owners, as it may indicate an underlying health issue that requires attention. Understanding the potential causes of droopy eye in dogs is crucial for identifying and addressing the root of the problem.
Dogs rely on their eyesight for various activities, including play, navigation, and interaction with their environment and human companions. Therefore, any abnormality in their eye health can significantly impact their overall well-being. While droopy eye may seem like a minor cosmetic issue, it can be a symptom of an underlying medical condition that requires prompt veterinary care.
In this article, we will delve into the anatomy of the eye in dogs, explore the common causes of droopy eye in our canine companions, and discuss potential treatment options. By gaining insight into this condition, pet owners can become more attuned to their dog's health and well-being, enabling them to provide the necessary support and care when needed. Understanding the potential causes and treatment options for droopy eye in dogs is essential for promoting the health and happiness of our beloved canine friends.
Read more: What Causes A Dog’s Eye To Twitch
Anatomy of the Eye in Dogs
The eyes are a vital sensory organ for dogs, playing a crucial role in their daily activities and overall well-being. Understanding the intricate anatomy of a dog's eye is essential for comprehending the potential causes and implications of droopy eye conditions in these beloved pets.
The canine eye consists of several key components, each contributing to its function and structure. The outermost layer, known as the cornea, serves as a protective barrier, shielding the inner eye from external elements and potential damage. Beneath the cornea lies the iris, the colorful part of the eye that controls the amount of light entering the eye through its adjustable pupil. This mechanism allows dogs to adapt to varying light conditions, ensuring optimal vision in different environments.
The lens, located behind the iris, focuses incoming light onto the retina, a light-sensitive layer at the back of the eye. The retina contains specialized cells called photoreceptors, which convert light into electrical signals, initiating the visual process. These signals are then transmitted through the optic nerve to the brain, where they are interpreted as images, enabling dogs to perceive their surroundings and navigate their environment effectively.
Surrounding the eye, a series of muscles and connective tissues facilitate its movement and positioning, allowing dogs to track objects and focus on specific points of interest. Additionally, tear glands produce and distribute tears across the surface of the eye, maintaining moisture and protecting against potential irritants.
Understanding the intricate anatomy of a dog's eye provides insight into the complexity of this sensory organ and the delicate balance required for optimal function. Any disruption or abnormality within these intricate structures can manifest as various eye conditions, including droopy eye, signaling the need for veterinary attention and care.
By comprehending the anatomy of the eye in dogs, pet owners can appreciate the importance of proactive eye care and recognize the significance of addressing any abnormalities promptly. This understanding empowers pet owners to advocate for their dog's eye health, ensuring that they receive the necessary support and treatment to maintain clear vision and overall well-being.
Common Causes of Droopy Eye in Dogs
Droopy eye, or ptosis, in dogs can stem from various underlying causes, ranging from neurological conditions to physical trauma and genetic predispositions. Understanding these potential triggers is crucial for identifying the root of the issue and seeking appropriate veterinary care. Here are some common causes of droopy eye in dogs:
Neurological Conditions
Neurological disorders, such as Horner's syndrome, can lead to droopy eye in dogs. This condition arises from damage to the sympathetic nerve pathway that controls the muscles around the eye. As a result, affected dogs may exhibit drooping of the upper eyelid, constriction of the pupil, and a sunken appearance of the eye. Additionally, neurological conditions like facial nerve paralysis can also manifest as droopy eye, often accompanied by other facial muscle weakness.
Trauma or Injury
Physical trauma to the eye or surrounding structures can result in ptosis in dogs. Blunt force trauma, foreign object penetration, or injury to the muscles and nerves around the eye can lead to droopy eyelids. Additionally, head trauma or impact injuries can cause damage to the delicate structures supporting the eye, resulting in noticeable drooping and impaired function.
Read more: What Causes A Dog’s Eye To Bulge
Infections
Infections affecting the eye or its surrounding tissues can contribute to droopy eye in dogs. Conditions such as canine distemper, a viral disease, can lead to ocular manifestations, including droopy eyelids and discharge. Bacterial or fungal infections of the eye can also cause inflammation and weakness in the muscles supporting the eyelids, leading to a drooping appearance.
Genetics
Some dog breeds may be predisposed to congenital or hereditary conditions that result in droopy eye. Certain genetic abnormalities or inherited traits can affect the development and function of the muscles and nerves around the eye, leading to ptosis. Understanding the breed-specific predispositions to eye-related conditions can aid in early detection and management of droopy eye in dogs.
Identifying the potential causes of droopy eye in dogs is essential for guiding appropriate diagnostic and treatment approaches. By recognizing the underlying triggers, pet owners can work closely with veterinarians to address the specific needs of their canine companions, ensuring optimal eye health and overall well-being.
Neurological Conditions
Neurological conditions can significantly impact a dog's eye health, potentially leading to droopy eye or ptosis. One notable neurological disorder associated with this manifestation is Horner's syndrome. This condition arises from damage to the sympathetic nerve pathway that controls the muscles around the eye. As a result, affected dogs may exhibit drooping of the upper eyelid, constriction of the pupil, and a sunken appearance of the eye. The underlying causes of Horner's syndrome can vary, including trauma, tumors, or vascular issues affecting the nerves involved. Additionally, neurological conditions like facial nerve paralysis can also manifest as droopy eye, often accompanied by other facial muscle weakness.
When a dog presents with droopy eye due to neurological conditions, thorough diagnostic evaluation is crucial to identify the specific underlying cause. Veterinary professionals may conduct neurological examinations, imaging studies, and specialized tests to pinpoint the source of the neurological impairment. Understanding the precise nature of the neurological condition is essential for formulating an effective treatment plan tailored to the individual dog's needs.
Treatment for droopy eye stemming from neurological conditions often focuses on addressing the underlying neurological disorder. Depending on the cause, treatment may involve medication, surgical intervention, or supportive care to manage associated symptoms and promote recovery. In some cases, the underlying neurological condition may be managed rather than completely resolved, requiring ongoing monitoring and supportive measures to maintain the dog's eye health and overall well-being.
Pet owners play a crucial role in supporting dogs with neurological conditions affecting their eyes. By closely following the guidance of veterinary professionals and administering prescribed treatments, pet owners can contribute to their dog's comfort and quality of life. Additionally, vigilant observation of any changes in the affected eye and overall behavior can aid in early detection of potential complications or the need for adjustments in the treatment approach.
Understanding the impact of neurological conditions on a dog's eye health underscores the importance of comprehensive veterinary care and ongoing support for affected canine companions. By addressing the specific needs arising from neurological disorders, pet owners can help their dogs navigate challenges related to droopy eye, promoting their well-being and enhancing their quality of life.
Trauma or Injury
Trauma or injury to the eye or its surrounding structures can result in ptosis, or droopy eye, in dogs. This can occur due to various incidents, including blunt force trauma, foreign object penetration, or impact injuries. The delicate nature of the eye and its supporting tissues makes it susceptible to damage when exposed to physical trauma.
In cases of blunt force trauma, such as a direct impact or collision, the muscles, nerves, or connective tissues around the eye can sustain injury, leading to noticeable drooping of the eyelids. Additionally, foreign objects that penetrate the eye or surrounding structures can cause damage, resulting in ptosis and potential complications.
Head trauma, often associated with vehicular accidents or falls, can also have a significant impact on the eye and its supportive structures. The force of impact can lead to damage within the eye socket, affecting the positioning and function of the eyelids. Furthermore, injuries to the muscles and nerves responsible for controlling eyelid movement can result in droopy eye as a visible manifestation of the trauma.
When a dog experiences trauma or injury leading to droopy eye, prompt veterinary evaluation is essential to assess the extent of the damage and determine the appropriate course of action. Diagnostic measures, including ocular examinations and imaging studies, can aid in identifying the specific areas affected and guiding treatment decisions.
Treatment for droopy eye resulting from trauma or injury may involve a combination of medical interventions and supportive care. Depending on the severity of the trauma, surgical procedures may be necessary to repair damaged tissues and restore normal function. Additionally, pain management and measures to prevent secondary complications, such as infection or inflammation, are crucial for promoting the dog's recovery and overall well-being.
Pet owners play a vital role in supporting their dogs through the recovery process following trauma or injury. Adhering to the guidance of veterinary professionals, administering prescribed medications, and providing a comfortable environment for rest and recuperation are essential components of the caregiving process. Additionally, vigilant monitoring for any changes in the affected eye and overall behavior can help detect potential complications and ensure timely intervention.
Understanding the impact of trauma or injury on a dog's eye health underscores the importance of proactive measures to prevent such incidents and the need for prompt veterinary care in the event of an injury. By addressing the specific needs arising from trauma-related droopy eye, pet owners can contribute to their dog's recovery and long-term well-being.
Infections
Infections affecting the eye or its surrounding tissues can contribute to droopy eye in dogs, presenting a range of potential challenges for both the affected pets and their owners. Canine distemper, a viral disease, stands out as a significant contributor to ocular manifestations, including droopy eyelids and discharge. This highly contagious virus can impact various bodily systems, including the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and neurological systems, with ocular involvement being a notable concern. Dogs affected by distemper may exhibit a range of ocular symptoms, such as conjunctivitis, discharge, and drooping of the eyelids, highlighting the multifaceted nature of the disease's impact on eye health.
Furthermore, bacterial or fungal infections of the eye can also lead to inflammation and weakness in the muscles supporting the eyelids, resulting in a drooping appearance. These infections can arise from various sources, including environmental exposure, compromised immune function, or pre-existing ocular conditions. The presence of infectious agents in the eye can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to tissue damage and functional impairment, including the development of droopy eye.
When a dog presents with droopy eye due to infections, prompt veterinary attention is crucial to address the underlying cause and initiate appropriate treatment. Diagnostic assessments, including ocular examinations, swabs for microbial analysis, and laboratory tests, can aid in identifying the specific infectious agents involved and guiding targeted interventions. Treatment for infections contributing to droopy eye may involve antimicrobial medications, supportive care to alleviate ocular discomfort, and measures to bolster the dog's immune response against the causative agents.
Pet owners play a pivotal role in supporting their dogs through the challenges posed by infectious causes of droopy eye. Adhering to prescribed treatment regimens, providing a comfortable and hygienic environment, and minimizing potential sources of re-infection are essential aspects of caregiving. Additionally, proactive measures to prevent exposure to known infectious agents, such as maintaining up-to-date vaccinations and practicing good hygiene, can contribute to the overall well-being of dogs susceptible to ocular infections.
Understanding the impact of infections on a dog's eye health underscores the importance of vigilance and proactive measures to address potential risks. By recognizing the signs of ocular infections and seeking timely veterinary care, pet owners can play a crucial role in safeguarding their dog's eye health and promoting their overall quality of life.
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in shaping the health and characteristics of dogs, including their susceptibility to certain medical conditions. When it comes to droopy eye, genetic predispositions can contribute to the development of ptosis in certain dog breeds. Some breeds may be inherently prone to congenital or hereditary conditions that affect the muscles and nerves around the eye, leading to a droopy or sagging appearance of the eyelids.
Certain genetic abnormalities or inherited traits can impact the development and function of the muscles and nerves responsible for maintaining the proper positioning of the eyelids. This can result in a range of manifestations, including unilateral or bilateral droopy eye, which may become apparent at an early age or gradually emerge over time. Understanding the breed-specific predispositions to eye-related conditions is crucial for early detection and management of droopy eye in dogs with genetic susceptibilities.
In some cases, breed-specific genetic traits may contribute to structural weaknesses or imbalances in the muscles and connective tissues supporting the eyelids, leading to a propensity for droopy eye. Additionally, inherited neurological conditions can also play a role in the development of ptosis, further underscoring the influence of genetics on a dog's eye health.
Identifying the genetic factors contributing to droopy eye in dogs can aid in early intervention and proactive management of the condition. By recognizing the potential genetic predispositions within specific breeds, veterinarians and pet owners can implement targeted screening measures and preventive strategies to address the unique needs of at-risk dogs. This proactive approach can help mitigate the impact of genetic influences on a dog's eye health, promoting early detection and tailored interventions to support optimal vision and overall well-being.
Understanding the role of genetics in the development of droopy eye highlights the importance of breed-specific considerations and proactive measures to address potential genetic predispositions. By leveraging this knowledge, pet owners and veterinary professionals can collaborate to provide tailored care and support for dogs susceptible to genetic influences on their eye health.
Treatment Options
Addressing droopy eye in dogs often involves a multifaceted approach aimed at managing the underlying cause while addressing the specific needs of the affected eye. Treatment options may vary depending on the root cause of the ptosis and the individual dog's overall health status. Here are some common treatment modalities employed in managing droopy eye in dogs:
Medical Management
In cases where droopy eye stems from underlying infections, such as bacterial or fungal ocular conditions, medical management may be the primary course of action. Veterinarians may prescribe antimicrobial medications, such as antibiotics or antifungal agents, to combat the causative pathogens and alleviate associated inflammation. Additionally, supportive care, including ocular lubricants and soothing solutions, may be recommended to promote ocular comfort and aid in the healing process.
Read more: What Causes Sarcoma Cancer In Dogs
Surgical Intervention
In instances of trauma-related droopy eye or structural abnormalities contributing to ptosis, surgical intervention may be necessary to address the underlying issues. Surgical procedures can range from eyelid repair and reconstruction to addressing damage within the eye socket or surrounding structures. These interventions aim to restore normal eyelid function, correct anatomical abnormalities, and alleviate discomfort associated with the droopy eye.
Neurological Treatments
For dogs affected by neurological conditions leading to droopy eye, targeted treatments focused on managing the underlying neurological disorder may be employed. This can involve the administration of specific medications to address nerve damage, supportive therapies to promote nerve regeneration, and rehabilitative measures to enhance the dog's overall neurological function. Additionally, physical therapy and specialized exercises may be recommended to aid in the recovery of facial and ocular muscle function.
Symptomatic Support
In cases where the underlying cause of droopy eye may not be fully reversible, symptomatic support plays a crucial role in promoting the affected dog's comfort and quality of life. This can include the use of protective eyewear to prevent ocular injury, regular monitoring of the affected eye for signs of irritation or infection, and adjustments in the dog's environment to minimize potential hazards to the affected eye.
Ongoing Monitoring and Care
Regardless of the specific treatment approach, ongoing monitoring and care are essential components of managing droopy eye in dogs. This involves regular veterinary check-ups to assess the eye's condition, evaluate treatment efficacy, and make any necessary adjustments to the management plan. Additionally, pet owners play a vital role in observing their dog's behavior, comfort level, and any changes in the affected eye, providing valuable insights for the ongoing care and support of their canine companions.
By leveraging a combination of targeted treatments, supportive care, and ongoing monitoring, veterinary professionals and pet owners can collaborate to address the unique needs of dogs with droopy eye, promoting their eye health and overall well-being. Each treatment approach is tailored to the individual dog's condition, aiming to alleviate discomfort, restore function, and enhance their quality of life.
Read more: What Causes Blood Cancer In Dogs
Conclusion
In conclusion, droopy eye, or ptosis, in dogs can stem from a variety of underlying causes, including neurological conditions, trauma or injury, infections, and genetic predispositions. Understanding these potential triggers is crucial for identifying the root of the issue and seeking appropriate veterinary care. The intricate anatomy of a dog's eye underscores the delicate balance required for optimal function, highlighting the significance of proactive eye care and prompt attention to any abnormalities.
Neurological conditions, such as Horner's syndrome and facial nerve paralysis, can significantly impact a dog's eye health, leading to droopy eye as a visible manifestation. Trauma or injury to the eye or its surrounding structures can result in ptosis, necessitating prompt veterinary evaluation and targeted treatment. Infections affecting the eye, such as those associated with canine distemper, can contribute to droopy eye, emphasizing the importance of vigilance and proactive measures to address potential risks. Additionally, genetic predispositions within specific dog breeds can influence the development of droopy eye, highlighting the need for breed-specific considerations and tailored interventions.
Addressing droopy eye in dogs often involves a multifaceted approach, including medical management, surgical intervention, neurological treatments, symptomatic support, and ongoing monitoring and care. Each treatment modality is tailored to the individual dog's condition, aiming to alleviate discomfort, restore function, and enhance their quality of life. By recognizing the underlying causes and treatment options for droopy eye in dogs, pet owners can play a crucial role in advocating for their canine companions' eye health, ensuring that they receive the necessary support and care when needed.
Ultimately, the well-being of our beloved canine friends hinges on our ability to recognize and address potential eye health concerns, including droopy eye. By gaining insight into the causes and treatment options for this condition, pet owners can become more attuned to their dog's health, promoting optimal vision and overall well-being. Through collaboration with veterinary professionals and a commitment to proactive eye care, we can ensure that our canine companions enjoy clear vision and a vibrant, fulfilling life.