Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Muscular and Joint Health>Difference Between Shockwave And Laser Therapy For Dogs With Arthritis

Muscular and Joint Health
Difference Between Shockwave And Laser Therapy For Dogs With Arthritis
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about the differences between shockwave and laser therapy for dogs with arthritis. Discover the best options for muscular and joint health.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When our furry companions experience discomfort or reduced mobility due to arthritis, it can be distressing for both the pet and their human family. Fortunately, advancements in veterinary medicine have led to the development of innovative therapies to alleviate the symptoms of arthritis in dogs. Two popular treatment options that have gained attention in recent years are shockwave therapy and laser therapy.
These non-invasive and drug-free modalities offer promising results in managing arthritis-related pain and promoting healing. As pet owners, it's essential to understand the differences between these therapies to make informed decisions about the best approach for our beloved canine friends. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of shockwave therapy and laser therapy for dogs with arthritis, exploring their unique mechanisms and potential benefits. By gaining insight into these treatment options, pet owners can empower themselves to make well-informed choices that prioritize the well-being and comfort of their furry companions.
Understanding Arthritis in Dogs
Arthritis, a condition commonly associated with aging, affects not only humans but also our canine companions. In dogs, arthritis refers to the inflammation of one or more joints, leading to pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. This degenerative joint disease can significantly impact a dog's quality of life, causing discomfort and hindering their ability to engage in regular activities such as walking, running, and playing.
The most prevalent form of arthritis in dogs is osteoarthritis, which occurs when the protective cartilage within the joints wears down over time, resulting in friction between the bones. This friction triggers inflammation, leading to pain and restricted movement. While osteoarthritis is often linked to aging, it can also develop as a result of joint injuries, genetic predisposition, or developmental disorders.
Recognizing the signs of arthritis in dogs is crucial for early intervention and effective management. Common symptoms include limping, reluctance to climb stairs or jump, decreased activity levels, stiffness, and noticeable changes in gait. Additionally, dogs with arthritis may exhibit behavioral changes such as irritability or reluctance to be touched in specific areas.
Understanding the impact of arthritis on dogs is essential for pet owners, as it enables them to provide the necessary support and seek appropriate treatment. By recognizing the signs of discomfort and restricted mobility, pet owners can take proactive measures to improve their canine companions' well-being and alleviate their pain.
Armed with this understanding of arthritis in dogs, pet owners can explore various treatment options, including innovative modalities such as shockwave therapy and laser therapy, to help their furry friends lead happier, more comfortable lives.
Understanding the nuances of arthritis in dogs equips pet owners with the knowledge needed to recognize the signs of discomfort and take proactive steps to improve their canine companions' well-being. This awareness also facilitates informed decision-making when exploring treatment options, such as shockwave therapy and laser therapy, to alleviate the symptoms of arthritis and enhance the quality of life for dogs.
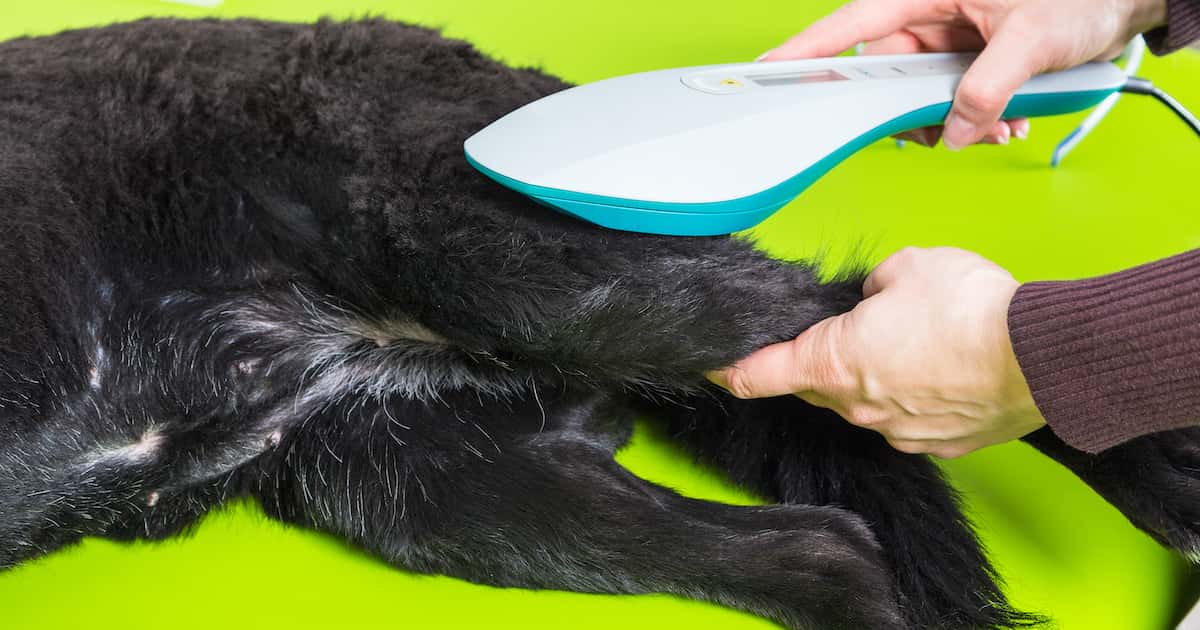
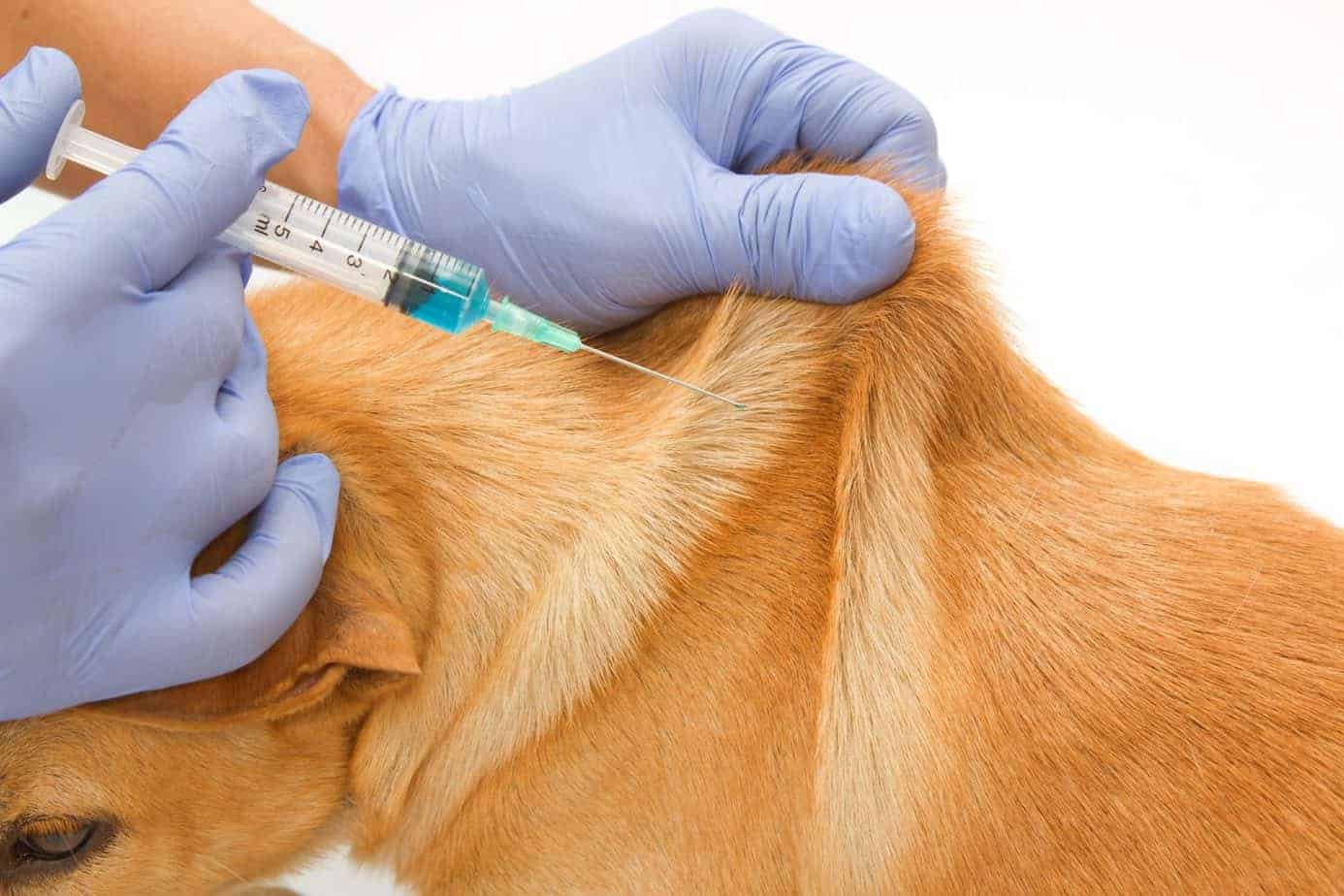
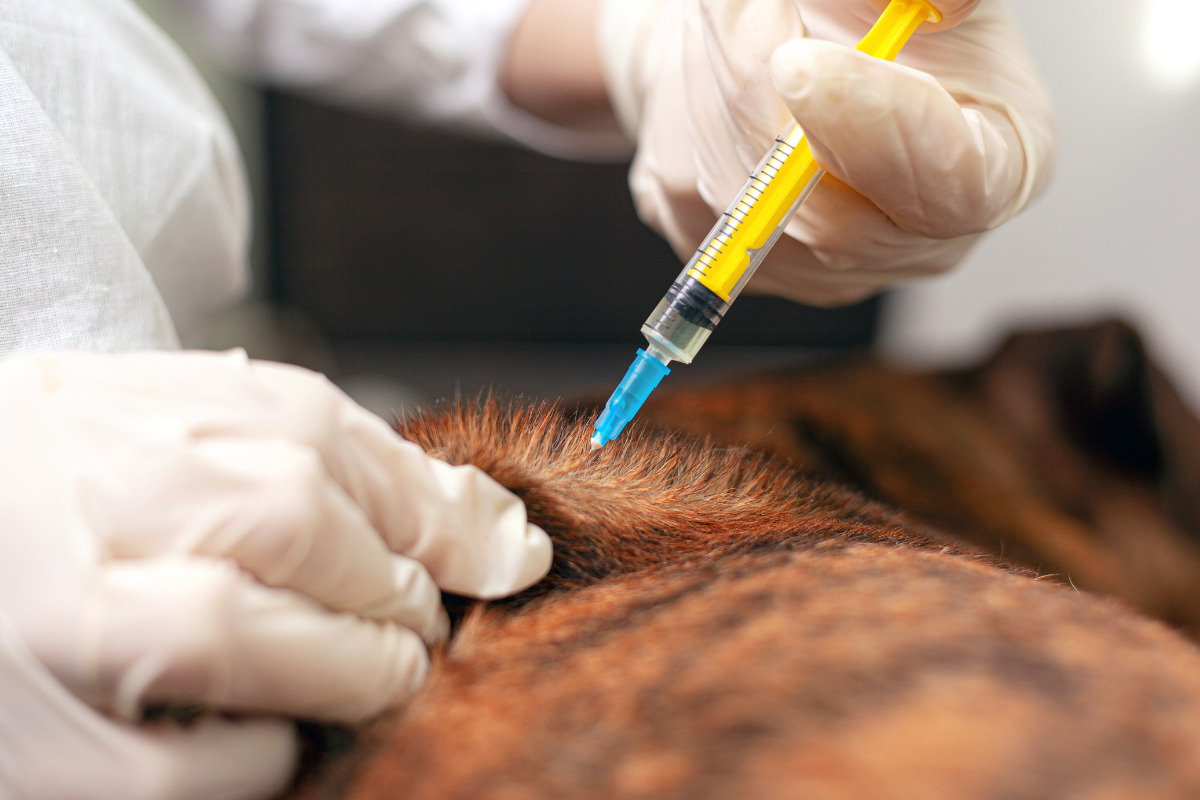
Shockwave Therapy for Dogs with Arthritis
Shockwave therapy, also known as extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT), has emerged as a promising non-invasive treatment for dogs suffering from arthritis. This innovative modality harnesses the power of acoustic waves to stimulate the body's natural healing processes and alleviate the symptoms associated with arthritis.
During a shockwave therapy session, a specialized device delivers high-energy acoustic waves to the affected joint or area of discomfort. These acoustic waves propagate through the tissues, exerting mechanical stress and triggering a cascade of biological responses. The mechanical stimulation induced by shockwave therapy promotes increased blood flow to the targeted area, facilitating tissue regeneration and reducing inflammation.
One of the key benefits of shockwave therapy is its ability to promote the production of growth factors, which play a crucial role in tissue repair and regeneration. By stimulating the release of growth factors, shockwave therapy accelerates the healing process within the affected joints, offering relief from pain and improving mobility for dogs with arthritis.
Furthermore, shockwave therapy has been shown to have analgesic effects, providing pain relief for dogs experiencing discomfort due to arthritis. The modulation of pain signaling pathways through shockwave therapy contributes to enhanced comfort and improved mobility, enabling dogs to engage in physical activities with reduced hindrance.
In addition to its regenerative and analgesic properties, shockwave therapy is well-tolerated by dogs and does not require sedation or anesthesia, making it a safe and convenient treatment option for canine arthritis. The non-invasive nature of shockwave therapy minimizes the risk of complications, allowing for repeated sessions as part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
As a non-pharmacological approach, shockwave therapy offers a valuable alternative for pet owners seeking drug-free solutions to manage their dogs' arthritis. By harnessing the body's innate healing mechanisms, shockwave therapy presents a holistic and effective means of addressing the discomfort and mobility limitations associated with canine arthritis.
In summary, shockwave therapy stands as a promising modality for dogs with arthritis, offering regenerative, analgesic, and non-invasive benefits. Its ability to stimulate tissue repair, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain makes it a valuable addition to the spectrum of treatment options available for managing arthritis in dogs, ultimately contributing to improved quality of life for our beloved canine companions.
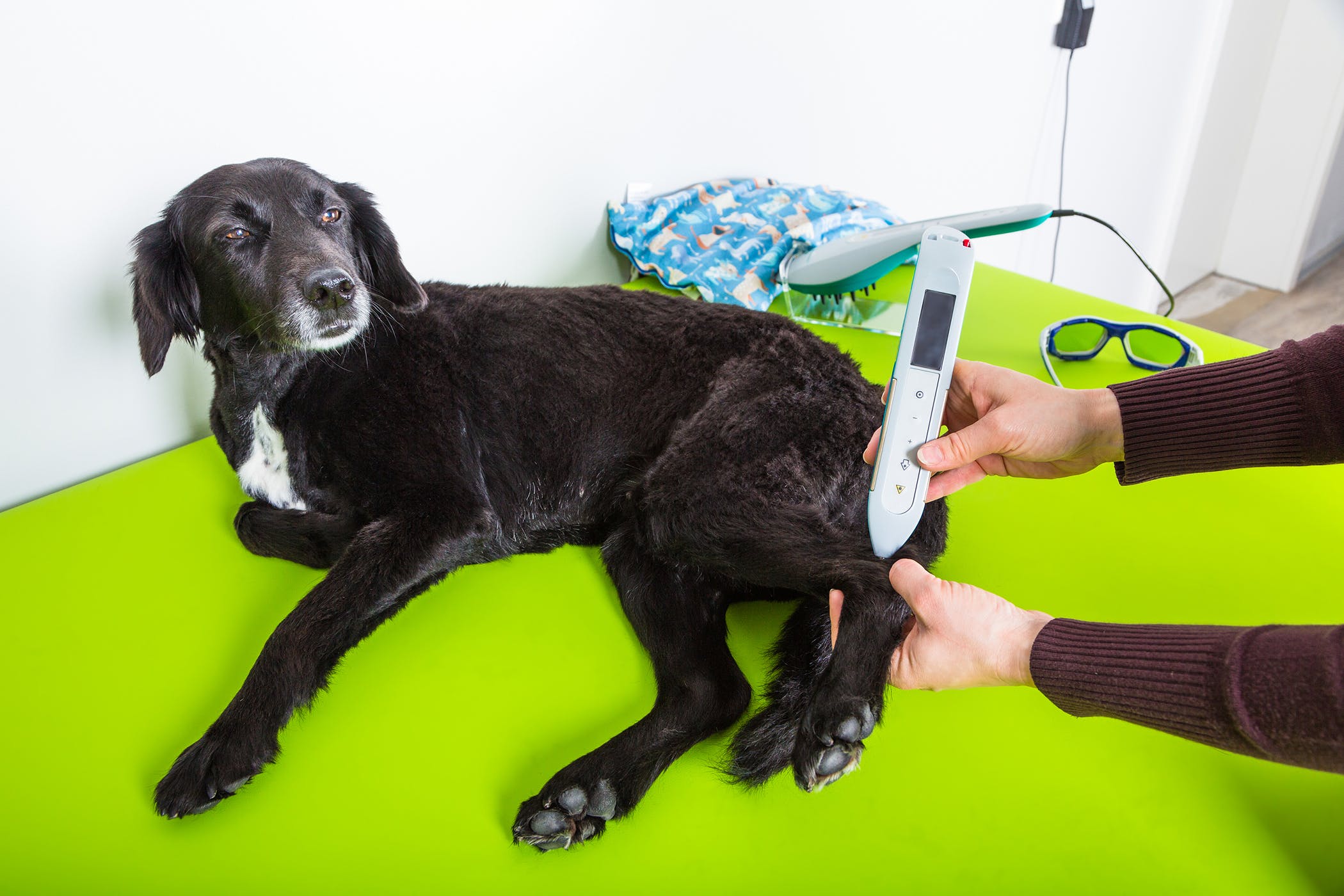
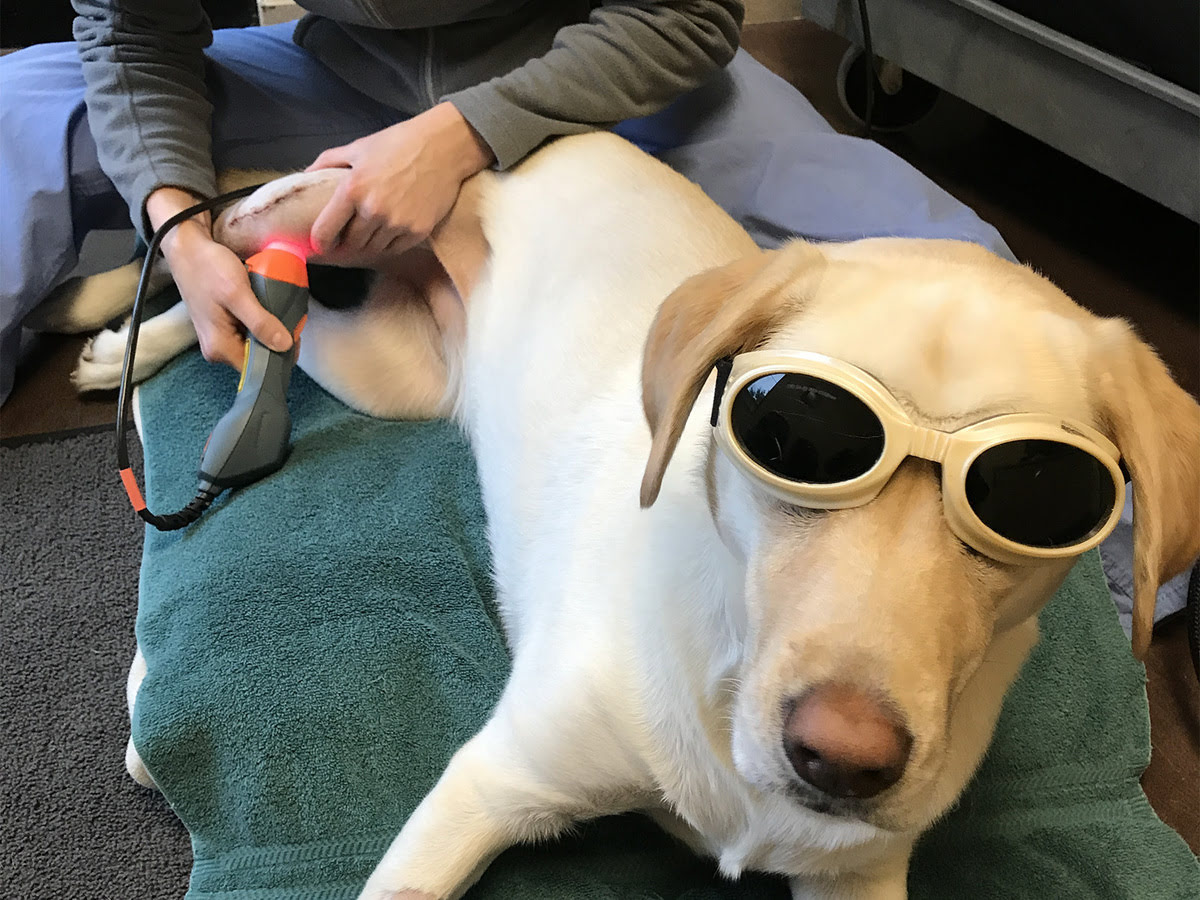
Laser Therapy for Dogs with Arthritis
Laser therapy, also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT) or photobiomodulation, has gained recognition as a non-invasive and effective treatment modality for dogs suffering from arthritis. This innovative approach harnesses the power of light energy to stimulate cellular activity and promote healing within the affected joints, offering a drug-free and gentle solution for managing arthritis-related discomfort in dogs.
During a laser therapy session, a specialized device emits a focused beam of light that penetrates the tissues and is absorbed by the cells within the targeted area. This interaction between light energy and cellular components triggers a series of biological responses, including the release of endorphins, the reduction of inflammation, and the stimulation of cellular metabolism. These processes contribute to pain relief, tissue repair, and improved circulation, ultimately alleviating the symptoms of arthritis and enhancing the overall well-being of dogs.
One of the key advantages of laser therapy is its ability to modulate inflammatory pathways, leading to a reduction in swelling and discomfort within the affected joints. By targeting the inflammatory response at a cellular level, laser therapy helps mitigate the underlying causes of arthritis-related pain, allowing dogs to experience improved mobility and a higher level of comfort.
Furthermore, laser therapy promotes the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) within the cells, which serves as a fundamental energy source for cellular processes. This increase in ATP production enhances cellular metabolism and accelerates the repair of damaged tissues, facilitating the regeneration of cartilage and joint structures affected by arthritis. As a result, dogs undergoing laser therapy may experience enhanced joint function and reduced stiffness, enabling them to engage in physical activities with greater ease.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory and regenerative effects, laser therapy has been shown to have analgesic properties, providing relief from pain and discomfort for dogs with arthritis. The stimulation of endorphin release through laser therapy contributes to a natural and sustainable reduction in pain perception, allowing dogs to experience improved comfort and a higher quality of life.
Moreover, laser therapy sessions are well-tolerated by dogs and do not require sedation or anesthesia, making it a safe and stress-free treatment option for managing arthritis. The non-invasive nature of laser therapy minimizes the risk of adverse effects, allowing for regular sessions as part of a comprehensive treatment plan tailored to the individual needs of each dog.
In summary, laser therapy offers a gentle, non-invasive, and effective approach to managing arthritis in dogs, leveraging the power of light energy to promote healing, reduce inflammation, and alleviate pain. Its ability to stimulate cellular activity, enhance tissue repair, and modulate inflammatory pathways makes it a valuable therapeutic option for pet owners seeking to improve the well-being and comfort of their canine companions.
Comparison of Shockwave and Laser Therapy
When considering the optimal treatment approach for dogs with arthritis, the comparison between shockwave therapy and laser therapy becomes pivotal in making an informed decision. Both modalities offer non-invasive, drug-free solutions for managing arthritis-related discomfort and promoting healing, yet they differ in their mechanisms and therapeutic effects.
Shockwave therapy harnesses high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate tissue regeneration, increase blood flow, and promote the release of growth factors within the affected joints. In contrast, laser therapy utilizes focused light energy to modulate inflammatory pathways, enhance cellular metabolism, and stimulate the production of endorphins and ATP. These distinct mechanisms underpin the unique therapeutic properties of each modality.
In terms of regenerative effects, shockwave therapy excels in promoting tissue repair and regeneration through the stimulation of growth factors, contributing to the restoration of joint structures affected by arthritis. On the other hand, laser therapy's ability to enhance cellular metabolism and ATP production facilitates the regeneration of cartilage and joint tissues, leading to improved joint function and reduced stiffness.
When addressing pain management, both modalities offer analgesic benefits, albeit through different mechanisms. Shockwave therapy modulates pain signaling pathways, providing sustainable pain relief and improved mobility for dogs with arthritis. Laser therapy, on the other hand, stimulates the release of endorphins, resulting in a natural reduction in pain perception and enhanced comfort for canine patients.
Furthermore, the safety and tolerability of these modalities play a crucial role in treatment considerations. Shockwave therapy is well-tolerated by dogs and does not require sedation or anesthesia, offering a convenient and stress-free treatment option. Similarly, laser therapy sessions are gentle and non-invasive, ensuring minimal risk of adverse effects and allowing for regular sessions tailored to the individual needs of each dog.
In summary, the comparison between shockwave therapy and laser therapy underscores their distinct yet complementary therapeutic benefits for dogs with arthritis. While shockwave therapy excels in promoting tissue regeneration and growth factor stimulation, laser therapy stands out in modulating inflammatory pathways and enhancing cellular metabolism. Both modalities offer analgesic effects and are well-tolerated, providing pet owners with valuable options to improve the well-being and comfort of their furry companions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the management of arthritis in dogs presents a multifaceted challenge that demands thoughtful consideration and informed decision-making from pet owners. The emergence of innovative treatment modalities such as shockwave therapy and laser therapy offers promising avenues for addressing the discomfort and mobility limitations experienced by dogs with arthritis. By understanding the unique mechanisms and therapeutic effects of these modalities, pet owners can make well-informed choices that prioritize the well-being and comfort of their beloved canine companions.
Both shockwave therapy and laser therapy represent non-invasive, drug-free solutions for managing arthritis-related pain and promoting healing within the affected joints. Shockwave therapy harnesses high-energy acoustic waves to stimulate tissue regeneration, increase blood flow, and promote the release of growth factors, ultimately contributing to the restoration of joint structures and sustainable pain relief. On the other hand, laser therapy utilizes focused light energy to modulate inflammatory pathways, enhance cellular metabolism, and stimulate the production of endorphins and ATP, leading to reduced inflammation, improved joint function, and natural pain relief.
The comparison between these modalities highlights their distinct yet complementary therapeutic benefits, underscoring the value of considering individualized treatment approaches tailored to the specific needs of each dog. While shockwave therapy excels in promoting tissue regeneration and growth factor stimulation, laser therapy stands out in modulating inflammatory pathways and enhancing cellular metabolism. Both modalities offer analgesic effects and are well-tolerated, providing pet owners with valuable options to improve the well-being and comfort of their furry companions.
Ultimately, the decision regarding the most suitable treatment modality for a dog with arthritis should be guided by a comprehensive understanding of the pet's condition, in consultation with a qualified veterinary professional. By collaborating with veterinarians and exploring the potential benefits of shockwave therapy and laser therapy, pet owners can play an active role in enhancing the quality of life for their canine companions, enabling them to enjoy greater comfort, improved mobility, and a renewed sense of vitality.
As the field of veterinary medicine continues to advance, the integration of innovative modalities such as shockwave therapy and laser therapy holds promise for transforming the landscape of arthritis management in dogs. By staying informed and proactive, pet owners can navigate the complexities of arthritis with confidence, empowered to make decisions that prioritize the well-being and happiness of their cherished four-legged family members.