Home>Health & Wellness>Behavior & Cognitive Care>How To Tell If Your Senior Dog Has Tumors

Behavior & Cognitive Care
How To Tell If Your Senior Dog Has Tumors
Published: February 1, 2024
Learn how to recognize signs of tumors in senior dogs with our guide on behavior and cognitive care. Keep your furry friend healthy and happy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
As our beloved canine companions age, they become more susceptible to various health issues, including tumors. Tumors in senior dogs can be a cause of concern for pet parents, prompting the need for understanding the signs, symptoms, and treatment options available. It's essential to be proactive in monitoring our senior dogs for any indications of tumors, as early detection can significantly impact the prognosis and treatment outcomes.
Understanding the potential impact of tumors on senior dogs is crucial for providing them with the best possible care and support. This article aims to shed light on the signs and symptoms of tumors in senior dogs, the types of tumors commonly found in this age group, the diagnostic process, available treatment options, and practical tips for supporting senior dogs diagnosed with tumors.
By delving into these aspects, pet parents and caregivers can gain valuable insights into recognizing, addressing, and managing tumors in their senior canine companions. This knowledge empowers them to take proactive measures in safeguarding their dog's well-being and ensuring a high quality of life during their golden years.
The journey of navigating through the complexities of tumors in senior dogs requires compassion, patience, and a deep understanding of the unique needs of aging canine companions. With the right information and support, pet parents can make informed decisions and provide the best possible care for their senior dogs facing this health challenge.
Read more: How To Tell If Your Dog Has Dental Problems
Signs and Symptoms of Tumors in Senior Dogs
Senior dogs, like their human counterparts, are more susceptible to health issues as they age. Tumors are among the potential health concerns that can affect senior dogs, and being aware of the signs and symptoms is crucial for early detection and intervention.
-
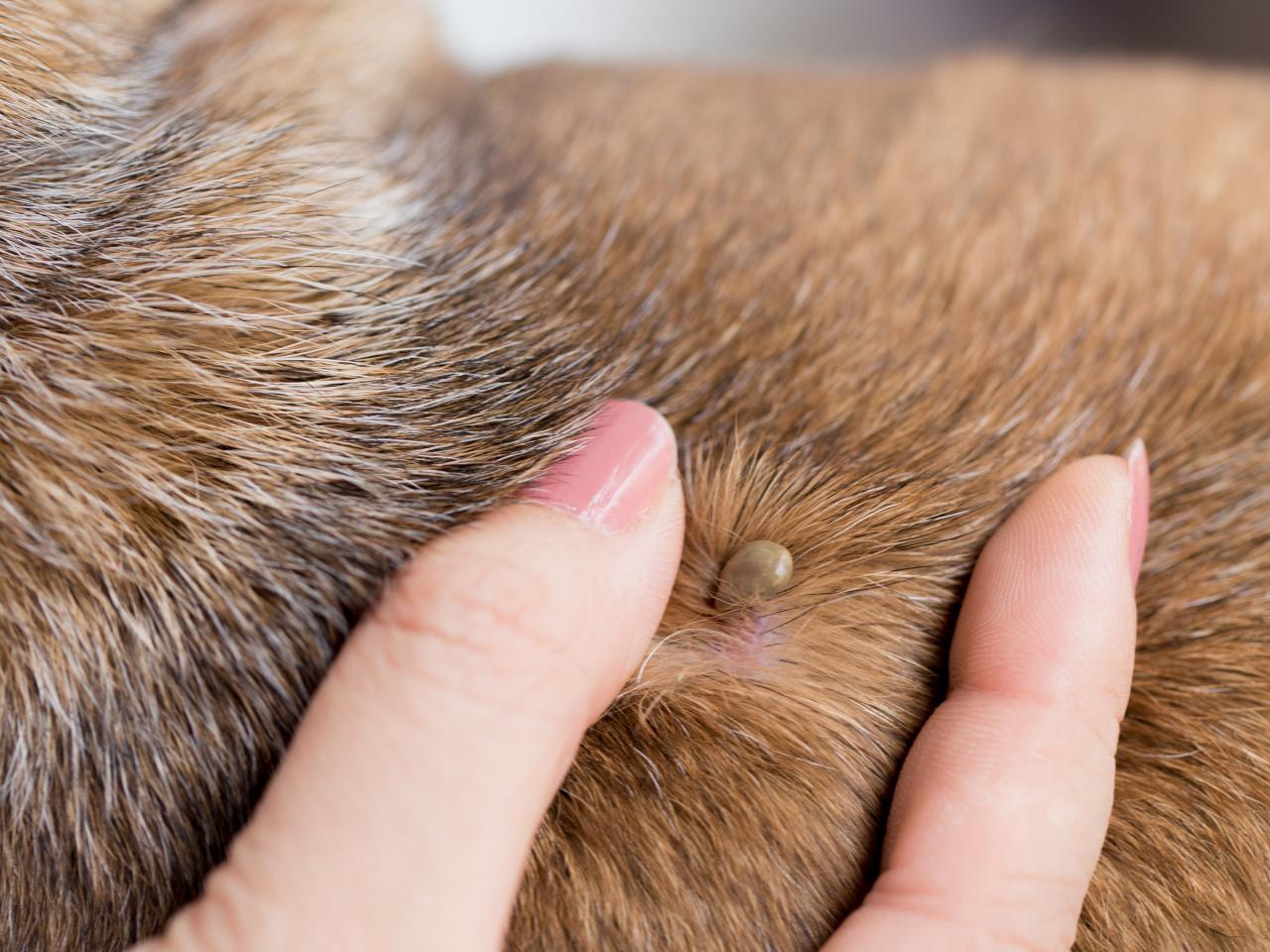
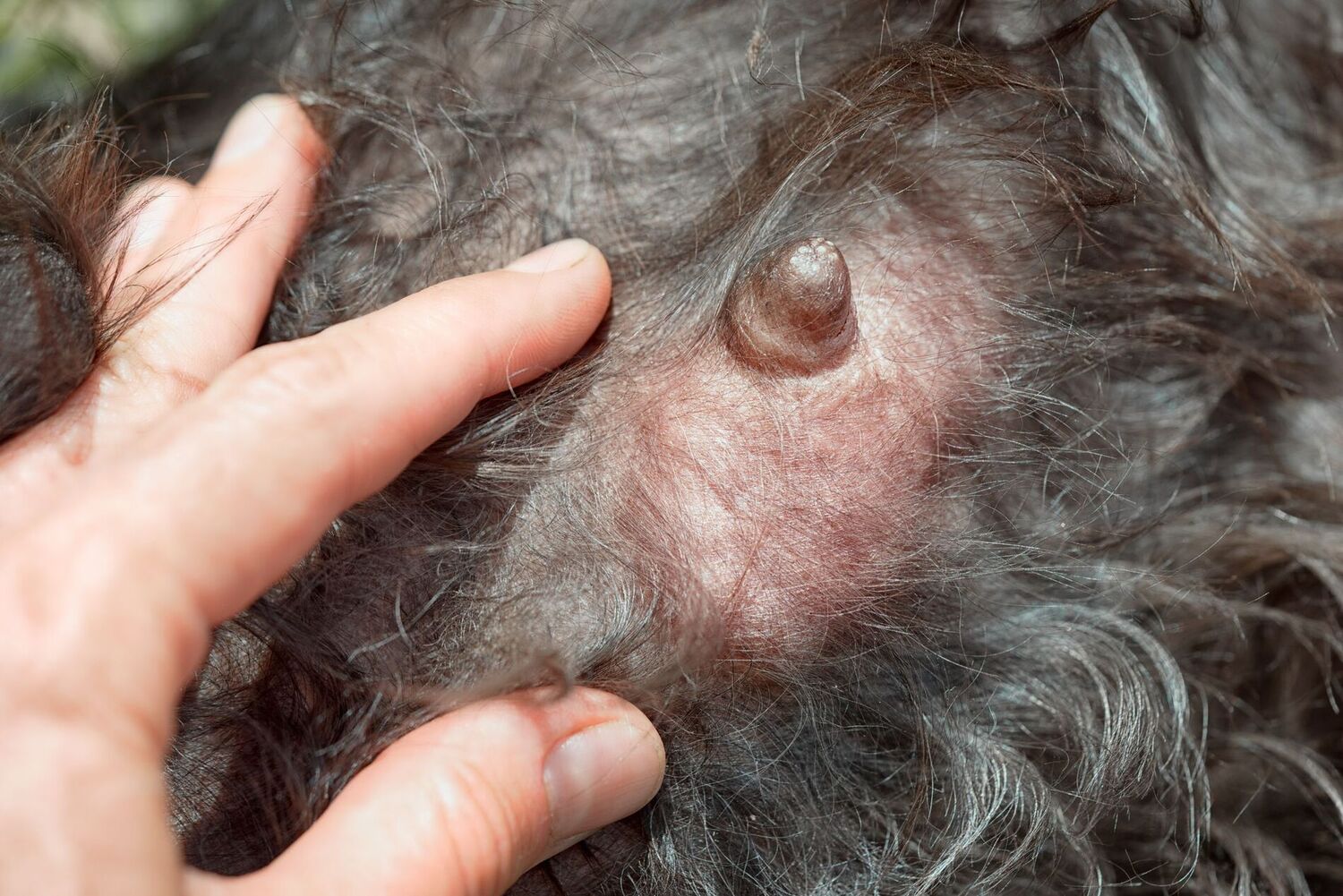
Lumps and Swellings: One of the most noticeable signs of tumors in senior dogs is the presence of lumps or swellings on their body. These may be felt during regular petting or grooming sessions. It's essential to monitor any new growths or changes in existing lumps, as they can indicate the presence of tumors.
-
Changes in Behavior: Senior dogs with tumors may exhibit changes in their behavior. This can manifest as increased irritability, reluctance to engage in physical activities they once enjoyed, or signs of discomfort when being touched or handled. Additionally, a decrease in appetite or unexplained weight loss can be indicative of an underlying health issue, including tumors.
-
Difficulty Breathing or Swallowing: Tumors located in the chest or throat can lead to difficulty breathing or swallowing in senior dogs. Pet parents should be attentive to any labored breathing, persistent coughing, or signs of discomfort when eating or drinking.
-
Unexplained Bleeding: Any unexplained bleeding from the nose, mouth, or other bodily orifices should prompt immediate veterinary attention. While there can be various causes for bleeding, tumors are among the potential culprits, especially in senior dogs.
-
Changes in Bathroom Habits: Senior dogs with tumors may experience changes in their bathroom habits. This can include difficulty urinating or defecating, blood in the urine or stool, or an increased frequency of accidents in the house.
-
Lethargy and Weakness: Tumors can sap a senior dog's energy, leading to increased lethargy and weakness. Pet parents should take note of any significant decrease in their dog's activity levels or overall vitality.
-
Visible Pain or Discomfort: Senior dogs may exhibit signs of pain or discomfort when tumors are present. This can be observed through vocalizations, restlessness, or a reluctance to move or be touched in specific areas of their body.
Being attuned to these signs and symptoms is essential for proactive monitoring of a senior dog's health. Regular veterinary check-ups and prompt attention to any concerning changes can contribute to early detection and improved treatment outcomes for senior dogs facing the challenge of tumors.
Types of Tumors Common in Senior Dogs
Senior dogs can be susceptible to various types of tumors, each with its own characteristics and potential impact on the dog's health. Understanding the common types of tumors found in senior dogs is essential for pet parents and caregivers to recognize and address these health concerns effectively.
-
Mammary Tumors: Female dogs can develop mammary tumors, which are more common in unspayed or late-spayed females. These tumors can be benign or malignant, and early spaying can significantly reduce the risk of their development.
-
Skin Tumors: Senior dogs often develop skin tumors, including mast cell tumors, melanomas, and soft tissue sarcomas. These tumors can vary in their aggressiveness and may require surgical removal or other treatment modalities.
-
Lipomas: Lipomas are benign fatty tumors commonly found in senior dogs. While they are generally harmless, they can grow to a size that causes discomfort or impedes movement, necessitating surgical removal.
-
Osteosarcoma: This aggressive bone tumor is prevalent in large and giant breeds of senior dogs. Osteosarcoma can cause lameness, swelling, and significant pain in the affected limb, often requiring a combination of surgery and chemotherapy for treatment.
-
Hemangiosarcoma: Commonly affecting the spleen, liver, or heart, hemangiosarcoma is a highly malignant tumor that can lead to internal bleeding and life-threatening complications in senior dogs. Early detection and prompt intervention are critical for managing this type of tumor.
-
Lymphoma: Lymphoma is a prevalent cancer in senior dogs, affecting the lymphatic system and leading to symptoms such as enlarged lymph nodes, weight loss, and lethargy. Chemotherapy and other treatment options can be employed to manage lymphoma in senior dogs.
-
Mast Cell Tumors: These tumors originate from a type of white blood cell and can occur in the skin or internal organs of senior dogs. Depending on their grade and stage, mast cell tumors may require surgical removal, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
-
Transitional Cell Carcinoma: This type of tumor commonly affects the bladder and urinary tract of senior dogs, leading to symptoms such as blood in the urine, frequent urination, and straining to urinate. Treatment may involve surgery, chemotherapy, or other targeted therapies.
Understanding the characteristics and potential impact of these common tumors in senior dogs empowers pet parents and caregivers to remain vigilant for any signs or symptoms indicative of these health concerns. Early detection and timely veterinary intervention play a crucial role in addressing tumors in senior dogs and optimizing their quality of life during their golden years.
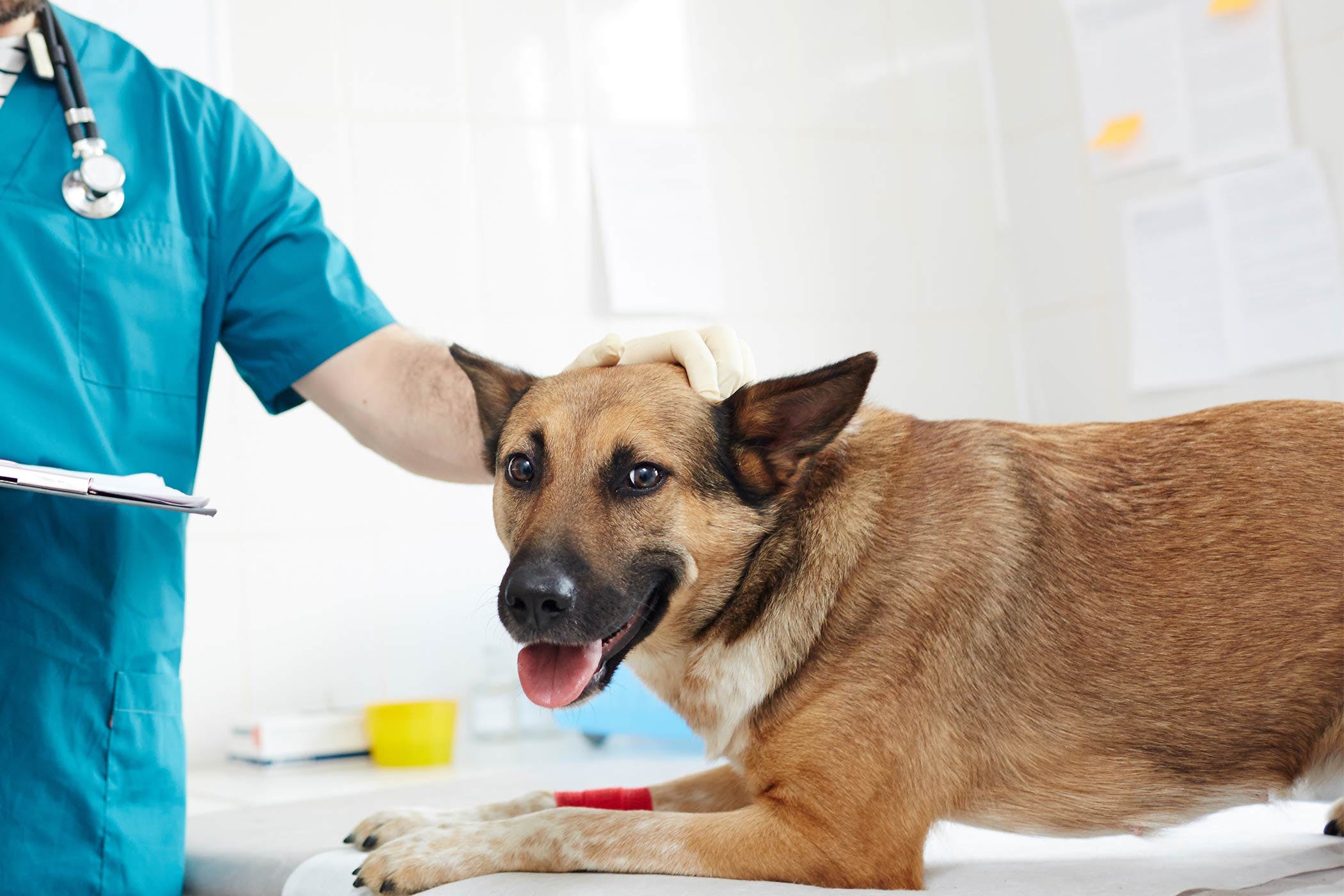
Diagnosing Tumors in Senior Dogs
Diagnosing tumors in senior dogs requires a comprehensive approach that encompasses clinical evaluations, diagnostic imaging, and, in some cases, tissue sampling for definitive analysis. When a senior dog exhibits potential signs or symptoms of tumors, prompt veterinary attention is crucial to initiate the diagnostic process and determine the nature of the underlying health concern.
Veterinarians employ various diagnostic methods to assess and diagnose tumors in senior dogs. These may include:
-
Physical Examination: A thorough physical examination is the initial step in diagnosing tumors in senior dogs. Veterinarians palpate the dog's body to identify any lumps, swellings, or abnormalities. Additionally, they assess the dog's overall condition, including vital signs and any observable signs of discomfort or pain.
-
Diagnostic Imaging: Imaging techniques such as X-rays, ultrasound, and in some cases, advanced imaging modalities like CT scans or MRIs, are utilized to visualize the internal structures of the dog's body. These imaging studies can reveal the presence of tumors, their location, and potential impact on surrounding tissues and organs.
-
Fine Needle Aspiration or Biopsy: In cases where palpable lumps or masses are identified, veterinarians may perform fine needle aspiration or recommend a biopsy. Fine needle aspiration involves extracting cells from the tumor for microscopic examination, providing preliminary insights into the nature of the growth. Biopsy, on the other hand, involves the surgical removal of a tissue sample for detailed analysis, aiding in the definitive diagnosis of the tumor and determination of its characteristics.
-
Blood Tests: Blood work, including complete blood counts and serum chemistry profiles, can offer valuable information about the dog's overall health and potential indicators of underlying tumors. Specific markers or abnormalities in the blood may raise suspicion of certain types of tumors, guiding further diagnostic steps.
-
Specialized Tests: Depending on the suspected type and location of the tumor, veterinarians may recommend specialized tests such as cytology, histopathology, or immunohistochemistry to gain a comprehensive understanding of the tumor's nature, including its cellular composition, grade, and potential for metastasis.
Once the diagnostic evaluations are completed, veterinarians can formulate a precise diagnosis and develop a tailored treatment plan based on the specific characteristics of the tumor and the overall health status of the senior dog. Early and accurate diagnosis is pivotal in initiating timely interventions and optimizing the outcomes for senior dogs facing the challenge of tumors.
The diagnostic process for tumors in senior dogs underscores the importance of proactive monitoring, regular veterinary care, and a collaborative approach between pet parents and veterinary professionals to safeguard the well-being of aging canine companions.
Treatment Options for Tumors in Senior Dogs
When it comes to addressing tumors in senior dogs, the treatment approach is tailored to the specific type of tumor, its location, size, and the overall health status of the dog. Treatment options for tumors in senior dogs encompass a range of modalities aimed at managing the growth, alleviating symptoms, and improving the dog's quality of life. The primary treatment modalities include:
-
Surgical Removal: In cases where the tumor is localized and deemed operable, surgical excision may be recommended. This involves the removal of the tumor and, in some instances, a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete eradication. Surgical removal is often employed for skin tumors, mammary tumors, and certain soft tissue tumors.
-
Chemotherapy: For tumors that have the potential to metastasize or are not amenable to surgical intervention alone, chemotherapy may be employed. Chemotherapeutic agents are used to target and inhibit the growth of cancer cells, either to shrink the tumor prior to surgery or to manage systemic spread in cases of advanced tumors.
-
Radiation Therapy: This modality utilizes targeted radiation to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors. It is often employed for tumors that are inoperable or when complete surgical removal is not feasible. Radiation therapy can be effective in managing certain types of tumors, including localized bone tumors and soft tissue sarcomas.
-
Immunotherapy: Emerging as a promising treatment avenue, immunotherapy harnesses the dog's immune system to recognize and combat cancer cells. This approach can be beneficial in managing certain types of tumors and may be used in conjunction with other treatment modalities.
-
Palliative Care: In cases where the tumor cannot be completely eradicated, palliative care focuses on alleviating pain, managing symptoms, and enhancing the dog's comfort and well-being. This may involve pain management medications, dietary adjustments, and supportive care to optimize the dog's quality of life.
-
Targeted Therapies: Advancements in veterinary oncology have led to the development of targeted therapies that specifically interfere with the molecular processes driving tumor growth. These therapies are tailored to the characteristics of the tumor and can offer effective treatment options for certain types of tumors in senior dogs.
The selection of the most appropriate treatment modality for a senior dog with tumors involves a comprehensive assessment by veterinary oncologists, considering factors such as the tumor type, stage, potential side effects, and the dog's overall health. Additionally, supportive care and close monitoring play a crucial role in ensuring the well-being of senior dogs undergoing tumor treatment.
By leveraging these treatment options and providing compassionate care, pet parents and veterinary professionals can work together to support senior dogs facing the challenge of tumors, aiming to enhance their comfort, prolong their quality of life, and celebrate the enduring bond shared with these cherished companions.
Tips for Supporting a Senior Dog with Tumors
Supporting a senior dog diagnosed with tumors requires a holistic approach that encompasses physical care, emotional support, and attentive monitoring. Here are essential tips for pet parents and caregivers to provide the best possible support for their senior canine companions facing the challenge of tumors:
-
Comfort-Oriented Environment: Create a comfortable and safe environment for your senior dog, ensuring easy access to resting areas, food, water, and bathroom facilities. Soft bedding and gentle lighting can contribute to their overall comfort, especially if they experience mobility challenges or discomfort due to the tumors.
-
Nutritional Support: Consult with your veterinarian to develop a tailored nutrition plan that meets the specific dietary needs of your senior dog with tumors. Adequate nutrition plays a vital role in supporting their immune system, managing potential side effects of treatment, and maintaining overall well-being.
-
Pain Management: Work closely with your veterinarian to assess and manage any pain or discomfort experienced by your senior dog. This may involve the use of pain medications, alternative therapies, or supportive measures to alleviate discomfort and enhance their quality of life.
-
Regular Veterinary Monitoring: Schedule regular veterinary check-ups to monitor the progression of the tumors, assess treatment responses, and address any emerging health concerns. Open communication with your veterinarian is essential for optimizing the care and support provided to your senior dog.
-
Emotional Support: Senior dogs facing health challenges, including tumors, may benefit from increased emotional support and companionship. Spend quality time with your dog, engage in gentle activities they enjoy, and provide reassurance and comfort to alleviate any anxiety or stress they may experience.
-
Adapted Exercise and Activity: Modify your senior dog's exercise routine and activities to accommodate any physical limitations or discomfort associated with the tumors. Gentle, low-impact exercises can help maintain mobility and muscle tone while minimizing strain on their body.
-
Quality Bonding Time: Cherish and celebrate the bond you share with your senior dog by engaging in activities that bring joy and comfort to both of you. Whether it's quiet moments of companionship, leisurely walks, or engaging in their favorite pastimes, nurturing the bond can have a positive impact on their well-being.
-
Education and Advocacy: Stay informed about the specific type of tumors affecting your senior dog and be an advocate for their care. Understanding the treatment options, potential side effects, and prognosis empowers you to make informed decisions and actively participate in their treatment journey.
-
Supportive Community: Seek support from fellow pet parents, online communities, or local support groups for senior dog caregivers. Sharing experiences, seeking advice, and finding emotional support from others who understand the challenges can be invaluable.
-
Celebrating Moments: Embrace each moment with your senior dog, celebrating their unique personality, resilience, and the enduring bond you share. While facing tumors can be a challenging journey, treasuring the moments of joy, love, and companionship can uplift both you and your senior canine companion.
By implementing these tips and providing unwavering support, pet parents and caregivers can navigate the complexities of supporting a senior dog with tumors, fostering a nurturing and compassionate environment that prioritizes the well-being and comfort of their cherished canine companion.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the journey of caring for a senior dog diagnosed with tumors is a multifaceted endeavor that demands compassion, vigilance, and a deep commitment to providing the best possible support. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of tumors in senior dogs, understanding the common types of tumors prevalent in this age group, and navigating the diagnostic and treatment processes are pivotal aspects of safeguarding the well-being of our aging canine companions.
As pet parents and caregivers, it is essential to approach the challenge of tumors in senior dogs with a proactive mindset, prioritizing regular veterinary check-ups, attentive monitoring, and open communication with veterinary professionals. Early detection of tumors, coupled with timely intervention, can significantly impact the prognosis and treatment outcomes, offering senior dogs the opportunity to maintain a high quality of life during their golden years.
The treatment journey for senior dogs with tumors encompasses a spectrum of modalities, including surgical interventions, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and palliative care, tailored to the specific characteristics of the tumors and the individual needs of the dog. By leveraging these treatment options and providing compassionate care, pet parents can play a pivotal role in supporting their senior dogs through the challenges posed by tumors, aiming to enhance their comfort, alleviate symptoms, and celebrate the enduring bond shared with these cherished companions.
Furthermore, the holistic support provided to senior dogs with tumors extends beyond physical care, encompassing emotional support, adapted activities, nutritional considerations, and a nurturing environment that prioritizes their well-being. By implementing these comprehensive measures, pet parents and caregivers can create a supportive and comforting environment for their senior dogs, fostering a sense of security, companionship, and unwavering dedication throughout the journey of managing tumors in their aging canine companions.
Ultimately, the journey of caring for a senior dog with tumors is a testament to the enduring bond and unwavering commitment shared between pet parents and their beloved companions. By remaining informed, proactive, and deeply attuned to the needs of senior dogs facing tumors, pet parents can navigate this health challenge with resilience, empathy, and a profound dedication to providing the best possible care for their cherished senior canine companions.