Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Dogs Get Tick Fever


Common Health Issues
How Dogs Get Tick Fever
Published: February 5, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs, including how they can get tick fever and ways to prevent it. Keep your furry friend healthy and happy!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Tick fever, also known as ehrlichiosis, is a common health issue that affects dogs worldwide. This potentially serious illness is caused by the bite of an infected tick, leading to the transmission of harmful bacteria into the dog's bloodstream. As a responsible pet owner, it's crucial to understand the risks associated with tick fever and take proactive measures to protect your furry companion.
Tick fever can have detrimental effects on a dog's overall health and well-being, making it essential to recognize the symptoms and seek prompt veterinary care. By gaining insight into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tick fever, you can empower yourself to safeguard your dog from this prevalent and concerning condition.
Understanding the intricacies of tick fever is pivotal in ensuring the optimal health of your canine companion. This article aims to provide comprehensive information on tick fever in dogs, equipping you with the knowledge to identify, address, and prevent this ailment effectively. Let's delve into the world of tick fever and explore the various facets of this prevalent health issue in dogs.
Read more: How To Get Rid Of Fleas And Ticks On My Dog
Understanding Tick Fever in Dogs
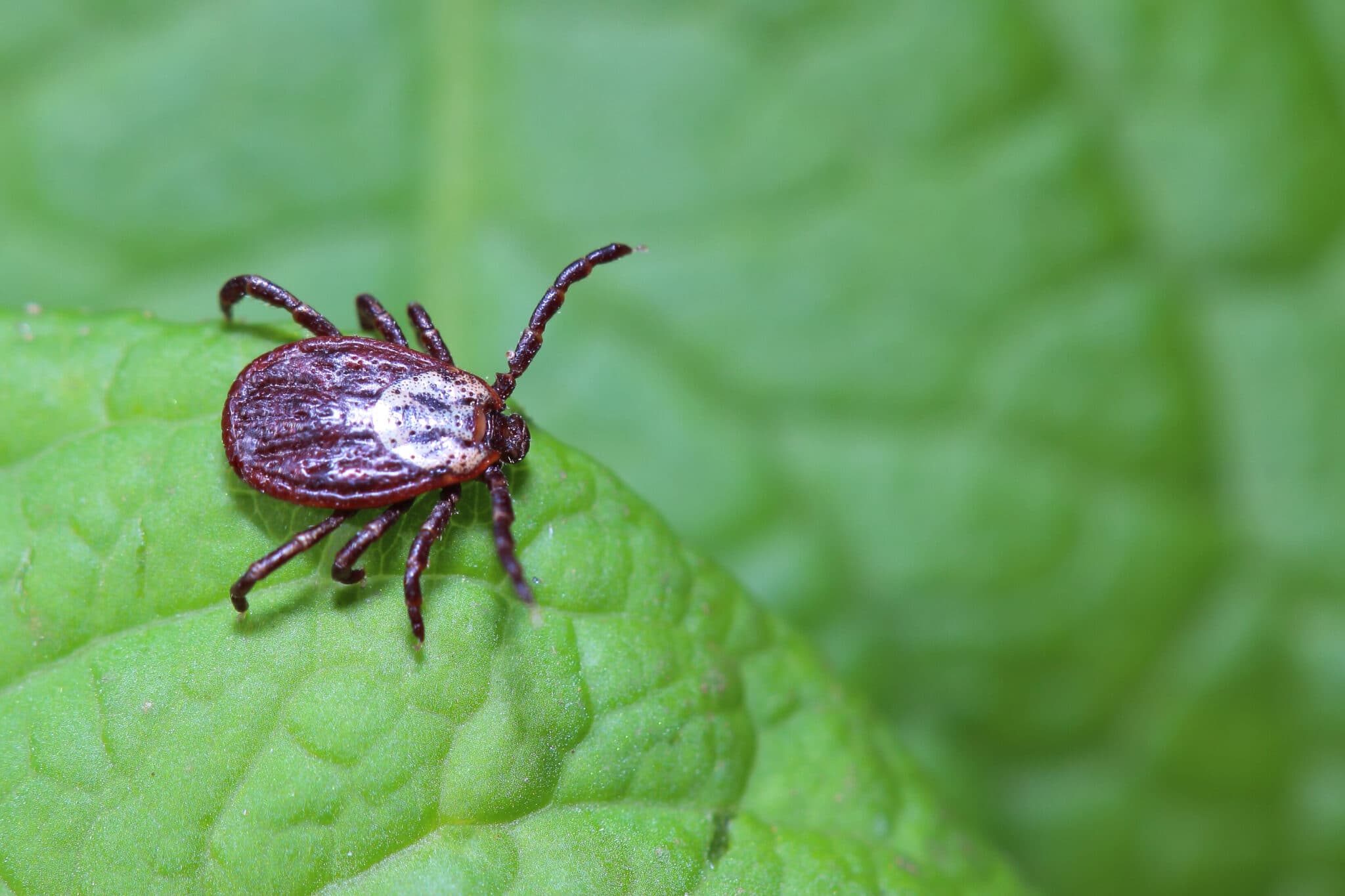
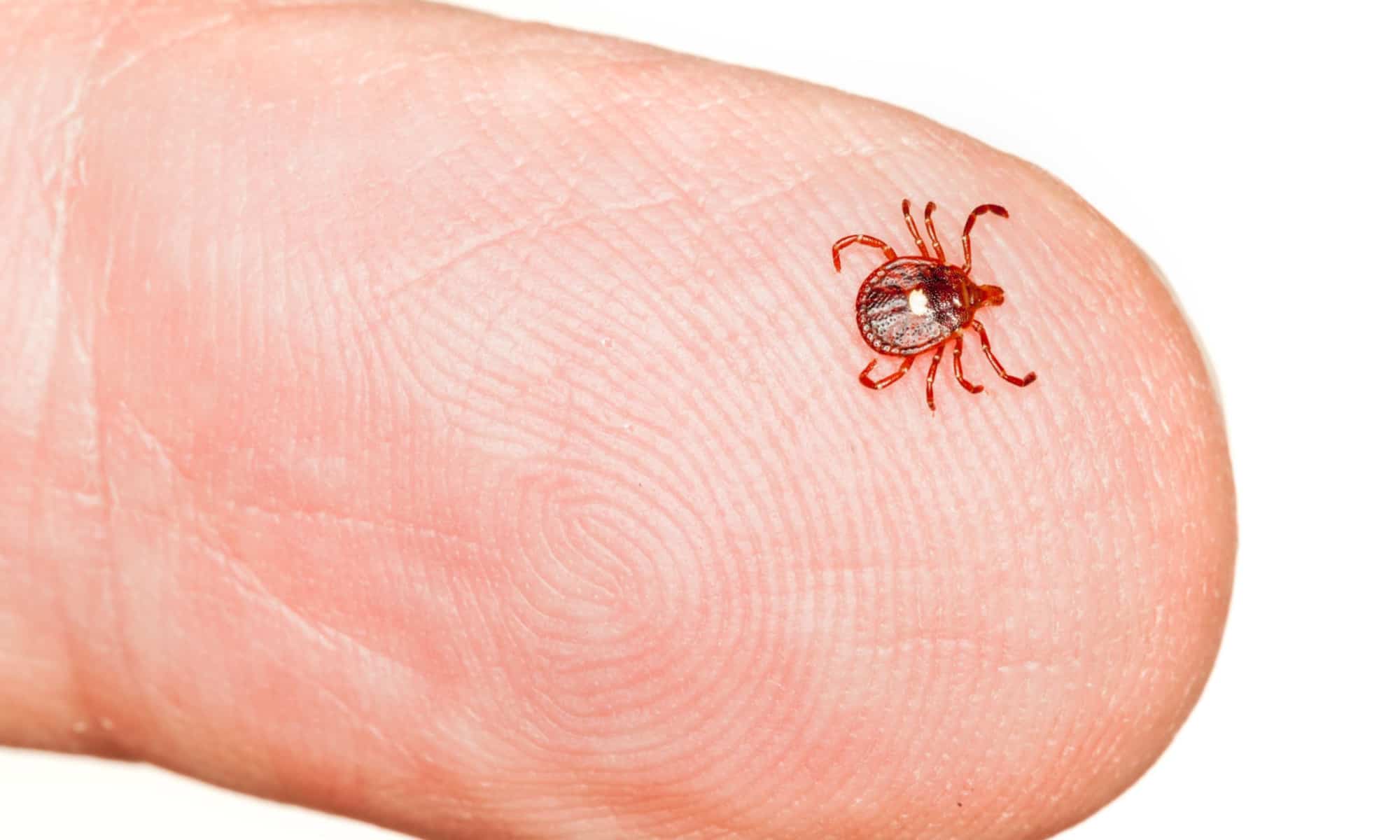
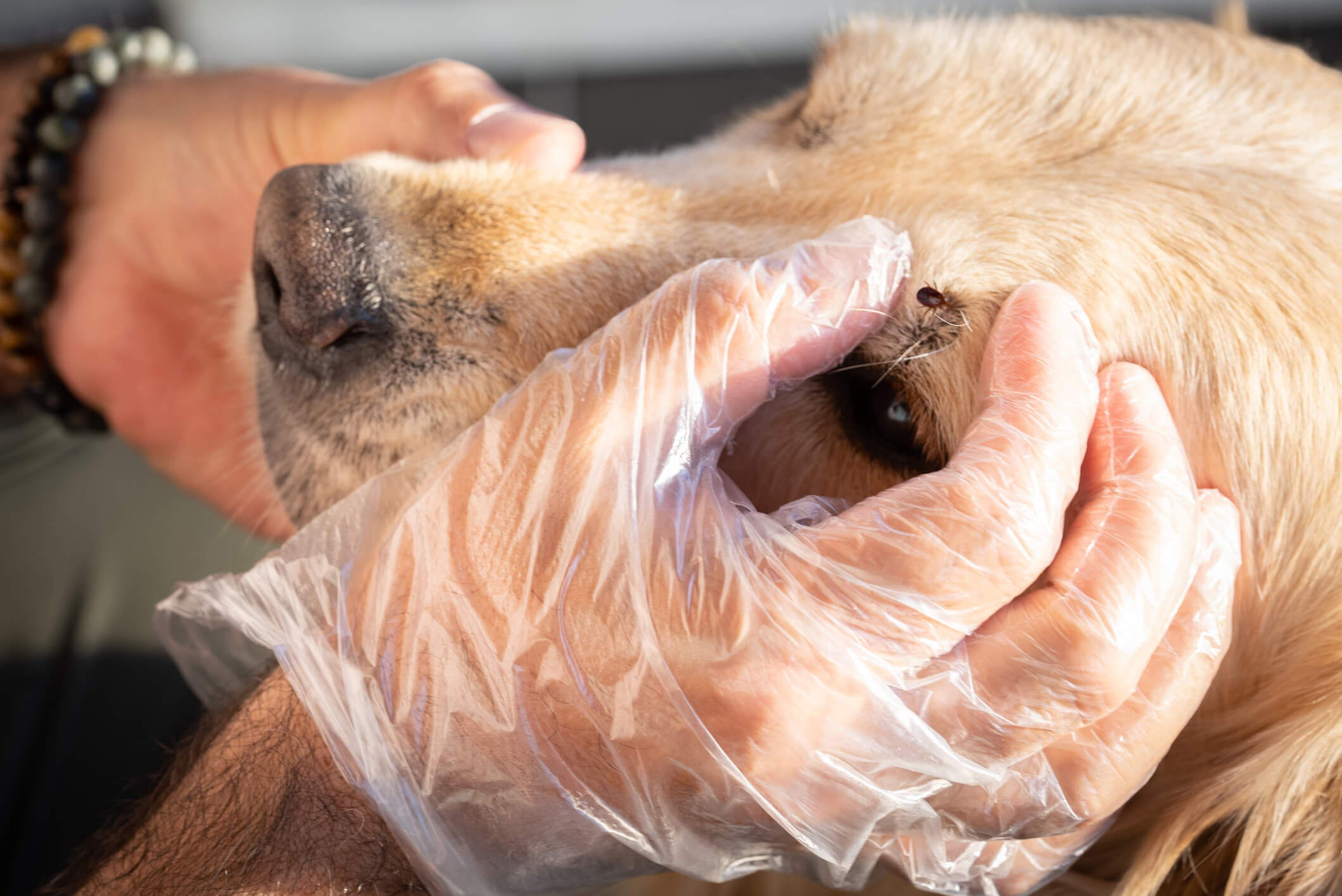
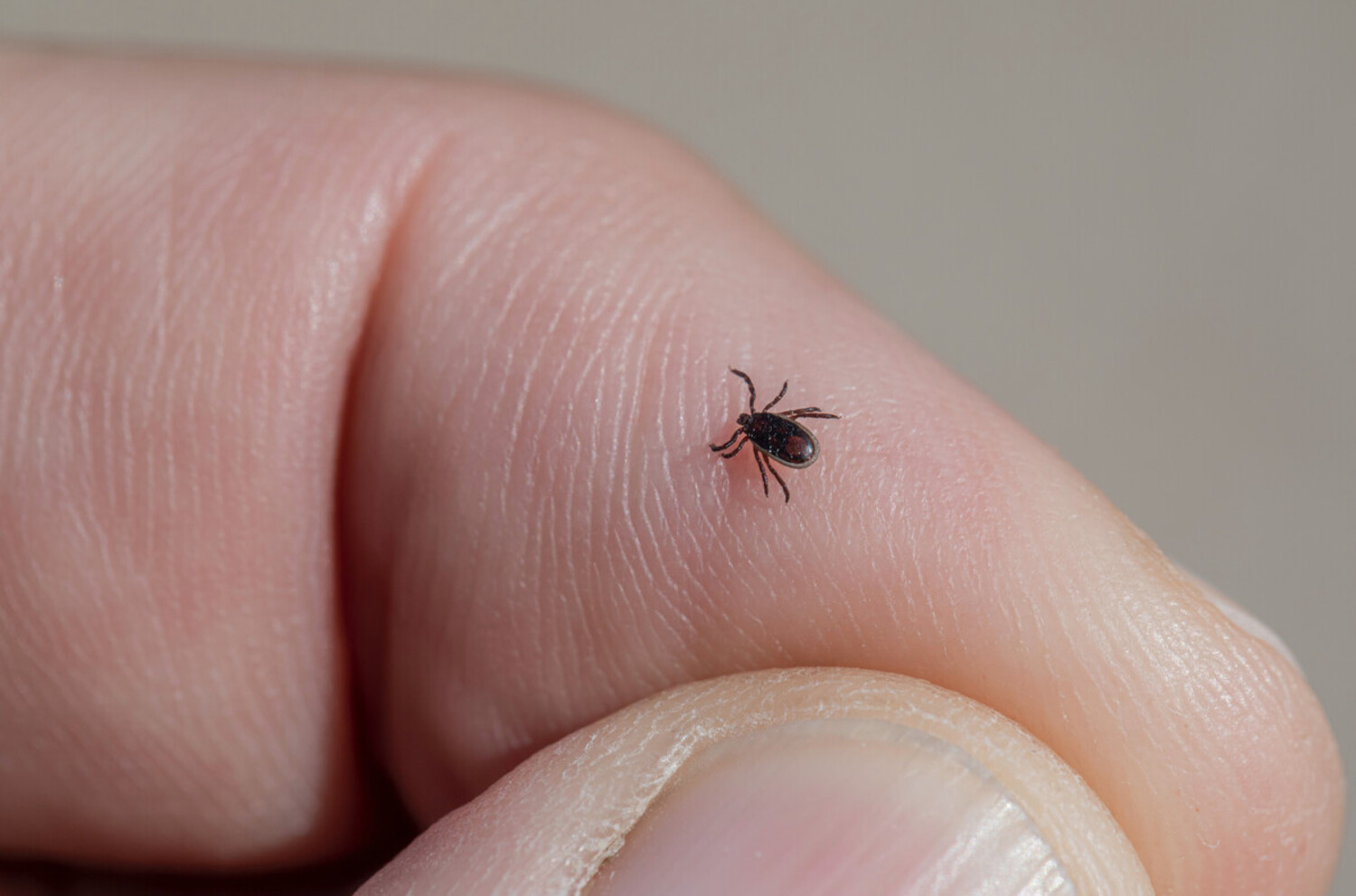
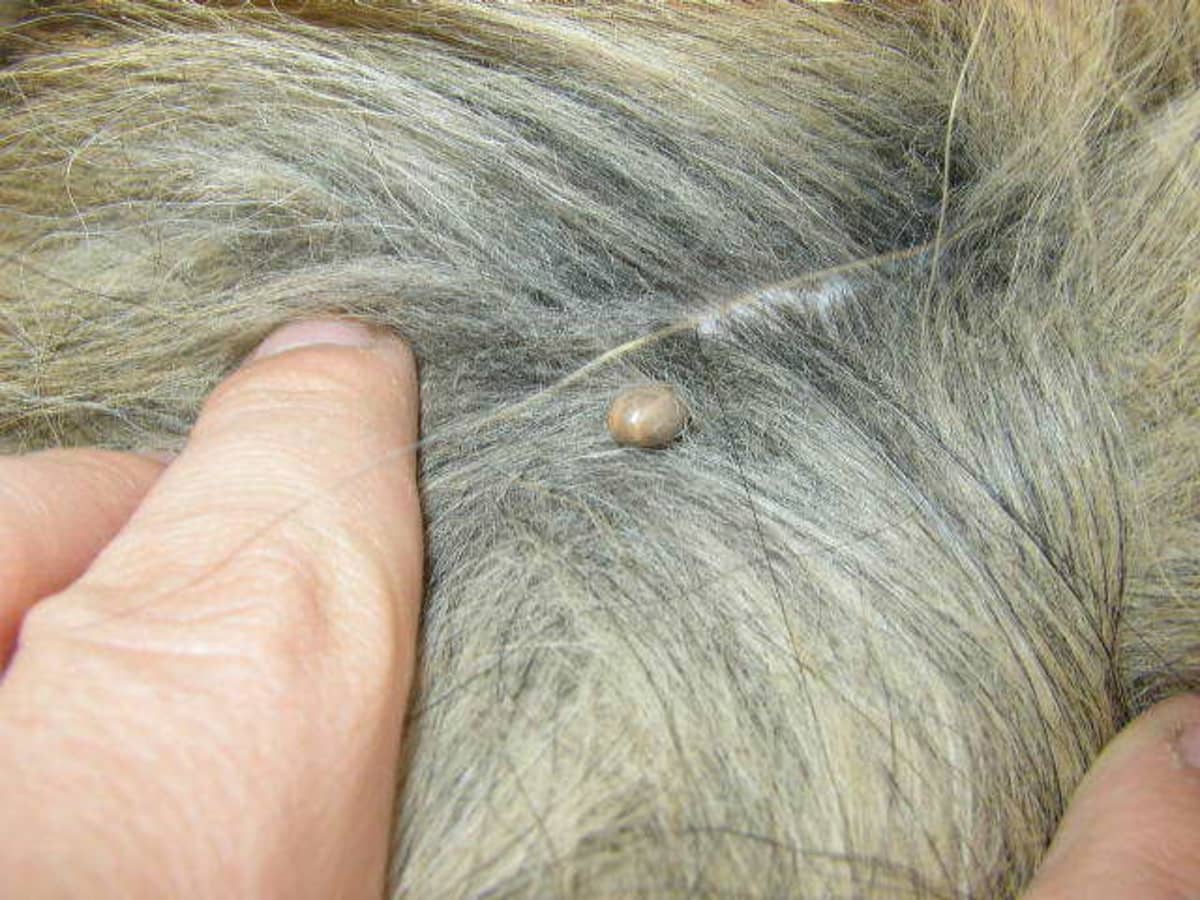
Tick fever, scientifically referred to as ehrlichiosis, is a prevalent and potentially severe health concern for dogs. This condition is primarily transmitted through the bite of an infected tick, which introduces harmful bacteria, specifically Ehrlichia canis, into the dog's bloodstream. Once the bacteria enter the dog's system, they target white blood cells, leading to a range of adverse effects on the canine's health.
The lifecycle of the tick plays a crucial role in the transmission of tick fever. When an infected tick latches onto a dog and feeds on its blood, it can transfer the Ehrlichia canis bacteria, initiating the onset of the illness. The bacteria then multiply within the dog's body, primarily targeting the white blood cells, which are vital components of the immune system. As a result, the dog's immune response is compromised, making it susceptible to various health complications.
Understanding the progression of tick fever within a dog's body is essential for pet owners. The initial stage, known as the acute phase, typically occurs within 1-3 weeks after the infected tick bite. During this phase, the dog may exhibit symptoms such as fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, and swollen lymph nodes. If left untreated, the disease progresses to the subclinical phase, where the dog may appear asymptomatic despite the ongoing damage to its immune system. Without intervention, the chronic phase may manifest, leading to severe and potentially life-threatening complications, including bleeding disorders, organ damage, and persistent fever.
It's important to note that tick fever can affect dogs of all ages and breeds, making it a widespread concern for pet owners. Additionally, dogs living in or frequently visiting areas with high tick populations are at an increased risk of contracting tick fever. Therefore, understanding the environmental factors that contribute to tick infestations is crucial for preventing this illness.
By comprehending the mechanisms of tick fever transmission, the lifecycle of the infective tick, and the progression of the disease within a dog's body, pet owners can proactively protect their furry companions from this debilitating condition. Through heightened awareness and preventive measures, such as regular tick checks, the use of tick preventatives, and prompt veterinary care, pet owners can significantly reduce the risk of tick fever in their dogs.
Symptoms of Tick Fever in Dogs
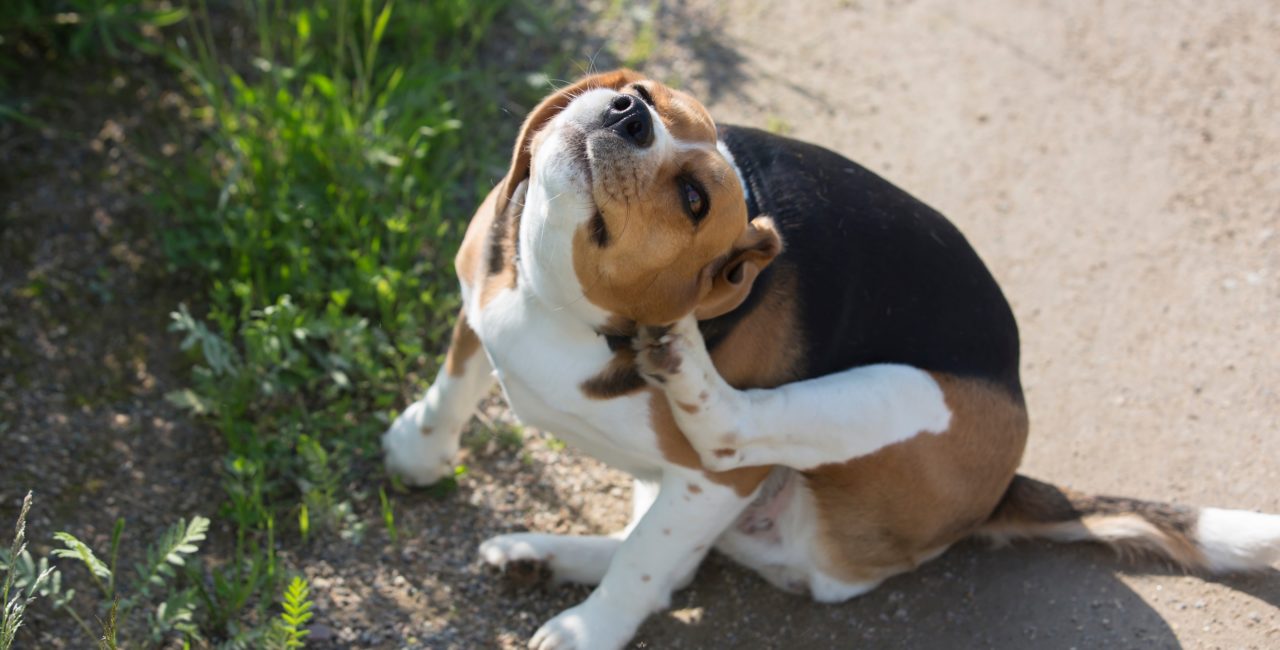
Recognizing the symptoms of tick fever in dogs is paramount for timely intervention and effective management of this potentially debilitating condition. The manifestation of symptoms may vary depending on the stage of the disease, with distinct signs emerging during the acute, subclinical, and chronic phases.
During the acute phase, which typically occurs within 1-3 weeks following the infected tick bite, dogs may exhibit a range of concerning symptoms. One of the primary indicators of tick fever is a persistent fever, often accompanied by lethargy and a noticeable loss of appetite. Additionally, affected dogs may display signs of weakness, reluctance to engage in physical activities, and a general sense of malaise. Swollen lymph nodes, particularly around the neck, may also be palpable, indicating the body's immune response to the invading bacteria.
As the disease progresses to the subclinical phase, dogs may appear asymptomatic, masking the ongoing damage to their immune system. However, underlying complications continue to develop, potentially leading to more severe symptoms in the chronic phase. In this stage, dogs may experience persistent and intermittent fever, accompanied by episodes of bleeding from the nose, mouth, or other mucous membranes. Additionally, they may demonstrate signs of bruising, indicating potential clotting abnormalities and platelet deficiencies. Other symptoms may include joint pain, lameness, neurological abnormalities, and swelling of the limbs or abdomen.
It's important to note that the symptoms of tick fever can mimic those of other illnesses, underscoring the significance of seeking veterinary attention for an accurate diagnosis. By closely monitoring their dogs for the aforementioned symptoms, pet owners can promptly seek professional medical care, facilitating early detection and intervention.
Understanding the diverse array of symptoms associated with tick fever empowers pet owners to remain vigilant and proactive in safeguarding their dogs' well-being. By promptly recognizing and addressing these symptoms, pet owners can play a pivotal role in mitigating the impact of tick fever on their canine companions, ultimately enhancing their quality of life and overall health.
Diagnosis and Treatment
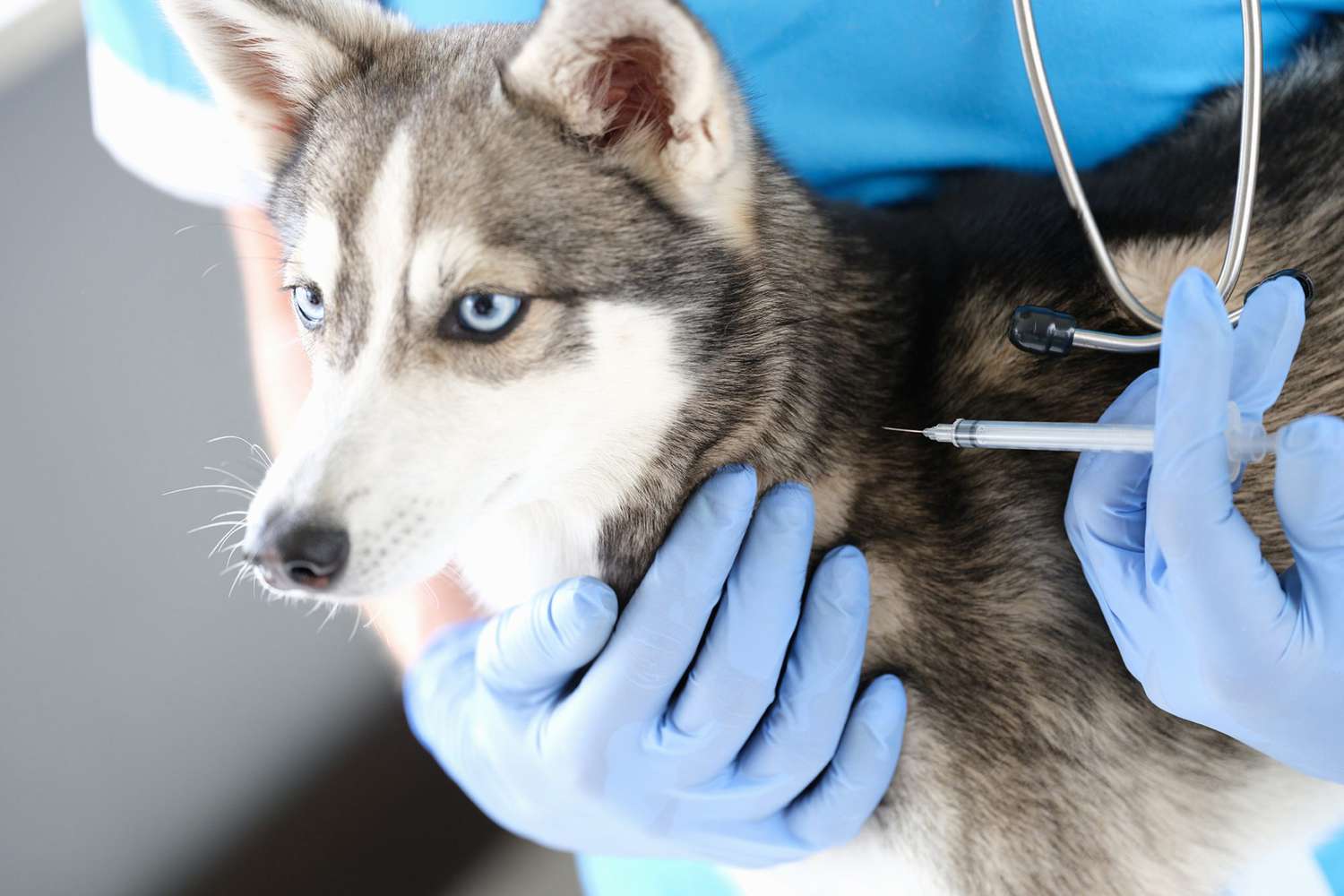
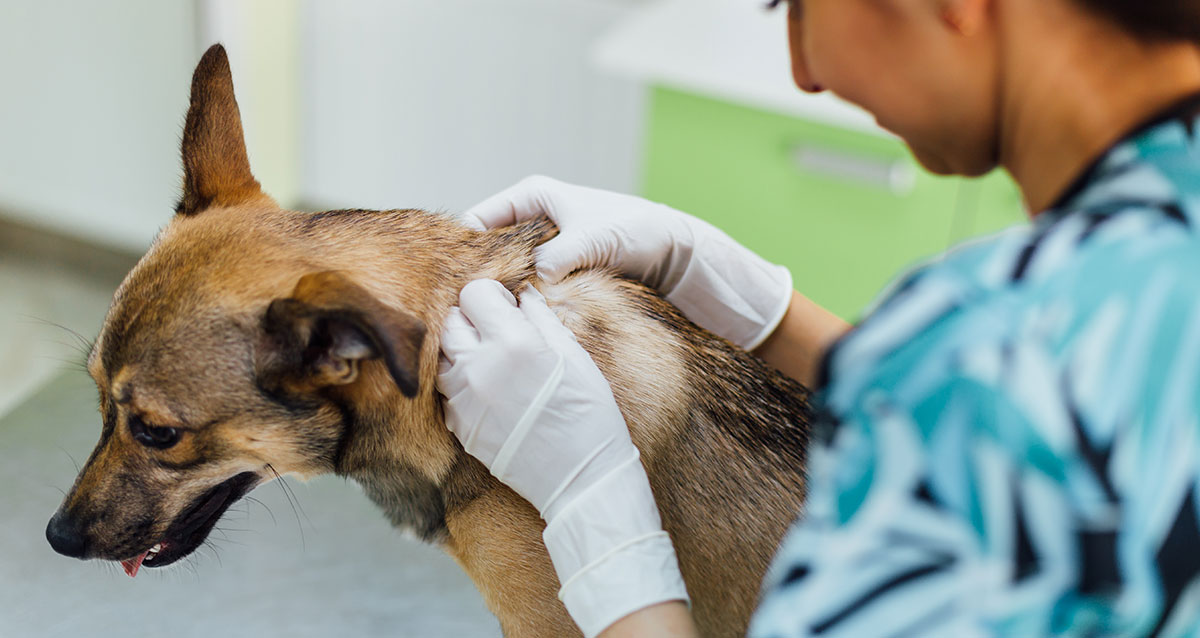
Diagnosing tick fever in dogs involves a comprehensive approach that encompasses clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and a thorough understanding of the dog's medical history. When a dog presents with symptoms suggestive of tick fever, the veterinarian will conduct a physical examination to assess the dog's overall health and look for specific signs associated with the illness. Additionally, the veterinarian may inquire about the dog's recent activities, including potential exposure to ticks and outdoor environments conducive to tick infestations.
Laboratory tests play a crucial role in confirming the diagnosis of tick fever. Blood tests, including complete blood count (CBC) and serological tests, are commonly employed to detect the presence of Ehrlichia canis antibodies or the bacteria itself within the dog's bloodstream. These tests aid in evaluating the dog's white blood cell count, platelet count, and identifying any abnormalities indicative of tick fever. Furthermore, diagnostic imaging, such as radiographs and ultrasound, may be utilized to assess the dog's internal organs for potential damage caused by the infection.
Upon confirming the diagnosis of tick fever, the veterinarian will initiate a tailored treatment plan to address the illness and alleviate the dog's symptoms. The primary course of treatment typically involves the administration of antibiotics, such as doxycycline, which effectively targets the Ehrlichia canis bacteria. It is essential for pet owners to adhere to the prescribed antibiotic regimen and follow the veterinarian's instructions diligently to ensure the successful eradication of the bacteria from the dog's system.
In addition to antibiotic therapy, supportive care may be necessary to manage the dog's symptoms and promote recovery. This may include measures to address fever, alleviate pain and discomfort, and support the dog's overall well-being during the treatment process. Close monitoring of the dog's response to treatment is imperative, allowing the veterinarian to make necessary adjustments and ensure the dog's gradual improvement.
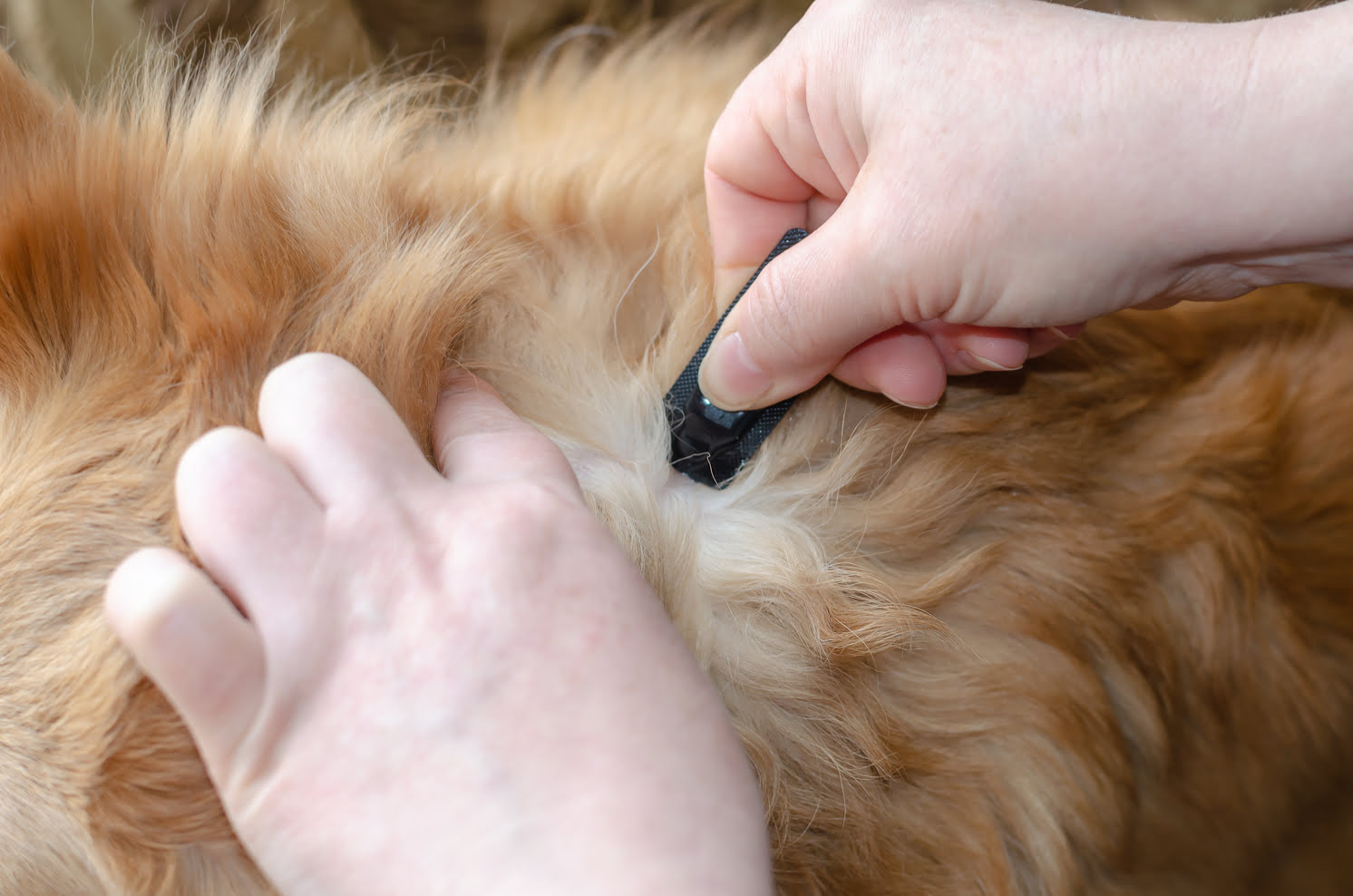
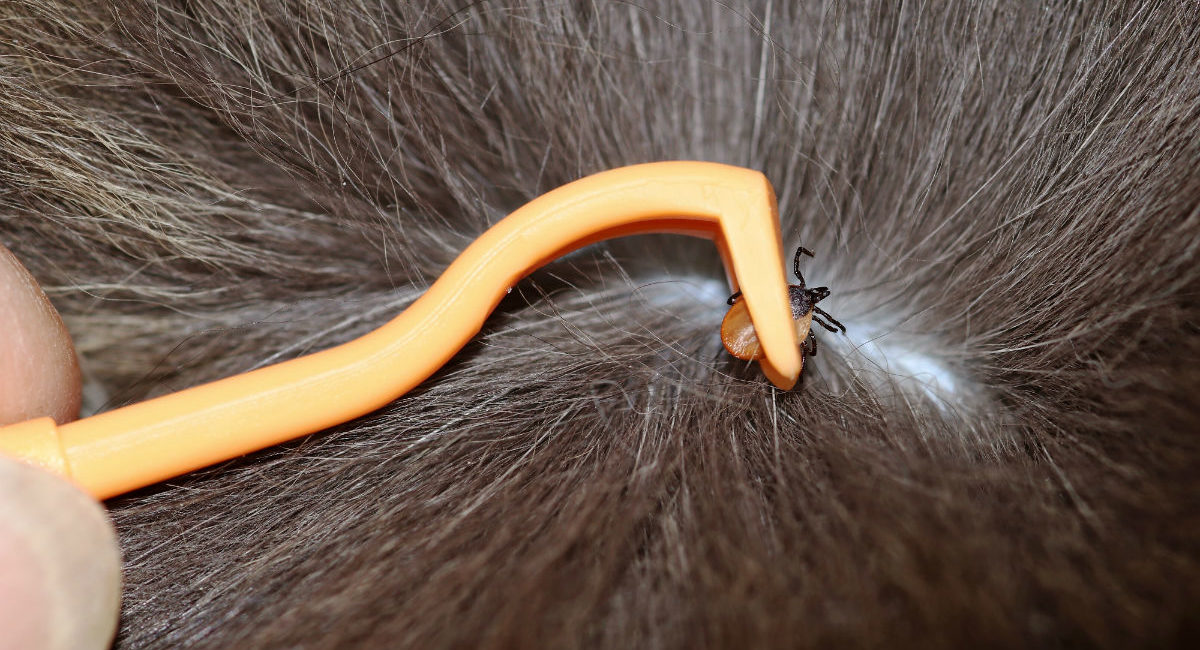
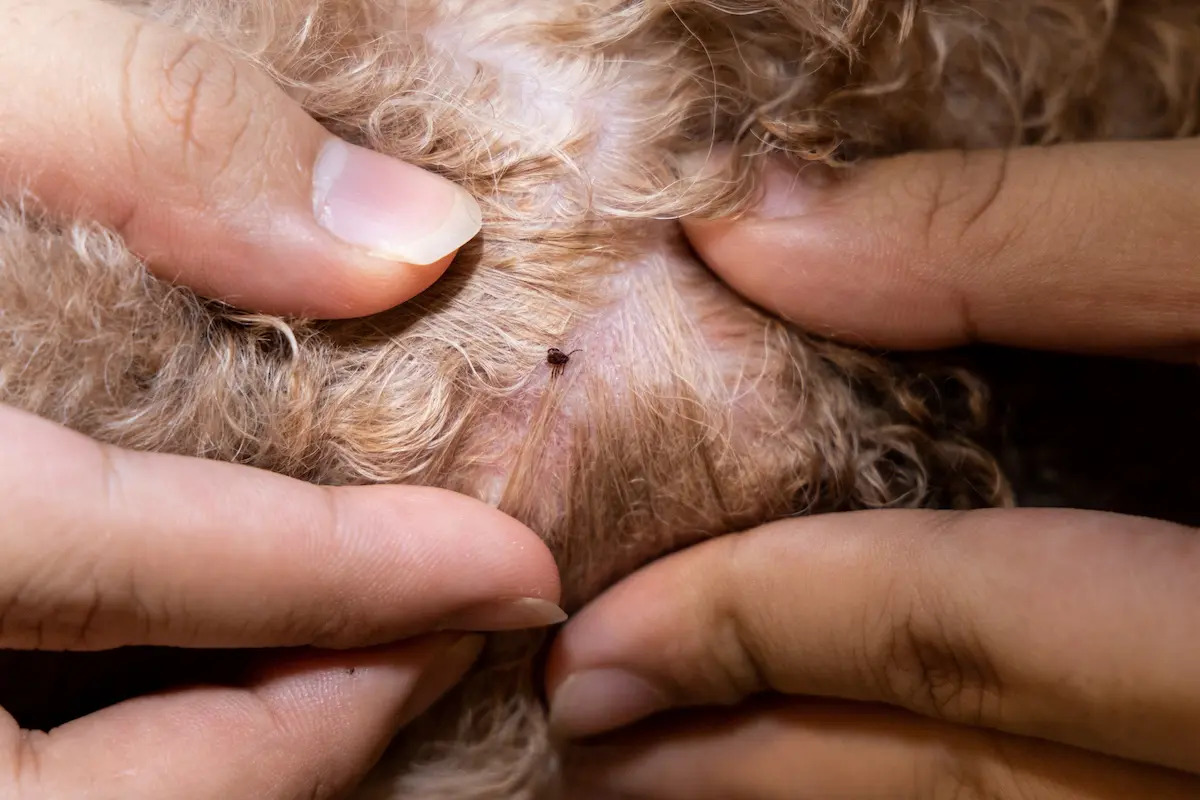
Preventing tick re-infestation is paramount during the treatment phase and beyond. Pet owners should implement rigorous tick control measures, including the use of tick preventatives, regular grooming and inspection for ticks, and minimizing the dog's exposure to tick-infested environments. These preventive measures are instrumental in safeguarding the dog from recurrent tick fever and other tick-borne illnesses.
By promptly diagnosing tick fever and implementing a comprehensive treatment approach, veterinarians can effectively manage the illness and improve the dog's prognosis. Pet owners play a pivotal role in supporting the treatment process by closely adhering to the veterinarian's recommendations and providing the necessary care and attention to facilitate their dog's recovery from tick fever.
Prevention of Tick Fever in Dogs
Preventing tick fever in dogs is a proactive and essential aspect of responsible pet ownership. By implementing effective preventive measures, pet owners can significantly reduce the risk of their canine companions contracting this debilitating illness. Here are key strategies to safeguard dogs from tick fever:
-
Tick Control Products: Utilizing tick control products, such as topical treatments, collars, and oral medications, is fundamental in preventing tick infestations. These products are designed to repel ticks or eliminate them upon contact, effectively reducing the likelihood of tick bites and the transmission of tick-borne diseases, including tick fever.
-
Regular Tick Checks: Performing thorough tick checks on dogs after outdoor activities is crucial for early detection and removal of ticks. Paying close attention to areas where ticks commonly attach, such as the ears, neck, and between the toes, allows pet owners to promptly remove any ticks before they have the chance to transmit harmful bacteria.
-
Environmental Management: Maintaining a well-groomed and tick-safe environment for dogs is essential. This includes keeping lawns mowed, removing leaf litter, and minimizing exposure to areas with dense vegetation where ticks thrive. Creating a tick-resistant outdoor space for dogs reduces the risk of tick encounters and subsequent infections.
-
Vaccination: In regions where tick fever is prevalent, veterinarians may recommend vaccinations to provide additional protection against the illness. Vaccines can bolster the dog's immune response to tick-borne pathogens, offering an extra layer of defense against tick fever.
-
Education and Awareness: Educating oneself about the local prevalence of ticks and the associated risks is paramount. Understanding the peak seasons for tick activity and the specific types of ticks prevalent in the area enables pet owners to implement targeted preventive measures and remain vigilant during high-risk periods.
-
Prompt Veterinary Care: Seeking prompt veterinary care for any suspected tick bites or symptoms of tick fever is crucial. Veterinarians can conduct thorough examinations, recommend appropriate preventive measures, and provide guidance on tick control products best suited for the dog's individual needs.
By integrating these preventive strategies into their routine care practices, pet owners can effectively mitigate the risk of tick fever in their dogs. Consistency in tick prevention measures, coupled with regular veterinary consultations, empowers pet owners to safeguard their canine companions from the detrimental effects of tick fever and other tick-borne illnesses.
Read more: Where Do Dogs Get Ticks?
Conclusion
In conclusion, tick fever poses a significant threat to the health and well-being of dogs, necessitating proactive measures to mitigate its impact. Understanding the transmission, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of tick fever is paramount for pet owners in safeguarding their canine companions from this prevalent and potentially debilitating illness.
By delving into the intricacies of tick fever, pet owners gain valuable insights into the disease's progression and its potential implications for their dogs. Recognizing the symptoms of tick fever, ranging from persistent fever and lethargy to bleeding disorders and organ damage, empowers pet owners to promptly seek veterinary care, facilitating early detection and intervention.
The diagnostic and treatment processes play a pivotal role in addressing tick fever effectively. Through comprehensive clinical evaluations, laboratory tests, and tailored treatment plans, veterinarians can diagnose tick fever and initiate targeted interventions, including antibiotic therapy and supportive care, to alleviate the dog's symptoms and promote recovery. Additionally, preventive measures, such as tick control products, regular tick checks, and environmental management, are instrumental in reducing the risk of tick infestations and subsequent infections.
Ultimately, the prevention of tick fever is a collaborative effort between pet owners and veterinary professionals. By integrating proactive strategies, such as vaccination, education, and prompt veterinary care, pet owners can create a safe and tick-resistant environment for their dogs, minimizing the likelihood of tick fever and enhancing their overall well-being.
In essence, the comprehensive understanding and proactive management of tick fever are essential components of responsible pet ownership. By prioritizing preventive measures, remaining vigilant for symptoms, and seeking timely veterinary care, pet owners can effectively protect their canine companions from the detrimental effects of tick fever, ensuring a healthier and happier life for their beloved pets.