Home>Health & Wellness>Behavior & Cognitive Care>What Is Considered A Senior Dog Age


Behavior & Cognitive Care
What Is Considered A Senior Dog Age
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about the behaviors and cognitive care for senior dogs. Discover what is considered a senior dog age and how to support their well-being. Gain insights and tips for caring for your aging canine companion.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
As our beloved canine companions age, it becomes increasingly important to understand and address their changing needs. Just like humans, dogs undergo a natural aging process that can bring about various physical and behavioral changes. Recognizing the signs of aging and providing appropriate care are essential for ensuring the well-being and comfort of senior dogs.
Understanding what is considered a senior dog age is crucial for pet owners and caregivers. This knowledge enables them to anticipate and accommodate the evolving requirements of aging dogs, ultimately enhancing their quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the concept of senior dog age, explore the factors that influence it, and discuss the signs of aging in dogs. Additionally, we will provide valuable insights into the specialized care that senior dogs may require, offering guidance on how to support them through their golden years.
By gaining a deeper understanding of senior dog age and the associated considerations, pet owners can proactively address the unique needs of their aging companions. This proactive approach fosters a nurturing and supportive environment that allows senior dogs to continue enjoying a fulfilling and comfortable life. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the intricacies of senior dog age and discover the best practices for providing exceptional care to our aging canine friends.
Read more: At What Age Does A Dog Need Heartworm Meds
Defining Senior Dog Age
Defining senior dog age is a crucial aspect of understanding the unique requirements of aging dogs. While there is no universally agreed-upon definition of when a dog is considered a senior, it is generally recognized that larger breeds tend to age more rapidly than smaller breeds. As a result, the classification of senior dog age varies based on factors such as breed size, genetics, and overall health.
In general, dogs are typically considered seniors when they reach the age of 7 to 10 years. However, this can vary significantly depending on the breed. Smaller breeds, such as Chihuahuas and Toy Poodles, may not exhibit signs of aging until they are well into their senior years, often around 10 to 12 years of age. On the other hand, larger breeds, such as Great Danes and Saint Bernards, may be considered seniors as early as 5 to 6 years old due to their shorter lifespans and accelerated aging process.
It's important to note that individual dogs may age at different rates based on their genetics, lifestyle, and overall health. Factors such as genetics, nutrition, exercise, and preventive healthcare play a significant role in determining when a dog transitions into the senior stage of life. Additionally, certain breeds are predisposed to age-related health issues, which may necessitate earlier consideration as seniors.
Understanding the defining factors of senior dog age empowers pet owners and caregivers to tailor their approach to meet the specific needs of aging dogs. By recognizing the individuality of each dog and considering their unique characteristics, it becomes possible to provide personalized care that supports their well-being as they enter their senior years. This proactive and attentive approach lays the foundation for promoting a comfortable and fulfilling life for senior dogs, ensuring that they receive the care and attention they deserve as valued members of the family.
Factors Affecting Senior Dog Age
Several factors influence the age at which a dog is considered a senior, encompassing a diverse range of elements that contribute to the aging process. Understanding these factors is essential for comprehending the varying needs of senior dogs and tailoring appropriate care to support their well-being.
1. Breed and Size:
The breed and size of a dog play a significant role in determining its senior dog age. Larger breeds tend to have shorter lifespans and may exhibit signs of aging at an earlier age compared to smaller breeds. For instance, a Great Dane may be considered a senior dog at around 5 to 6 years old, while a Chihuahua may not display typical signs of aging until 10 to 12 years of age.
2. Genetics:
Genetics play a crucial role in the aging process of dogs. Certain breeds are predisposed to age-related health issues, which can influence when they are classified as seniors. Understanding the genetic predispositions of specific breeds enables pet owners and caregivers to anticipate potential health challenges and provide proactive care to support their aging dogs.
Read more: What Age Do Boxer Dogs Develop Arthritis
3. Nutrition and Health:
The quality of nutrition and overall health maintenance significantly impacts the aging trajectory of dogs. A well-balanced diet, tailored to the specific needs of senior dogs, can contribute to their overall health and vitality as they age. Additionally, preventive healthcare, including regular veterinary check-ups and vaccinations, plays a vital role in supporting the well-being of aging dogs.
4. Lifestyle and Exercise:
The lifestyle and exercise regimen of a dog can influence its aging process. Regular physical activity tailored to the dog's age and health status can help maintain muscle tone, joint flexibility, and cognitive function. Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle may contribute to accelerated aging and age-related health issues.
5. Environmental Factors:
Environmental elements, such as exposure to toxins, pollutants, and stress, can impact the aging process of dogs. Providing a safe and nurturing environment, free from potential hazards, can contribute to the overall well-being of senior dogs and support their longevity.
By considering these multifaceted factors that affect senior dog age, pet owners and caregivers can gain valuable insights into the unique needs of aging dogs. This comprehensive understanding enables them to implement tailored care strategies that prioritize the health, comfort, and happiness of their senior canine companions.
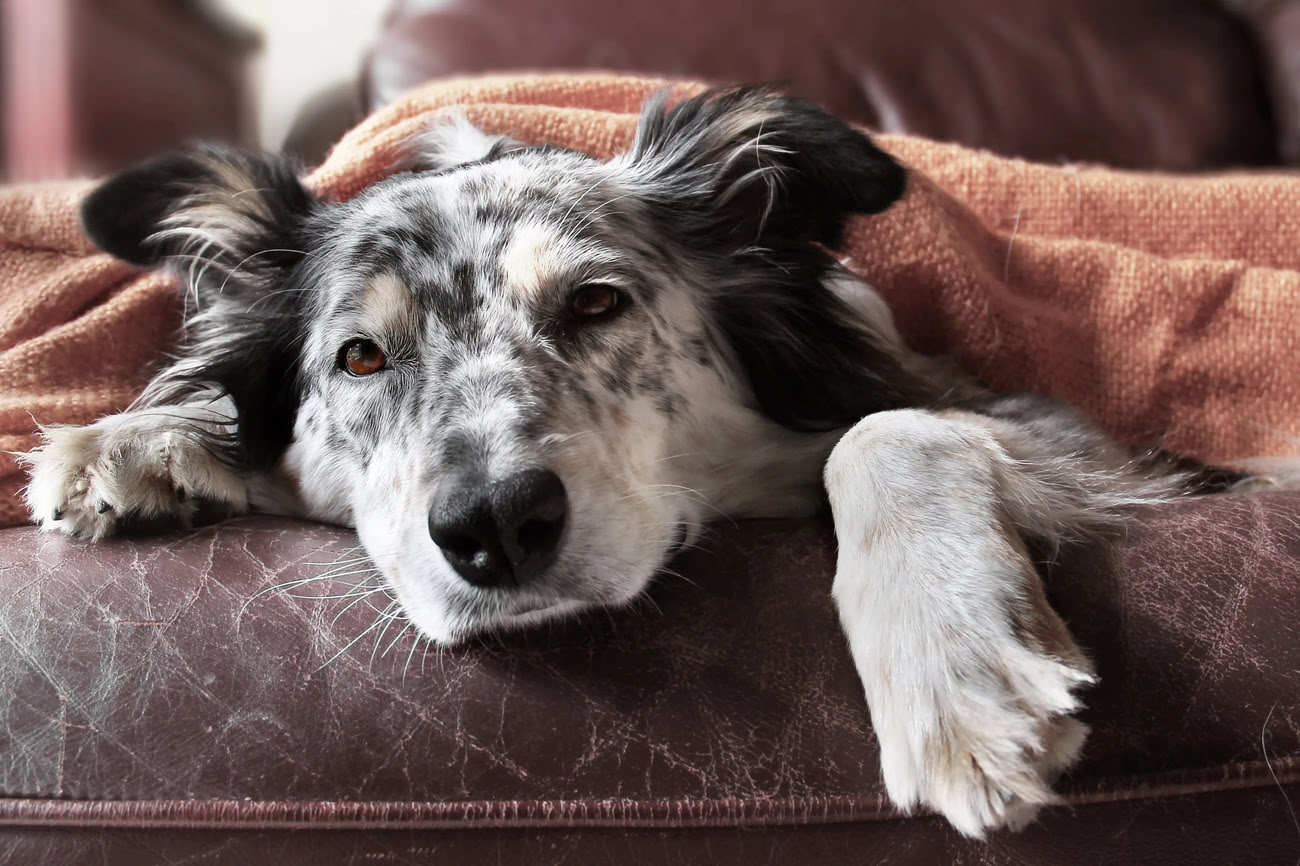
Signs of Aging in Dogs
As dogs transition into their senior years, they undergo various physical and behavioral changes that signify the natural aging process. Recognizing these signs is crucial for pet owners and caregivers to provide appropriate support and care for their aging canine companions.
Read more: What Age Do Dogs Get Arthritis
Physical Signs:
- Gray Hair and Coat Changes: Just like humans, dogs may develop gray hair as they age. Additionally, their coat may undergo changes in texture and thickness, often becoming dull or coarse.
- Reduced Mobility: Senior dogs may experience stiffness, reduced mobility, and reluctance to engage in physical activities that they once enjoyed. Joint stiffness and arthritis are common age-related issues that can impact a dog's mobility.
- Weight Changes: Aging dogs may exhibit changes in weight, with some experiencing weight gain due to reduced activity levels, while others may struggle with maintaining a healthy weight due to decreased muscle mass and metabolism.
- Dental Issues: Dental problems, such as tooth decay and gum disease, are prevalent in senior dogs. Bad breath, difficulty chewing, and reluctance to eat hard food can indicate age-related dental issues.
Behavioral Signs:
- Increased Sleep: Senior dogs tend to sleep more and may show a preference for quiet and comfortable resting spots. Changes in sleep patterns, such as restlessness or difficulty settling, can also be indicative of aging-related discomfort.
- Altered Behavior: Aging can bring about changes in a dog's behavior, including increased irritability, anxiety, or disorientation. Cognitive decline and sensory changes may contribute to alterations in behavior.
- Decreased Interest: Senior dogs may exhibit reduced interest in activities they once enjoyed, such as playing fetch or going for long walks. This diminished enthusiasm can stem from physical discomfort or decreased energy levels.
- Incontinence: Older dogs may experience urinary or fecal incontinence due to weakened bladder or bowel control, necessitating additional support and understanding from their caregivers.
Cognitive Signs:
- Memory Loss: Canine cognitive dysfunction, akin to dementia in humans, can lead to memory loss and disorientation in senior dogs. They may exhibit confusion, forgetfulness, and difficulty recognizing familiar people or surroundings.
- Disorientation: Senior dogs may display signs of disorientation, such as getting lost in familiar surroundings or appearing confused about their daily routines.
- Anxiety and Agitation: Cognitive changes can manifest as increased anxiety, restlessness, or agitation in senior dogs, often stemming from their struggle to comprehend their surroundings and experiences.
By recognizing these signs of aging in dogs, pet owners and caregivers can proactively address the evolving needs of their senior companions. This awareness enables them to implement tailored care strategies that prioritize the comfort, well-being, and overall quality of life for their aging canine friends.
Care for Senior Dogs
Providing specialized care for senior dogs is essential to ensure their comfort, well-being, and overall quality of life as they navigate the challenges of aging. Tailoring a comprehensive care regimen that addresses their evolving physical, emotional, and cognitive needs is paramount for supporting senior dogs through their golden years.
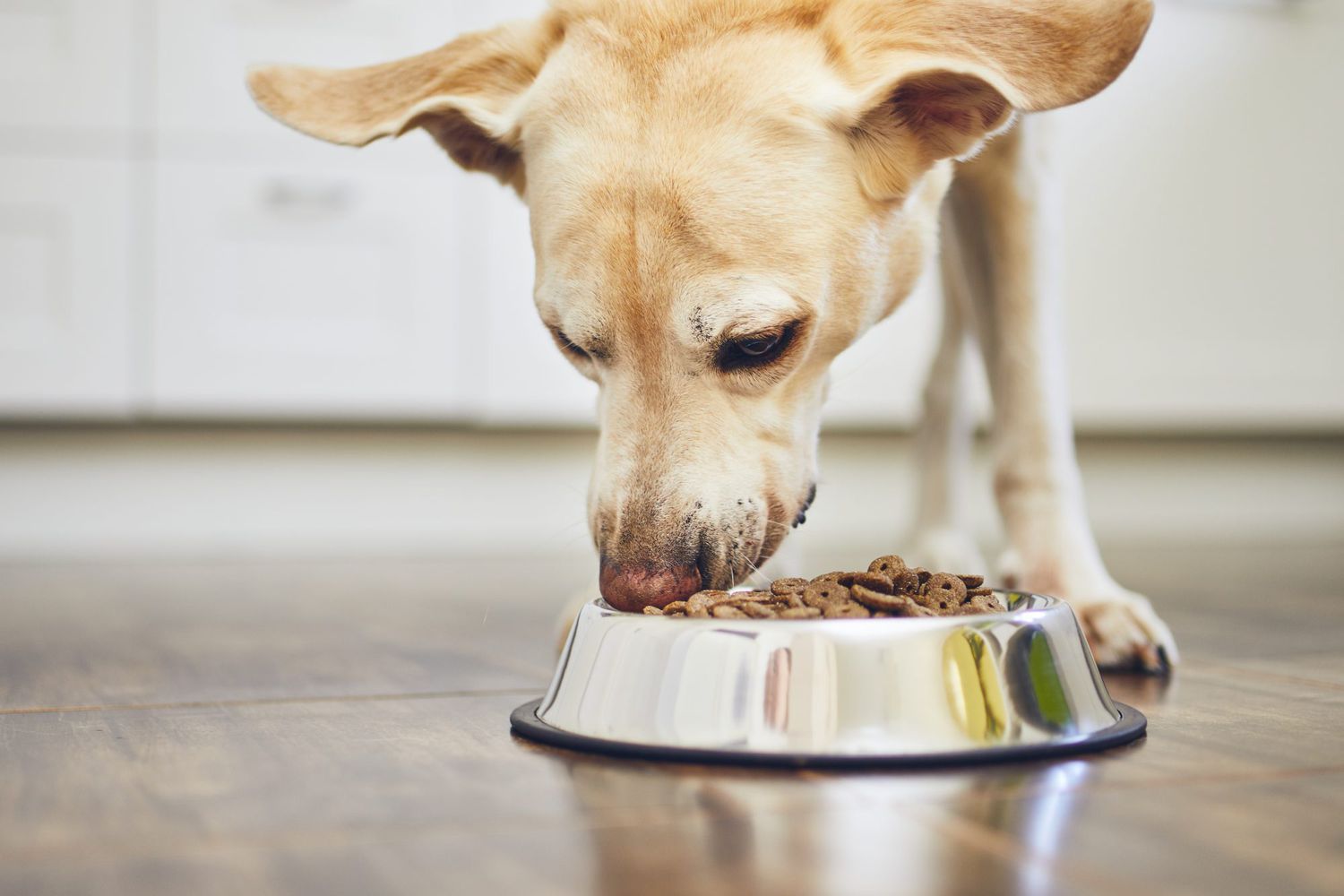
1. Nutrition and Diet
Senior dogs often require a modified diet that caters to their changing nutritional needs. High-quality, age-appropriate dog food formulated for senior dogs can help address issues such as weight management, joint health, and digestive sensitivities. Additionally, incorporating supplements such as glucosamine and omega-3 fatty acids can support joint health and cognitive function in aging dogs.
2. Veterinary Care
Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial for monitoring the health of senior dogs and addressing age-related concerns. Comprehensive physical examinations, dental assessments, and screenings for common senior dog health issues, such as arthritis, diabetes, and cognitive dysfunction, are essential for early detection and proactive management.
3. Exercise and Mental Stimulation
Tailored exercise routines that accommodate the physical limitations of senior dogs are vital for maintaining muscle tone, joint flexibility, and overall mobility. Low-impact activities, such as gentle walks and swimming, can help keep senior dogs active while minimizing stress on their aging joints. Mental stimulation through interactive toys, puzzle games, and positive reinforcement training can also support cognitive function and emotional well-being.
4. Comfort and Safety
Creating a comfortable and safe environment for senior dogs is essential for promoting their overall well-being. Providing orthopedic bedding to alleviate joint pressure, ensuring easy access to food and water, and minimizing environmental hazards can enhance the comfort and safety of aging canine companions.
5. Emotional Support and Affection
Senior dogs benefit greatly from emotional support and affection from their caregivers. Spending quality time with them, engaging in gentle grooming sessions, and maintaining familiar routines can provide reassurance and comfort as they navigate the changes associated with aging.
6. Adapted Living Spaces
Adapting the living spaces of senior dogs to accommodate their needs is crucial for promoting their independence and comfort. Installing ramps or steps to facilitate access to elevated areas, ensuring non-slip flooring to prevent falls, and providing easy access to resting areas can enhance the overall living experience for senior dogs.
7. Palliative Care and End-of-Life Planning
For senior dogs with chronic health conditions or nearing the end of their life, palliative care focused on pain management, comfort, and quality of life becomes paramount. Compassionate end-of-life planning, including discussions with veterinary professionals regarding hospice care and euthanasia, allows pet owners to make informed decisions that prioritize the well-being of their beloved senior dogs.
By implementing a holistic care approach that encompasses nutrition, veterinary attention, physical and mental stimulation, emotional support, environmental adaptations, and end-of-life considerations, pet owners and caregivers can provide exceptional care for their senior dogs. This comprehensive and attentive approach fosters a nurturing and supportive environment that allows senior dogs to continue enjoying a fulfilling and comfortable life as cherished members of the family.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding what is considered a senior dog age and the associated factors and signs of aging is pivotal for providing exceptional care to our aging canine companions. The concept of senior dog age is multifaceted, influenced by breed, genetics, nutrition, lifestyle, and environmental factors. By recognizing the individuality of each dog and considering their unique characteristics, pet owners and caregivers can tailor their approach to meet the specific needs of aging dogs.
As dogs transition into their senior years, they undergo various physical, behavioral, and cognitive changes that signify the natural aging process. Recognizing these signs is crucial for pet owners and caregivers to provide appropriate support and care for their aging canine companions. From gray hair and reduced mobility to altered behavior and cognitive decline, understanding these signs empowers caregivers to proactively address the evolving needs of their senior dogs.
Providing specialized care for senior dogs is essential to ensure their comfort, well-being, and overall quality of life as they navigate the challenges of aging. Tailoring a comprehensive care regimen that addresses their evolving physical, emotional, and cognitive needs is paramount for supporting senior dogs through their golden years. From nutrition and veterinary care to exercise, comfort, emotional support, and end-of-life planning, a holistic approach to senior dog care fosters a nurturing and supportive environment that allows senior dogs to continue enjoying a fulfilling and comfortable life as cherished members of the family.
By gaining a deeper understanding of senior dog age and the associated considerations, pet owners can proactively address the unique needs of their aging companions. This proactive approach fosters a nurturing and supportive environment that allows senior dogs to continue enjoying a fulfilling and comfortable life. Ultimately, by implementing tailored care strategies that prioritize the health, comfort, and happiness of senior dogs, pet owners and caregivers can ensure that their aging canine friends receive the exceptional care and attention they deserve as valued members of the family.