Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Is A Fast-Moving Parasite On The Body Of A Dog?


Common Health Issues
What Is A Fast-Moving Parasite On The Body Of A Dog?
Published: February 7, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs, including fast-moving parasites that can affect their bodies. Understand the signs, symptoms, and treatment options for these conditions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Fast-moving parasites can pose a significant threat to the health and well-being of our beloved canine companions. These tiny organisms have the ability to rapidly infest a dog's body, causing a range of health issues that can be both distressing and potentially life-threatening. Understanding the nature of fast-moving parasites and their impact on dogs is crucial for pet owners to ensure the health and happiness of their furry friends.
Fast-moving parasites are organisms that have evolved to quickly and efficiently infest a dog's body, often causing a rapid onset of symptoms and complications. These parasites can include various types of worms, ticks, fleas, and mites, each with its own unique characteristics and potential health risks for dogs. The ability of these parasites to move swiftly within a dog's body can lead to a rapid deterioration of the animal's health if left untreated.
As responsible pet owners, it is essential to be aware of the potential threat posed by fast-moving parasites and to take proactive measures to protect our canine companions. By gaining a deeper understanding of these parasites and their impact, we can better equip ourselves to recognize the symptoms, seek appropriate treatment, and implement preventive measures to safeguard our dogs from these insidious invaders.
In the following sections, we will delve into the various types of fast-moving parasites that can affect dogs, explore the symptoms associated with infestations, and discuss the available treatment options and preventive measures. By arming ourselves with this knowledge, we can take proactive steps to protect our furry friends from the harmful effects of fast-moving parasites and ensure that they lead healthy, happy lives.
Read more: What Is Giardia Parasite In Dogs?
Understanding Fast-Moving Parasites
Fast-moving parasites are organisms that have evolved to quickly and efficiently infest a dog's body, often causing a rapid onset of symptoms and complications. These parasites encompass a variety of organisms, including worms, ticks, fleas, and mites, each with its own unique characteristics and potential health risks for dogs.
Worms
Worms are one of the most common types of fast-moving parasites that can affect dogs. These internal parasites, such as roundworms, hookworms, and tapeworms, have the ability to rapidly multiply within a dog's gastrointestinal tract, leading to severe health issues. The fast-moving nature of these worms allows them to quickly spread and cause extensive damage if left untreated.
Ticks
Ticks are external parasites that can latch onto a dog's skin and feed on its blood. These fast-moving parasites are capable of rapidly transmitting harmful diseases, such as Lyme disease and ehrlichiosis, to dogs. Their swift movement across a dog's body makes them challenging to detect and remove, increasing the risk of disease transmission and skin irritation.
Fleas
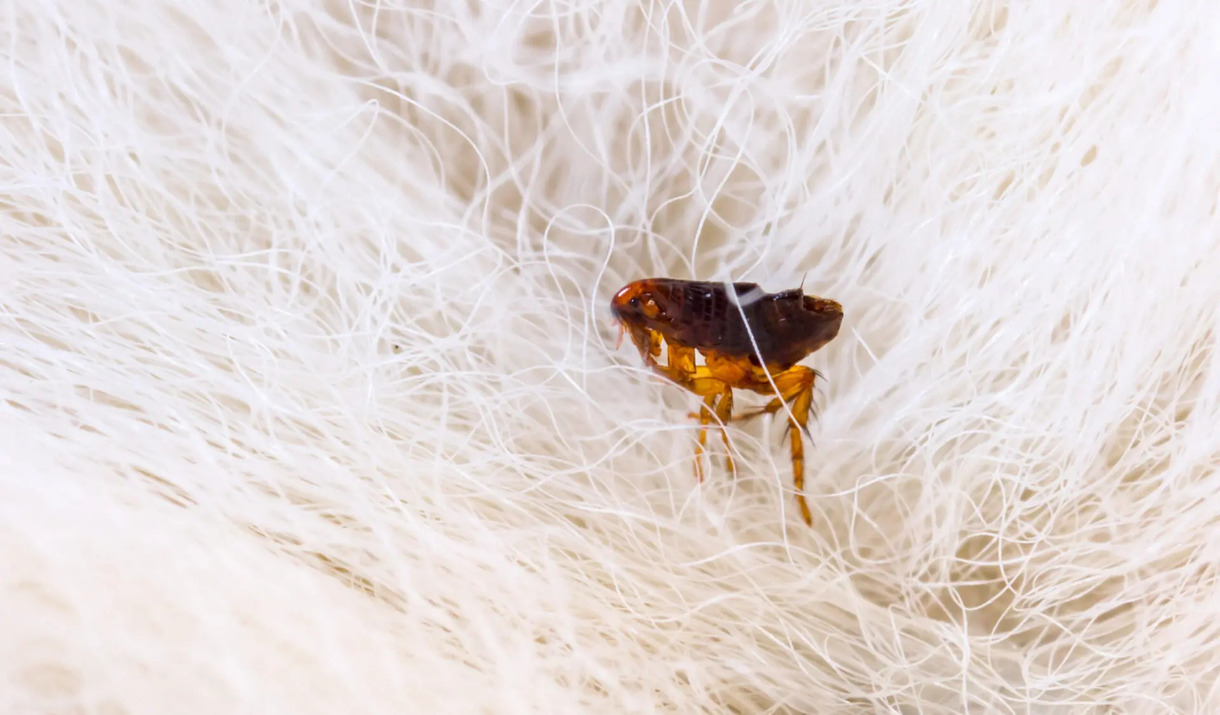
Fleas are another type of fast-moving parasite that can wreak havoc on a dog's well-being. These tiny insects have the ability to rapidly infest a dog's fur, causing intense itching, skin irritation, and potential allergic reactions. Their quick reproductive cycle allows them to multiply rapidly, leading to widespread infestations if not promptly addressed.
Read more: Why Is My Senior Dog Breathing Fast?
Mites
Mites are microscopic parasites that can quickly infest a dog's skin, leading to conditions such as mange. These fast-moving parasites can cause intense itching, hair loss, and skin inflammation, posing a significant threat to a dog's overall health and comfort. Their rapid reproduction cycle enables them to spread swiftly and exacerbate skin-related issues.
Understanding the nature of fast-moving parasites is crucial for pet owners to recognize the potential risks and take proactive measures to protect their dogs. By gaining insight into the characteristics and behaviors of these parasites, pet owners can better equip themselves to identify symptoms, seek appropriate treatment, and implement preventive measures to safeguard their canine companions from the harmful effects of fast-moving parasites.
Types of Fast-Moving Parasites on Dogs
Worms
Worms are among the most prevalent fast-moving parasites that can affect dogs. These internal parasites, including roundworms, hookworms, and tapeworms, have the ability to rapidly multiply within a dog's gastrointestinal tract, leading to severe health issues. The fast-moving nature of these worms allows them to quickly spread and cause extensive damage if left untreated. Roundworms, for example, can rapidly grow and reproduce within a dog's intestines, leading to symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, and a potbellied appearance. Hookworms, known for their fast movement within a dog's intestines, can cause anemia and weakness due to their rapid blood-feeding behavior. Tapeworms, with their segmented bodies, can swiftly infest a dog's digestive system, leading to weight loss, scooting, and irritation around the anus.
Ticks
Ticks are external parasites that can latch onto a dog's skin and feed on its blood. These fast-moving parasites are capable of rapidly transmitting harmful diseases, such as Lyme disease and ehrlichiosis, to dogs. Their swift movement across a dog's body makes them challenging to detect and remove, increasing the risk of disease transmission and skin irritation. Ticks can quickly move from one location to another on a dog's body, making it crucial for pet owners to regularly inspect their pets for these parasites, especially after outdoor activities in grassy or wooded areas.
Fleas
Fleas are another type of fast-moving parasite that can wreak havoc on a dog's well-being. These tiny insects have the ability to rapidly infest a dog's fur, causing intense itching, skin irritation, and potential allergic reactions. Their quick reproductive cycle allows them to multiply rapidly, leading to widespread infestations if not promptly addressed. Fleas can move swiftly through a dog's fur, making them elusive and challenging to eliminate. Their rapid movement and ability to lay numerous eggs make flea control a critical aspect of canine parasite prevention.
Read more: Why Is My Senior Dog Breathing Fast?
Mites
Mites are microscopic parasites that can quickly infest a dog's skin, leading to conditions such as mange. These fast-moving parasites can cause intense itching, hair loss, and skin inflammation, posing a significant threat to a dog's overall health and comfort. Their rapid reproduction cycle enables them to spread swiftly and exacerbate skin-related issues. Mites can move rapidly across a dog's skin, making it essential for pet owners to seek prompt veterinary care if symptoms of mange or other mite-related conditions are observed.
Understanding the types of fast-moving parasites that can affect dogs is essential for pet owners to recognize the potential risks and take proactive measures to protect their canine companions. By gaining insight into the characteristics and behaviors of these parasites, pet owners can better equip themselves to identify symptoms, seek appropriate treatment, and implement preventive measures to safeguard their dogs from the harmful effects of fast-moving parasites.
Symptoms of Fast-Moving Parasites
Fast-moving parasites can manifest a range of symptoms in dogs, indicating their presence and potential health impact. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and treatment. The symptoms of fast-moving parasites on dogs can vary depending on the type of parasite and the severity of infestation. Here are the common symptoms associated with fast-moving parasites:
General Signs of Discomfort
Dogs infested with fast-moving parasites may exhibit general signs of discomfort, including restlessness, excessive scratching or licking, and agitation. These behaviors can indicate the presence of external parasites such as fleas or mites, which can cause intense itching and skin irritation.
Read more: What Is Blood Parasite Test For Dogs
Gastrointestinal Distress
Internal parasites like worms can cause gastrointestinal distress in dogs. Symptoms may include vomiting, diarrhea, weight loss, and a potbellied appearance. Dogs infested with fast-moving worms may also show a decreased appetite and overall lethargy due to the impact of these parasites on their digestive system.
Skin Irritation and Hair Loss
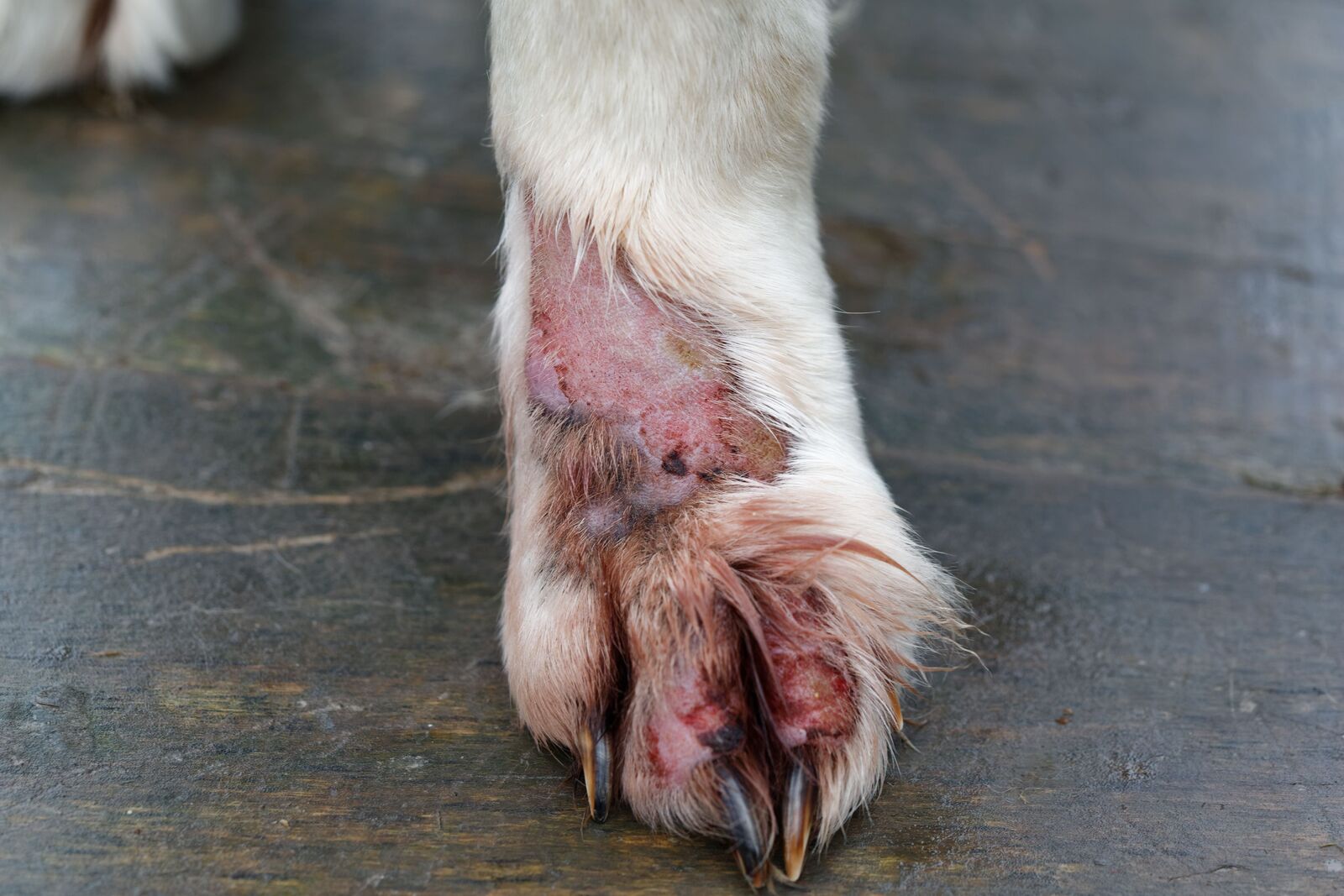
Fast-moving parasites such as fleas and mites can lead to skin irritation, redness, and hair loss in dogs. Flea infestations often result in intense itching, leading to skin damage and potential allergic reactions. Mites, on the other hand, can cause mange, characterized by hair loss, crusty skin, and intense itching, particularly in the ear and paw areas.
Anemia and Weakness
Certain fast-moving parasites, such as hookworms, are blood-feeding parasites that can lead to anemia in dogs. Anemic dogs may exhibit weakness, pale gums, and lethargy due to the loss of red blood cells caused by the parasites' feeding activities.
Visible Parasites
In some cases, pet owners may visually observe the fast-moving parasites on their dogs. Ticks can be visible to the naked eye, especially when inspecting the dog's skin and fur, while fleas may be observed scurrying through the fur or on the dog's bedding.
Read more: What Parasite Is Found In Dog Feces
Behavioral Changes
Dogs infested with fast-moving parasites may display behavioral changes, such as increased irritability, decreased activity, and reluctance to eat or play. These changes can be indicative of the discomfort and distress caused by the presence of parasites within their bodies or on their skin.
Recognizing these symptoms is essential for prompt veterinary intervention and appropriate treatment. By staying vigilant for these signs of fast-moving parasite infestations, pet owners can ensure the well-being and health of their canine companions. Regular veterinary check-ups and preventive measures can aid in early detection and effective management of fast-moving parasites, safeguarding the overall health and happiness of dogs.
Treatment and Prevention of Fast-Moving Parasites
Effective treatment and prevention strategies are essential for managing fast-moving parasites and safeguarding the health of dogs. Here's a detailed look at the approaches to address and prevent infestations:
Treatment
-
Medication: Upon diagnosis of fast-moving parasite infestations, veterinarians may prescribe specific medications to target and eliminate the parasites. For instance, deworming medications are commonly used to eradicate internal parasites, while topical or oral treatments are employed to combat external parasites such as fleas and ticks.
-
Follow Veterinary Guidance: It's crucial for pet owners to follow the prescribed treatment regimen as directed by the veterinarian. Adhering to the recommended dosage and duration of treatment is vital to ensure the effective elimination of parasites and prevent reinfestation.
-
Regular Monitoring: After initiating treatment, regular monitoring of the dog's health and well-being is essential. This includes observing for any lingering symptoms, such as persistent itching or gastrointestinal issues, and promptly reporting any concerns to the veterinarian.
Prevention
-
Routine Parasite Control: Implementing a comprehensive parasite control program is key to preventing infestations. This may involve the regular administration of preventive medications, such as monthly oral or topical treatments for fleas and ticks, as well as periodic deworming to address internal parasites.
-
Environmental Management: Maintaining a clean and hygienic living environment for dogs can help minimize the risk of parasite infestations. Regular cleaning of bedding, vacuuming of living spaces, and yard maintenance can reduce the presence of fleas, ticks, and other parasites in the dog's surroundings.
-
Regular Veterinary Visits: Scheduling routine veterinary check-ups allows for proactive parasite screening and early detection of infestations. Veterinarians can recommend suitable preventive measures based on the dog's lifestyle, geographic location, and specific parasite risks.
-
Education and Awareness: Pet owners should educate themselves about the prevalent parasites in their region and the associated risks. Understanding the lifecycle and behaviors of fast-moving parasites can aid in implementing effective preventive measures and recognizing potential infestation signs.
By combining targeted treatment with proactive prevention strategies, pet owners can effectively manage fast-moving parasites and minimize the impact on their dogs' health. Consistent adherence to preventive measures, coupled with regular veterinary care, plays a pivotal role in ensuring the well-being and vitality of canine companions.
Read more: What Parasite Is Passed From Dog To Human
Conclusion
In conclusion, the presence of fast-moving parasites poses a significant threat to the health and well-being of dogs. These insidious organisms, including worms, ticks, fleas, and mites, have the ability to rapidly infest a dog's body, leading to a range of distressing symptoms and potential health complications. Understanding the nature of fast-moving parasites and their impact on dogs is crucial for pet owners to ensure the health and happiness of their furry companions.
The diverse types of fast-moving parasites, each with its unique characteristics and potential health risks, underscore the importance of proactive measures to protect dogs from infestations. From internal parasites like roundworms and hookworms to external pests such as ticks and fleas, the swift movement and reproductive capabilities of these parasites necessitate vigilance and preventive action.
Recognizing the symptoms of fast-moving parasite infestations, including gastrointestinal distress, skin irritation, anemia, and behavioral changes, empowers pet owners to seek timely veterinary care and appropriate treatment. Additionally, implementing preventive measures, such as routine parasite control, environmental management, and regular veterinary visits, plays a pivotal role in mitigating the risk of infestations and safeguarding the overall health of dogs.
By combining targeted treatment with proactive prevention strategies, pet owners can effectively manage fast-moving parasites and minimize their impact on their dogs' well-being. The commitment to regular veterinary care, education about prevalent parasites, and the implementation of preventive measures are essential components of responsible pet ownership.
Ultimately, the well-being and vitality of canine companions depend on the proactive efforts of pet owners to combat fast-moving parasites. By gaining a deeper understanding of these organisms and taking proactive measures, pet owners can ensure that their beloved dogs lead healthy, happy lives, free from the harmful effects of fast-moving parasites.