Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>Why Is My Dog’s Eye White


Eye and Ear Health
Why Is My Dog’s Eye White
Published: February 11, 2024
Learn about the causes of white eyes in dogs and how to maintain their eye and ear health. Find expert tips and advice on eye and ear care for your furry friend.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
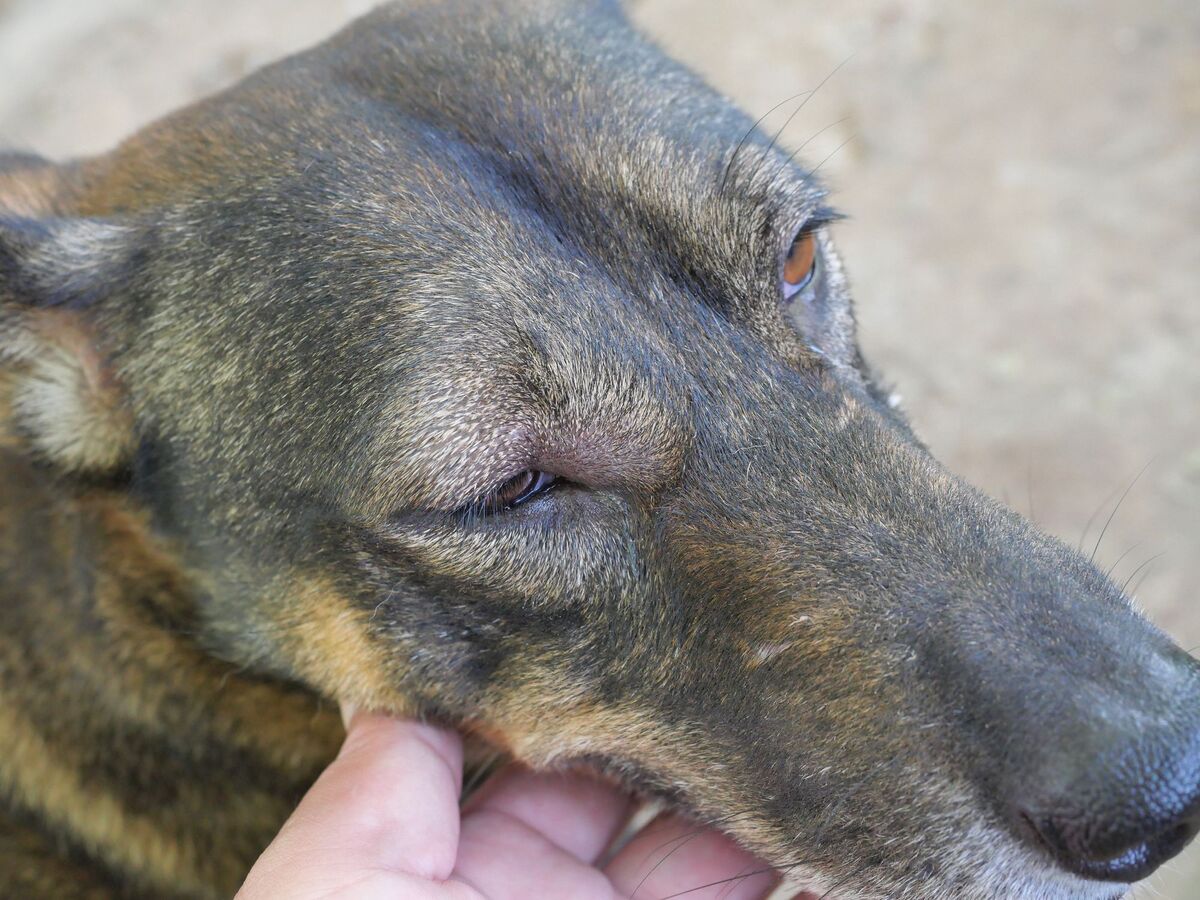
When you look into your dog's eyes, you see a world of emotion and connection. Those soulful gazes can convey joy, love, and trust. However, if you notice that your dog's eyes have a white appearance, it can be a cause for concern. The eyes are not only the windows to the soul but also a vital indicator of your dog's overall health. Understanding why your dog's eyes may appear white and the potential implications is crucial for their well-being.
The appearance of white eyes in dogs can be alarming, but it's essential to approach the situation with a calm and informed mindset. There are various reasons why a dog's eyes may exhibit a white hue, ranging from benign conditions to more serious health issues. As a responsible pet owner, being aware of the potential causes and knowing when to seek veterinary care is paramount in ensuring the best possible outcome for your furry companion.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the common causes of white eyes in dogs, the symptoms to look out for, when to seek veterinary care, available treatment options, and preventive measures to safeguard your dog's ocular health. By gaining insight into these aspects, you will be better equipped to recognize any concerning changes in your dog's eyes and take appropriate action to address them.
Understanding the significance of eye health in dogs and being proactive in monitoring and addressing any abnormalities can contribute to maintaining your dog's overall well-being. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the mysteries behind white eyes in dogs and empower ourselves to provide the best care for our beloved canine companions.
Common Causes of White Eyes in Dogs
The appearance of white eyes in dogs can stem from various underlying causes, each with its own implications for the dog's ocular health. Understanding these potential triggers is crucial for identifying the root of the issue and seeking appropriate care. Here are some common causes of white eyes in dogs:
-
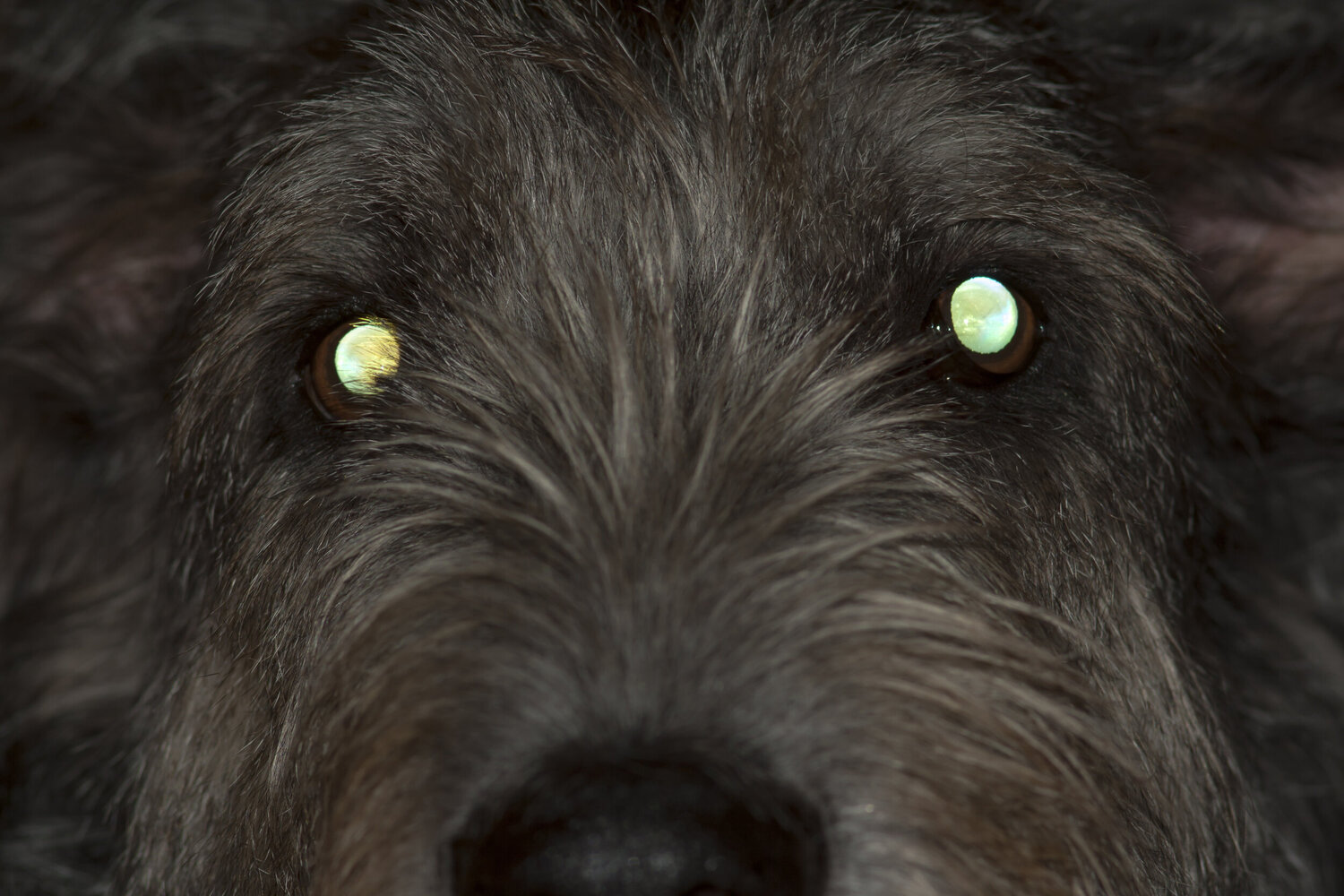
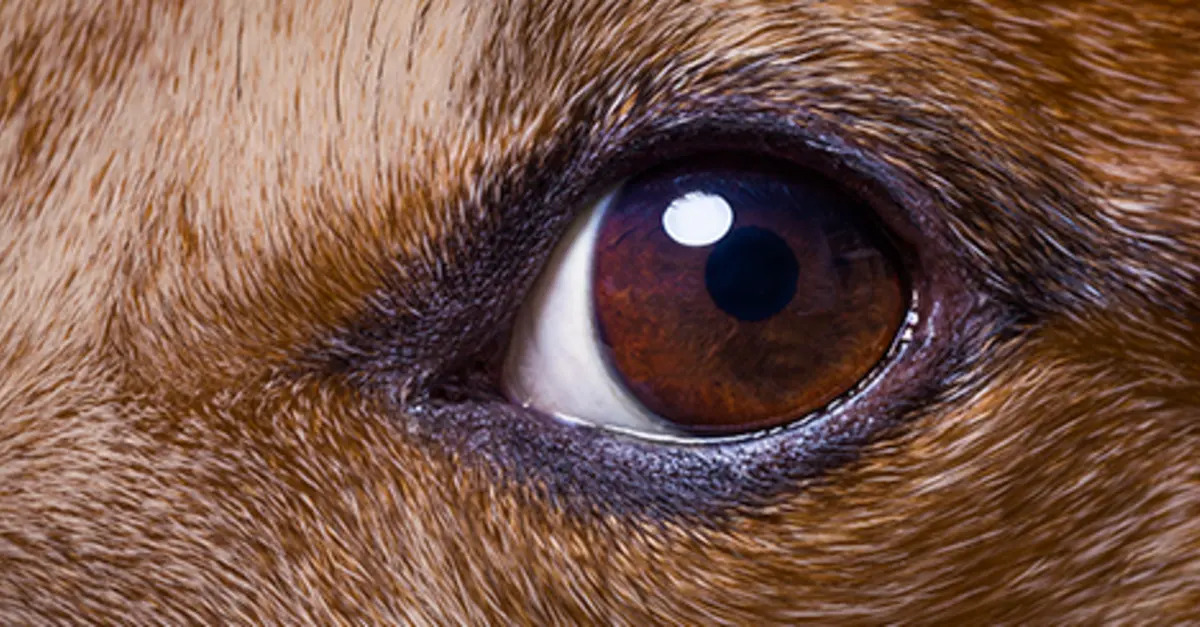
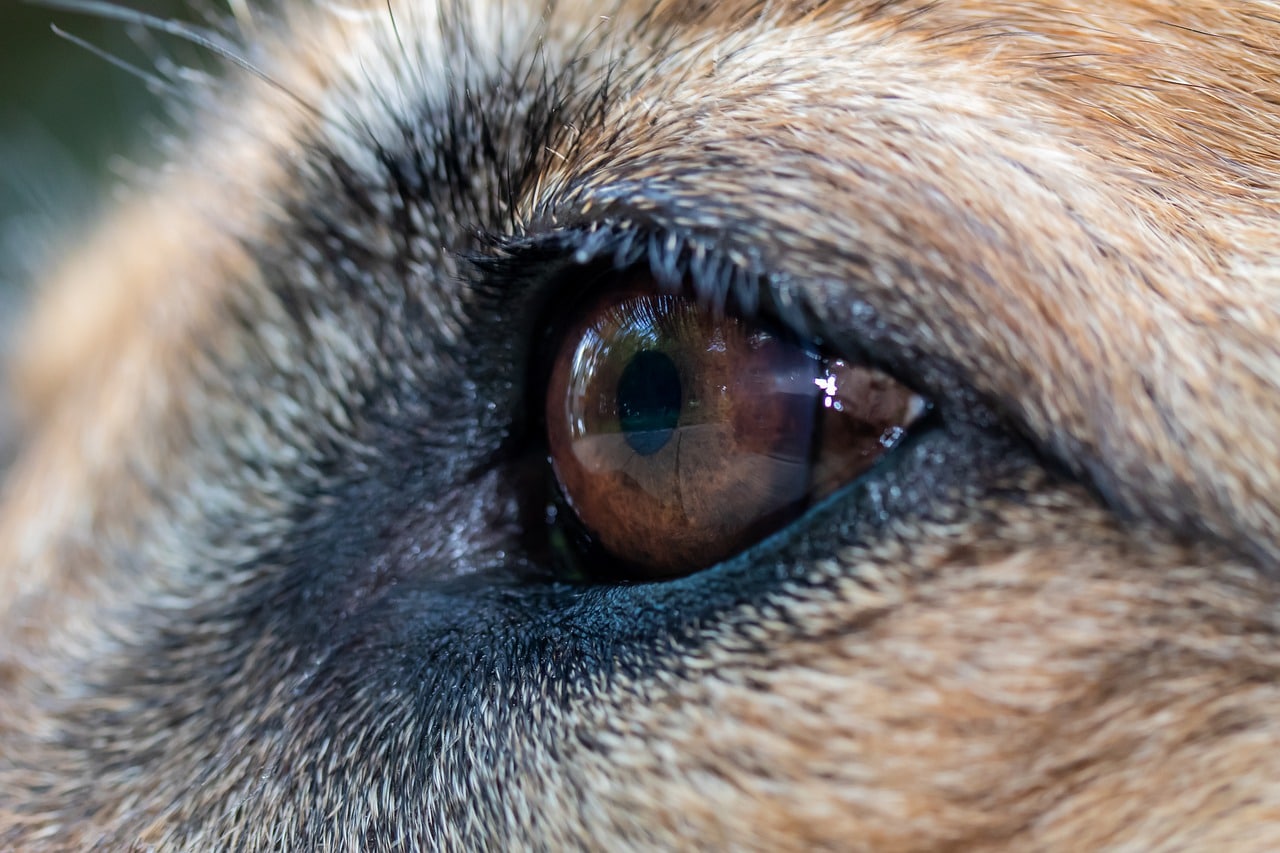
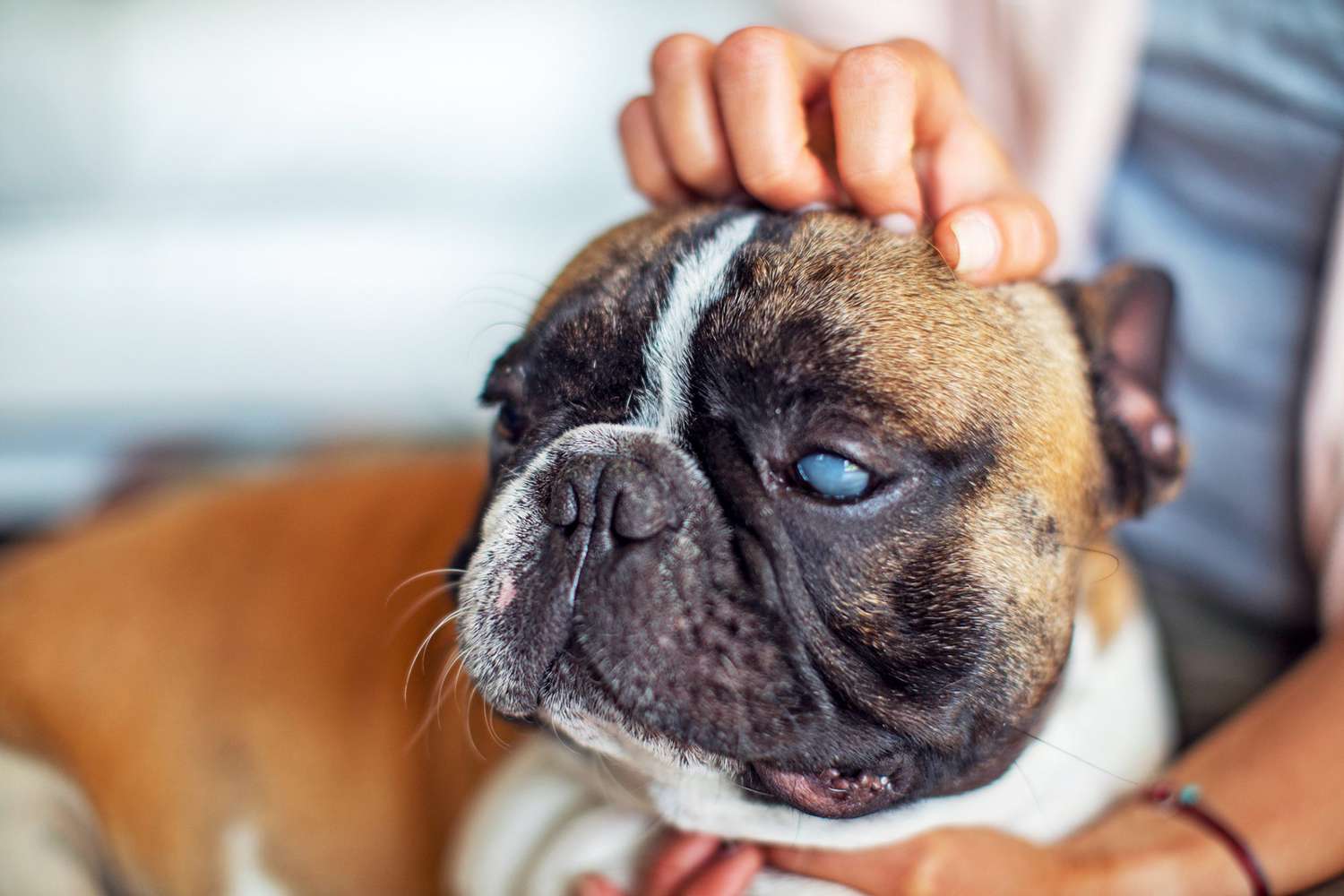
Cataracts: One of the primary culprits behind white eyes in dogs is the development of cataracts. These cloudy or opaque areas in the lens of the eye can cause the affected eye to appear white or bluish-gray. Cataracts can impede vision and may lead to discomfort for the dog.
-
Corneal Dystrophy: This condition involves the accumulation of lipid or cholesterol deposits in the cornea, leading to a cloudy or white appearance in the affected eye. Corneal dystrophy can affect specific breeds and may manifest in both eyes.
-
Glaucoma: When a dog experiences increased pressure within the eye, a condition known as glaucoma, the eye may appear enlarged and hazy, giving it a white or bluish tint. Glaucoma can be painful and requires prompt veterinary attention.
-
Uveitis: Inflammation of the uvea, the middle layer of the eye, can result in a white or cloudy appearance in the affected eye. Uveitis can be caused by various factors, including infections, trauma, or autoimmune conditions.
-
Lens Luxation: This condition involves the displacement of the lens from its normal position, leading to a white or cloudy appearance in the eye. Lens luxation can be painful and may require surgical intervention.
-
Injury or Trauma: Physical trauma to the eye can cause a white or cloudy appearance due to damage to the cornea, lens, or other structures within the eye. Foreign objects or chemical irritants can also lead to this presentation.
-
Inherited Conditions: Certain genetic or hereditary conditions can predispose dogs to developing white eyes. Breed-specific genetic predispositions may contribute to the manifestation of ocular abnormalities.
-
Systemic Health Issues: Underlying systemic health issues, such as diabetes or hypertension, can manifest in ocular changes, including a white appearance in the eyes. Monitoring a dog's overall health is crucial in addressing potential systemic contributors to ocular abnormalities.
Understanding these common causes of white eyes in dogs empowers pet owners to recognize potential issues and take proactive measures to address them. By staying vigilant and seeking prompt veterinary care when necessary, pet owners can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their dog's ocular health.
Symptoms to Look Out For
Recognizing the symptoms associated with white eyes in dogs is essential for identifying potential ocular issues and seeking timely veterinary care. While the appearance of white or cloudy eyes is a prominent indicator, several accompanying symptoms warrant attention. These symptoms may vary depending on the underlying cause of the ocular abnormality. Here are the key symptoms to look out for:
-
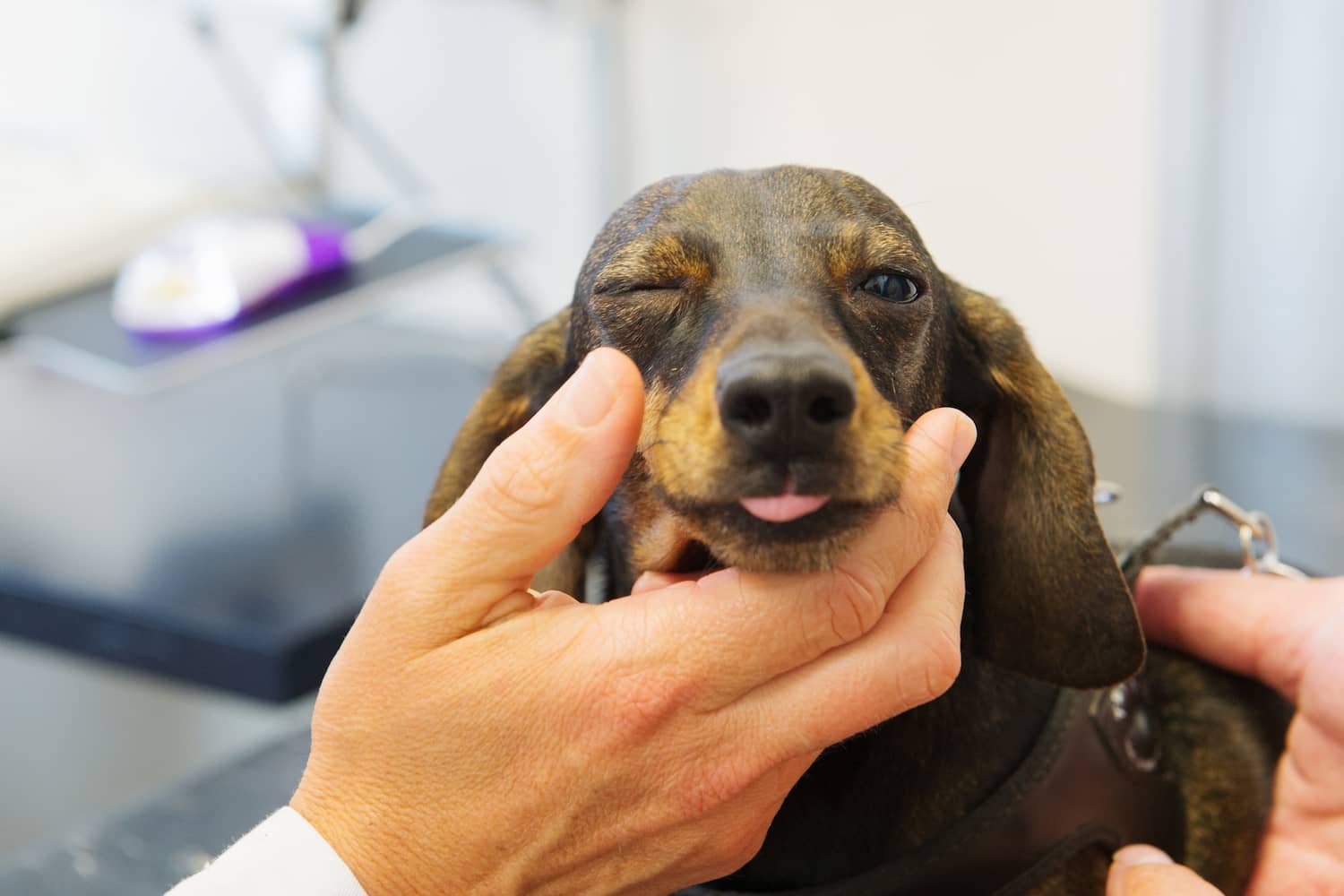
Changes in Eye Color: The most apparent sign is a noticeable change in the color of the dog's eyes, with a white or cloudy appearance indicating potential issues such as cataracts, corneal dystrophy, or glaucoma.
-
Squinting or Blinking: Dogs experiencing discomfort or pain due to ocular abnormalities may exhibit increased squinting, blinking, or rubbing of the affected eye. This behavior signifies potential irritation or sensitivity.
-
Excessive Tearing or Discharge: Ocular abnormalities can lead to increased tear production or the presence of abnormal discharge, indicating underlying issues such as uveitis, infection, or injury.
-
Visible Redness or Inflammation: Inflammation of the eye, characterized by redness or swelling, may accompany the white or cloudy appearance, signaling potential conditions such as uveitis or trauma.
-
Changes in Behavior: Dogs may display changes in behavior, such as reluctance to engage in activities that involve visual focus, indicating discomfort or impaired vision associated with ocular abnormalities.
-
Avoidance of Bright Light: Sensitivity to light, known as photophobia, can manifest as the dog avoiding bright light or exhibiting discomfort in well-lit environments, suggesting potential ocular issues.
-
Visible Changes in Eye Structure: In some cases, structural changes in the eye, such as enlargement, bulging, or irregular pupil size, may accompany the white or cloudy appearance, indicating conditions like glaucoma or lens luxation.
-
Impaired Vision: Observable signs of impaired vision, such as bumping into objects, difficulty navigating familiar spaces, or reluctance to move in dimly lit areas, may indicate the impact of ocular abnormalities on the dog's vision.
By remaining attentive to these symptoms and promptly seeking veterinary evaluation when observed, pet owners can contribute to the early detection and management of ocular issues in their dogs. Timely intervention can mitigate potential discomfort, preserve visual function, and address underlying health concerns, ultimately promoting the well-being of canine companions.
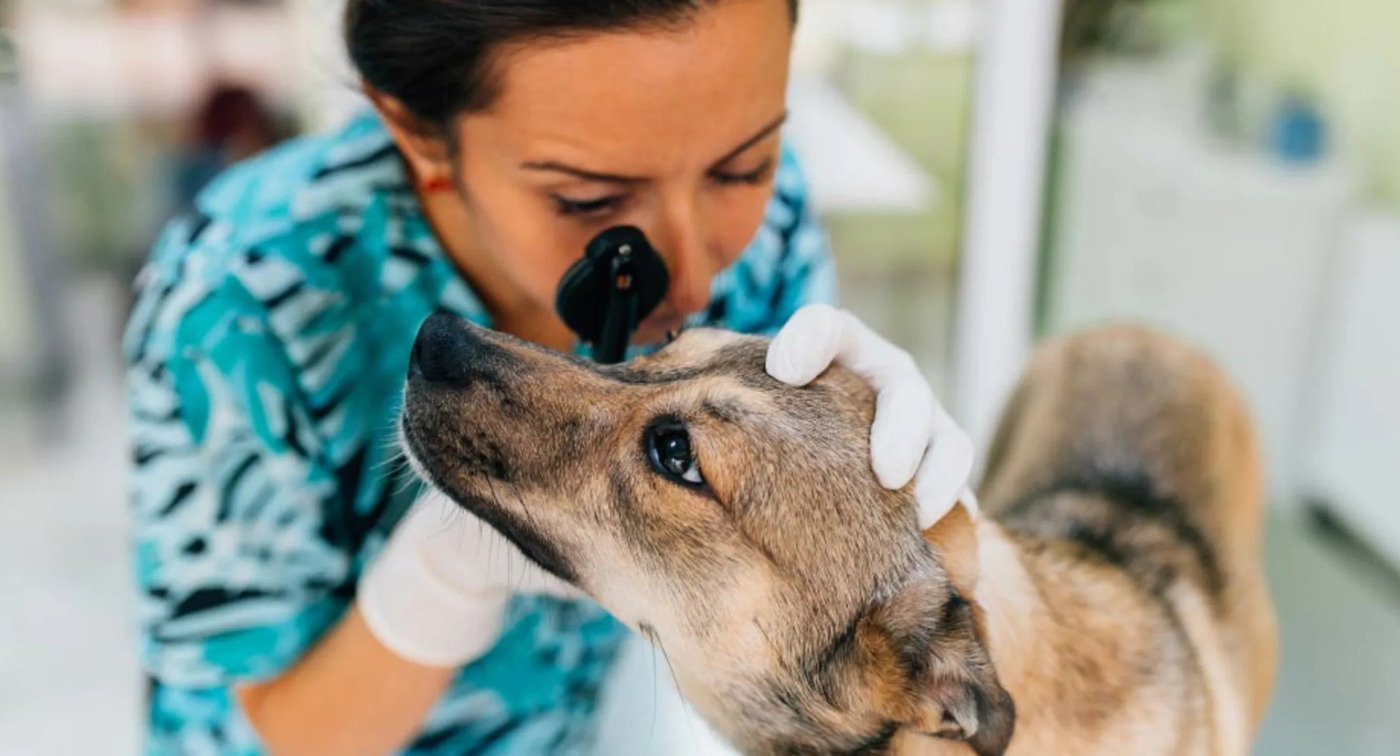
When to Seek Veterinary Care
Recognizing the appropriate timing to seek veterinary care for a dog exhibiting white or cloudy eyes is paramount in addressing potential ocular issues and safeguarding the animal's well-being. Prompt intervention can facilitate early diagnosis, effective management, and the preservation of ocular health. Here are the circumstances that warrant seeking veterinary care for a dog with white eyes:
-
Sudden Onset: If the white or cloudy appearance in the dog's eyes develops suddenly or progresses rapidly, immediate veterinary attention is crucial. Abrupt changes in ocular presentation may signify acute conditions such as glaucoma, severe trauma, or acute uveitis, necessitating urgent evaluation.
-
Persistent Symptoms: When the white or cloudy appearance in the dog's eyes persists for an extended period or is accompanied by persistent symptoms such as squinting, excessive tearing, or visible discomfort, veterinary assessment is warranted. Prolonged ocular abnormalities may indicate underlying conditions that require professional evaluation and management.
-
Visible Discharge or Redness: The presence of abnormal discharge, redness, or inflammation in conjunction with white eyes necessitates veterinary care. These signs may indicate ocular infections, uveitis, or corneal abnormalities that require targeted treatment to prevent progression and alleviate discomfort.
-
Changes in Behavior: If the dog exhibits changes in behavior, such as reluctance to engage in activities that involve visual focus, bumping into objects, or displaying signs of visual impairment, prompt veterinary care is essential. Behavioral changes associated with ocular abnormalities warrant thorough assessment to address potential vision impairment and discomfort.
-
Signs of Pain or Discomfort: Dogs displaying signs of pain, discomfort, or sensitivity related to their eyes, such as increased squinting, rubbing of the eyes, or avoidance of bright light, require prompt veterinary evaluation. These behaviors may indicate ocular pain or irritation that necessitates professional intervention.
-
Preexisting Health Conditions: For dogs with preexisting health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or genetic predispositions to ocular abnormalities, regular veterinary monitoring is essential. Any changes in ocular appearance or behavior should prompt timely veterinary care to address potential exacerbations or complications related to existing health issues.
By remaining vigilant and responsive to these indicators, pet owners can prioritize their dog's ocular health and collaborate with veterinary professionals to ensure timely assessment, accurate diagnosis, and tailored management strategies. Seeking veterinary care at the appropriate juncture can mitigate potential complications, alleviate discomfort, and optimize the overall well-being of dogs experiencing white or cloudy eyes.
Treatment Options
The treatment of white eyes in dogs encompasses a multifaceted approach aimed at addressing the underlying cause, alleviating discomfort, preserving visual function, and promoting overall ocular health. The specific treatment options employed depend on the diagnosed condition and the individual needs of the affected dog. Here are the primary treatment modalities utilized in managing white eyes in dogs:
-
Medication: In cases where ocular abnormalities are attributed to conditions such as uveitis, corneal dystrophy, or ocular infections, veterinary professionals may prescribe topical or systemic medications. These may include anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, or specific eye drops tailored to address the underlying cause and alleviate associated symptoms.
-
Surgical Intervention: Certain conditions, such as cataracts, lens luxation, or severe trauma, may necessitate surgical intervention to restore ocular health and visual function. Surgical procedures, including cataract removal, lens replacement, or corneal repair, are performed by veterinary ophthalmologists to address structural abnormalities and optimize ocular well-being.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: In cases where ocular abnormalities are linked to systemic health issues such as diabetes or hypertension, lifestyle modifications may be recommended to manage the underlying conditions. This may involve dietary adjustments, weight management strategies, or the administration of medications to address systemic contributors to ocular abnormalities.
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Care: Following the initiation of treatment, ongoing monitoring and care are essential to assess treatment efficacy, manage potential complications, and ensure the long-term ocular health of the affected dog. Regular veterinary examinations, ocular assessments, and adherence to prescribed treatment regimens are integral to optimizing treatment outcomes.
-
Environmental Adaptations: For dogs undergoing treatment for ocular abnormalities, environmental adaptations may be recommended to minimize potential stressors and optimize their comfort. This may include reducing exposure to bright light, providing supportive bedding, and creating a safe and navigable living space to accommodate potential visual impairments.
-
Comprehensive Ocular Care: In addition to addressing the specific condition causing the white eyes, comprehensive ocular care involves promoting overall ocular health through measures such as regular eye cleaning, tear supplementation, and the use of protective eyewear when appropriate. These measures contribute to maintaining ocular hygiene and minimizing the risk of secondary complications.
By tailoring treatment to the individual needs of the affected dog and addressing the specific underlying cause of white eyes, veterinary professionals strive to optimize ocular health, alleviate discomfort, and preserve visual function. Collaborative efforts between pet owners and veterinary professionals are pivotal in implementing comprehensive treatment strategies and promoting the well-being of dogs experiencing ocular abnormalities.
Read more: Why Does My Dog Have A White Spot In His Eye
Preventing White Eyes in Dogs
Preventing white eyes in dogs encompasses proactive measures aimed at preserving ocular health, minimizing the risk of ocular abnormalities, and promoting overall well-being. By implementing preventive strategies, pet owners can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their canine companions from potential ocular issues. Here are essential steps to prevent white eyes in dogs:
-
Regular Veterinary Examinations: Scheduling routine veterinary check-ups is fundamental in monitoring a dog's ocular health. Comprehensive eye examinations conducted by veterinary professionals can facilitate the early detection of potential issues, enabling timely intervention and management.
-
Maintaining a Balanced Diet: Providing a nutritionally balanced diet rich in essential vitamins and antioxidants supports overall ocular health. Nutrients such as vitamin A, C, and E, as well as omega-3 fatty acids, contribute to maintaining healthy eyes and may help mitigate the risk of certain ocular conditions.
-
Environmental Safety Measures: Creating a safe and hazard-free environment for dogs minimizes the risk of ocular trauma. Removing potential hazards, securing sharp objects, and ensuring safe outdoor spaces can prevent injuries that may lead to white eyes or other ocular abnormalities.
-
Regular Exercise and Mental Stimulation: Engaging dogs in regular exercise and mental stimulation supports their overall well-being, including ocular health. Physical activity and mental enrichment contribute to maintaining systemic health, which in turn can positively impact ocular function.
-
Eye Protection: In specific situations where dogs are exposed to potential eye irritants or trauma, such as during outdoor activities or in environments with airborne debris, protective eyewear can offer an additional layer of defense against ocular injuries.
-
Monitoring Systemic Health: Regular monitoring and management of systemic health conditions, such as diabetes or hypertension, are integral in preventing ocular manifestations that may lead to white eyes. Collaborating with veterinary professionals to manage underlying health issues can mitigate potential ocular complications.
-
Ocular Hygiene: Implementing regular eye cleaning and maintenance practices can contribute to preventing ocular issues. Gentle cleaning of the area around the eyes and the removal of debris or discharge help maintain ocular hygiene and reduce the risk of secondary complications.
-
Breed-Specific Considerations: Understanding breed-specific predispositions to ocular abnormalities enables proactive measures tailored to the unique needs of specific breeds. Awareness of potential genetic factors influencing ocular health empowers pet owners to implement targeted preventive strategies.
By integrating these preventive measures into the care regimen for dogs, pet owners can proactively mitigate the risk of white eyes and contribute to the long-term ocular health and well-being of their beloved canine companions. Prioritizing preventive care not only minimizes the likelihood of ocular abnormalities but also fosters a holistic approach to maintaining a dog's overall health and quality of life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the appearance of white eyes in dogs can serve as a crucial indicator of underlying ocular abnormalities, necessitating prompt attention and proactive measures from pet owners. By gaining insight into the common causes, symptoms, and appropriate responses to white eyes in dogs, individuals can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their canine companions' ocular health and overall well-being.
Understanding the diverse array of potential causes, including cataracts, corneal dystrophy, glaucoma, uveitis, and trauma, empowers pet owners to recognize concerning changes in their dog's eyes and seek timely veterinary care. The recognition of accompanying symptoms such as squinting, excessive tearing, and changes in behavior serves as a vital cue for intervention, enabling early detection and management of ocular abnormalities.
Moreover, the proactive pursuit of preventive measures, including regular veterinary examinations, balanced nutrition, environmental safety, and breed-specific considerations, contributes to mitigating the risk of ocular issues and promoting long-term ocular health in dogs. By integrating these preventive strategies into their care regimen, pet owners can foster a holistic approach to maintaining their dog's ocular health and overall quality of life.
In the event of white eyes in dogs, the collaboration between pet owners and veterinary professionals is paramount in implementing tailored treatment strategies, addressing the underlying cause, and optimizing ocular health outcomes. From medication and surgical interventions to ongoing monitoring and environmental adaptations, the comprehensive management of ocular abnormalities aims to alleviate discomfort, preserve visual function, and promote the overall well-being of affected dogs.
Ultimately, the journey to unravel the mysteries behind white eyes in dogs serves as a testament to the unwavering commitment of pet owners in prioritizing the health and happiness of their beloved canine companions. By remaining vigilant, proactive, and responsive to potential ocular abnormalities, individuals can embark on a shared mission to ensure that their dogs continue to experience the world through bright, clear, and healthy eyes, fostering a bond built on trust, compassion, and unwavering care.