Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Which Dogs Can Sense Cancer


Common Health Issues
Which Dogs Can Sense Cancer
Published: February 5, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs and discover which breeds are known for their ability to sense cancer. Understanding your dog's health is crucial for their well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The ability of dogs to detect cancer has long fascinated and intrigued both the scientific community and the general public. Dogs, often referred to as "man's best friend," possess an extraordinary sense of smell, which is estimated to be tens of thousands of times more sensitive than that of humans. This remarkable olfactory prowess enables them to detect subtle changes in the body's chemistry, including the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with various types of cancer.
The notion of dogs being able to sniff out cancer may seem like something out of a science fiction novel, but numerous studies have provided compelling evidence of their remarkable ability to detect the presence of cancer in humans. This has sparked a growing interest in harnessing the potential of these four-legged friends as valuable allies in the early detection and diagnosis of cancer.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of canine cancer detection, exploring how dogs are able to sense cancer, the specific breeds known for their cancer-detecting abilities, the training methods employed to hone their skills, and real-life case studies that highlight their exceptional talent. Additionally, we will examine the ethical considerations surrounding the use of dogs in cancer detection and contemplate the future implications of this groundbreaking field of research.
Join us on this captivating journey as we unravel the extraordinary capabilities of our canine companions and the profound impact they have in the realm of cancer detection.
Read more: Which Dog Foods Cause Cancer
How Dogs Can Sense Cancer
Dogs possess an extraordinary sense of smell, which is estimated to be tens of thousands of times more sensitive than that of humans. This remarkable olfactory prowess enables them to detect subtle changes in the body's chemistry, including the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with various types of cancer.
The process through which dogs can sense cancer is attributed to their highly developed olfactory system. When cancer is present in the body, it produces distinct metabolic waste products, known as VOCs, which are released through breath, urine, and skin. These VOCs create a unique scent that dogs are capable of detecting, even at incredibly low concentrations.
Research has shown that dogs can detect these specific odors associated with cancer, often before any conventional medical tests can identify the presence of the disease. Their ability to discern these minute chemical changes in the body's odor profile has sparked immense interest in utilizing them as a non-invasive and potentially highly accurate method for early cancer detection.
Furthermore, dogs have been found to detect a wide range of cancer types, including lung, breast, ovarian, colorectal, and prostate cancer, among others. Their remarkable olfactory acuity allows them to differentiate between healthy and cancerous samples, showcasing their potential as valuable allies in the fight against this pervasive disease.
The intricate workings of a dog's sense of smell involve a complex interplay of biological mechanisms. The olfactory receptors in a dog's nose are adept at capturing scent molecules, which are then processed in the olfactory bulb, a specialized structure in the brain. This intricate process enables dogs to not only detect a wide array of scents but also to discern the subtle chemical changes indicative of cancer.
In essence, the ability of dogs to sense cancer is a testament to the awe-inspiring capabilities of their olfactory system. Their acute sense of smell, coupled with their remarkable capacity to discern minute changes in the body's odor, positions them as invaluable assets in the realm of cancer detection.
This innate ability of dogs to sense cancer has paved the way for groundbreaking research and has the potential to revolutionize early cancer detection methods, offering hope for improved patient outcomes and enhanced survival rates.
Breeds Known for Cancer Detection
Certain dog breeds have garnered attention for their exceptional ability to detect cancer in humans. While all dogs possess a remarkable sense of smell, specific breeds have been identified as particularly adept at cancer detection due to their heightened olfactory capabilities and trainable nature. These breeds have been the focus of extensive research and training programs aimed at harnessing their innate talent for cancer detection.
One of the most renowned breeds known for their cancer-detecting abilities is the Labrador Retriever. Renowned for their intelligence, trainability, and gentle demeanor, Labrador Retrievers have been successfully trained to detect various types of cancer, including lung, breast, and ovarian cancer. Their keen sense of smell, coupled with their unwavering loyalty and willingness to work closely with humans, makes them ideal candidates for cancer detection tasks.
Another notable breed recognized for its cancer-detecting prowess is the German Shepherd. With their exceptional intelligence, strong work ethic, and acute sense of smell, German Shepherds have demonstrated remarkable success in detecting cancer through scent. Their versatility and adaptability have made them valuable assets in cancer detection research and practical applications.
The Belgian Malinois is also esteemed for its remarkable olfactory abilities, making it a promising candidate for cancer detection work. Their high energy levels, intelligence, and unwavering focus have positioned them as valuable allies in the quest to utilize dogs for early cancer detection.
Additionally, the Golden Retriever, known for its friendly disposition and exceptional scenting abilities, has shown promise in cancer detection efforts. Their gentle nature, coupled with their keen sense of smell, has made them valuable partners in research endeavors aimed at leveraging their innate abilities for cancer detection.
Furthermore, the Portuguese Water Dog has garnered attention for its keen sense of smell and remarkable intelligence, making it a potential contender for cancer detection tasks. Their strong work ethic and affinity for human companionship render them well-suited for the rigorous training and demanding tasks associated with cancer detection work.
These breeds, among others, have been the focus of extensive research and training programs aimed at honing their cancer-detecting abilities. Their exceptional olfactory capabilities, coupled with their trainable nature and strong bond with humans, position them as invaluable assets in the realm of cancer detection.
The remarkable potential exhibited by these breeds underscores the profound impact that dogs can have in the early detection and diagnosis of cancer, offering hope for improved patient outcomes and enhanced survival rates.
Training Dogs to Detect Cancer
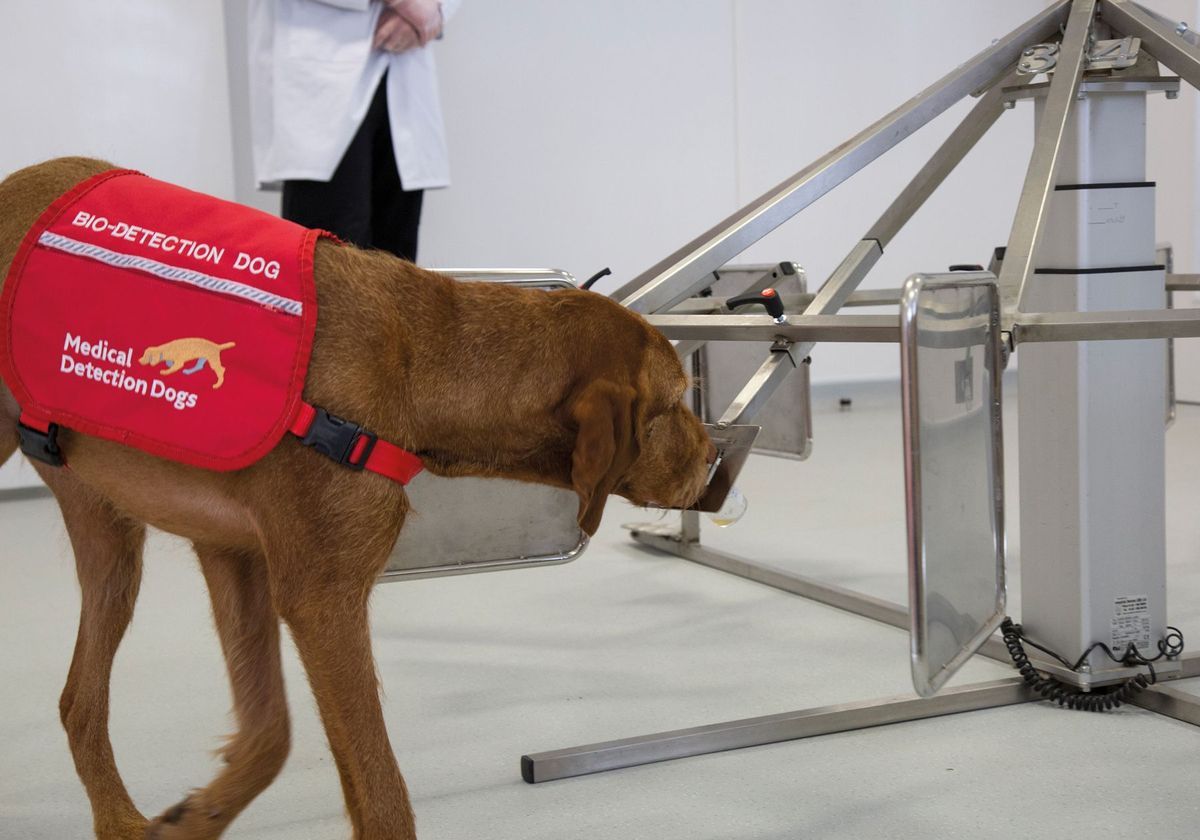
Training dogs to detect cancer involves a meticulous and systematic process aimed at harnessing their exceptional olfactory abilities and innate talent for scent discrimination. This specialized training equips dogs with the skills to identify the distinct odors associated with various types of cancer, paving the way for their invaluable role in early cancer detection efforts.
The training process typically begins by exposing the dogs to a wide range of scent samples, including those obtained from cancer patients and healthy individuals. Through positive reinforcement techniques, dogs are taught to associate the specific scent of cancer with a reward, such as a treat or playtime. This forms the foundation for their ability to differentiate between cancerous and non-cancerous odors.
As the training progresses, dogs undergo rigorous exercises designed to refine their olfactory acuity and enhance their ability to detect minute changes in scent profiles. They are exposed to a diverse array of cancer-related odors, allowing them to develop a keen sensitivity to the volatile organic compounds (VOCs) associated with different types of cancer. This intensive training regimen hones their scent detection skills and cultivates their proficiency in identifying cancer-specific odors amidst various environmental stimuli.
Furthermore, dogs are trained to exhibit specific behavioral responses, such as sitting or indicating the location of the cancerous scent, upon detection. This behavioral indication serves as a crucial communication tool, enabling them to convey the presence of cancer in a clear and discernible manner. Through consistent training and reinforcement, dogs learn to reliably signal the presence of cancer, laying the groundwork for their pivotal role in cancer detection scenarios.
The training process is characterized by patience, dedication, and a deep understanding of canine behavior and olfactory capabilities. Trainers employ positive reinforcement methods, patience, and a deep understanding of canine behavior to cultivate the dogs' cancer detection skills effectively. This collaborative effort between trainers and dogs fosters a strong bond and mutual trust, essential for the successful development of their cancer detection abilities.
The culmination of this rigorous training is the transformation of dogs into proficient cancer detection allies, capable of identifying cancer-specific odors with remarkable accuracy. Their keen olfactory prowess, coupled with their unwavering dedication and trainable nature, positions them as invaluable assets in the realm of cancer detection, offering a non-invasive and potentially highly effective method for early cancer detection.
In essence, the training of dogs to detect cancer represents a harmonious fusion of scientific rigor, canine intuition, and unwavering dedication, culminating in the cultivation of a remarkable partnership between humans and their canine companions in the fight against cancer.
Case Studies of Dogs Detecting Cancer
The remarkable ability of dogs to detect cancer has been substantiated by numerous compelling case studies, showcasing their exceptional talent in identifying the presence of cancer in humans. These real-life instances serve as poignant testaments to the profound impact that dogs can have in the realm of cancer detection, offering hope for improved patient outcomes and enhanced survival rates.
In one notable case, a trained Labrador Retriever named Daisy demonstrated remarkable proficiency in detecting cancer. Daisy participated in a clinical trial where she accurately identified the presence of lung cancer in breath samples provided by patients. Through her keen sense of smell and rigorous training, Daisy achieved an impressive level of accuracy, effectively discerning the distinct odor associated with lung cancer. This groundbreaking case underscored the potential of dogs as non-invasive and highly accurate allies in the early detection of lung cancer, offering a glimmer of hope for improved diagnostic methods.
Another compelling case involved a German Shepherd named Frankie, who showcased exceptional cancer detection abilities in a clinical setting. Frankie was trained to identify the scent of ovarian cancer through urine samples, and his remarkable accuracy in detecting the presence of this cancer type garnered widespread attention. His consistent and reliable indication of ovarian cancer in urine samples highlighted the invaluable role that dogs can play in the early detection of this challenging cancer type, potentially leading to earlier interventions and improved patient outcomes.
Furthermore, a Golden Retriever named Tucker participated in a study focusing on breast cancer detection. Tucker's remarkable olfactory acuity and unwavering dedication were evident as he successfully identified the presence of breast cancer in breath samples provided by patients. His consistent and reliable detection of breast cancer-specific odors exemplified the potential of dogs as sensitive and reliable allies in the early detection of this prevalent cancer type, offering a promising avenue for enhancing diagnostic capabilities.
These compelling case studies, among others, underscore the remarkable capabilities of dogs in detecting cancer and offer a glimpse into the transformative potential of leveraging their olfactory prowess for early cancer detection. The unwavering dedication, remarkable accuracy, and non-invasive nature of their detection abilities position dogs as invaluable partners in the ongoing battle against cancer, offering hope for improved patient outcomes and enhanced survival rates.
The remarkable potential exhibited by these case studies underscores the profound impact that dogs can have in the early detection and diagnosis of cancer, offering hope for improved patient outcomes and enhanced survival rates.
Ethical Considerations and Future Research
Ethical considerations play a pivotal role in the utilization of dogs for cancer detection, prompting careful reflection on the welfare and well-being of these remarkable animals. As dogs are enlisted as allies in the quest for early cancer detection, ethical guidelines and standards must be upheld to ensure their physical and emotional welfare. This encompasses the implementation of humane training methods, the provision of adequate rest and care, and the cultivation of a nurturing environment that prioritizes the dogs' overall well-being. Additionally, the ethical implications of integrating dogs into clinical settings for cancer detection must be thoughtfully examined, with a focus on minimizing stress and ensuring their comfort in these environments.
Looking ahead, future research endeavors hold immense promise in further elucidating the intricacies of canine cancer detection and expanding the scope of its practical applications. Ongoing research initiatives aim to delve deeper into the specific VOCs associated with different types of cancer, unraveling the complex scent profiles that dogs are capable of discerning. This in-depth understanding of cancer-related odors can potentially lead to the development of advanced diagnostic technologies inspired by the remarkable olfactory abilities of dogs.
Furthermore, future research efforts seek to optimize the training protocols and methodologies employed in honing dogs' cancer detection skills. By refining training techniques and exploring innovative approaches, researchers endeavor to enhance the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of dogs in detecting cancer, paving the way for their seamless integration into clinical and diagnostic settings.
Ethical considerations also extend to the equitable access and utilization of canine cancer detection methods, ensuring that these innovative approaches are accessible to diverse populations. Efforts to address disparities in cancer detection and diagnosis through the deployment of canine allies must be underpinned by a commitment to inclusivity and accessibility, thereby fostering equitable healthcare outcomes for all individuals.
Moreover, future research endeavors aim to explore the potential expansion of canine cancer detection beyond traditional clinical settings. This includes the exploration of canine detection capabilities in non-invasive screening programs, community health initiatives, and resource-limited settings, offering a beacon of hope for early cancer detection in diverse contexts.
In essence, the ethical considerations and future research directions in the realm of canine cancer detection underscore a commitment to the responsible and compassionate integration of dogs as invaluable allies in the fight against cancer. As research continues to unfold, the transformative potential of canine cancer detection holds promise for revolutionizing early cancer detection methods and enhancing patient outcomes on a global scale.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the remarkable ability of dogs to sense cancer represents a convergence of scientific ingenuity, canine intuition, and unwavering dedication, culminating in a transformative partnership in the fight against cancer. The innate olfactory prowess of dogs, coupled with their trainable nature and unwavering loyalty, positions them as invaluable allies in the realm of early cancer detection.
Through a deep understanding of canine olfactory capabilities and meticulous training, dogs have demonstrated exceptional proficiency in detecting the distinct odors associated with various types of cancer. Their remarkable accuracy in discerning cancer-specific volatile organic compounds (VOCs) offers a non-invasive and potentially highly effective method for early cancer detection, holding promise for improved patient outcomes and enhanced survival rates.
The case studies of dogs detecting cancer serve as poignant testaments to the profound impact that these remarkable animals can have in the realm of cancer detection. From identifying lung cancer in breath samples to detecting ovarian cancer in urine samples, dogs have showcased unwavering dedication and remarkable accuracy, offering hope for earlier interventions and improved diagnostic capabilities.
As we navigate the ethical considerations surrounding the integration of dogs into cancer detection efforts, a commitment to upholding their welfare and well-being remains paramount. Ethical guidelines and standards must be upheld to ensure the humane treatment and care of these remarkable animals, fostering a nurturing environment that prioritizes their overall well-being.
Looking ahead, future research endeavors hold immense promise in further elucidating the intricacies of canine cancer detection and expanding the scope of its practical applications. Ongoing research initiatives aim to optimize training protocols, explore innovative approaches, and address disparities in cancer detection and diagnosis, fostering equitable healthcare outcomes for all individuals.
In essence, the utilization of dogs in cancer detection represents a harmonious fusion of scientific rigor, compassionate care, and unwavering dedication, offering a beacon of hope for revolutionizing early cancer detection methods and enhancing patient outcomes on a global scale. The profound impact of canine cancer detection transcends scientific inquiry, embodying a testament to the unwavering bond between humans and their canine companions in the shared pursuit of combating cancer.