Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Is Dental Disease In Dogs?


Common Health Issues
What Is Dental Disease In Dogs?
Modified: February 21, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs, including dental disease. Discover the signs, symptoms, and treatment options to keep your pet healthy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
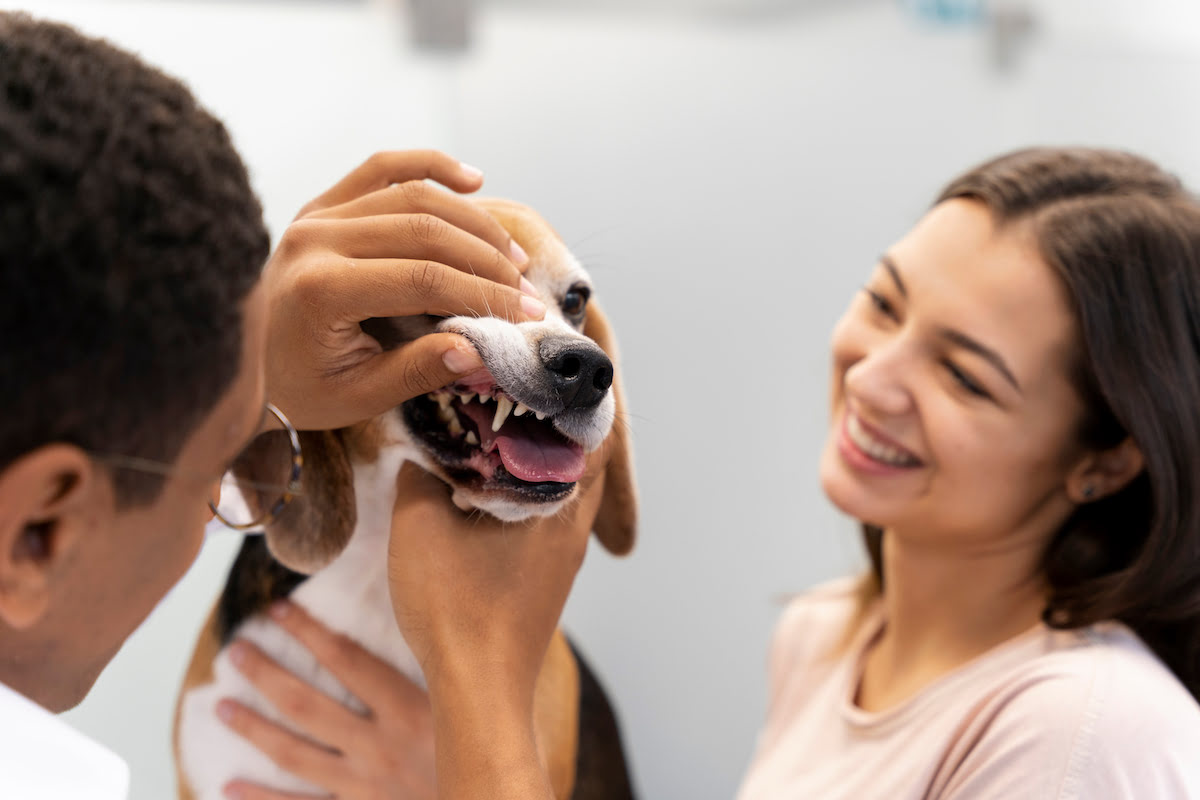
Dental disease is a prevalent health issue that affects dogs of all breeds and ages. It encompasses a range of conditions that impact the teeth, gums, and overall oral health of our beloved canine companions. Just like humans, dogs require proper dental care to maintain their overall well-being. Unfortunately, dental issues in dogs often go unnoticed, leading to discomfort, pain, and potential health complications.
Understanding the significance of dental health in dogs is crucial for pet owners. By recognizing the common dental diseases, their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures, we can take proactive steps to ensure our furry friends enjoy optimal oral health and a higher quality of life.
In this article, we will delve into the world of dental disease in dogs, shedding light on the various conditions that can affect their oral cavity. From the causes of dental disease to the signs and symptoms that pet owners should watch out for, we aim to provide comprehensive insights into this often overlooked aspect of canine health. Furthermore, we will explore the preventive measures and treatment options available to mitigate the impact of dental disease on our canine companions.
By gaining a deeper understanding of dental disease in dogs, pet owners can become proactive advocates for their pets' oral health. Let's embark on this enlightening journey to uncover the nuances of dental health in dogs and learn how to ensure that our furry friends maintain healthy, happy smiles.
Read more: What Is Sunken Eye Disease In Dogs?
Common Dental Diseases in Dogs
Dental diseases are a prevalent concern among dogs, impacting their overall well-being and quality of life. Understanding the common dental issues that affect our furry companions is essential for proactive dental care. Here are some of the most prevalent dental diseases in dogs:
1. Periodontal Disease:
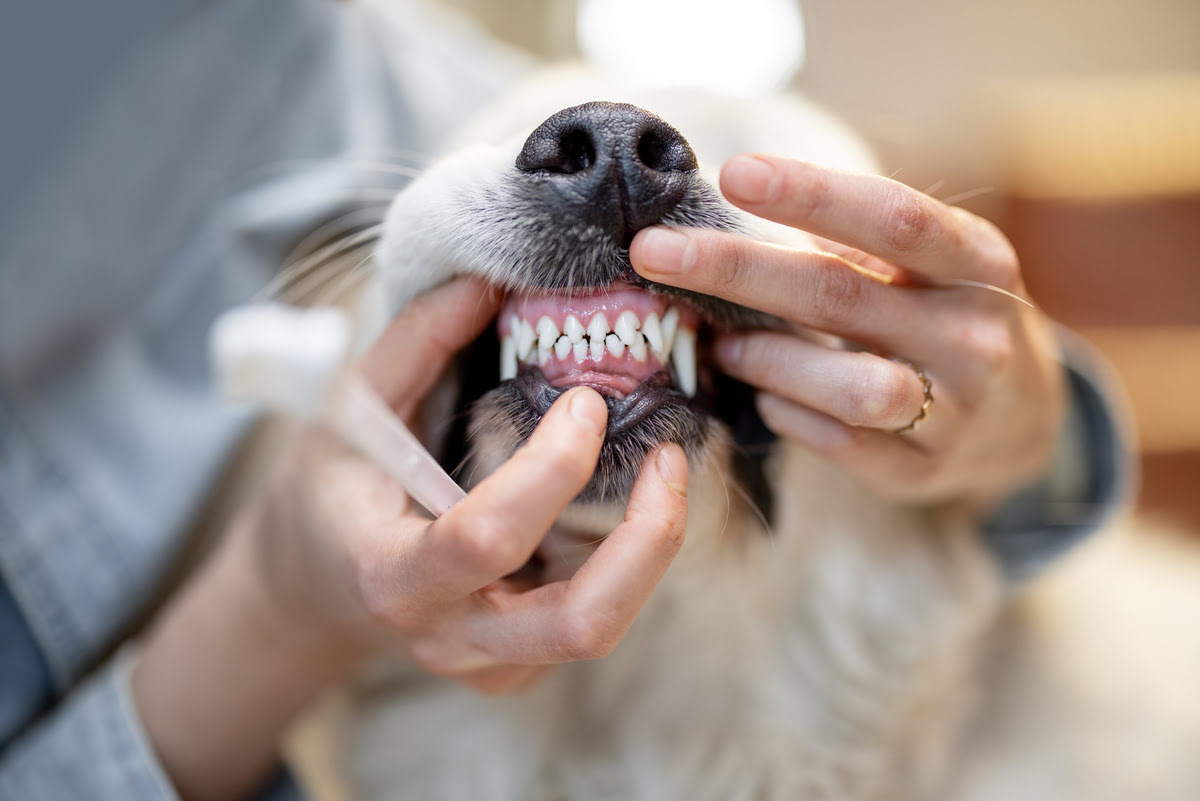
Periodontal disease is one of the most common dental issues in dogs, affecting a majority of adult canines. It involves the inflammation and infection of the gums, often leading to the deterioration of the supporting structures of the teeth. Plaque and tartar buildup on the teeth contribute to the development of periodontal disease, causing pain, bad breath, and potential tooth loss.
2. Tooth Decay:
Similar to humans, dogs can experience tooth decay, also known as dental caries. This condition occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that erode the enamel, leading to cavities. Tooth decay can cause discomfort and sensitivity in dogs, impacting their ability to eat and chew properly.
3. Gingivitis:
Gingivitis is characterized by inflammation of the gums, often resulting from the accumulation of plaque and bacteria along the gum line. It can cause redness, swelling, and tenderness in the gums, leading to discomfort for the affected dog. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to more severe forms of periodontal disease.
Read more: Who Performs Dental Prophylaxis In Dogs
4. Oral Tumors:
Oral tumors, including malignant growths, can affect the oral cavity of dogs, posing a serious threat to their dental health. These tumors can manifest as lumps or abnormal growths in the mouth, causing pain and difficulty in eating. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing oral tumors in dogs.
5. Malocclusion:
Malocclusion refers to misalignment of the teeth, which can lead to various dental issues in dogs. It can cause discomfort, difficulty in chewing, and increased susceptibility to dental diseases. Certain breeds are more prone to malocclusion, requiring proactive dental care to mitigate its impact.
By familiarizing ourselves with these common dental diseases in dogs, we can better recognize the signs and symptoms, enabling early intervention and preventive measures to safeguard our canine companions' oral health.
Causes of Dental Disease in Dogs
Dental disease in dogs can stem from various factors, contributing to the development and progression of oral health issues. Understanding the underlying causes of dental disease is crucial for implementing effective preventive measures and promoting proactive dental care for our furry companions.
-
Poor Dental Hygiene: Neglecting regular dental care, including brushing and professional cleanings, can lead to the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth, fostering an environment conducive to dental disease development.
-
Diet and Nutrition: Inadequate nutrition and a diet high in sugary or starchy foods can contribute to dental issues in dogs. Certain food particles can adhere to the teeth, promoting bacterial growth and plaque formation.
-
Genetics and Breed Predisposition: Some dog breeds are inherently more susceptible to certain dental conditions, such as malocclusion or periodontal disease. Genetic factors can influence the alignment of teeth and the overall oral health of dogs.
-
Age and Dental Health: As dogs age, they become more prone to dental disease due to the natural wear and tear on their teeth and gums. Aging can also lead to a weakened immune system, making older dogs more susceptible to oral health issues.
-
Lack of Chew Toys and Dental Treats: Insufficient opportunities for chewing and gnawing can contribute to the buildup of plaque and tartar. Chew toys and dental treats play a vital role in promoting dental health by reducing plaque and massaging the gums.
-
Systemic Health Conditions: Certain systemic health issues, such as diabetes and immune disorders, can impact a dog's oral health. These conditions can compromise the immune response in the oral cavity, increasing the risk of dental disease.
-
Environmental Factors: Environmental elements, such as exposure to tobacco smoke or air pollution, can have detrimental effects on a dog's oral health. Secondhand smoke, for instance, can exacerbate oral inflammation and contribute to the development of dental disease.
By recognizing these underlying causes of dental disease in dogs, pet owners can take proactive steps to mitigate risk factors and promote optimal oral health for their canine companions. Implementing a comprehensive dental care routine, providing a balanced diet, and seeking regular veterinary dental evaluations are essential in addressing and preventing dental issues in dogs.
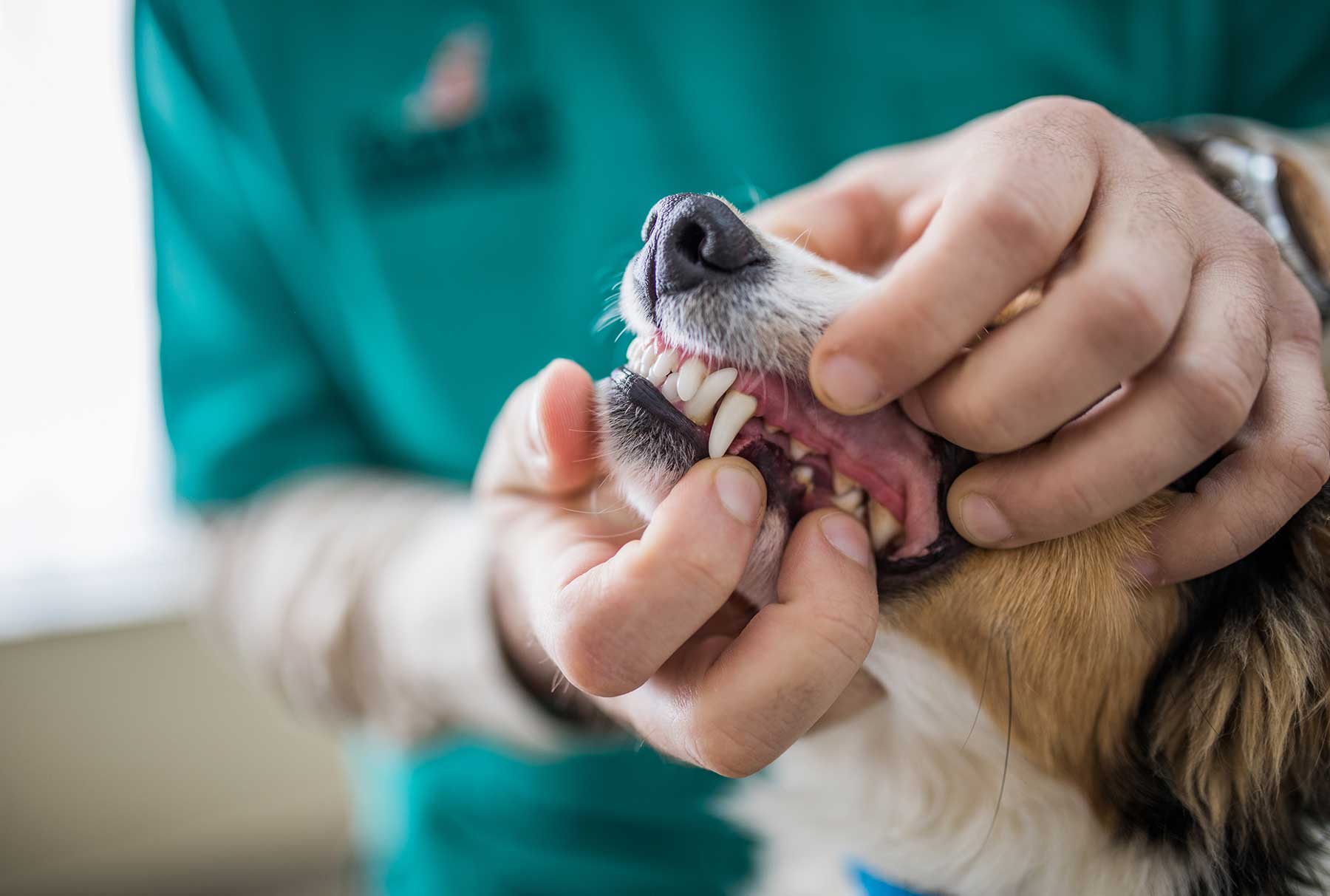
Signs and Symptoms of Dental Disease in Dogs
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of dental disease in dogs is crucial for early intervention and effective management of oral health issues. While dogs may not be able to verbally communicate their discomfort, there are observable indicators that can alert pet owners to potential dental problems. Here are the common signs and symptoms of dental disease in dogs:
-
Bad Breath (Halitosis): Persistent bad breath is often an early indication of dental disease in dogs. Foul-smelling breath can stem from the accumulation of bacteria in the mouth, leading to oral infections and inflammation.
-
Changes in Eating Habits: Dogs experiencing dental discomfort may exhibit changes in their eating habits. This can include reluctance to eat, dropping food from the mouth, or favoring one side of the mouth while chewing.
-
Excessive Drooling: Unusual or excessive drooling, especially when accompanied by other signs of oral discomfort, can signal the presence of dental issues in dogs.
-
Red or Inflamed Gums: Inflammation of the gums, characterized by redness, swelling, or tenderness, is a common indicator of gingivitis or periodontal disease in dogs.
-
Pawing at the Mouth: Dogs in discomfort may paw at their mouths or rub their faces against surfaces in an attempt to alleviate oral pain or irritation.
-
Visible Tartar or Discoloration: The presence of yellowish-brown tartar on the teeth or discoloration of the enamel can indicate the progression of dental disease in dogs.
-
Loose or Missing Teeth: Dental disease can lead to tooth mobility or loss, impacting a dog's ability to chew and causing significant discomfort.
-
Behavioral Changes: Dogs experiencing oral pain may exhibit changes in behavior, such as increased irritability, reluctance to play with chew toys, or withdrawal from social interactions.
-
Blood in Saliva or on Chew Toys: The presence of blood in a dog's saliva or on chew toys can be indicative of gum disease or oral injuries associated with dental disease.
-
Difficulty Swallowing: Dogs with advanced dental issues may experience difficulty swallowing, leading to reluctance to eat or drink.
By remaining vigilant for these signs and symptoms, pet owners can promptly seek veterinary care and implement appropriate dental interventions to alleviate their canine companions' oral discomfort and promote long-term oral health. Regular dental check-ups and proactive dental care routines are essential in mitigating the impact of dental disease on dogs' overall well-being.
Read more: What Diseases Do Dogs Get From Ticks
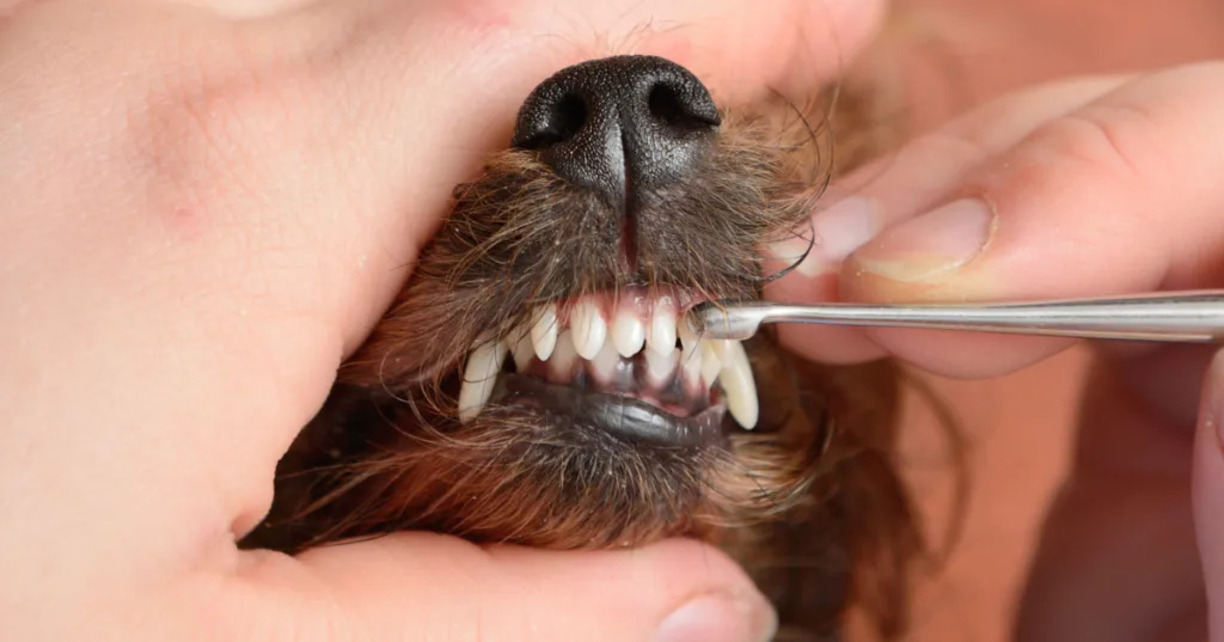
Prevention and Treatment of Dental Disease in Dogs
Preventing and treating dental disease in dogs is essential for maintaining their overall health and well-being. By implementing proactive measures and seeking timely veterinary care, pet owners can significantly mitigate the impact of dental issues on their canine companions. Here's a comprehensive overview of the preventive strategies and treatment options for dental disease in dogs:
Prevention
-
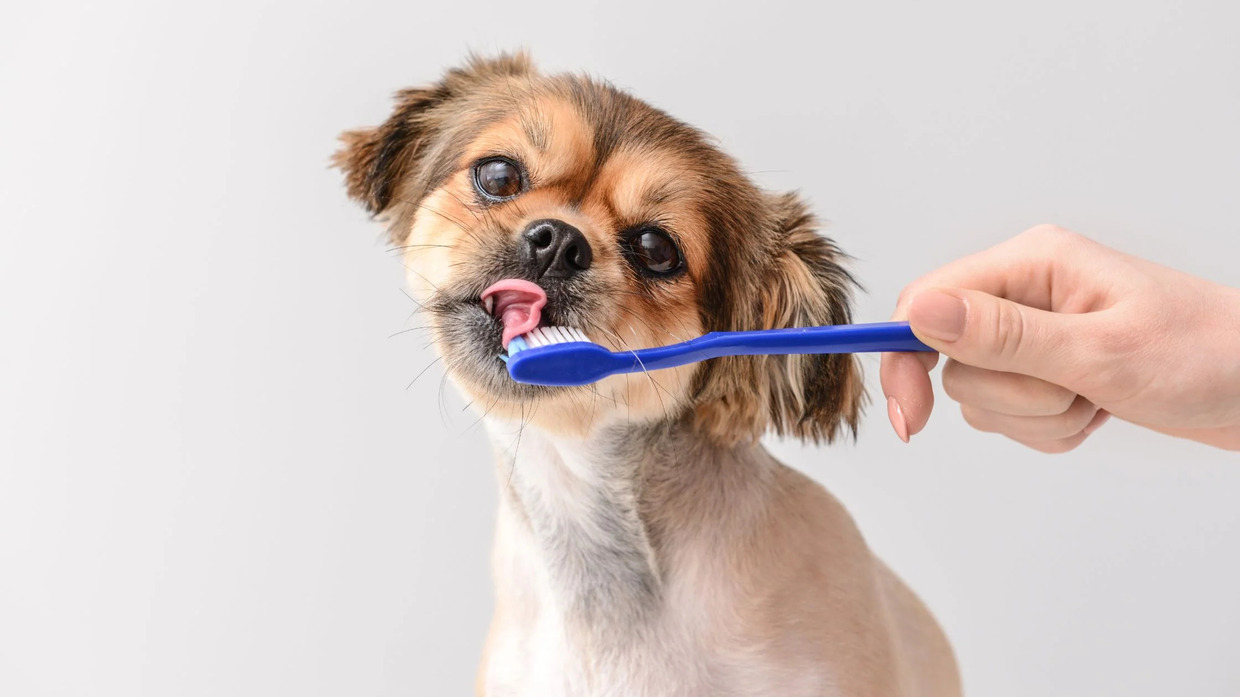
Regular Dental Care: Establishing a consistent dental care routine is paramount in preventing dental disease in dogs. This includes daily tooth brushing using veterinary-approved toothpaste, as well as providing dental chews and toys designed to promote oral health.
-
Balanced Diet: A nutritionally balanced diet plays a crucial role in supporting dental health. Opt for high-quality dog food that helps reduce plaque and tartar buildup, while avoiding excessive sugary or starchy treats that can contribute to dental issues.
-
Professional Dental Cleanings: Regular veterinary dental check-ups and professional cleanings are essential for maintaining optimal oral health in dogs. These cleanings involve the removal of plaque and tartar, as well as thorough oral examinations to detect early signs of dental disease.
-
Chew Toys and Dental Treats: Providing dogs with appropriate chew toys and dental treats can help reduce plaque, massage the gums, and promote healthy chewing behavior, contributing to overall dental wellness.
-
Supplemental Dental Care Products: Consider using dental rinses, water additives, or dental gels recommended by veterinarians to complement oral hygiene efforts and promote a healthy oral environment for dogs.
Treatment
-
Dental Procedures: In cases where dental disease has progressed, various dental procedures may be necessary to address the underlying issues. These procedures can include tooth extractions, periodontal treatments, and oral surgeries to alleviate pain and restore oral health.
-
Medication and Oral Care Products: Veterinarians may prescribe medications, such as antibiotics or pain relievers, to manage oral infections and discomfort associated with dental disease. Additionally, oral care products, such as plaque-reducing gels or medicated dental rinses, can aid in treatment and prevention.
-
Dietary Modifications: In some instances, dietary modifications may be recommended to support dental health. Specialized dental diets formulated to reduce plaque and tartar buildup can be beneficial in managing and preventing dental disease in dogs.
-
Behavioral and Environmental Adjustments: Pet owners can make adjustments to their dog's environment and behavior to promote dental health. This may include discouraging destructive chewing habits, providing appropriate chew toys, and creating a dental-friendly living space for dogs.
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-Up Care: After initiating treatment, ongoing monitoring and follow-up care with a veterinarian are crucial to assess the effectiveness of interventions and ensure the long-term oral health of dogs.
By prioritizing preventive measures and seeking prompt treatment when necessary, pet owners can play a pivotal role in safeguarding their dogs' dental health. Proactive dental care not only enhances the quality of life for canine companions but also minimizes the potential impact of dental disease on their overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, dental disease in dogs is a prevalent yet often overlooked health concern that can significantly impact the well-being of our canine companions. From common conditions such as periodontal disease and tooth decay to the potential complications associated with untreated oral health issues, the importance of proactive dental care for dogs cannot be overstated. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the causes, signs, and preventive measures related to dental disease, pet owners can take proactive steps to ensure their furry friends enjoy optimal oral health and a higher quality of life.
Recognizing the underlying causes of dental disease, including poor dental hygiene, diet and nutrition, genetic predispositions, and environmental factors, empowers pet owners to address risk factors and implement preventive strategies. Establishing a consistent dental care routine, providing a balanced diet, and seeking regular veterinary dental evaluations are essential components of proactive dental care for dogs. Additionally, the early recognition of signs and symptoms, such as bad breath, changes in eating habits, and visible tartar, enables pet owners to promptly seek veterinary care and implement appropriate interventions to alleviate their canine companions' oral discomfort.
Preventing dental disease in dogs involves a multi-faceted approach, encompassing regular dental care, balanced nutrition, professional cleanings, and the provision of chew toys and dental treats. These preventive measures, coupled with ongoing monitoring and follow-up care, play a pivotal role in promoting long-term oral health for dogs. Furthermore, in cases where dental disease has progressed, timely treatment, including dental procedures, medication, and dietary modifications, is crucial in addressing underlying issues and restoring oral wellness.
By prioritizing preventive measures and seeking prompt treatment when necessary, pet owners can significantly mitigate the impact of dental disease on their dogs' overall health and quality of life. Proactive dental care not only enhances the well-being of our furry companions but also fosters a strong bond between pet owners and their beloved dogs. Through ongoing education, awareness, and advocacy for canine dental health, we can ensure that our dogs maintain healthy, happy smiles for years to come.