Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Do You Do If Your Diabetic Dog Does Not Want To Eat?


Common Health Issues
What Do You Do If Your Diabetic Dog Does Not Want To Eat?
Published: January 30, 2024
Learn how to address common health issues in diabetic dogs, including what to do if your pet refuses to eat. Expert advice for managing your diabetic dog's health.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When your beloved furry friend is diagnosed with diabetes, it can be a challenging and emotional experience. Along with managing their blood sugar levels and administering insulin, ensuring that they maintain a healthy and consistent appetite is crucial for their well-being. However, it's not uncommon for diabetic dogs to experience a loss of appetite, which can be concerning for pet owners. Understanding the reasons behind this loss of appetite and learning how to address it is essential for providing the best care for your diabetic dog.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the various factors that can contribute to a diabetic dog's decreased appetite and provide practical tips to encourage them to eat. Additionally, we will discuss the importance of seeking veterinary assistance when dealing with persistent or severe cases of appetite loss in diabetic dogs.
Caring for a diabetic dog requires patience, empathy, and a deep understanding of their unique needs. By delving into the intricacies of managing their appetite, you can empower yourself to support your furry companion on their journey to better health and well-being. Let's embark on this enlightening exploration together, as we unravel the complexities of addressing appetite loss in diabetic dogs.
Read more: What To Do If Your Dog Eats Eye Drops
Understanding the reasons behind loss of appetite in diabetic dogs
Loss of appetite in diabetic dogs can stem from various underlying factors, and understanding these reasons is crucial for devising effective strategies to address the issue. Here are some common reasons behind the decreased appetite in diabetic dogs:
-
Fluctuating Blood Sugar Levels: Unstable blood sugar levels can significantly impact a dog's appetite. When blood sugar levels are too high or too low, it can lead to feelings of lethargy, nausea, and disinterest in food. Diabetic dogs may experience these fluctuations, causing them to lose their appetite.
-
Gastrointestinal Upset: Diabetic dogs are prone to gastrointestinal issues, such as pancreatitis or gastritis, which can cause discomfort and lead to a reduced desire to eat. Additionally, the presence of ketones in the blood, a common occurrence in unregulated diabetes, can result in nausea and a subsequent loss of appetite.
-
Secondary Health Complications: Diabetes in dogs can pave the way for secondary health complications, including urinary tract infections and dental problems. These issues can cause discomfort and pain, making it difficult for diabetic dogs to eat normally.
-
Side Effects of Medication: Some diabetic dogs may be on medications that have side effects impacting their appetite. For instance, certain medications used to manage diabetes or its related conditions can lead to gastrointestinal disturbances, resulting in a decreased appetite.
-
Stress and Anxiety: Changes in routine, environmental stressors, or underlying anxiety can affect a diabetic dog's eating habits. Stress and anxiety can manifest in various ways, including a loss of appetite, and it's important to consider these emotional factors when addressing decreased food intake in diabetic dogs.
Understanding these reasons behind a diabetic dog's loss of appetite provides valuable insights into their unique challenges. By recognizing the multifaceted nature of this issue, pet owners can approach the situation with empathy and a holistic perspective, paving the way for effective solutions to encourage their diabetic dogs to eat.
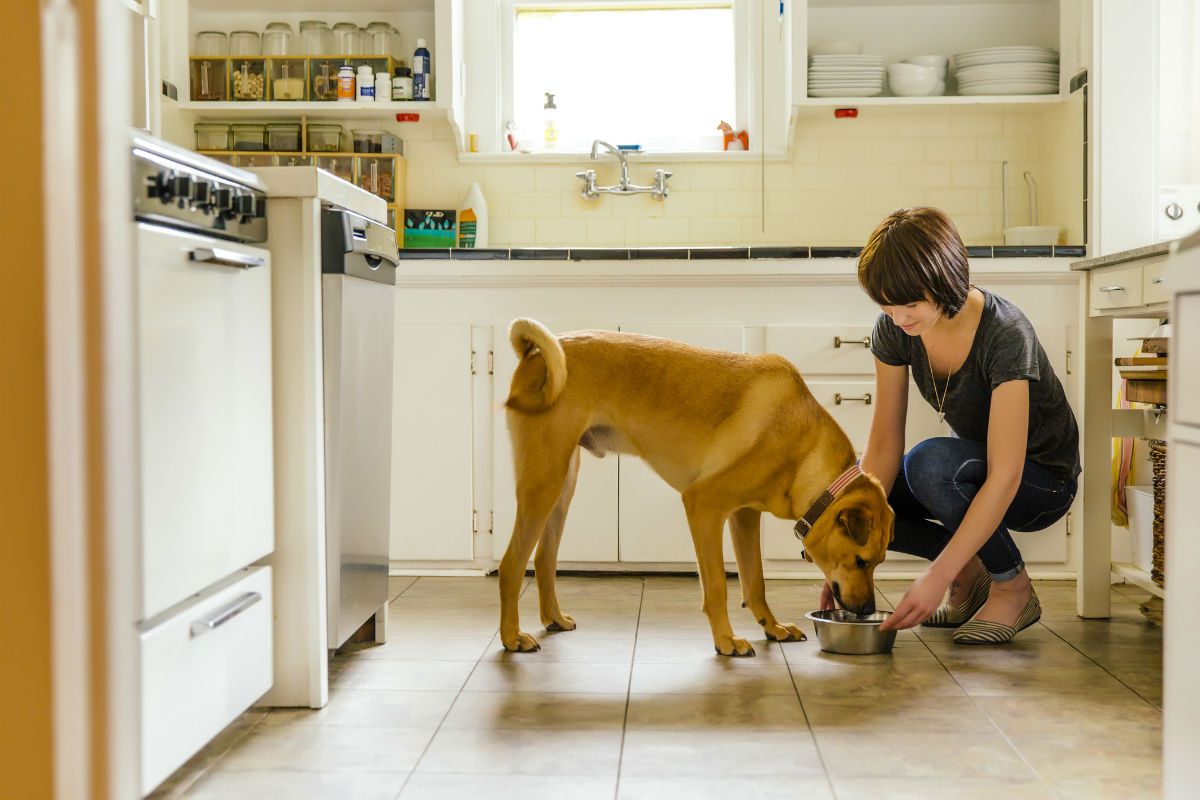
Tips for encouraging your diabetic dog to eat
Encouraging a diabetic dog to eat can be a delicate yet essential aspect of their care. Here are some practical tips to help stimulate your furry companion's appetite and ensure they receive the nourishment they need:
-
Consistent Feeding Schedule: Establish a regular feeding schedule for your diabetic dog. Consistency can help regulate their appetite and create a sense of routine, which is particularly beneficial for managing diabetes-related fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
-
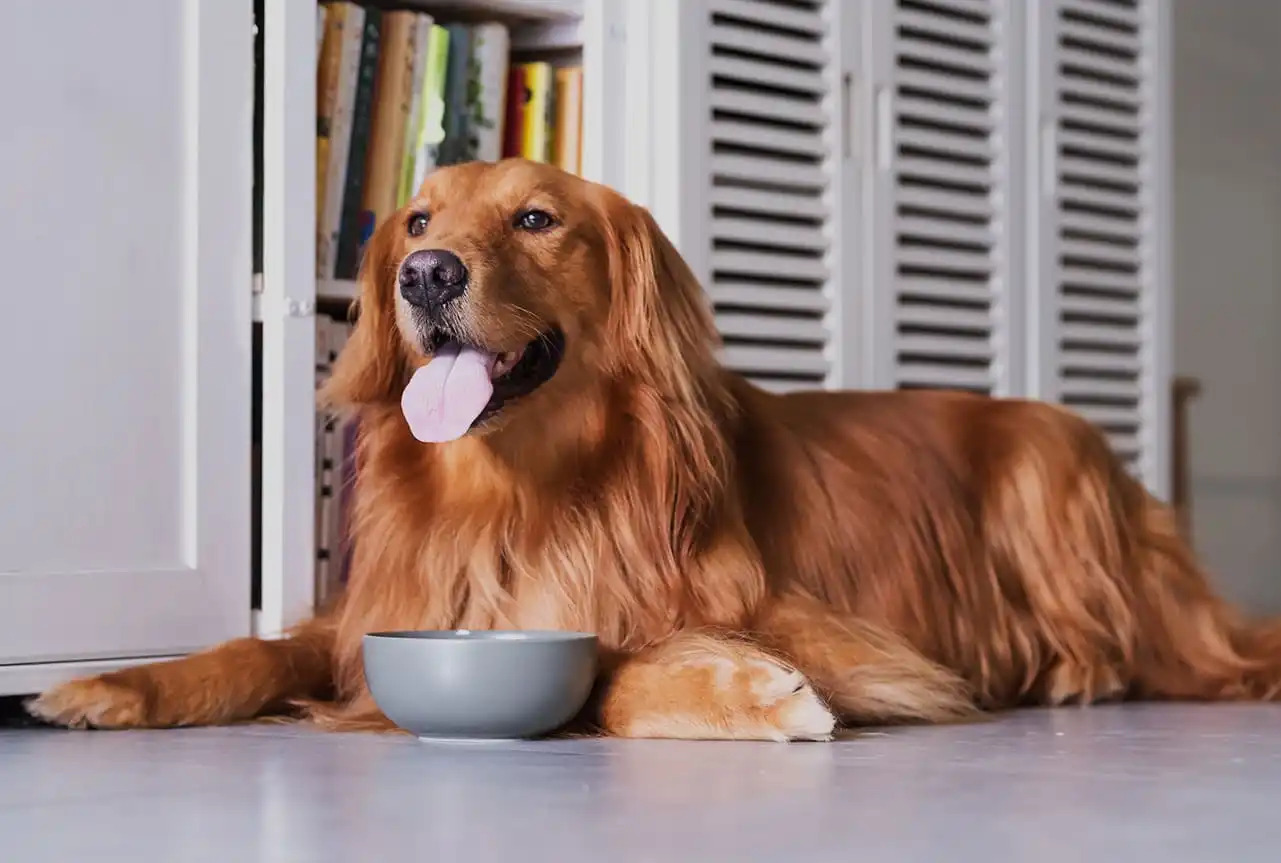
High-Quality, Palatable Food: Opt for high-quality, palatable dog food that appeals to your pet's taste buds. Diabetic dogs may be more inclined to eat when presented with flavorful and enticing meals. Additionally, consider warming the food slightly to enhance its aroma and make it more appealing.
-
Small, Frequent Meals: Instead of large meals, consider offering your diabetic dog smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day. This approach can prevent their blood sugar levels from spiking or dropping drastically, while also making it easier for them to consume their food.
-
Regular Exercise: Engage your diabetic dog in regular, moderate exercise to stimulate their appetite. Physical activity can boost their metabolism and promote a healthy appetite, contributing to their overall well-being.
-
Environmental Comfort: Create a calm and comfortable eating environment for your diabetic dog. Minimize stressors and distractions during meal times, providing them with a peaceful space to enjoy their food without anxiety or disruptions.
-
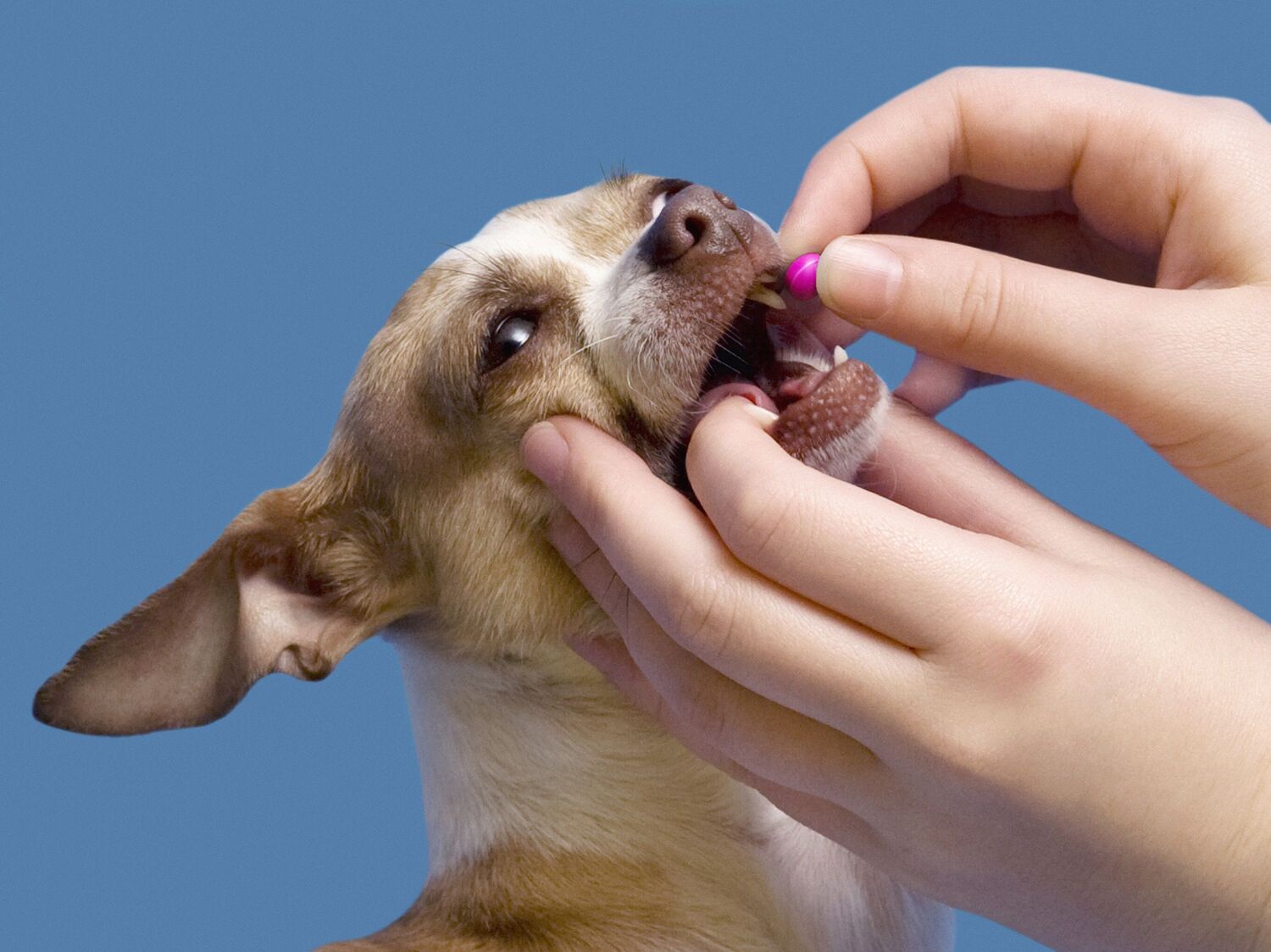
Supplemental Support: Consult with your veterinarian about incorporating appetite-stimulating supplements or prescribed medications, if necessary. These supplements can aid in enhancing your diabetic dog's appetite and ensuring they receive adequate nutrition.
-
Interactive Feeding: Consider interactive feeding methods, such as food puzzles or slow-feed bowls, to make meal times more engaging for your diabetic dog. These activities can pique their interest in food and encourage them to eat more enthusiastically.
-
Regular Veterinary Check-Ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your veterinarian to monitor your diabetic dog's overall health and address any underlying issues that may be impacting their appetite. A proactive approach to their well-being is essential for managing their diabetes and associated challenges.
By implementing these tips and tailoring them to your diabetic dog's individual preferences and needs, you can support them in maintaining a healthy appetite and thriving despite the complexities of diabetes.
Remember, patience and understanding are key when navigating your diabetic dog's eating habits. With your unwavering support and the guidance of veterinary professionals, you can help your furry companion enjoy their meals and lead a fulfilling life, brimming with vitality and joy.
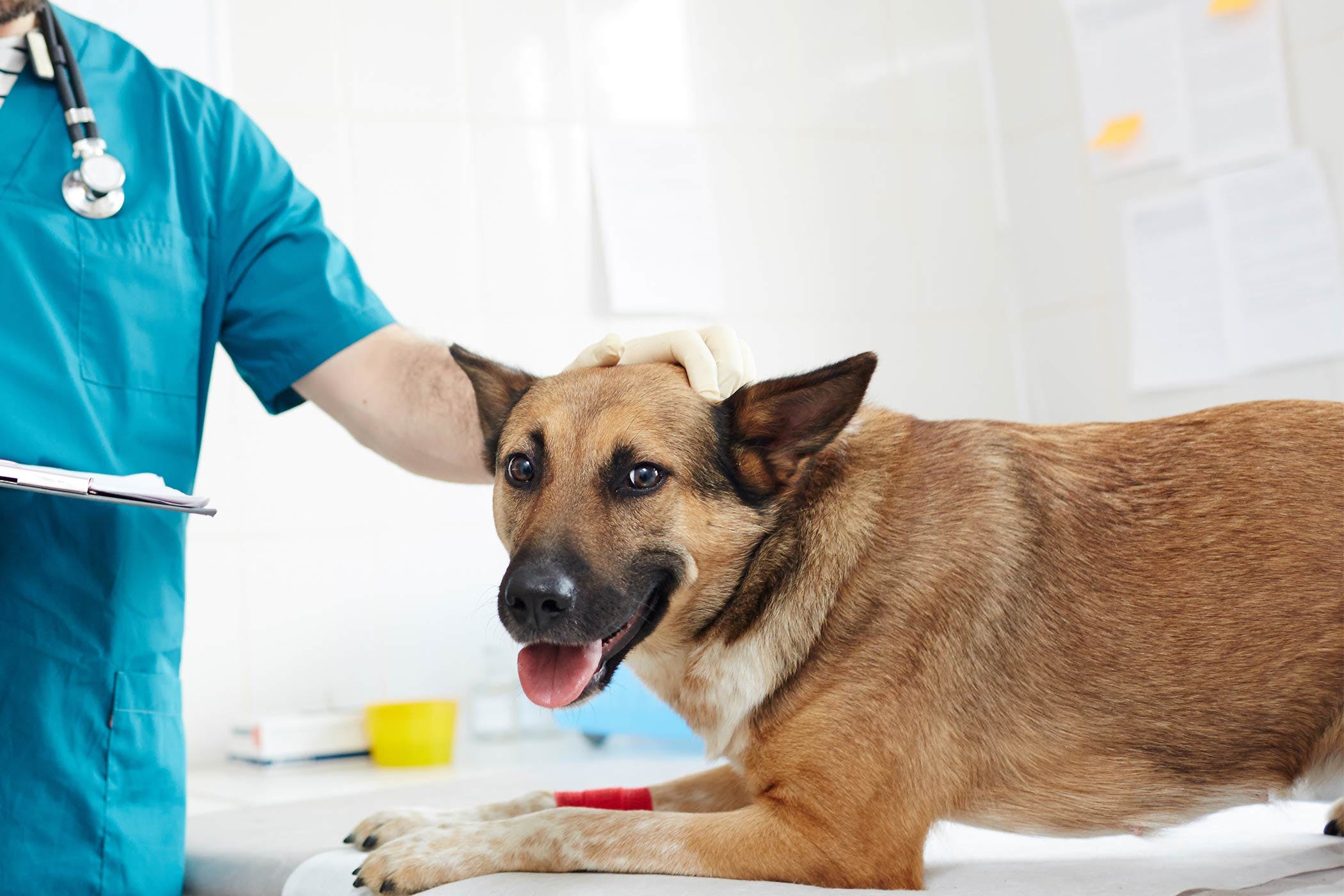
When to seek veterinary help for your diabetic dog's loss of appetite
While implementing strategies to encourage your diabetic dog to eat, it's essential to be vigilant for signs that may indicate the need for veterinary intervention. Loss of appetite in diabetic dogs can sometimes signal underlying health issues that require professional assessment and treatment. Here are the circumstances in which seeking veterinary help for your diabetic dog's loss of appetite is crucial:
-
Persistent Refusal to Eat: If your diabetic dog consistently refuses to eat or shows a significant decrease in food intake over an extended period, it's imperative to seek veterinary guidance. Prolonged loss of appetite can lead to nutritional deficiencies and exacerbate their diabetic condition, necessitating prompt evaluation by a veterinarian.
-
Unexplained Weight Loss: Noticeable weight loss in a diabetic dog, especially when accompanied by a diminished appetite, warrants veterinary attention. Unintentional weight loss can indicate an underlying health issue that requires thorough examination and diagnostic testing to identify and address the root cause.
-
Vomiting or Diarrhea: Persistent vomiting or diarrhea in diabetic dogs can contribute to a loss of appetite and may signify gastrointestinal distress or other health concerns. These symptoms can lead to dehydration and nutritional imbalances, necessitating veterinary assessment to prevent further complications.
-
Lethargy and Weakness: If your diabetic dog displays signs of lethargy, weakness, or a lack of energy in conjunction with a reduced appetite, it could indicate an underlying health issue that requires professional evaluation. These symptoms may be indicative of systemic health challenges that need to be addressed promptly.
-
Changes in Behavior or Activity: Any notable changes in your diabetic dog's behavior, activity level, or overall demeanor alongside a decreased appetite should prompt a visit to the veterinarian. Behavioral changes can be indicative of pain, discomfort, or underlying health issues that require expert assessment and management.
-
Persistent Bad Breath or Oral Health Issues: Diabetic dogs are susceptible to oral health problems, and persistent bad breath or signs of dental discomfort can contribute to a loss of appetite. Seeking veterinary assistance for comprehensive oral health evaluation and potential treatment is essential for maintaining your dog's overall well-being.
-
Uncontrolled Blood Sugar Levels: If your diabetic dog's blood sugar levels remain unregulated despite adherence to prescribed management strategies and dietary adjustments, it's crucial to consult with your veterinarian. Uncontrolled diabetes can impact appetite and overall health, necessitating professional guidance to achieve optimal blood sugar control.
When observing any of these concerning signs or experiencing uncertainty about your diabetic dog's well-being, reaching out to your veterinarian is paramount. Timely veterinary intervention can help identify and address underlying health issues, optimize your dog's diabetes management, and ensure their overall health and vitality.
By remaining attentive to your diabetic dog's well-being and seeking veterinary support when necessary, you can navigate the complexities of managing their loss of appetite with confidence and proactive care. Your commitment to their health and happiness is invaluable, and by working in tandem with veterinary professionals, you can provide your diabetic dog with the best possible support and guidance on their journey to well-being.
Conclusion
Caring for a diabetic dog encompasses a myriad of responsibilities, from monitoring their blood sugar levels to ensuring they maintain a healthy and consistent appetite. In the journey of addressing a diabetic dog's loss of appetite, understanding the multifaceted nature of this issue is paramount. By delving into the underlying reasons behind appetite loss, pet owners can gain valuable insights into their diabetic dog's unique challenges and tailor their care strategies accordingly.
The tips provided for encouraging a diabetic dog to eat serve as a compass for pet owners, guiding them toward practical and empathetic approaches to stimulate their furry companion's appetite. From establishing a consistent feeding schedule to creating a comfortable eating environment, each strategy is designed to support diabetic dogs in maintaining a healthy relationship with food. By implementing these tips with patience and attentiveness, pet owners can play a pivotal role in nurturing their diabetic dog's well-being.
Recognizing the pivotal role of veterinary intervention in cases of persistent or severe appetite loss is essential. Knowing when to seek professional help for a diabetic dog's diminished appetite empowers pet owners to prioritize their furry companion's health and address potential underlying health issues promptly. By remaining vigilant for concerning signs and proactively engaging with veterinary professionals, pet owners can navigate the complexities of managing their diabetic dog's appetite with confidence and diligence.
Ultimately, the journey of caring for a diabetic dog is a testament to the unwavering bond between pet and owner. Through empathy, understanding, and a commitment to proactive care, pet owners can provide their diabetic dogs with the support and guidance they need to thrive despite the challenges they may face. By embracing the complexities of managing a diabetic dog's appetite with resilience and compassion, pet owners can embark on a shared journey toward a fulfilling and vibrant life for their beloved furry companions.