Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Is Blood Parasite Test For Dogs

Common Health Issues
What Is Blood Parasite Test For Dogs
Modified: March 1, 2024
Learn about the importance of blood parasite testing for dogs and how it helps in detecting common health issues. Understand the significance of this test in maintaining your pet's well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Blood parasite infections are a significant concern for dogs, posing potential health risks and requiring timely detection and treatment. These infections are caused by various microorganisms that invade the bloodstream, leading to a range of symptoms and complications. Understanding the prevalence, symptoms, and testing methods for blood parasites in dogs is crucial for ensuring the well-being of our beloved canine companions.
Detecting blood parasites in dogs is a critical aspect of veterinary care, as it allows for early intervention and management of potential health issues. The blood parasite test serves as a vital tool for identifying the presence of these harmful organisms, enabling veterinarians to initiate appropriate treatment protocols and preventive measures.
By shedding light on the significance of blood parasite testing, dog owners can gain valuable insights into safeguarding their pets' health and well-being. This article aims to provide comprehensive information on blood parasite testing for dogs, including common parasites, symptoms of infection, testing procedures, treatment options, and preventive measures. Understanding these aspects can empower dog owners to take proactive steps in protecting their furry companions from the detrimental effects of blood parasite infections.
Understanding Blood Parasite Test
The blood parasite test for dogs is a diagnostic procedure designed to identify the presence of harmful microorganisms in the bloodstream. These parasites can include various organisms such as protozoa, bacteria, and microfilariae, which can lead to a range of health issues if left undetected and untreated. The test plays a crucial role in assessing the overall health of dogs and is particularly important for those showing symptoms of potential infection.
The blood parasite test typically involves the examination of a blood sample obtained from the dog. This sample is carefully analyzed to identify the presence of any abnormal cells, microorganisms, or other indicators of parasitic infection. The test helps veterinarians determine the specific type of blood parasite affecting the dog, allowing for targeted treatment and management strategies.
One of the key aspects of understanding the blood parasite test is recognizing the diverse range of parasites that can affect dogs. These parasites can vary in their characteristics, including size, shape, and mode of transmission. For example, certain blood parasites may be transmitted through the bites of infected insects, while others can be acquired through contaminated water sources or exposure to infected animals.
Furthermore, understanding the lifecycle of different blood parasites is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. Some parasites may undergo complex developmental stages within the dog's body, making it crucial to identify the specific life cycle characteristics during the testing process. This knowledge enables veterinarians to devise tailored treatment plans that target the parasites at various stages of their development.
Additionally, the blood parasite test serves as a proactive measure for assessing the risk of potential transmission to other animals or humans. By promptly identifying and addressing blood parasite infections in dogs, the likelihood of transmission to other pets or individuals can be significantly reduced, thereby contributing to public health and safety.
Overall, understanding the blood parasite test is essential for dog owners and veterinarians alike. By recognizing the significance of this diagnostic procedure and its role in safeguarding canine health, individuals can take proactive steps to ensure the well-being of their furry companions. Through regular testing and vigilant monitoring, potential blood parasite infections can be promptly identified and effectively managed, ultimately contributing to the overall health and happiness of dogs everywhere.
Common Blood Parasites in Dogs
Blood parasites in dogs encompass a diverse array of microorganisms that can have detrimental effects on canine health. Understanding the common blood parasites that can affect dogs is crucial for recognizing potential symptoms and seeking appropriate veterinary care. Here are some prevalent blood parasites found in dogs:
1. Babesia
Babesia is a protozoan parasite transmitted through the bites of infected ticks. This parasite invades the red blood cells of dogs, leading to symptoms such as fever, weakness, pale gums, and jaundice. Babesiosis, the disease caused by Babesia infection, can pose serious health risks if left untreated.
2. Ehrlichia
Ehrlichia is a type of bacteria transmitted by ticks, primarily the brown dog tick. This blood parasite infects white blood cells and platelets, causing symptoms such as fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, and bleeding disorders. Ehrlichiosis can manifest in acute or chronic forms, impacting various organ systems in affected dogs.
3. Dirofilaria immitis (Heartworm)
Heartworm is a well-known blood parasite transmitted through the bites of infected mosquitoes. The larvae of Dirofilaria immitis migrate through the bloodstream and eventually settle in the heart and pulmonary arteries, leading to severe cardiovascular complications. Symptoms of heartworm infection include coughing, exercise intolerance, and respiratory distress.
4. Leishmania
Leishmania is a protozoan parasite transmitted through the bites of infected sandflies. This blood parasite can cause visceral or cutaneous leishmaniasis in dogs, leading to symptoms such as weight loss, skin lesions, swollen lymph nodes, and lameness. Visceral leishmaniasis, in particular, can result in severe systemic illness if not promptly addressed.
5. Anaplasma
Anaplasma is a bacterial blood parasite transmitted by ticks, affecting white blood cells and causing symptoms such as fever, joint pain, lethargy, and decreased appetite. Anaplasmosis can manifest in acute or chronic forms, impacting the overall health and well-being of infected dogs.
6. Hepatozoon
Hepatozoon is a blood parasite transmitted through the ingestion of infected ticks or through the bites of infected dogs. This parasite can cause symptoms such as muscle pain, fever, and lethargy. Hepatozoonosis can lead to significant discomfort and health complications in affected dogs.
Recognizing the prevalence of these common blood parasites in dogs is essential for proactive prevention and timely intervention. By staying informed about the potential risks and symptoms associated with these parasites, dog owners can work closely with veterinarians to implement preventive measures and ensure the overall health and well-being of their canine companions.
Symptoms of Blood Parasite Infection
Blood parasite infections in dogs can manifest through a range of symptoms, indicating potential health complications resulting from the presence of harmful microorganisms in the bloodstream. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for prompt veterinary intervention and effective management of blood parasite infections. Here are the common symptoms associated with blood parasite infection in dogs:
-
Fever: Dogs infected with blood parasites may exhibit persistent or intermittent fever, often accompanied by other systemic signs of illness. Elevated body temperature is a common indicator of the body's immune response to parasitic invasion.
-
Weakness and Lethargy: Infected dogs may display increased lethargy, reluctance to engage in physical activities, and overall weakness. This can be attributed to the impact of blood parasites on the dog's energy levels and overall well-being.
-
Pale Gums and Mucous Membranes: Anemia resulting from blood parasite infections can lead to pale gums and mucous membranes in affected dogs. The reduction in red blood cell count can cause visible changes in the dog's oral and mucosal tissues.
-
Loss of Appetite: Dogs suffering from blood parasite infections may experience a decreased appetite, leading to reduced food intake and potential weight loss. Changes in eating habits can be indicative of underlying health issues.
-
Jaundice: Some blood parasite infections, such as Babesiosis, can lead to jaundice in dogs, characterized by yellowing of the skin, whites of the eyes, and mucous membranes. Jaundice is a result of the breakdown of red blood cells and the release of bilirubin into the bloodstream.
-
Respiratory Distress: In the case of heartworm infection, dogs may exhibit symptoms of respiratory distress, including coughing, wheezing, and difficulty breathing. This is attributed to the presence of heartworms in the pulmonary arteries and associated lung inflammation.
-
Skin Lesions and Abnormalities: Certain blood parasite infections, such as Leishmaniasis, can lead to skin lesions, hair loss, and other dermatological abnormalities. These visible changes in the skin and coat can be indicative of underlying parasitic infections.
-
Joint Pain and Lameness: Dogs infected with certain blood parasites may experience joint pain, stiffness, and lameness, impacting their mobility and overall comfort. These symptoms can significantly affect the dog's quality of life.
-
Bleeding Disorders: Some blood parasite infections, such as Ehrlichiosis, can lead to bleeding disorders, including nosebleeds, bruising, and abnormal bleeding from the gums. These manifestations are indicative of the impact of parasites on the dog's blood clotting mechanisms.
-
Neurological Symptoms: In severe cases, blood parasite infections can lead to neurological symptoms, including seizures, disorientation, and abnormal behavior. These manifestations indicate potential complications resulting from parasitic invasion of the central nervous system.
Recognizing these symptoms and seeking prompt veterinary care is essential for diagnosing and addressing blood parasite infections in dogs. By remaining vigilant and attentive to any signs of illness or discomfort in their canine companions, dog owners can play a proactive role in safeguarding their pets' health and well-being. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve the prognosis and outcomes for dogs affected by blood parasite infections.
Importance of Blood Parasite Test for Dogs
The blood parasite test holds immense significance in the realm of canine healthcare, serving as a pivotal tool for early detection, diagnosis, and management of potential health risks associated with parasitic infections. This diagnostic procedure plays a crucial role in safeguarding the well-being of dogs and holds several key implications for both veterinary professionals and dog owners.
First and foremost, the importance of the blood parasite test lies in its ability to identify the presence of harmful microorganisms in the bloodstream of dogs. By detecting parasites such as Babesia, Ehrlichia, Dirofilaria immitis (heartworm), Leishmania, Anaplasma, and Hepatozoon, the test enables veterinarians to initiate targeted treatment protocols, thereby preventing the progression of parasitic infections and mitigating associated health complications. Early detection through the blood parasite test is instrumental in preventing the advancement of these infections, which can have severe and potentially life-threatening consequences if left untreated.
Furthermore, the blood parasite test serves as a proactive measure for assessing the risk of potential transmission of parasites to other animals or humans. By promptly identifying and addressing blood parasite infections in dogs, the likelihood of transmission to other pets or individuals can be significantly reduced, thereby contributing to public health and safety. This aspect underscores the broader implications of the blood parasite test in mitigating zoonotic risks and preventing the spread of parasitic infections beyond the canine population.
Additionally, the test holds importance in the context of preventive healthcare for dogs. Regular screening through the blood parasite test allows for the early identification of asymptomatic infections, enabling veterinarians to implement preventive measures and tailored treatment plans. This proactive approach not only safeguards the health of individual dogs but also contributes to the broader goal of preventing the spread of blood parasites within canine communities.
Moreover, the blood parasite test plays a crucial role in guiding the implementation of preventive measures, such as parasite control and vector management strategies. By identifying the specific types of blood parasites affecting dogs in a given geographic region, veterinarians and public health authorities can develop targeted interventions to minimize the risk of parasitic infections, thereby promoting the overall health and well-being of canine populations.
In essence, the blood parasite test for dogs is of paramount importance in the realm of veterinary medicine and public health. Its role in early detection, preventive healthcare, and mitigating zoonotic risks underscores its significance in safeguarding the health and well-being of dogs, while also contributing to broader efforts aimed at preventing the spread of blood parasites within the animal kingdom. By recognizing the importance of this diagnostic procedure, dog owners and veterinary professionals can work collaboratively to ensure the proactive management and prevention of blood parasite infections in dogs.
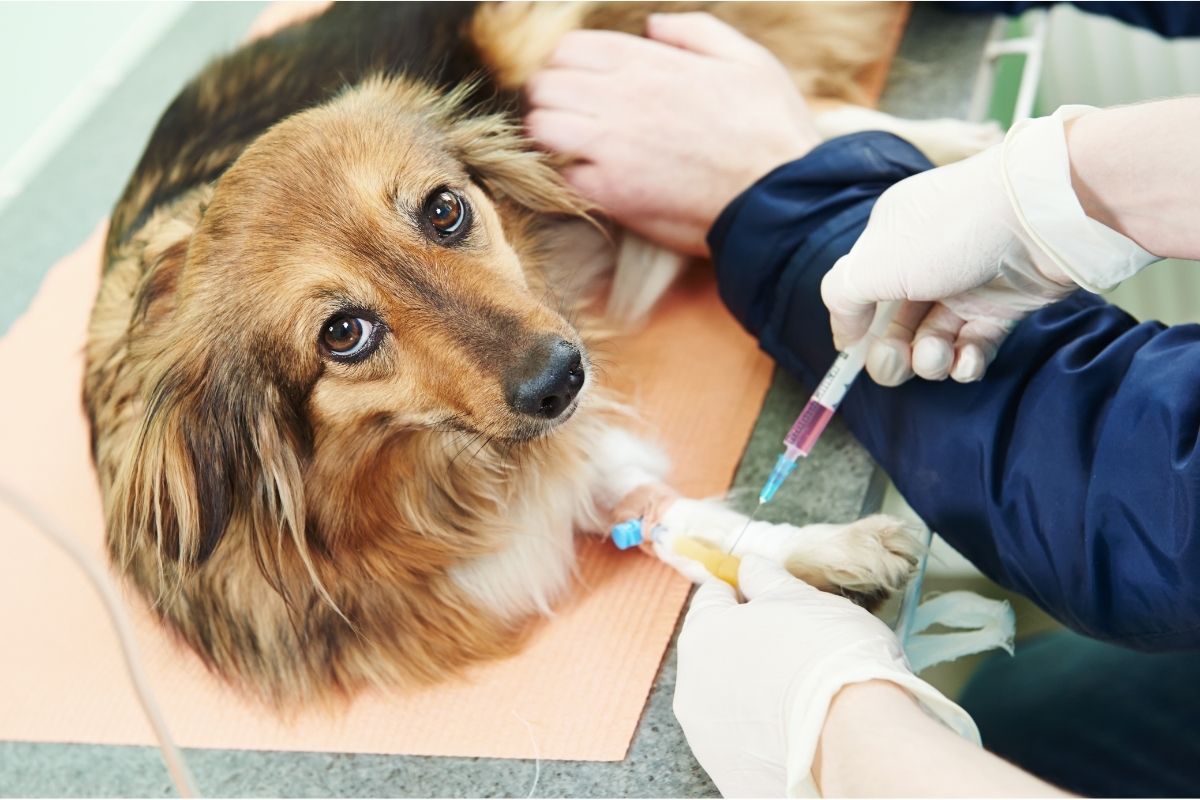
How Blood Parasite Test is Conducted
The blood parasite test for dogs involves a meticulous and comprehensive process aimed at identifying the presence of harmful microorganisms in the bloodstream. This diagnostic procedure is crucial for assessing the overall health of dogs and plays a pivotal role in early detection and management of potential parasitic infections.
The first step in conducting the blood parasite test is obtaining a blood sample from the dog. This is typically done through venipuncture, where a small amount of blood is drawn from a vein, often in the dog's leg or neck area. The blood sample is then carefully collected and handled to ensure its integrity for subsequent analysis.
Once the blood sample is obtained, it undergoes a series of laboratory analyses to identify the presence of blood parasites. One of the primary methods used is microscopic examination, where the blood sample is carefully observed under a microscope to detect the presence of abnormal cells, microorganisms, or other indicators of parasitic infection. This meticulous examination allows for the identification of specific blood parasites and their characteristic features, aiding in accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment.
In addition to microscopic examination, specialized diagnostic tests may be employed to detect specific blood parasites. For example, tests such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assays can be utilized to amplify and detect the genetic material of parasites, providing highly sensitive and specific results. These advanced diagnostic techniques enhance the accuracy and reliability of blood parasite testing, enabling veterinarians to precisely identify the types of parasites affecting the dog.
Furthermore, the blood parasite test may include serological assays, which detect the presence of antibodies produced by the dog's immune system in response to parasitic infections. These serological tests provide valuable insights into the dog's immune response and can aid in confirming the presence of specific blood parasites.
Overall, the blood parasite test for dogs involves a multidimensional approach, encompassing meticulous blood sample collection, microscopic examination, and advanced diagnostic techniques. By leveraging these comprehensive methods, veterinarians can accurately identify the presence of blood parasites, determine the specific types of parasites affecting the dog, and initiate targeted treatment and management strategies.
Through the diligent and precise execution of the blood parasite test, veterinarians can provide invaluable insights into the health status of dogs, enabling timely intervention and proactive measures to safeguard canine well-being. This diagnostic procedure serves as a cornerstone of veterinary care, empowering dog owners and veterinary professionals to take proactive steps in managing and preventing blood parasite infections in dogs.
Treatment for Blood Parasite Infection in Dogs
The treatment for blood parasite infection in dogs is a multifaceted approach aimed at addressing the specific type of parasite affecting the dog and mitigating associated health complications. Upon the confirmation of blood parasite infection through diagnostic testing, veterinarians devise tailored treatment protocols to effectively manage the presence of harmful microorganisms in the dog's bloodstream.
-
Antiparasitic Medications: Depending on the type of blood parasite identified, veterinarians may prescribe antiparasitic medications to target and eliminate the parasites from the dog's system. These medications may include specific anti-protozoal drugs, antibiotics, or anthelmintics, tailored to combat the particular blood parasite responsible for the infection.
-
Supportive Care: In cases where blood parasite infections have led to anemia, organ dysfunction, or other systemic complications, supportive care measures may be implemented. This can include blood transfusions to address anemia, intravenous fluids to maintain hydration, and supportive therapies to alleviate symptoms and promote recovery.
-
Vector Control: For certain blood parasites such as heartworm, concurrent measures to control the vectors responsible for transmission, such as mosquitoes, may be recommended. Preventive medications to protect against future infections and environmental management strategies to minimize exposure to vectors may be part of the comprehensive treatment plan.
-
Monitoring and Follow-Up: Following the initiation of treatment, close monitoring of the dog's response to therapy is essential. This may involve regular blood tests to assess the reduction of parasite levels, as well as ongoing veterinary examinations to evaluate the dog's overall health and well-being. Adjustments to the treatment plan may be made based on the dog's progress and response to therapy.
-
Preventive Measures: In addition to targeted treatment, veterinarians emphasize the importance of preventive measures to safeguard dogs from future blood parasite infections. This can include the administration of preventive medications, such as heartworm preventives, and adherence to parasite control protocols to minimize the risk of re-infection.
-
Environmental Management: Implementing environmental management practices, such as reducing exposure to ticks, mosquitoes, and other potential vectors, is integral to preventing recurrent blood parasite infections. This may involve measures such as regular tick checks, environmental treatments to control vectors, and minimizing outdoor exposure during peak parasite activity periods.
Overall, the treatment for blood parasite infection in dogs encompasses a comprehensive approach that addresses the specific parasite type, mitigates associated health complications, and focuses on preventive measures to safeguard canine well-being. By tailoring treatment plans to the individual needs of affected dogs and emphasizing preventive strategies, veterinarians play a pivotal role in managing blood parasite infections and promoting the overall health and longevity of canine companions.
Prevention of Blood Parasite Infection in Dogs
Preventing blood parasite infections in dogs is a fundamental aspect of responsible pet ownership and proactive veterinary care. By implementing preventive measures and adhering to targeted strategies, dog owners can significantly reduce the risk of their canine companions contracting harmful blood parasites. Here are key approaches to preventing blood parasite infections in dogs:
-
Parasite Control Products: Utilizing veterinarian-recommended parasite control products is essential for preventing blood parasite infections. This includes regular administration of flea and tick preventives to protect dogs from common vectors that transmit blood parasites. Additionally, heartworm preventives are crucial for safeguarding dogs from the potentially devastating effects of heartworm disease.
-
Regular Veterinary Examinations: Scheduling routine veterinary examinations allows for proactive monitoring of a dog's health and well-being. Veterinarians can assess the risk of blood parasite infections based on geographic location, environmental factors, and lifestyle, and recommend preventive measures tailored to the specific needs of the dog.
-
Environmental Management: Implementing environmental management practices plays a pivotal role in preventing blood parasite infections. This involves minimizing exposure to potential vectors, such as ticks and mosquitoes, by maintaining clean living spaces, utilizing insect repellents, and employing environmental treatments to control parasites in outdoor areas.
-
Vector Avoidance: Dog owners can minimize the risk of blood parasite infections by avoiding areas known to harbor parasites and their vectors. This includes steering clear of heavily wooded or grassy areas where ticks are prevalent, especially during peak activity periods. Additionally, reducing exposure to standing water sources can help mitigate the risk of mosquito-borne infections.
-
Education and Awareness: Educating dog owners about the risks of blood parasite infections and the importance of preventive measures is crucial. This includes raising awareness about the prevalence of specific parasites in different regions, emphasizing the significance of regular parasite control, and providing guidance on environmental management practices to minimize exposure to vectors.
-
Compliance with Preventive Protocols: Adhering to recommended preventive protocols, such as regular administration of parasite control products and scheduled veterinary check-ups, is essential for comprehensive prevention of blood parasite infections. Consistent compliance with preventive measures significantly reduces the likelihood of dogs contracting these harmful parasites.
By integrating these preventive measures into their canine care routines, dog owners can effectively mitigate the risk of blood parasite infections and contribute to the overall health and well-being of their beloved pets. Proactive prevention not only safeguards individual dogs but also plays a crucial role in minimizing the prevalence of blood parasites within canine communities, ultimately fostering a healthier and happier canine population.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the significance of blood parasite testing for dogs cannot be overstated. This diagnostic procedure serves as a cornerstone of proactive veterinary care, enabling early detection, targeted treatment, and preventive measures to safeguard the health and well-being of canine companions. By understanding the common blood parasites that can affect dogs, recognizing the symptoms of blood parasite infection, and embracing preventive strategies, dog owners and veterinary professionals can work collaboratively to mitigate the risks associated with these harmful microorganisms.
The comprehensive nature of the blood parasite test, encompassing meticulous blood sample collection, microscopic examination, and advanced diagnostic techniques, underscores its pivotal role in identifying specific blood parasites and guiding tailored treatment protocols. Through the diligent execution of this diagnostic procedure, veterinarians can provide invaluable insights into the health status of dogs, empowering timely intervention and proactive measures to manage and prevent blood parasite infections.
Furthermore, the treatment and prevention of blood parasite infections in dogs emphasize the multifaceted approach required to address the specific parasite type, mitigate associated health complications, and focus on preventive strategies. By tailoring treatment plans to the individual needs of affected dogs and emphasizing preventive measures, veterinarians play a pivotal role in managing blood parasite infections and promoting the overall health and longevity of canine companions.
Ultimately, the proactive management and prevention of blood parasite infections in dogs contribute to the broader goal of fostering a healthier and happier canine population. By prioritizing preventive measures, adhering to recommended parasite control protocols, and staying informed about the risks associated with blood parasites, dog owners can significantly reduce the likelihood of their pets contracting these harmful microorganisms. This proactive approach not only safeguards individual dogs but also contributes to the broader efforts aimed at preventing the spread of blood parasites within the animal kingdom.
In essence, the comprehensive understanding of blood parasite testing, treatment, and prevention is essential for ensuring the well-being of dogs and promoting responsible pet ownership. By recognizing the importance of these aspects and embracing proactive measures, dog owners and veterinary professionals can collectively contribute to a safer and healthier environment for canine companions, free from the detrimental effects of blood parasite infections.
