Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Long For Dog Anti Parasite Medicine To Work


Common Health Issues
How Long For Dog Anti Parasite Medicine To Work
Published: February 8, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs and how long it takes for anti-parasite medicine to work. Understand the timeline for treating your dog's health concerns.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
When it comes to the well-being of our furry companions, protecting them from parasites is a top priority for responsible pet owners. Parasites such as fleas, ticks, and worms can pose serious health risks to dogs, causing discomfort, illness, and in severe cases, even fatalities. To combat these potential threats, veterinarians often prescribe anti-parasite medications tailored to address specific infestations. Understanding the effectiveness and timeframe of these medications is crucial for ensuring the health and happiness of our canine friends.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of dog anti-parasite medicine, shedding light on the factors influencing its effectiveness and the typical timeframe for it to take effect. By gaining insights into these aspects, pet owners can make informed decisions and provide the best care for their beloved dogs. So, let's embark on this enlightening journey to unravel the mysteries of dog anti-parasite medicine and empower ourselves to safeguard our furry companions against these pesky invaders.
Understanding Dog Anti Parasite Medicine
Dog anti-parasite medicine encompasses a wide range of treatments designed to combat various types of parasites that can afflict our canine companions. These parasites include fleas, ticks, heartworms, roundworms, hookworms, and tapeworms, among others. Each type of parasite requires a specific approach for effective treatment, and anti-parasite medications are formulated to target these parasites while minimizing potential side effects on the dog.
Types of Dog Anti-Parasite Medicine
-
Topical Treatments: These are applied directly to the dog's skin and are effective against fleas and ticks. They often come in the form of spot-on treatments or medicated shampoos.
-
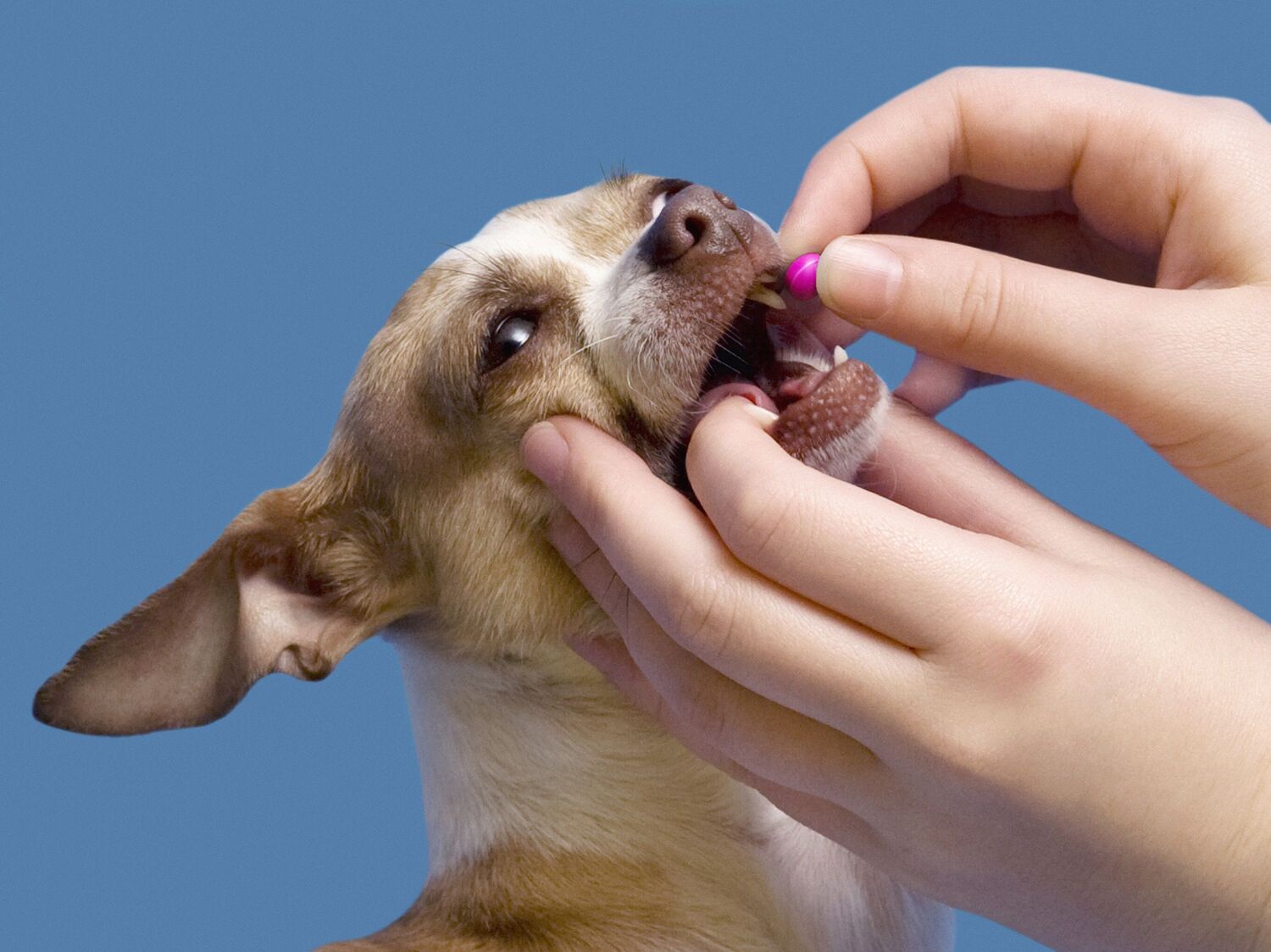
Oral Medications: These are administered by mouth and are effective against internal parasites such as heartworms, roundworms, hookworms, and tapeworms. They are available in various forms, including chewable tablets and flavored liquids.
-
Injectable Treatments: These are administered by a veterinarian and provide long-lasting protection against certain parasites, such as heartworms.
Mechanism of Action
Dog anti-parasite medications work through different mechanisms depending on the type of parasite they target. For instance, flea and tick treatments often contain insecticides that kill adult parasites on contact and disrupt the life cycle of the parasites to prevent reinfestation. Oral medications for internal parasites may contain anthelmintic drugs that paralyze or kill the parasites, allowing them to be expelled from the dog's body.
Importance of Proper Diagnosis
Before administering any anti-parasite medication, it is crucial for veterinarians to accurately diagnose the type of parasite infestation affecting the dog. This may involve conducting fecal tests, blood tests, skin scrapings, or other diagnostic procedures to identify the specific parasites present. Proper diagnosis ensures that the most appropriate and effective medication is prescribed for the dog's condition.
Safety Considerations
While anti-parasite medications are designed to target parasites, it is important to use them with caution and under the guidance of a veterinarian. Some medications may have potential side effects or interactions with other medications, and their safety can vary based on factors such as the dog's age, weight, and overall health. Therefore, it is essential to follow the prescribed dosage and administration instructions to ensure the safety and well-being of the dog.
By understanding the types of dog anti-parasite medicine, their mechanisms of action, the importance of proper diagnosis, and safety considerations, pet owners can gain valuable insights into the complexities of these medications. This knowledge empowers them to work closely with veterinarians to choose the most suitable anti-parasite treatments for their dogs, ultimately contributing to the overall health and happiness of their beloved pets.
Factors Affecting the Effectiveness of Dog Anti Parasite Medicine
The effectiveness of dog anti-parasite medicine can be influenced by various factors, each playing a crucial role in determining the outcome of the treatment. Understanding these factors is essential for pet owners and veterinarians to optimize the efficacy of anti-parasite medications and ensure the well-being of dogs.
1. Parasite Species and Life Cycle
Different parasites have unique life cycles and vulnerabilities, which can impact the effectiveness of anti-parasite medicine. For example, some medications may target specific stages of a parasite's life cycle, such as eggs, larvae, or adult parasites. Understanding the life cycle of the targeted parasites is essential for selecting the most appropriate medication to disrupt their development and eliminate infestations.
2. Resistance and Sensitivity
Parasites can develop resistance to certain medications over time, rendering them less effective. This phenomenon is particularly relevant in the case of flea and tick treatments, where repeated use of the same class of medications can lead to resistance in parasite populations. Conversely, some parasites may exhibit varying degrees of sensitivity to different medications, highlighting the importance of choosing treatments based on the specific parasites affecting the dog.
3. Dog's Health and Immune System
The overall health and immune response of the dog can significantly influence the effectiveness of anti-parasite medicine. A strong immune system can aid in combating parasite infestations, while underlying health conditions or compromised immunity may impact the dog's ability to respond to treatment. Additionally, certain medications may have different effects on dogs with pre-existing health issues, necessitating careful consideration of the dog's health status when selecting anti-parasite treatments.
4. Environmental Factors
Environmental conditions, such as climate and geographical location, can impact the prevalence of parasites and the effectiveness of anti-parasite medicine. For instance, dogs in warmer regions may be more susceptible to flea and tick infestations, requiring tailored preventive measures and treatments. Understanding the environmental factors influencing parasite exposure is crucial for implementing comprehensive parasite control strategies.
5. Compliance with Treatment Regimens
The consistent and proper administration of anti-parasite medications is essential for their effectiveness. Compliance with treatment regimens, including dosage, frequency, and duration of medication, plays a pivotal role in achieving successful outcomes. Pet owners must adhere to veterinary recommendations and guidelines to maximize the efficacy of anti-parasite treatments and prevent reinfestations.
By considering these factors, pet owners and veterinarians can make informed decisions regarding the selection and administration of dog anti-parasite medicine, ultimately contributing to the successful management of parasite infestations and the overall well-being of dogs.
Typical Timeframe for Dog Anti Parasite Medicine to Work
The timeframe for dog anti-parasite medicine to take effect can vary significantly based on the type of medication, the targeted parasites, and individual factors related to the dog's health and environment. Understanding the typical timelines associated with different anti-parasite treatments is essential for managing expectations and monitoring the progress of the dog's response to the medication.
-
Topical Treatments:
- Topical anti-parasite treatments, such as spot-on solutions and medicated shampoos, often provide rapid relief by targeting adult fleas and ticks on the dog's coat. In many cases, these treatments can start killing parasites within a few hours of application. However, it's important to note that complete eradication of parasites may take several days, as the medication continues to work and disrupts the life cycle of the parasites.
-
Oral Medications:
- Oral anti-parasite medications, particularly those targeting internal parasites such as heartworms, roundworms, and tapeworms, typically require a longer timeframe to take full effect. For example, medications designed to eliminate intestinal worms may start working within hours to days, causing the parasites to be expelled from the dog's body. However, multiple doses administered over several weeks may be necessary to ensure the complete elimination of the parasites and prevent reinfestations.
-
Injectable Treatments:
- Injectable anti-parasite treatments, often administered by veterinarians, can provide extended protection against certain parasites. For instance, injectable heartworm preventives may offer coverage for several months, gradually eliminating existing heartworm larvae and preventing new infections. The timeframe for these treatments to work is characterized by a sustained release of medication, leading to a gradual reduction in parasite burdens over an extended period.
-
Environmental Considerations:
- It's important to recognize that the effectiveness of anti-parasite medicine is not solely determined by the medication itself. Environmental factors, such as the presence of parasite reservoirs in the dog's living environment, can influence the overall timeframe for the medication to work. For example, even after treating a dog with anti-flea medication, it may take time to eliminate fleas present in the surrounding environment, necessitating ongoing environmental management to prevent reinfestations.
-
Individual Variability:
- Dogs may exhibit individual variability in their response to anti-parasite medicine. Factors such as the dog's age, overall health, and immune function can impact the rate at which the medication takes effect. Additionally, the severity of the parasite infestation and the presence of concurrent health conditions may influence the timeframe for observable improvements in the dog's condition.
In summary, the typical timeframe for dog anti-parasite medicine to work spans from immediate effects in the case of topical treatments to a more gradual and sustained impact with oral and injectable medications. Monitoring the dog's response to the medication, adhering to prescribed treatment regimens, and addressing environmental considerations are essential for maximizing the effectiveness of anti-parasite treatments and ensuring the well-being of our canine companions.
Read more: If Your House Is Infested With Fleas On Two Dogs, How Long Does It Take For Capstar To Work?
Monitoring Your Dog's Response to Anti Parasite Medicine
Monitoring your dog's response to anti-parasite medicine is a crucial aspect of ensuring the effectiveness of the treatment and the overall well-being of your canine companion. By closely observing your dog's behavior, physical condition, and any changes in parasite infestations, you can proactively assess the response to the medication and make informed decisions regarding ongoing care and preventive measures.
Signs of Improvement
As you initiate anti-parasite treatment for your dog, it's essential to be vigilant for signs of improvement in their condition. These may include a reduction in scratching, licking, or biting at the skin, indicating relief from itching caused by fleas or other external parasites. Additionally, improvements in the dog's coat condition, such as reduced hair loss or the absence of visible parasites, can signify the effectiveness of the medication. Observing your dog for increased energy levels, improved appetite, and overall comfort can also indicate a positive response to the treatment.
Persistence of Symptoms
While monitoring your dog's response, it's important to note any persistence of symptoms associated with parasite infestations. If your dog continues to exhibit signs of discomfort, such as persistent scratching, skin irritation, or gastrointestinal disturbances, despite receiving anti-parasite medication, it may indicate the need for reevaluation of the treatment plan. Certain parasites or environmental factors could contribute to ongoing infestations, necessitating adjustments to the medication or additional preventive measures.
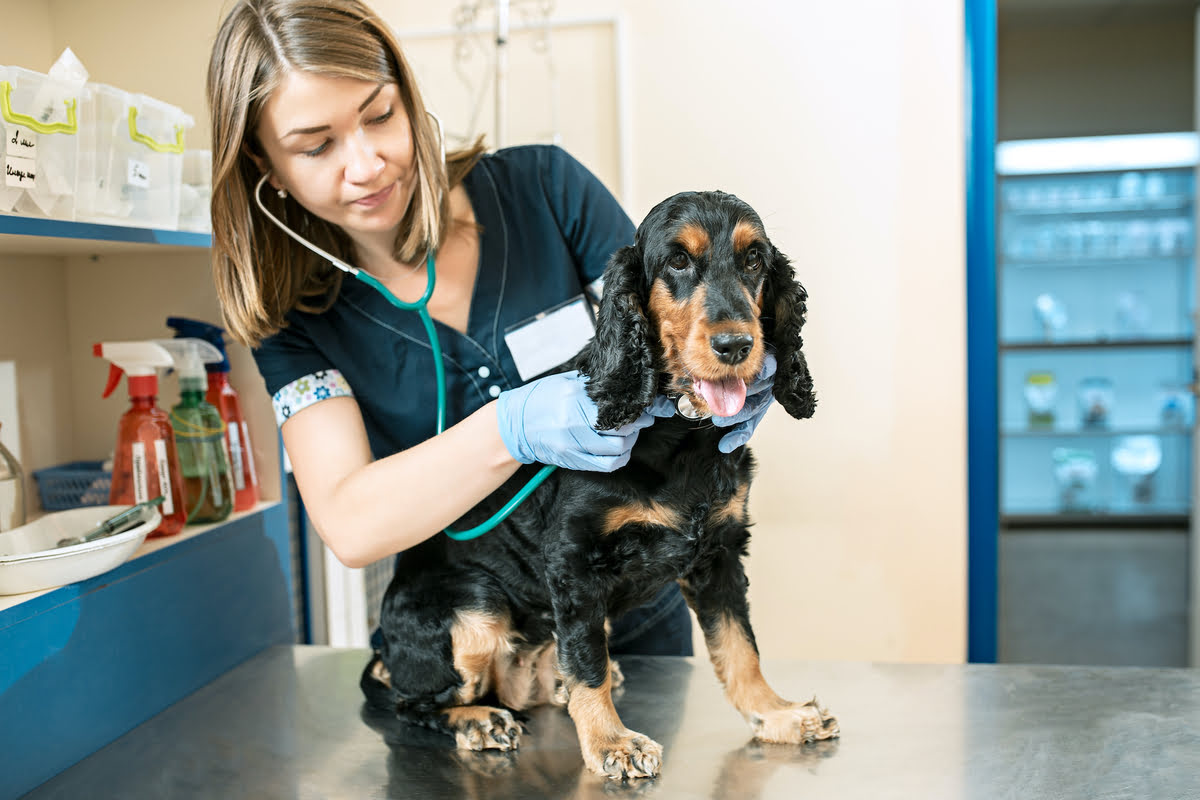
Follow-Up Veterinary Examinations
Regular follow-up examinations with your veterinarian play a pivotal role in monitoring your dog's response to anti-parasite medicine. These examinations allow the veterinarian to assess the progress of the treatment, evaluate any residual parasite burdens, and address any emerging health concerns. Through diagnostic tests, such as fecal examinations or skin assessments, veterinarians can gain insights into the effectiveness of the medication and tailor the treatment plan to meet the specific needs of your dog.
Environmental Management
In addition to monitoring your dog's physical response, environmental management is essential for preventing reinfestations and supporting the effectiveness of anti-parasite medicine. This involves implementing measures to control parasites in the dog's living environment, such as regular vacuuming, washing bedding, and using environmental flea and tick control products. By addressing potential sources of reinfestation, you can complement the effects of the medication and create a more favorable environment for your dog's well-being.
Adherence to Treatment Regimens
Adhering to the prescribed treatment regimens is fundamental to monitoring your dog's response to anti-parasite medicine. Ensuring that the medication is administered as directed, including the correct dosage and frequency, is essential for optimizing its effectiveness. Any deviations from the recommended treatment protocols should be promptly discussed with your veterinarian to maintain the integrity of the treatment plan and maximize the potential benefits for your dog.
By actively monitoring your dog's response to anti-parasite medicine and collaborating closely with your veterinarian, you can navigate the complexities of parasite management with confidence and compassion. This proactive approach empowers you to safeguard the health and happiness of your beloved canine companion, fostering a harmonious and parasite-free environment for your dog to thrive in.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the effective management of dog anti-parasite medicine is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a comprehensive understanding of the medications, the factors influencing their effectiveness, and the typical timeframe for them to work. By gaining insights into the diverse types of anti-parasite treatments, including topical, oral, and injectable medications, pet owners can make informed decisions in collaboration with veterinarians to address specific parasite infestations affecting their dogs.
The factors influencing the effectiveness of anti-parasite medicine, such as parasite species, resistance, the dog's health, environmental considerations, and treatment compliance, underscore the importance of a tailored and holistic approach to parasite management. By considering these factors, pet owners and veterinarians can optimize the efficacy of anti-parasite treatments and mitigate the risks associated with parasite infestations.
Understanding the typical timeframe for dog anti-parasite medicine to work is essential for managing expectations and monitoring the dog's response to the medication. From immediate effects with topical treatments to a more gradual impact with oral and injectable medications, pet owners can proactively assess the progress of the treatment and make informed decisions regarding ongoing care and preventive measures.
Furthermore, the proactive monitoring of the dog's response to anti-parasite medicine, including observing signs of improvement, addressing persistent symptoms, engaging in follow-up veterinary examinations, implementing environmental management, and adhering to treatment regimens, empowers pet owners to actively participate in their dog's well-being and contribute to the successful management of parasite infestations.
By embracing a collaborative and vigilant approach to dog anti-parasite medicine, pet owners can create a safe, comfortable, and parasite-free environment for their beloved dogs to thrive in. This proactive stance not only safeguards the health and happiness of dogs but also fosters a harmonious bond between pet owners and their canine companions, enriching the lives of both parties.
In essence, the journey of dog anti-parasite medicine is one of compassion, responsibility, and empowerment, where informed decisions and proactive measures converge to create a haven of well-being for our loyal and cherished canine friends.