Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Why Fleas Bite Dogs

Common Health Issues
Why Fleas Bite Dogs
Published: February 14, 2024
Learn why fleas bite dogs and how to prevent it. Discover common health issues affecting dogs and how to keep them healthy.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
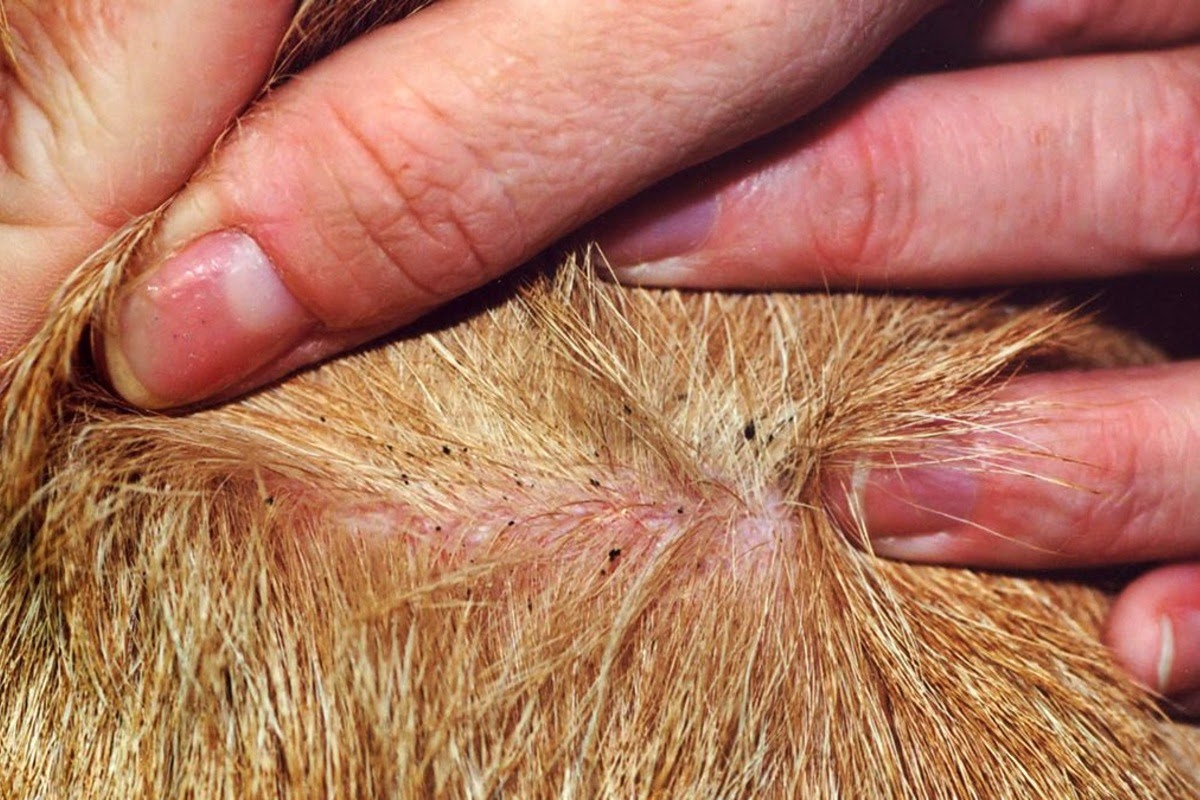
Fleas are a common nuisance for dogs and their owners. These tiny, blood-sucking parasites can cause discomfort and health issues for our beloved canine companions. Understanding why fleas bite dogs and how to prevent and treat flea infestations is crucial for maintaining the well-being of our furry friends.
Flea bites can lead to itching, irritation, and even allergic reactions in dogs. In severe cases, flea infestations can cause anemia and transmit diseases. Therefore, it's essential for dog owners to be well-informed about the behavior of fleas and the potential impact of their bites on dogs.
In this article, we will delve into the world of fleas and explore why they are attracted to dogs. We will also discuss the physical impact of flea bites on dogs and provide valuable insights into preventing these pesky parasites from infesting our canine companions. By gaining a deeper understanding of fleas and their behavior, dog owners can take proactive measures to safeguard their pets from the discomfort and health risks associated with flea infestations.
Understanding Fleas and Their Behavior
Fleas are small, wingless insects that belong to the order Siphonaptera. These agile parasites have flattened bodies, enabling them to move swiftly through the fur of their hosts. Fleas are equipped with powerful hind legs, allowing them to jump impressive distances relative to their size. Their exceptional jumping ability enables them to easily transfer from one host to another, making them adept at infesting multiple animals within a short period.
Fleas thrive in warm and humid environments, making them particularly prevalent during the spring and summer months. They prefer temperatures ranging from 65 to 80 degrees Fahrenheit and humidity levels of 75-85%. These conditions are conducive to their reproduction and development, contributing to the rapid spread of flea infestations.
One of the most remarkable aspects of flea behavior is their feeding habits. Fleas are ectoparasites, meaning they feed on the blood of their hosts. When a flea bites a dog, it pierces the skin with its specialized mouthparts to access the blood supply. The saliva of fleas contains anticoagulants, which prevent the host's blood from clotting during feeding. This allows the flea to consume a sufficient amount of blood before detaching from the host.
Fleas are highly resilient and can survive for extended periods without feeding. In fact, adult fleas can live for several months without a blood meal, making it challenging to eradicate infestations once they take hold. Additionally, flea eggs can remain dormant for weeks or even months, hatching when conditions are favorable for their development.
Understanding the behavior of fleas is crucial for implementing effective prevention and control measures. By comprehending their life cycle, feeding habits, and environmental preferences, dog owners can take proactive steps to protect their pets from flea infestations. This knowledge empowers pet owners to make informed decisions regarding flea prevention products, environmental management, and veterinary care, ultimately safeguarding the well-being of their canine companions.
Why Fleas are Attracted to Dogs
Fleas are naturally drawn to dogs due to various factors that make canines an ideal host for these blood-sucking parasites. Understanding why fleas are attracted to dogs is essential for implementing effective preventive measures and protecting our furry friends from infestations. Here are the primary reasons why fleas gravitate towards dogs:
-
Warmth and Comfort: Dogs provide an ideal environment for fleas to thrive. The fur of dogs offers warmth and protection, creating a cozy habitat for fleas to breed and feed. Additionally, the fur provides ample hiding places for fleas, allowing them to evade detection and grooming efforts by the host.
-
Abundant Food Source: Fleas are attracted to the blood of warm-blooded animals, and dogs serve as a readily available food source. The blood of dogs meets the nutritional requirements of fleas, providing sustenance for their survival and reproduction. The accessibility of a consistent blood supply makes dogs highly appealing to fleas seeking nourishment.
-
Scent and Chemical Signals: Dogs emit scents and chemical signals that attract fleas. These signals can include pheromones, body odors, and skin secretions that are irresistible to fleas. Additionally, the carbon dioxide exhaled by dogs serves as a powerful attractant for fleas, guiding them towards potential hosts.
-
Limited Grooming Behavior: Unlike some other animals, dogs may have limited grooming behaviors, especially in hard-to-reach areas such as the base of the tail and the back of the neck. These areas are prime locations for flea infestations, as the parasites can feed and reproduce without being disturbed by the host's grooming activities.
-
Social Interaction: Dogs often interact with other animals, increasing the likelihood of flea transmission. Whether it's during outdoor activities, visits to parks, or encounters with other pets, dogs are frequently exposed to environments where fleas may be present. This social interaction enhances the risk of flea infestations and underscores the importance of preventive measures.
By understanding the factors that attract fleas to dogs, pet owners can take proactive steps to minimize the risk of infestations. Regular grooming, preventive flea treatments, and environmental management are essential components of a comprehensive flea control strategy. By addressing the specific reasons why fleas are drawn to dogs, pet owners can effectively protect their canine companions from the discomfort and health risks associated with flea infestations.
The Physical Impact of Flea Bites on Dogs
Flea bites can have a significant impact on the physical well-being of dogs, causing a range of discomfort and potential health complications. When fleas infest a dog and begin feeding on its blood, the effects can extend beyond simple irritation. Understanding the physical impact of flea bites on dogs is crucial for recognizing the signs of infestation and taking prompt action to alleviate the associated discomfort. Here are the key aspects of the physical impact of flea bites on dogs:
Skin Irritation and Itching
Flea bites often trigger allergic reactions in dogs, leading to intense itching and skin irritation. Dogs may exhibit excessive scratching, biting, and licking in response to the discomfort caused by flea bites. The continuous scratching can result in skin abrasions, redness, and the formation of hot spots, exacerbating the dog's discomfort and potentially leading to secondary skin infections.
Hair Loss and Dermatitis
Prolonged flea infestations can contribute to hair loss in dogs, particularly in areas where fleas congregate and feed. The constant biting and feeding activity of fleas can damage the hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss and a dull, unkempt coat. Additionally, the saliva of fleas can trigger allergic dermatitis in dogs, resulting in inflamed and irritated skin.
Anemia
In severe cases of flea infestations, particularly in young or small dogs, the loss of blood due to repeated flea feeding can lead to anemia. Anemia occurs when the body's red blood cell count decreases, resulting in fatigue, weakness, and pale gums in affected dogs. Anemic dogs may exhibit lethargy, reduced appetite, and overall weakness, highlighting the serious health implications of untreated flea infestations.
Transmission of Diseases
Fleas can transmit various diseases and parasites to dogs through their bites. These include tapeworms, bartonellosis (causing cat scratch fever), and other pathogens that can compromise the dog's health. Additionally, the presence of fleas can exacerbate existing health conditions, making it essential to address flea infestations promptly to prevent the spread of diseases and ensure the overall well-being of the dog.
Psychological Distress
The constant discomfort and irritation caused by flea bites can lead to psychological distress in dogs. The incessant itching and discomfort can affect the dog's behavior, leading to restlessness, anxiety, and changes in temperament. Addressing flea infestations not only alleviates physical discomfort but also contributes to the overall mental well-being of the dog.
By understanding the physical impact of flea bites on dogs, pet owners can recognize the signs of infestation and take proactive measures to address the issue. Implementing regular flea prevention measures, such as topical treatments, oral medications, and environmental control, is essential for safeguarding the physical and emotional well-being of dogs and ensuring a comfortable, healthy life for our beloved canine companions.
Preventing Flea Bites on Dogs
Preventing flea bites on dogs is essential for maintaining their health and well-being. By implementing proactive measures, pet owners can effectively protect their canine companions from the discomfort and potential health risks associated with flea infestations. Here are key strategies for preventing flea bites on dogs:
-
Regular Grooming: Regular grooming practices, including brushing and bathing, can help in the early detection of fleas and reduce the likelihood of infestations. Grooming also aids in removing flea eggs and larvae from the dog's coat, disrupting the flea life cycle and preventing further infestations.
-
Use of Flea Preventive Products: Utilizing veterinarian-recommended flea preventive products such as spot-on treatments, oral medications, collars, and shampoos can effectively repel and kill fleas. These products provide a protective barrier against fleas, preventing bites and infestations.
-
Environmental Management: Maintaining a clean and flea-free environment is crucial for preventing flea bites on dogs. Regular vacuuming, washing pet bedding, and treating indoor and outdoor areas with flea control products can help eliminate flea eggs, larvae, and adult fleas, reducing the risk of infestations.
-
Regular Veterinary Care: Seeking regular veterinary care for dogs is essential for preventing flea bites and monitoring the overall health of the pet. Veterinarians can recommend suitable flea preventive measures and detect early signs of flea infestations, enabling prompt intervention.
-
Flea Control for the Household: Implementing flea control measures for the entire household, including other pets, is vital for preventing flea bites on dogs. Treating all pets in the household for fleas and maintaining a consistent preventive regimen can minimize the risk of infestations.
-
Monitoring Outdoor Activities: Monitoring and limiting a dog's outdoor activities in areas where fleas are prevalent can reduce the risk of exposure. Avoiding tall grass, wooded areas, and known flea habitats can help minimize the likelihood of flea bites.
-
Regular Inspections: Conducting routine inspections of the dog's coat and skin for signs of fleas, such as excessive scratching, flea dirt, or redness, can aid in early detection and prompt intervention.
By incorporating these preventive measures into a comprehensive flea control strategy, pet owners can effectively protect their dogs from flea bites and the associated discomfort. Proactive flea prevention not only ensures the physical well-being of dogs but also contributes to their overall quality of life, allowing them to thrive in a flea-free and comfortable environment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding why fleas bite dogs and the potential impact of their bites is crucial for safeguarding the well-being of our canine companions. Fleas are naturally drawn to dogs due to factors such as warmth, abundant food supply, chemical signals, and limited grooming behaviors. By comprehending these factors, pet owners can take proactive measures to minimize the risk of infestations and protect their dogs from the discomfort and health risks associated with flea bites.
The physical impact of flea bites on dogs extends beyond simple irritation, encompassing skin irritation, hair loss, anemia, disease transmission, and psychological distress. Recognizing the signs of flea infestations and understanding the implications of flea bites empowers pet owners to address the issue promptly, ensuring the overall health and comfort of their dogs.
Preventing flea bites on dogs involves a multi-faceted approach, including regular grooming, the use of flea preventive products, environmental management, veterinary care, household flea control, and monitoring outdoor activities. By incorporating these preventive measures into a comprehensive flea control strategy, pet owners can effectively protect their dogs from flea bites and the associated discomfort, contributing to their overall quality of life.
Ultimately, by gaining a deeper understanding of fleas and their behavior, pet owners can take proactive steps to safeguard their dogs from flea infestations, promoting a comfortable and healthy life for their beloved companions. Through regular preventive measures and attentive care, dogs can thrive in a flea-free environment, free from the discomfort and health risks posed by these persistent parasites.
