Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How Big Are Ticks On Dogs


Common Health Issues
How Big Are Ticks On Dogs
Published: February 5, 2024
Learn about common health issues for dogs, including how big ticks can get on dogs. Protect your pet from potential health risks with this helpful information.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Ticks are tiny creatures that can cause big problems for our furry friends. These blood-sucking parasites are commonly found in grassy and wooded areas, making them a potential threat to dogs who love to explore the great outdoors. Understanding the size of ticks and their impact on dogs is crucial for pet owners to ensure the well-being of their beloved companions.
Ticks come in various sizes, ranging from as small as a poppy seed to as large as a pencil eraser. Despite their small stature, ticks can pose significant health risks to dogs, including the transmission of diseases such as Lyme disease, ehrlichiosis, and anaplasmosis. Identifying and addressing tick infestations promptly is essential for safeguarding the health of dogs and preventing potential complications.
In this article, we will delve into the world of ticks and their impact on dogs. We will explore the different sizes of ticks, how to identify them on dogs, the potential health risks they pose, and the importance of prevention and treatment. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of ticks and their effects, pet owners can take proactive measures to protect their canine companions from these pesky parasites.
Read more: How To Kill Ticks On Dogs
Understanding the Size of Ticks
Ticks come in a range of sizes, and understanding their dimensions is crucial for effectively identifying and addressing infestations on dogs. These blood-feeding parasites progress through various stages of development, each characterized by distinct sizes and appearances. The size of a tick can vary depending on its species, life stage, and whether it has fed recently.
Tick Sizes at Different Life Stages
-
Larvae: When ticks hatch from eggs, they emerge as tiny, six-legged larvae that are typically no larger than a poppy seed. Due to their minuscule size, larvae can be challenging to spot, making early detection a considerable challenge.
-
Nymphs: After feeding on blood, larvae molt into eight-legged nymphs. At this stage, they are slightly larger than larvae, resembling a small sesame seed. Nymphs are more visible than larvae but can still evade detection due to their size and ability to hide in a dog's fur.
-
Adults: Once nymphs have engorged themselves on blood, they molt into adult ticks. Adult ticks are the largest and most noticeable stage, with sizes varying based on the species. Some adult ticks can grow as large as a pencil eraser, while others may remain smaller, depending on their species and feeding history.
Size Discrepancies Among Tick Species
It's important to note that tick sizes can differ significantly among species. For instance, the common dog tick (Dermacentor variabilis) is generally larger than the black-legged tick (Ixodes scapularis), also known as the deer tick. Additionally, the size of a tick can change after it has fed, as engorged ticks become visibly larger due to the blood they consume.
Importance of Size Awareness
Understanding the varying sizes of ticks is essential for dog owners, as it enables them to conduct thorough tick checks and promptly remove any parasites they find. Regular grooming and physical examinations of a dog's skin and coat can aid in the early detection of ticks, regardless of their size. By being aware of the potential sizes of ticks at different life stages and species, pet owners can take proactive measures to protect their canine companions from these pesky parasites.
By comprehending the diverse sizes of ticks and their life stages, pet owners can better equip themselves to identify and address tick infestations on their dogs, ultimately safeguarding their pets from potential health risks associated with these blood-feeding parasites.
Read more: How To Naturally Kill Ticks On Dogs
Identifying Ticks on Dogs
Identifying ticks on dogs is a crucial skill for pet owners, as it enables them to promptly address infestations and protect their furry companions from potential health risks. Ticks can latch onto a dog's skin and coat, making it essential for pet owners to conduct regular tick checks to ensure early detection and removal. Here are some key methods for identifying ticks on dogs:
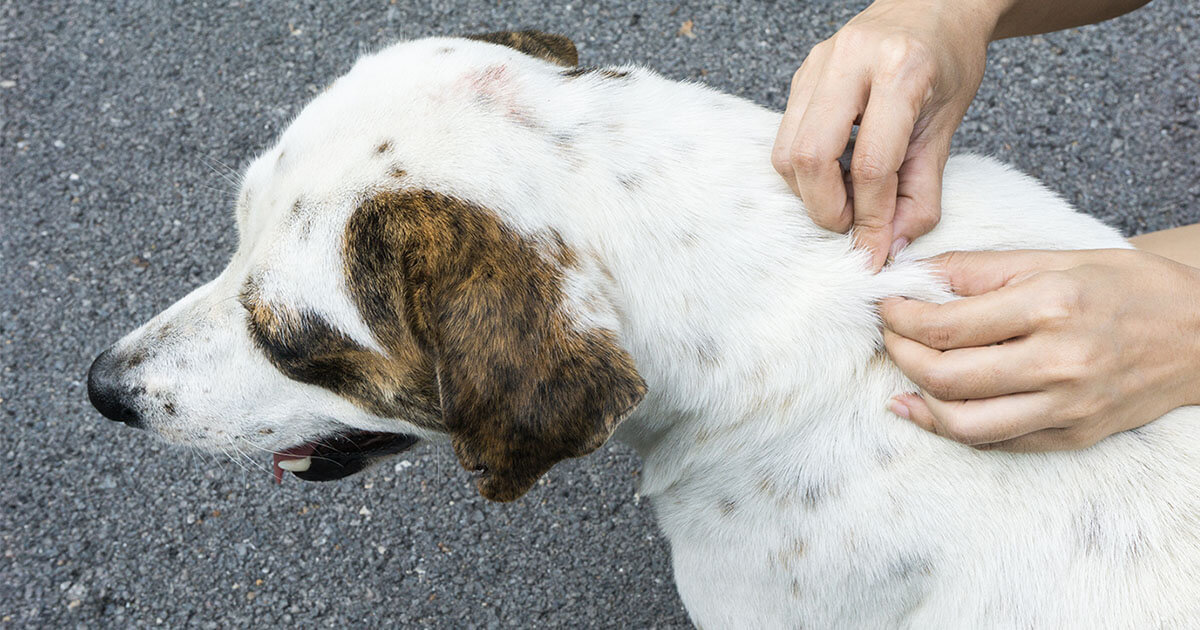
Visual Inspection
Regular visual inspections of a dog's skin and coat are fundamental for identifying ticks. Ticks can vary in size and color, ranging from tiny, dark specks to larger, engorged parasites. When examining a dog, pay close attention to areas where ticks are commonly found, such as the ears, neck, head, and between the toes. Ticks may appear as small bumps or dark spots on the skin, and their presence should prompt immediate removal.
Physical Sensation
In addition to visual inspections, pet owners can run their hands over their dog's body to feel for any unusual bumps or rough textures. Ticks can be detected through touch, especially when conducting thorough grooming sessions. Running fingers through the fur and feeling for any irregularities can help identify ticks that may be hidden from plain sight.
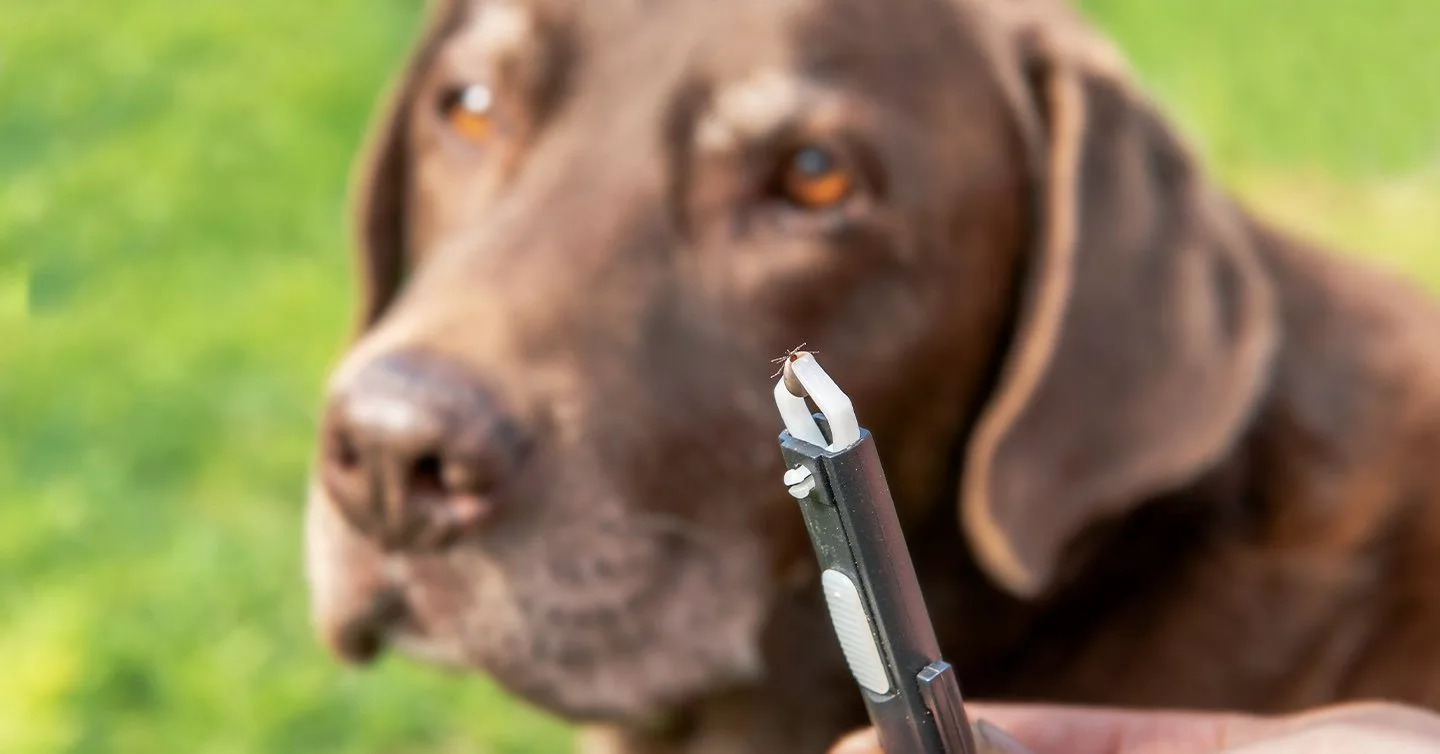
Tick Removal Tools
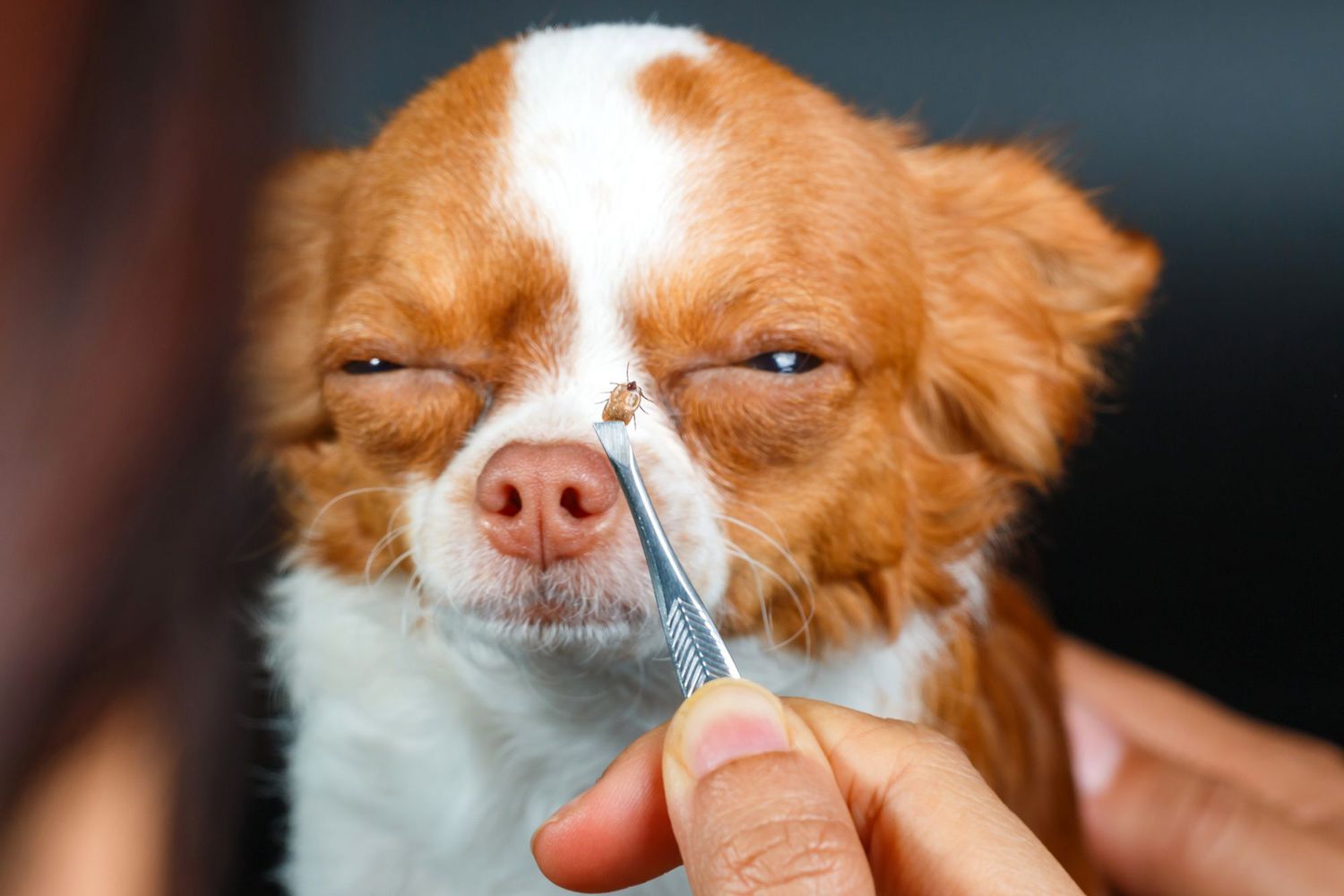
Utilizing specialized tick removal tools can aid in the identification and extraction of ticks from a dog's skin. These tools, such as tick twisters or fine-tipped tweezers, are designed to grasp the tick at the mouthparts and facilitate safe removal. When using these tools, pet owners can visually confirm the presence of ticks before carefully extracting them to prevent leaving behind any mouthparts in the skin.
Read more: How To Tell If There’s A Tick On Your Dog
Behavioral Changes
Observing changes in a dog's behavior can also serve as an indicator of potential tick infestations. Dogs may exhibit increased scratching, licking, or discomfort in areas where ticks are present. Persistent scratching or agitation in specific areas should prompt pet owners to conduct a thorough inspection for ticks and address any infestations promptly.
Professional Assistance
In cases where tick infestations are extensive or challenging to manage, seeking professional assistance from a veterinarian is advisable. Veterinarians can conduct comprehensive examinations, provide guidance on tick prevention, and administer appropriate treatments to ensure the well-being of the dog.
By familiarizing themselves with these methods for identifying ticks on dogs, pet owners can effectively safeguard their canine companions from the potential health risks associated with tick infestations. Early detection and prompt removal of ticks are essential for maintaining the health and comfort of dogs, making regular tick checks an integral part of responsible pet care.
Potential Health Risks
Tick infestations pose significant health risks to dogs, making it imperative for pet owners to be aware of the potential consequences and take proactive measures to protect their furry companions. When ticks attach themselves to a dog's skin and feed on their blood, they can transmit a variety of diseases and cause discomfort and distress to the affected animal.
Transmission of Diseases
Ticks are notorious vectors for various diseases that can have severe implications for a dog's health. One of the most well-known tick-borne illnesses is Lyme disease, caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. This disease can lead to symptoms such as lameness, fever, joint swelling, and lethargy, significantly impacting a dog's overall well-being if left untreated.
In addition to Lyme disease, ticks can transmit ehrlichiosis, a bacterial infection that affects white blood cells and can lead to symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, and lethargy. Anaplasmosis, another tick-borne disease, can cause similar symptoms and negatively impact a dog's immune system, leading to prolonged discomfort and potential complications.
Anemia and Dermatitis
In addition to disease transmission, tick infestations can result in anemia, a condition characterized by a low red blood cell count. When ticks feed on a dog's blood, especially in large numbers, they can cause significant blood loss, leading to anemia and its associated symptoms, including weakness, pale gums, and fatigue.
Furthermore, the saliva of ticks contains substances that can trigger allergic reactions in dogs, leading to dermatitis and skin irritation. Dogs may experience intense itching, redness, and inflammation at the site of tick bites, causing discomfort and potential secondary infections if the affected areas are excessively scratched or licked.
Secondary Infections
The act of a tick attaching and feeding on a dog's skin can create an entry point for bacteria, increasing the risk of secondary infections. If a dog excessively scratches or bites at the site of a tick bite, it can break the skin and introduce harmful bacteria, potentially leading to localized infections that require veterinary attention and treatment.
Psychological Impact
Beyond the physical health risks, tick infestations can also have a psychological impact on dogs. The discomfort and irritation caused by tick bites can lead to behavioral changes, including increased agitation, restlessness, and decreased appetite. Dogs may experience heightened stress and anxiety as a result of persistent itching and discomfort, affecting their overall well-being and quality of life.
By understanding the potential health risks associated with tick infestations, pet owners can prioritize preventive measures and prompt tick removal to protect their dogs from the detrimental effects of these blood-feeding parasites. Regular tick checks, preventive medications, and prompt veterinary care are essential components of responsible pet ownership, ensuring the health and happiness of canine companions.
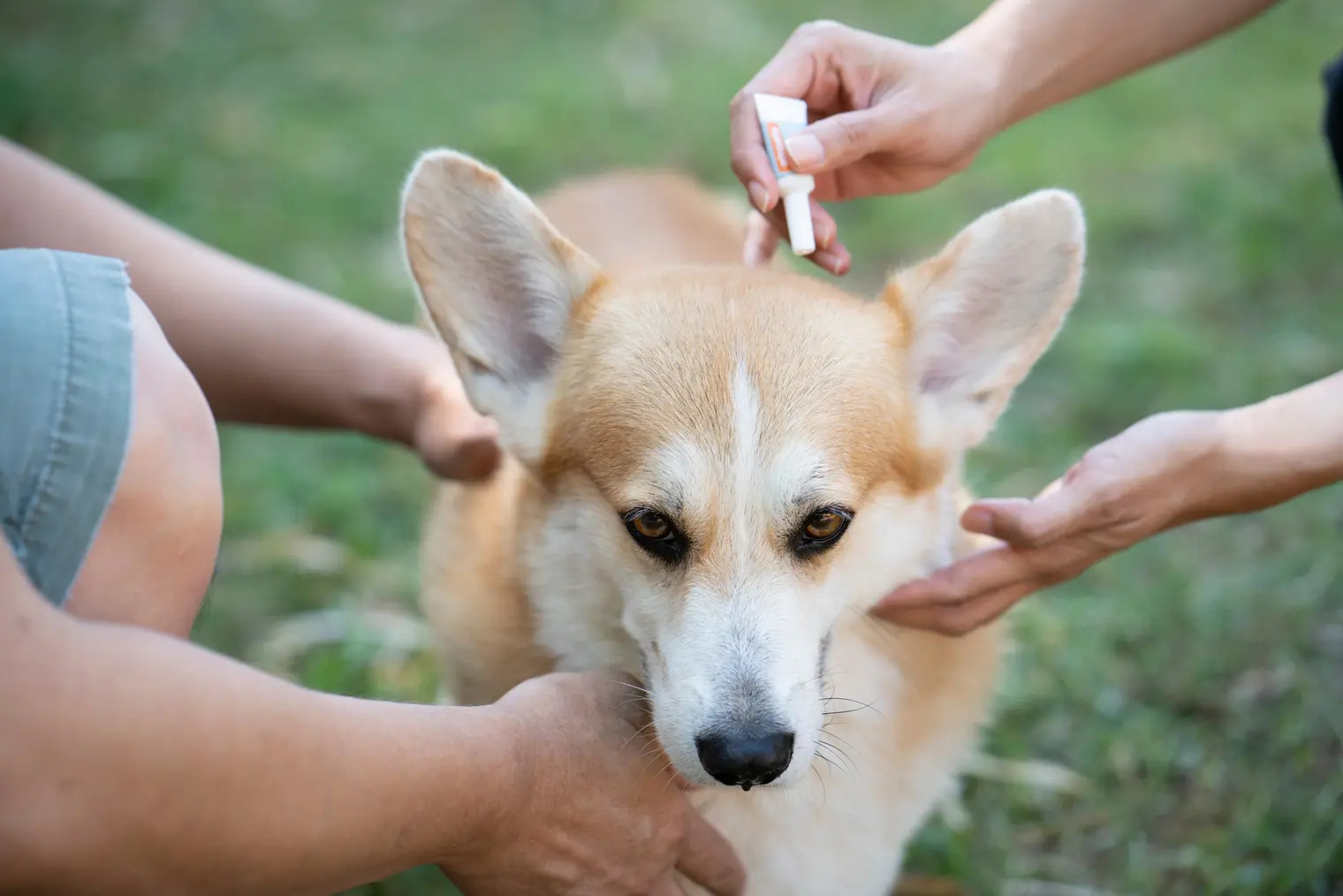
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing tick infestations and implementing effective treatment strategies are essential aspects of responsible dog care. By proactively addressing the risk of ticks and promptly managing infestations, pet owners can safeguard their canine companions from potential health complications and ensure their overall well-being.
Preventive Measures
-
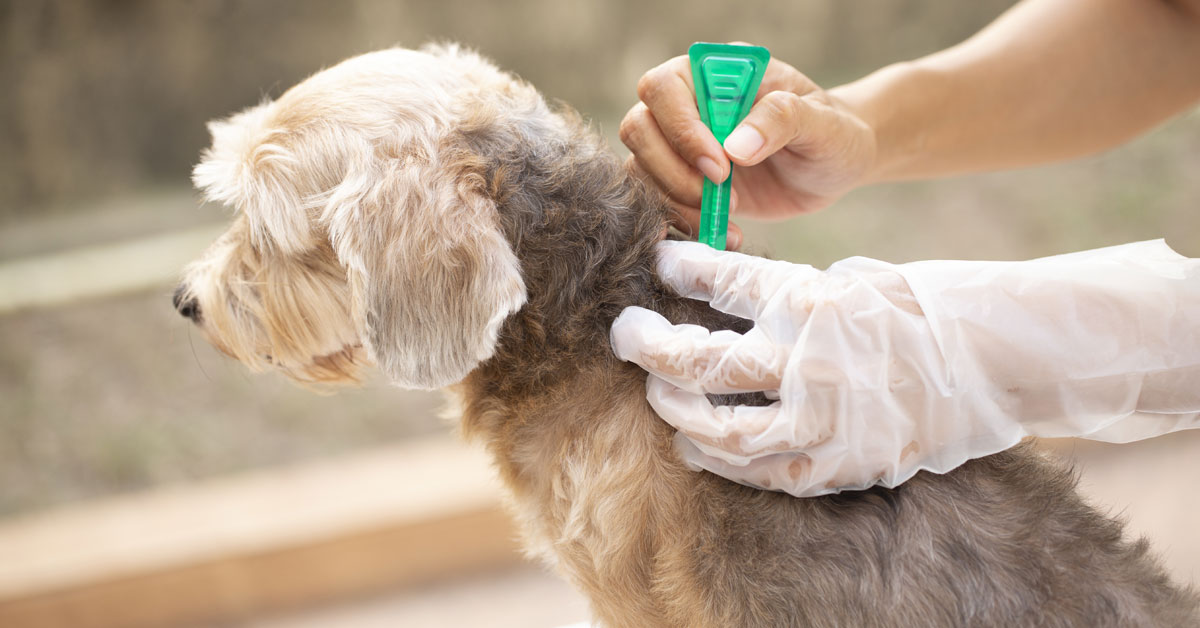
Tick Control Products: Utilizing tick control products, such as topical treatments, collars, and oral medications, can help prevent tick infestations in dogs. These products are designed to repel ticks or eliminate them upon contact, providing a layer of protection against these parasites.
-
Environmental Management: Regularly maintaining outdoor spaces, such as yards and hiking trails, can reduce the presence of ticks in the surrounding areas. Clearing tall grass, removing leaf litter, and minimizing brush and shrubbery can create a less hospitable environment for ticks, lowering the risk of exposure for dogs.
-
Tick Checks: Implementing routine tick checks on dogs after outdoor activities is crucial for early detection and removal. Thoroughly inspecting a dog's skin and coat, paying close attention to potential tick hotspots, allows pet owners to identify and address any attached ticks promptly.
-
Vaccination: In regions where tick-borne diseases are prevalent, vaccination against specific illnesses, such as Lyme disease, can provide an additional layer of protection for dogs. Consulting with a veterinarian to determine the appropriate vaccination protocols based on the dog's lifestyle and geographical location is essential for comprehensive preventive care.
Treatment Approaches
-
Tick Removal: Swift and proper removal of ticks is paramount in preventing disease transmission and minimizing discomfort for dogs. Using fine-tipped tweezers or specialized tick removal tools, grasp the tick as close to the skin as possible and gently pull it straight out, ensuring that no mouthparts remain embedded in the skin.
-
Veterinary Consultation: Seeking guidance from a veterinarian is crucial when addressing tick infestations, especially if a dog exhibits symptoms of tick-borne illnesses. Veterinarians can conduct thorough examinations, recommend appropriate treatments, and provide valuable insights on managing tick-related health concerns.
-
Medication: In cases where dogs have been exposed to ticks or diagnosed with tick-borne diseases, veterinarians may prescribe medications, such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs, to address the underlying conditions and alleviate associated symptoms. Adhering to the prescribed treatment regimens is essential for the dog's recovery and well-being.
-
Environmental Control: Implementing environmental control measures, such as treating outdoor areas with tick-repellent products or seeking professional pest control services, can help reduce the risk of tick infestations in the dog's living environment, contributing to long-term prevention efforts.
By prioritizing preventive measures, conducting regular tick checks, and promptly addressing infestations through appropriate treatment approaches, pet owners can effectively protect their dogs from the potential harm posed by ticks. Proactive management of tick-related concerns is integral to promoting the health, comfort, and vitality of canine companions, enabling them to enjoy a fulfilling and tick-free lifestyle.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the size of ticks and their impact on dogs is paramount for responsible pet ownership. Ticks, ranging from minuscule larvae to engorged adult parasites, can pose significant health risks to dogs, including the transmission of debilitating diseases and the potential for discomfort and distress. By familiarizing themselves with the diverse sizes of ticks at different life stages and species, pet owners can proactively engage in tick prevention and prompt removal, ultimately safeguarding the well-being of their beloved canine companions.
Identifying ticks on dogs through visual inspections, physical sensation, and the use of specialized tick removal tools is essential for early detection and prompt removal. Additionally, observing behavioral changes in dogs and seeking professional assistance when necessary are integral components of effective tick identification and management. By incorporating these methods into regular pet care routines, pet owners can minimize the risk of tick infestations and mitigate potential health consequences for their dogs.
The potential health risks associated with tick infestations, including the transmission of diseases, anemia, dermatitis, and the psychological impact on dogs, underscore the importance of preventive measures and prompt treatment. Through the utilization of tick control products, environmental management, routine tick checks, and vaccination where applicable, pet owners can create a protective shield against tick-borne illnesses and ensure the well-being of their dogs.
In the event of tick infestations, swift and proper tick removal, veterinary consultation, and adherence to prescribed treatments are crucial for mitigating health risks and promoting the recovery of affected dogs. Furthermore, environmental control measures contribute to long-term prevention efforts, creating a safer living environment for dogs and reducing the risk of recurrent infestations.
By prioritizing preventive measures, conducting regular tick checks, and promptly addressing infestations through appropriate treatment approaches, pet owners play a pivotal role in protecting their dogs from the potential harm posed by ticks. This proactive approach not only safeguards the health and comfort of canine companions but also fosters a fulfilling and tick-free lifestyle for dogs to thrive in the company of their devoted human companions.