Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Why Do Dogs With Diabetes Go Blind?


Common Health Issues
Why Do Dogs With Diabetes Go Blind?
Published: January 30, 2024
Learn about common health issues in dogs, including why diabetes can lead to blindness. Understand the importance of managing your dog's health to prevent complications.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Diabetes is a common health issue that affects not only humans but also our beloved canine companions. When a dog is diagnosed with diabetes, it can be a concerning and challenging time for pet owners. One of the distressing complications associated with diabetes in dogs is the potential for blindness. Understanding the connection between diabetes and blindness in dogs is crucial for pet owners to provide the best care for their furry friends.
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, occurs when the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. This condition can lead to various health complications, including blindness, if left unmanaged. Dogs, like humans, can develop both type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas fails to produce enough insulin, while type 2 diabetes involves insulin resistance.
As responsible pet owners, it's essential to recognize the signs of diabetes in dogs, such as increased thirst, frequent urination, sudden weight loss, and lethargy. Once diagnosed, it's crucial to work closely with a veterinarian to develop a comprehensive treatment plan to manage the condition and minimize the risk of complications, including blindness.
In this article, we will delve into the intricate relationship between diabetes and blindness in dogs. By gaining a deeper understanding of this connection, pet owners can take proactive measures to prevent and manage blindness in their diabetic dogs. Let's explore the factors contributing to blindness in diabetic dogs and discover effective strategies for preventing and addressing this distressing complication.
Read more: Why Do Dogs With Diabetes Pee In The House
Understanding Diabetes in Dogs
Diabetes in dogs shares similarities with the condition in humans, albeit with some distinct differences. Canine diabetes, like its human counterpart, involves the body's inability to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. This metabolic disorder can lead to a range of health issues if left unmanaged, including the potential for blindness.
There are two primary types of diabetes that can affect dogs: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the pancreas fails to produce an adequate amount of insulin, the hormone responsible for regulating blood sugar. On the other hand, type 2 diabetes involves insulin resistance, where the body's cells do not respond effectively to insulin.
Recognizing the signs of diabetes in dogs is crucial for early detection and intervention. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, sudden weight loss despite a hearty appetite, lethargy, and recurrent urinary tract infections. If a dog displays these symptoms, it is imperative to seek veterinary care promptly for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Once diagnosed, managing diabetes in dogs requires a multifaceted approach. This typically involves dietary modifications, regular exercise, and, in some cases, insulin therapy. Monitoring blood glucose levels is also essential to ensure they remain within a healthy range.
Understanding the nuances of diabetes in dogs empowers pet owners to provide the necessary support and care for their furry companions. By working closely with veterinarians and adhering to prescribed treatment plans, pet owners can help their diabetic dogs lead fulfilling and healthy lives while minimizing the risk of complications, including blindness.
The Link Between Diabetes and Blindness in Dogs
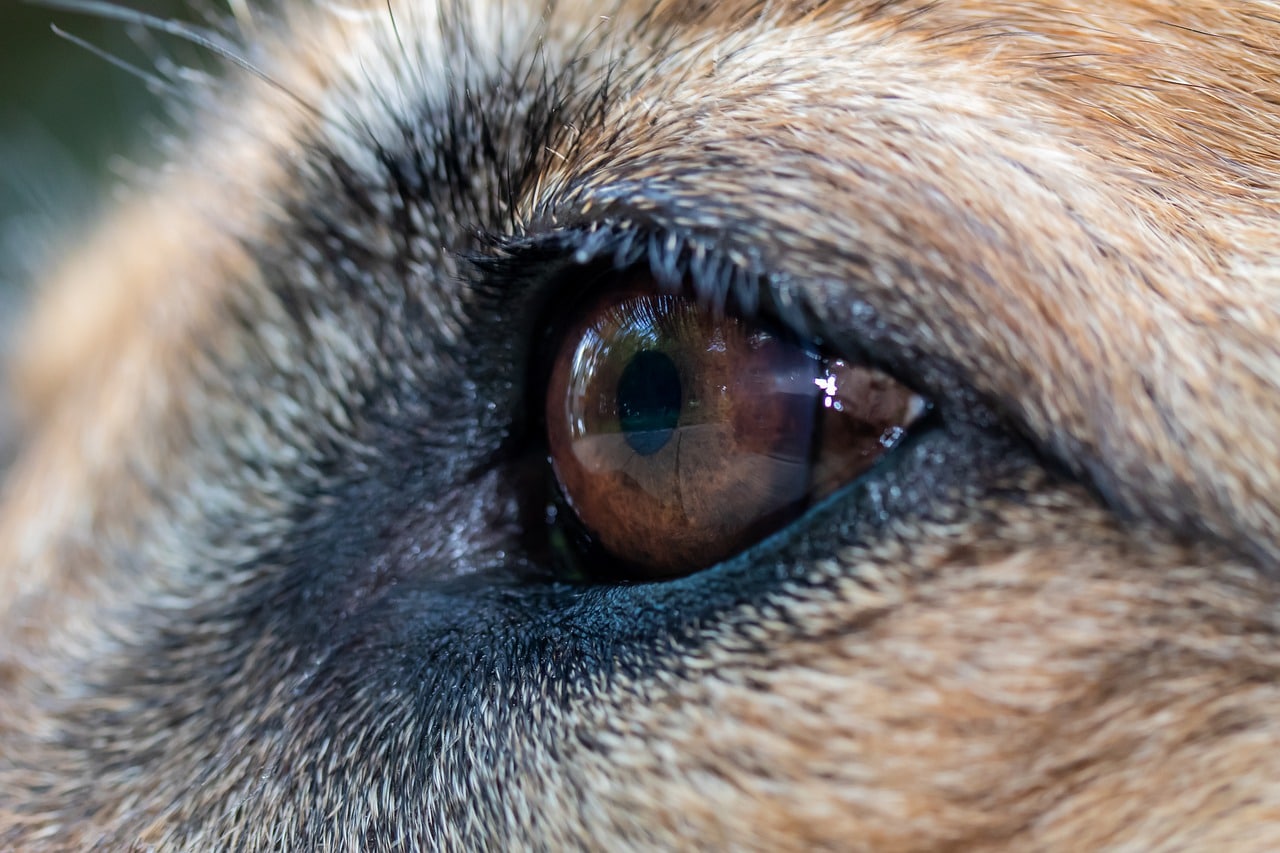
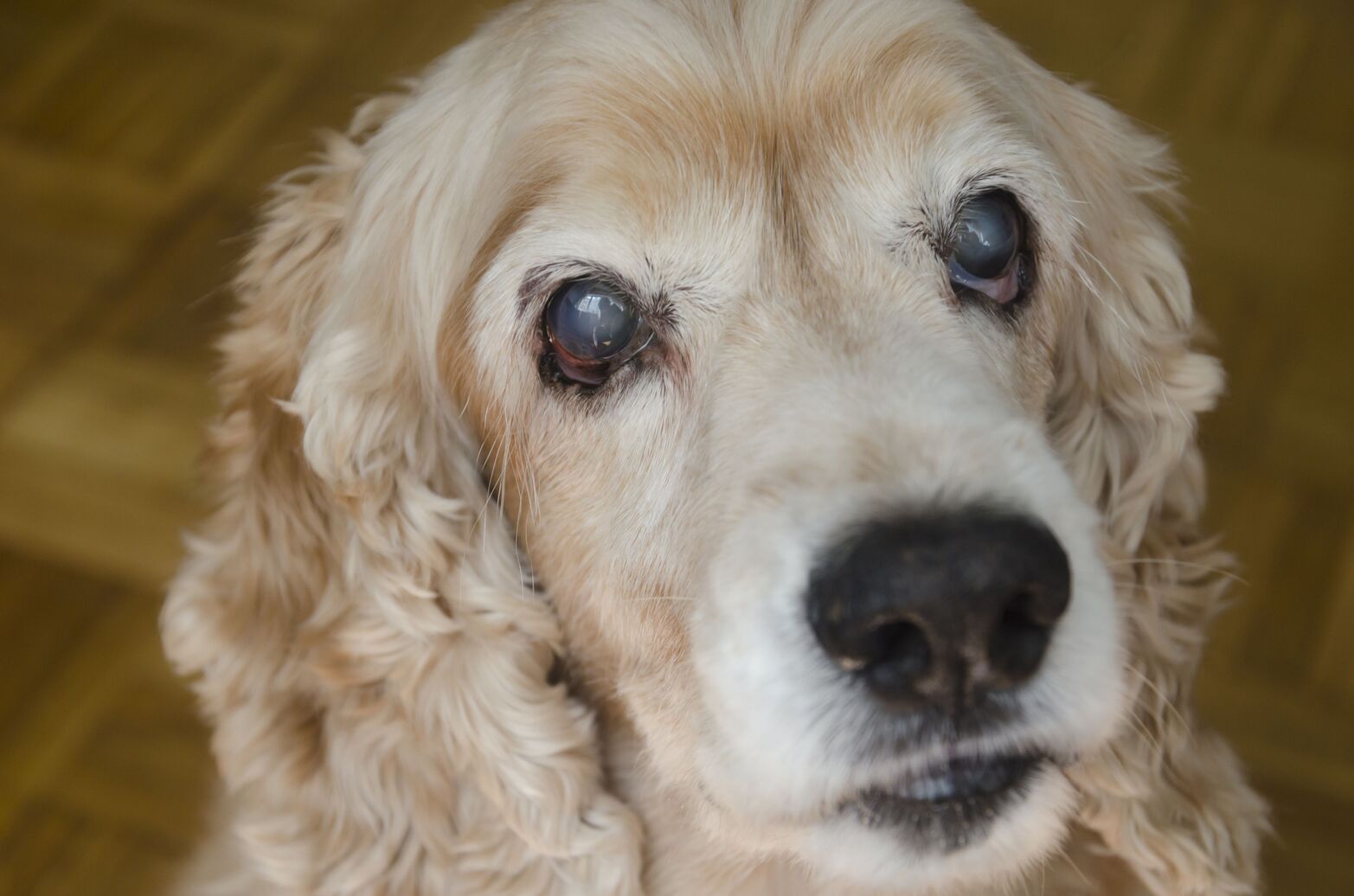
The intricate link between diabetes and blindness in dogs underscores the profound impact of this metabolic disorder on canine health. Diabetic dogs are at an increased risk of developing a condition known as diabetic retinopathy, which can ultimately lead to vision impairment and, in severe cases, blindness. Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive eye disease characterized by damage to the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye.
When a dog has diabetes, the persistently high levels of glucose in the bloodstream can damage the delicate blood vessels that nourish the retina. Over time, this damage can result in impaired blood flow to the retina, leading to a cascade of detrimental effects on vision. As the disease progresses, the retina may become deprived of oxygen and essential nutrients, further exacerbating the deterioration of vision.
Moreover, diabetic dogs are also susceptible to the development of cataracts, another significant contributor to blindness. Cataracts occur when the eye's lens becomes clouded, obstructing the passage of light and causing vision impairment. Dogs with diabetes are predisposed to developing cataracts at an accelerated rate, significantly increasing the likelihood of vision loss.
The impact of diabetes on a dog's vision is a sobering reality for pet owners, underscoring the importance of proactive management and vigilant monitoring of the condition. By understanding the profound link between diabetes and blindness in dogs, pet owners can prioritize preventive measures and early intervention to safeguard their canine companions' vision.
It is essential for pet owners of diabetic dogs to work closely with veterinarians to implement a comprehensive care plan that includes regular eye examinations to detect early signs of diabetic retinopathy and other ocular complications. Additionally, maintaining strict glycemic control through proper diet, exercise, and, if necessary, insulin therapy is paramount in mitigating the risk of vision impairment.
By recognizing the intricate interplay between diabetes and blindness in dogs, pet owners can take proactive steps to preserve their furry friends' vision and enhance their overall quality of life. Through diligent management and a deep understanding of the link between diabetes and blindness, pet owners can navigate the complexities of this condition with compassion and expertise, ensuring the best possible outcomes for their beloved diabetic dogs.
Factors Contributing to Blindness in Diabetic Dogs
The development of blindness in diabetic dogs is influenced by a myriad of factors, each playing a significant role in the progression of vision impairment. Understanding these contributing factors is essential for pet owners to proactively address and mitigate the risk of blindness in their diabetic canine companions.
-
Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetic retinopathy, a hallmark complication of diabetes in dogs, is a primary factor contributing to blindness. The persistently elevated levels of glucose in the bloodstream can lead to damage of the delicate blood vessels that supply the retina, resulting in impaired blood flow and compromised retinal function. As the disease advances, the retina may experience ischemia, hemorrhages, and the growth of abnormal blood vessels, ultimately leading to vision impairment.
-
Cataracts: Dogs with diabetes are predisposed to the rapid development of cataracts, which significantly heightens the risk of blindness. Cataracts occur when the eye's lens becomes clouded, obstructing the passage of light and causing vision impairment. The presence of cataracts in diabetic dogs can lead to progressive vision loss if left unaddressed, underscoring the critical role of timely intervention.
-
Glaucoma: Diabetic dogs are also susceptible to developing glaucoma, a condition characterized by increased pressure within the eye. Glaucoma can result in optic nerve damage and irreversible vision loss if not promptly diagnosed and managed. The combination of diabetes and glaucoma poses a heightened risk of blindness, emphasizing the importance of regular eye examinations for early detection and intervention.
-
Ocular Inflammation: Chronic hyperglycemia in diabetic dogs can contribute to ocular inflammation, further exacerbating the risk of vision impairment. Inflammation within the eye can lead to structural damage and functional deficits, compromising visual acuity and overall ocular health. Proactive management of diabetes is crucial in mitigating the inflammatory processes that can impact a dog's vision.
-
Secondary Infections: Diabetic dogs are more susceptible to ocular infections, which can exacerbate existing ocular complications and accelerate vision loss. The compromised immune response associated with diabetes can predispose dogs to recurrent and persistent ocular infections, necessitating diligent monitoring and prompt treatment to safeguard their vision.
By comprehensively understanding the factors contributing to blindness in diabetic dogs, pet owners can prioritize proactive measures to mitigate these risks. Through close collaboration with veterinarians and adherence to prescribed treatment regimens, pet owners can play a pivotal role in preserving their diabetic dogs' vision and enhancing their overall quality of life.
Preventing and Managing Blindness in Dogs with Diabetes
Preventing and managing blindness in dogs with diabetes is a multifaceted endeavor that requires proactive measures, vigilant monitoring, and a comprehensive care approach. By prioritizing preventive strategies and implementing effective management techniques, pet owners can significantly mitigate the risk of vision impairment in their diabetic canine companions.
Read more: Why Do Dogs With Diabetes Get Cataracts
Strict Glycemic Control
Maintaining strict glycemic control is paramount in preventing the progression of diabetic ocular complications. Consistent monitoring of blood glucose levels, adherence to prescribed insulin therapy, and a carefully regulated diet are essential components of managing diabetes in dogs. By working closely with veterinarians to establish and maintain optimal blood sugar levels, pet owners can minimize the risk of diabetic retinopathy and other vision-threatening conditions.
Regular Eye Examinations
Routine eye examinations are crucial for early detection of diabetic ocular complications. Veterinarians can assess the health of the retina, identify signs of diabetic retinopathy, monitor for the development of cataracts, and evaluate overall ocular function. Early intervention based on findings from these examinations can help address potential vision-threatening issues before they escalate, preserving the dog's eyesight and overall ocular health.
Nutritional Support
A well-balanced and carefully managed diet plays a pivotal role in managing diabetes and supporting ocular health in dogs. Proper nutrition, tailored to the dog's specific needs and health status, can contribute to overall well-being and may help minimize the risk of diabetic complications, including those affecting vision. Pet owners should work with veterinarians to develop a nutritionally sound diet plan that aligns with their diabetic dog's unique requirements.
Environmental Adaptations
Creating a safe and supportive environment for diabetic dogs can help minimize the risk of accidents and injuries that could compromise their vision. Pet owners can make simple yet impactful adaptations, such as ensuring clear pathways, using non-slip surfaces, and removing potential hazards from the dog's living space. These adjustments can enhance the dog's safety and reduce the likelihood of ocular trauma, particularly in cases where vision may already be compromised.
Read more: Why Do Dogs With Diabetes Lose Weight
Collaborative Care
Effective management of diabetes and its potential ocular complications necessitates collaborative care between pet owners and veterinary professionals. Open communication, regular check-ups, and a proactive approach to addressing any changes in the dog's health or behavior are essential. By working as a team, pet owners and veterinarians can optimize the dog's care plan, address emerging concerns promptly, and make informed decisions to safeguard the dog's vision and overall well-being.
By implementing these preventive and management strategies, pet owners can play a pivotal role in preserving their diabetic dogs' vision and enhancing their quality of life. Through a combination of proactive measures, attentive care, and a deep understanding of the complexities of diabetes and its impact on ocular health, pet owners can navigate the challenges associated with this condition with compassion and expertise, ensuring the best possible outcomes for their beloved canine companions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the intricate relationship between diabetes and blindness in dogs underscores the profound impact of this metabolic disorder on canine health. Diabetic retinopathy, accelerated cataract development, glaucoma, ocular inflammation, and susceptibility to secondary infections collectively contribute to the heightened risk of vision impairment in diabetic dogs. Understanding these factors is crucial for pet owners to proactively address and mitigate the risk of blindness in their diabetic canine companions.
Preventing and managing blindness in dogs with diabetes requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses strict glycemic control, regular eye examinations, tailored nutritional support, environmental adaptations, and collaborative care. By prioritizing preventive strategies and implementing effective management techniques, pet owners can significantly mitigate the risk of vision impairment in their diabetic dogs.
The proactive measures outlined in this article, including maintaining strict glycemic control, prioritizing regular eye examinations, providing tailored nutritional support, making environmental adaptations, and fostering collaborative care, empower pet owners to play a pivotal role in preserving their diabetic dogs' vision and enhancing their overall quality of life.
By recognizing the intricate interplay between diabetes and blindness in dogs, pet owners can take proactive steps to safeguard their furry friends' vision. Through diligent management and a deep understanding of the link between diabetes and blindness, pet owners can navigate the complexities of this condition with compassion and expertise, ensuring the best possible outcomes for their beloved diabetic dogs.
In essence, by implementing these preventive and management strategies, pet owners can significantly enhance the well-being of their diabetic dogs, minimize the risk of vision impairment, and foster a fulfilling and healthy life for their beloved companions. Through a combination of proactive measures, attentive care, and a deep understanding of the complexities of diabetes and its impact on ocular health, pet owners can navigate the challenges associated with this condition, ensuring the best possible outcomes for their beloved canine companions.