Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes Insipidus In Dogs?


Common Health Issues
What Are The Symptoms Of Diabetes Insipidus In Dogs?
Published: January 30, 2024
Learn about the symptoms of diabetes insipidus in dogs and other common health issues. Understand the signs and seek proper care for your pet.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Diabetes insipidus is a condition that affects dogs, causing excessive thirst and urination. It is essential for pet owners to be aware of the symptoms and treatment options for this condition to ensure the well-being of their furry companions. Understanding the signs of diabetes insipidus can help in early detection and prompt intervention, leading to improved outcomes for affected dogs.
Diabetes insipidus is a rare disorder that impacts a dog's ability to regulate water balance within the body. Unlike diabetes mellitus, which involves blood sugar regulation, diabetes insipidus affects the kidneys' ability to conserve water, leading to excessive urination and dehydration. This condition can be challenging to manage, but with proper veterinary care and monitoring, affected dogs can lead happy and fulfilling lives.
In the following sections, we will delve into the common symptoms of diabetes insipidus in dogs, the diagnostic process, and the available treatment options. By gaining a deeper understanding of this condition, pet owners can be better equipped to recognize potential signs in their dogs and seek timely veterinary care. Let's explore the world of diabetes insipidus in dogs and learn how to support our beloved pets through this health challenge.
Understanding Diabetes Insipidus in Dogs
Diabetes insipidus in dogs is a rare condition that affects their ability to regulate water balance within the body. Unlike diabetes mellitus, which involves blood sugar regulation, diabetes insipidus primarily impacts the kidneys' ability to conserve water, leading to excessive urination and increased thirst. This disorder can be challenging to manage and can significantly impact a dog's quality of life if left untreated.
There are two primary forms of diabetes insipidus in dogs: central diabetes insipidus and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. Central diabetes insipidus occurs when the pituitary gland fails to produce enough antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as vasopressin, which is responsible for regulating the body's water balance. On the other hand, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus occurs when the kidneys do not respond appropriately to ADH, leading to excessive water excretion.
The symptoms of diabetes insipidus in dogs can be distressing for both the pet and the owner. Dogs affected by this condition often display excessive thirst, leading to frequent consumption of water. As a result, they experience increased urination, which may occur both indoors and outdoors. Additionally, affected dogs may show signs of dehydration, such as sunken eyes, lethargy, and a dry nose and mouth.
Understanding the underlying causes of diabetes insipidus in dogs is crucial for effective management. While the condition can be genetic, it can also result from head trauma, tumors, infections, or certain medications. Additionally, certain dog breeds, such as the Samoyed and the Miniature Pinscher, may be predisposed to developing diabetes insipidus.
Diagnosing diabetes insipidus in dogs typically involves a thorough physical examination, blood tests, and urinalysis to assess kidney function and urine concentration. In some cases, a water deprivation test may be conducted to evaluate the dog's ability to concentrate urine when water is restricted.
Once diagnosed, treatment options for diabetes insipidus in dogs aim to manage the symptoms and improve the dog's quality of life. This may involve the administration of synthetic ADH, also known as desmopressin, to replace the hormone that the dog's body is unable to produce. Additionally, dietary adjustments and access to ample fresh water are essential components of managing diabetes insipidus in dogs.
By understanding the complexities of diabetes insipidus in dogs, pet owners can be proactive in recognizing potential symptoms and seeking prompt veterinary care. With proper management and ongoing support, dogs affected by diabetes insipidus can lead fulfilling lives, bringing joy and companionship to their human families.
Common Symptoms of Diabetes Insipidus in Dogs
Recognizing the common symptoms of diabetes insipidus in dogs is crucial for early detection and intervention. While this condition may initially manifest differently in individual dogs, there are several hallmark signs that pet owners should be mindful of. Understanding these symptoms can help in promptly seeking veterinary care and improving the overall well-being of affected dogs.
-
Excessive Thirst: One of the primary symptoms of diabetes insipidus in dogs is an unquenchable thirst, known as polydipsia. Affected dogs may constantly seek out water, often drinking large volumes in a short period. This excessive thirst is a result of the body's inability to conserve water, leading to a persistent sensation of dehydration.
-
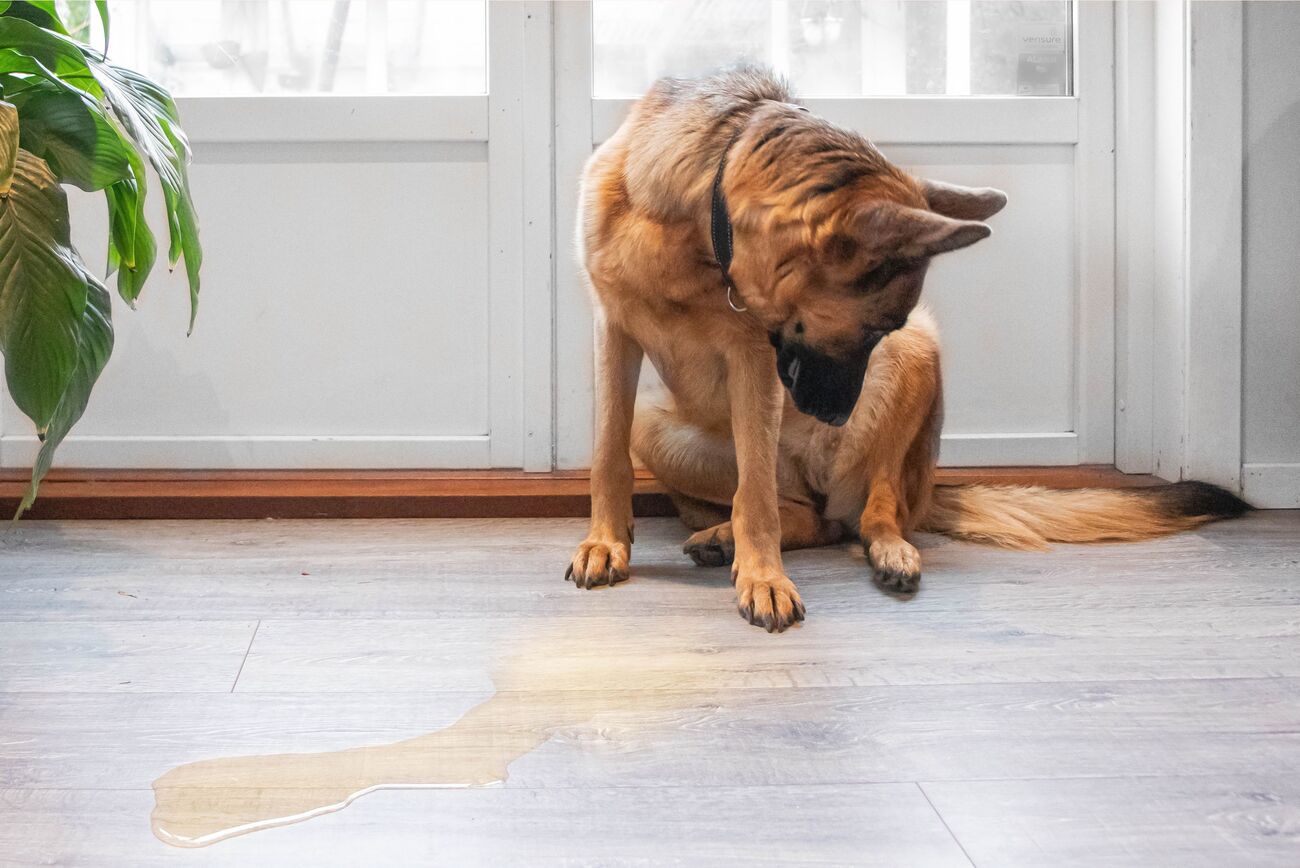
Frequent Urination: Dogs with diabetes insipidus exhibit polyuria, which refers to excessive urination. This symptom is closely linked to the increased thirst experienced by affected dogs. Pet owners may notice that their dogs need to urinate more frequently, and in larger quantities, both during the day and at night.
-
Accidents Indoors: Due to the increased frequency and urgency of urination, dogs with diabetes insipidus may struggle to control their bladder, leading to accidents indoors. This can be distressing for both the dog and the owner and may indicate an underlying health issue that requires attention.
-
Dehydration: Prolonged water imbalance in dogs with diabetes insipidus can lead to dehydration. Signs of dehydration may include sunken eyes, lethargy, dry nose and mouth, and decreased skin elasticity. It is essential for pet owners to monitor their dog's hydration status and seek veterinary care if dehydration is suspected.
-
Weight Loss: In some cases, dogs with diabetes insipidus may experience unexplained weight loss despite maintaining a regular appetite. This can be attributed to the body's inability to retain essential fluids, leading to a loss of body mass over time.
-
Lethargy and Weakness: The persistent imbalance in water regulation can take a toll on a dog's energy levels, leading to lethargy and weakness. Affected dogs may appear less active and enthusiastic, showing reduced interest in physical activities they once enjoyed.
-
Changes in Urine Color and Odor: The urine of dogs with diabetes insipidus may appear diluted and almost colorless due to the excessive excretion of water. Additionally, the urine may have a distinct odor, which can be noticeable to pet owners.
By being attentive to these common symptoms, pet owners can play a proactive role in identifying potential signs of diabetes insipidus in their dogs. Seeking veterinary guidance for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis is essential to ensure the appropriate management of this condition and the well-being of the affected pet.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Diagnosing diabetes insipidus in dogs involves a comprehensive approach to assess the underlying causes and determine the most effective treatment plan. Veterinary professionals utilize a combination of physical examinations, blood tests, urinalysis, and specialized diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of diabetes insipidus and identify its specific form. Understanding the diagnostic process is crucial for pet owners seeking to support their dogs through this health challenge.
Upon suspecting diabetes insipidus in a dog, the veterinarian will conduct a thorough physical examination to evaluate the dog's overall health and assess for any visible symptoms. Blood tests may be performed to measure the dog's hormone levels, kidney function, and electrolyte balance. Additionally, urinalysis helps in assessing the concentration of the dog's urine and identifying any abnormalities that may indicate kidney dysfunction.
In some cases, a water deprivation test may be recommended to evaluate the dog's ability to concentrate urine when water intake is restricted. This test involves monitoring the dog's response to water deprivation and assessing urine concentration at specific intervals. The results of this test provide valuable insights into the dog's kidney function and water regulation capabilities.
Once a diagnosis of diabetes insipidus is confirmed, the veterinarian will discuss the available treatment options with the pet owner. The primary goal of treatment is to manage the symptoms of excessive thirst and urination while addressing the underlying cause of the condition. Treatment options for diabetes insipidus in dogs typically involve the administration of synthetic antidiuretic hormone (ADH), also known as desmopressin.
Desmopressin is available in various forms, including nasal sprays and oral medications, and works to replace the deficient ADH in the dog's body, thereby aiding in water retention and reducing excessive urination. The dosage and administration schedule of desmopressin are tailored to the individual dog's needs, and regular monitoring by the veterinarian is essential to ensure the treatment's effectiveness.
In addition to medication, dietary adjustments may be recommended to support the management of diabetes insipidus in dogs. Providing access to ample fresh water at all times is crucial to prevent dehydration and support the dog's increased water intake. Pet owners play a vital role in ensuring that their dogs have constant access to clean water, especially during warm weather or periods of physical activity.
Regular veterinary check-ups are essential for monitoring the dog's response to treatment and adjusting the management plan as needed. Through ongoing collaboration with the veterinarian, pet owners can provide their dogs with the necessary support and care to effectively manage diabetes insipidus and maintain their overall well-being.
By understanding the diagnostic process and available treatment options, pet owners can actively participate in their dog's healthcare journey, contributing to improved outcomes and a higher quality of life for dogs affected by diabetes insipidus. With proper veterinary guidance and ongoing support, dogs can thrive despite the challenges posed by this condition, bringing joy and companionship to their human families.
Conclusion
In conclusion, diabetes insipidus in dogs is a complex condition that significantly impacts their water regulation and overall well-being. By recognizing the common symptoms, such as excessive thirst, frequent urination, and dehydration, pet owners can play a proactive role in seeking timely veterinary care and support for their beloved companions. Understanding the diagnostic process and available treatment options is crucial for effectively managing diabetes insipidus in dogs and improving their quality of life.
As responsible pet owners, it is essential to remain vigilant and attentive to any changes in our dogs' behavior and physical health. Early detection of diabetes insipidus can lead to prompt intervention, enabling veterinarians to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to the specific needs of each affected dog. Through collaboration with veterinary professionals, pet owners can provide their dogs with the necessary care, including regular access to clean water, medication administration, and ongoing monitoring to ensure treatment effectiveness.
Furthermore, the emotional support and companionship that dogs provide are invaluable, and it is our responsibility to reciprocate by prioritizing their health and well-being. Despite the challenges posed by diabetes insipidus, affected dogs can lead fulfilling lives with the appropriate support and management. By fostering a strong bond with our canine companions and remaining dedicated to their care, we can navigate the complexities of diabetes insipidus together, ensuring that our dogs continue to enrich our lives with their unwavering loyalty and affection.
In closing, the journey of supporting a dog with diabetes insipidus may present obstacles, but with compassion, knowledge, and collaborative care, pet owners can make a meaningful difference in their dogs' lives. By staying informed, proactive, and dedicated to the well-being of our furry friends, we can navigate the challenges of diabetes insipidus, providing our dogs with the love and support they deserve as cherished members of our families.