Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>Eye and Ear Health>What Does It Mean When There Is A Dent Behind The Eye Of My Dog?


Eye and Ear Health
What Does It Mean When There Is A Dent Behind The Eye Of My Dog?
Published: February 11, 2024
Learn about the causes and treatment of a dent behind your dog's eye, and how it may affect their eye and ear health. Understanding the implications of this condition is crucial for your pet's well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
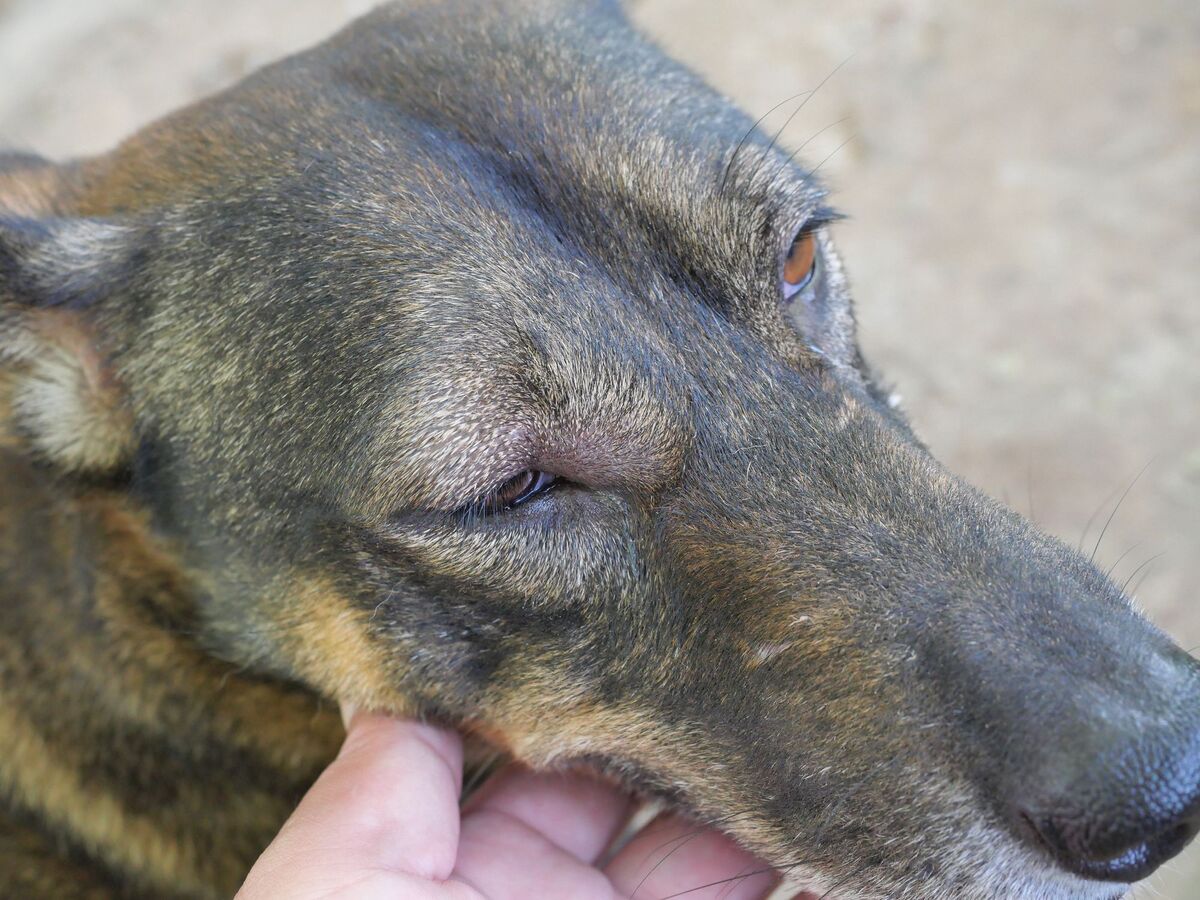
When you notice a dent behind your dog's eye, it can be a cause for concern and may prompt a flurry of questions and worries. As a responsible pet owner, it's natural to seek answers and understand the potential implications of this unusual occurrence. The presence of a dent behind the eye of your beloved canine companion may raise questions about their health and well-being. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of this issue, exploring the possible causes, symptoms to watch for, and when to seek professional veterinary care. Understanding the anatomy of a dog's eye and the potential reasons for a dent behind it is crucial for ensuring the best possible care for your furry friend. Let's embark on this journey to unravel the mysteries behind this concerning phenomenon and equip ourselves with the knowledge to provide the best support for our canine companions.
Understanding the anatomy of a dog's eye
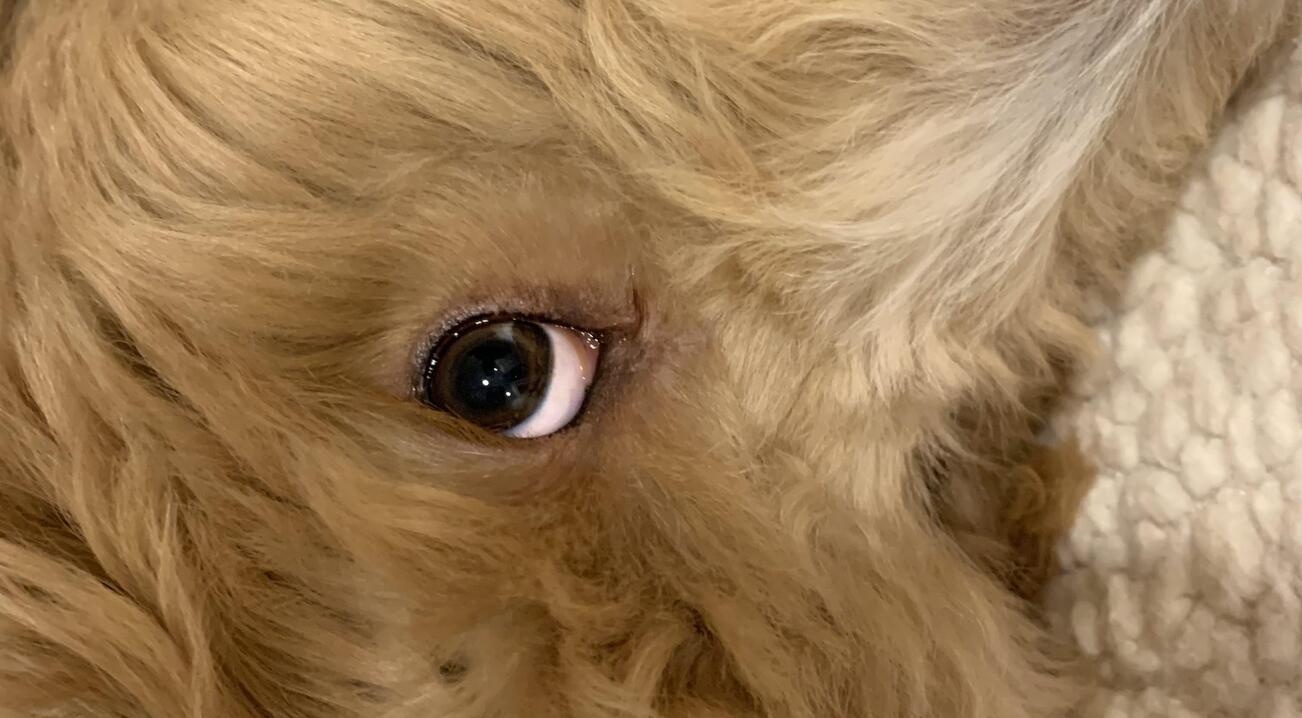
The anatomy of a dog's eye is a marvel of intricate structures designed to facilitate vision and protect the delicate inner components. Understanding the various parts of a dog's eye is essential for comprehending the potential implications of a dent behind the eye.
The outermost layer of the eye is the cornea, a transparent dome-shaped structure that acts as a protective barrier, allowing light to enter the eye. Beneath the cornea lies the iris, the colorful part of the eye, which controls the size of the pupil to regulate the amount of light entering the eye. The lens, located behind the iris, further focuses the incoming light onto the retina, a layer of cells at the back of the eye responsible for converting light into neural signals.
The vitreous body, a gel-like substance, fills the space between the lens and the retina, maintaining the shape of the eye and providing structural support. The retina contains photoreceptor cells called rods and cones, which detect light and transmit visual information to the brain via the optic nerve.
The eye is also equipped with accessory structures, including the eyelids, which protect the eye from foreign objects and distribute tears to keep the surface moist. The lacrimal glands produce tears, essential for lubricating and nourishing the eye.
Understanding the intricate anatomy of a dog's eye provides valuable insights into the potential impact of a dent behind the eye. Any alteration in the normal structure of the eye, such as a dent, can disrupt its delicate functions and warrant prompt attention to ensure the well-being of your canine companion.
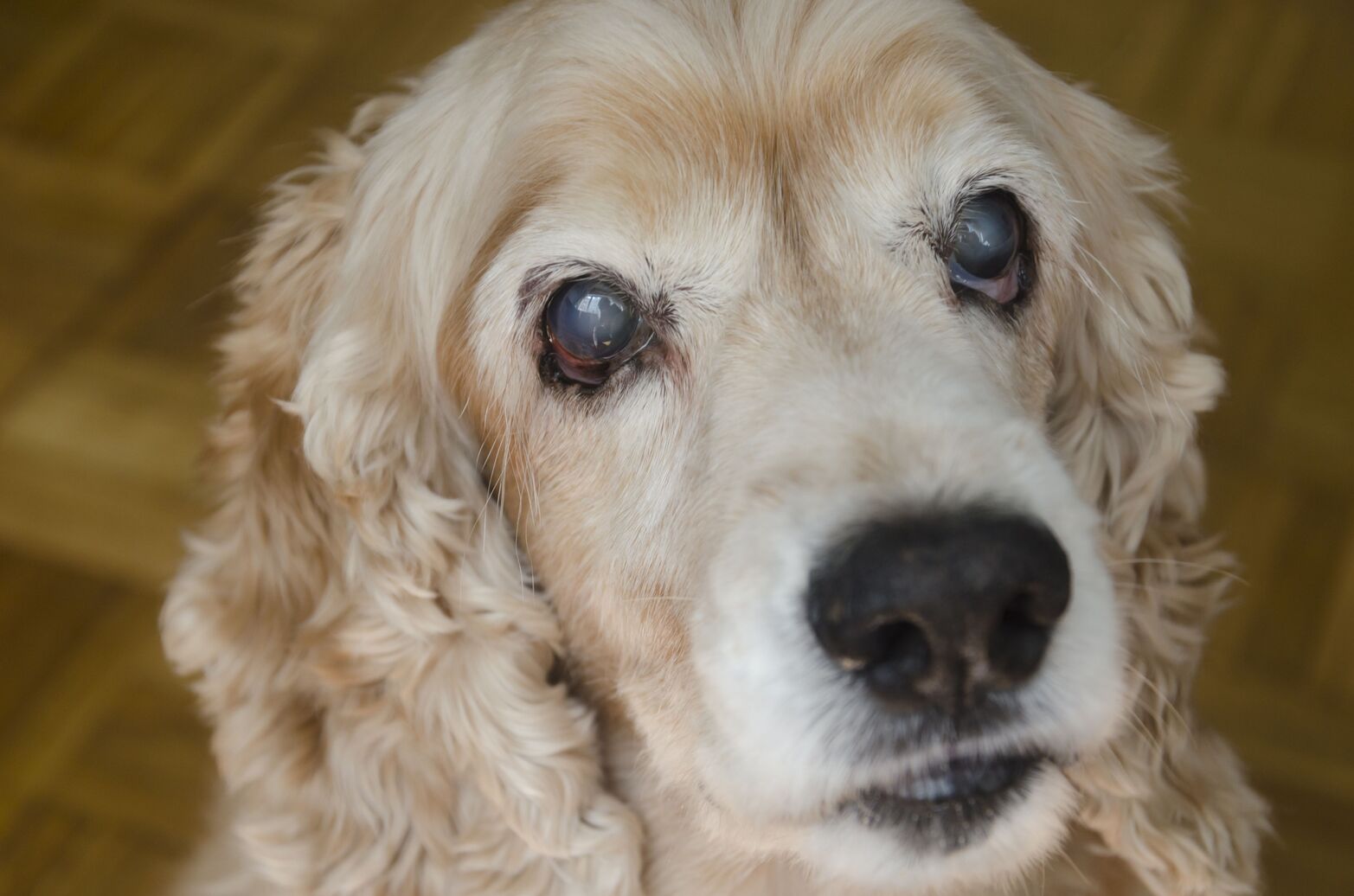
Possible causes of a dent behind the eye
-
Trauma or Injury: A significant blow to the head or face can result in a dent behind the eye. This type of trauma can cause the delicate structures surrounding the eye to shift or deform, leading to a noticeable indentation.
-
Orbital Bone Abnormalities: Anomalies in the orbital bone, which forms the eye socket, can contribute to the development of a dent behind the eye. Conditions such as a congenital defect or bone resorption may lead to structural changes, impacting the appearance of the eye area.
-
Tumor or Mass: The presence of a tumor or mass behind the eye can exert pressure, causing the surrounding tissues to indent. Tumors can arise from various tissues, including the bone, muscle, or connective tissue, and may necessitate thorough evaluation by a veterinarian.
-
Inflammatory Conditions: Inflammation of the tissues surrounding the eye, known as orbital cellulitis, can lead to localized swelling and subsequent indentation. Inflammatory processes, whether due to infection or autoimmune disorders, can alter the normal contours of the eye area.
-
Fluid Accumulation: An accumulation of fluid, such as blood or pus, behind the eye can create a noticeable dent. This may occur as a result of trauma, infection, or underlying medical conditions affecting the eye and its surrounding structures.
-
Dental Abscess: In some cases, a dental abscess in the upper jaw can cause a dent behind the eye. The proximity of the dental structures to the eye area means that an abscess can impact the surrounding tissues, leading to visible changes.
Understanding the potential causes of a dent behind the eye is crucial for identifying the underlying issue and determining the appropriate course of action. While some causes may be relatively benign, others can signify more serious health concerns that require prompt veterinary attention. Observing any changes in your dog's eye area and seeking professional evaluation can aid in addressing the root cause of the dent and ensuring the well-being of your canine companion.
Symptoms to look out for
Identifying potential symptoms associated with a dent behind your dog's eye is essential for proactive monitoring and timely intervention. While the presence of a dent itself is a visible indicator of an underlying issue, observing accompanying symptoms can provide valuable insights into the nature and severity of the condition. Here are key symptoms to be vigilant for:
-
Changes in Eye Appearance: Keep a close watch for alterations in the affected eye's appearance, such as asymmetry, unusual bulging, or sunken appearance. These visual changes, when observed alongside a dent behind the eye, can indicate underlying issues affecting the eye and its surrounding structures.
-
Eye Discharge: The presence of abnormal discharge from the affected eye, including pus, blood, or excessive tearing, can signal an underlying infection, inflammation, or injury. Monitoring the type and frequency of eye discharge can aid in assessing the severity of the condition.
-
Pain or Discomfort: Dogs may exhibit signs of discomfort or pain related to the affected eye, such as pawing at the eye, rubbing the face against surfaces, or displaying sensitivity to touch around the eye area. These behaviors can indicate discomfort and the need for prompt evaluation by a veterinarian.
-
Altered Behavior: Changes in your dog's behavior, such as increased irritability, reluctance to be touched around the head, or decreased activity, can be indicative of discomfort or distress related to the dent behind the eye. Observing any shifts in behavior can provide valuable clues regarding your dog's well-being.
-
Vision Changes: Any noticeable alterations in your dog's vision, such as bumping into objects, reluctance to navigate familiar spaces, or dilated pupils, warrant attention. Vision changes in conjunction with a dent behind the eye may signify underlying issues impacting ocular function.
-
Systemic Symptoms: In some cases, systemic symptoms such as fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, or weight loss may accompany a dent behind the eye. These broader indicators can point to underlying health concerns that require comprehensive evaluation and management.
Vigilantly monitoring these symptoms and promptly seeking veterinary care upon their observation is crucial for addressing potential underlying issues and safeguarding your dog's ocular and overall health. By remaining attentive to these signs, you can play a proactive role in ensuring the well-being of your canine companion.
When to seek veterinary care
Recognizing the appropriate timing to seek veterinary care for a dent behind your dog's eye is paramount in addressing potential underlying issues and ensuring the best possible outcome for your canine companion. Prompt intervention can significantly impact the prognosis and treatment efficacy, making it essential to be vigilant for specific indicators that warrant professional evaluation.
If you observe any of the following concerning signs or symptoms in conjunction with the presence of a dent behind your dog's eye, it is imperative to seek veterinary care without delay:
-
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms: If the dent behind the eye persists or worsens over time, it indicates a persistent underlying issue that necessitates professional assessment. Any progressive changes in the appearance of the eye area should prompt immediate veterinary attention to determine the cause and initiate appropriate management.
-
Pain or Discomfort: Dogs exhibiting signs of pain, discomfort, or sensitivity around the affected eye require prompt evaluation by a veterinarian. Persistent pawing at the eye, rubbing the face against surfaces, or vocalizing when the eye area is touched are indicative of discomfort and necessitate professional assessment to alleviate any underlying distress.
-
Vision Changes: Any noticeable alterations in your dog's vision, such as bumping into objects, reluctance to navigate familiar spaces, or dilated pupils, warrant immediate veterinary care. Vision changes in conjunction with a dent behind the eye may signify underlying issues impacting ocular function, necessitating thorough evaluation and intervention.
-
Systemic Symptoms: The presence of systemic symptoms such as fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, or weight loss alongside a dent behind the eye indicates potential broader health concerns. These symptoms necessitate comprehensive veterinary assessment to identify and address any underlying medical conditions affecting your dog's overall well-being.
-
Unexplained Eye Discharge: Abnormal discharge from the affected eye, including pus, blood, or excessive tearing, requires prompt veterinary evaluation. The type and frequency of eye discharge can provide valuable insights into the nature and severity of the underlying issue, guiding appropriate treatment measures.
-
Behavioral Changes: Any shifts in your dog's behavior, such as increased irritability, reluctance to be touched around the head, or decreased activity, warrant professional assessment. Behavioral changes can indicate discomfort or distress related to the dent behind the eye, necessitating prompt veterinary care to address the underlying cause.
By remaining attentive to these indicators and promptly seeking veterinary care upon their observation, you can play a proactive role in safeguarding your dog's ocular and overall health. Veterinary professionals possess the expertise to conduct thorough evaluations, provide accurate diagnoses, and implement tailored treatment plans to address the underlying causes of a dent behind the eye. Prioritizing timely veterinary care empowers you to advocate for your dog's well-being and ensure that any potential health concerns are promptly addressed with the utmost care and expertise.
Treatment options for a dent behind the eye
Upon identifying a dent behind your dog's eye, prompt veterinary intervention is crucial to address the underlying cause and ensure the best possible outcome for your canine companion. The treatment approach for a dent behind the eye is contingent upon the specific cause and associated symptoms, necessitating a comprehensive evaluation by a qualified veterinarian. Here are potential treatment options that may be considered based on the underlying factors contributing to the dent behind the eye:
-
Medical Management: In cases where the dent is attributed to inflammatory conditions, such as orbital cellulitis, or fluid accumulation behind the eye, medical management may be employed. This can involve the administration of anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics to combat underlying infections, or therapeutic measures to address fluid accumulation. Medical treatment aims to alleviate inflammation, resolve infections, and promote the restoration of normal eye contours.
-
Surgical Intervention: If the dent behind the eye is linked to structural abnormalities, such as orbital bone anomalies or the presence of a tumor or mass, surgical intervention may be necessary. Surgical procedures can involve the correction of bone defects, excision of tumors, or drainage of fluid accumulations. Surgical options are tailored to address the specific underlying cause and restore the normal anatomy and function of the eye area.
-
Dental Care: In instances where a dental abscess is identified as the cause of the dent behind the eye, dental care and treatment are essential. This may encompass dental procedures to address the abscess, such as tooth extraction, root canal therapy, or periodontal treatment. Resolving the dental issue can alleviate the impact on the surrounding eye structures, contributing to the restoration of normal eye contours.
-
Supportive Care: Regardless of the underlying cause, supportive care plays a pivotal role in the overall management of a dent behind the eye. This can include measures to alleviate pain and discomfort, promote ocular health, and support your dog's well-being throughout the treatment process. Supportive care may involve the use of pain management strategies, ocular lubrication, and attentive monitoring to ensure your dog's comfort and recovery.
-
Ongoing Monitoring and Follow-Up: Following the initiation of treatment, ongoing monitoring and follow-up with your veterinarian are essential. This allows for the assessment of treatment efficacy, the identification of any potential complications, and adjustments to the treatment plan as needed. Regular veterinary consultations enable comprehensive care and ensure that your dog's progress is closely monitored.
The selection of the most appropriate treatment option for a dent behind the eye hinges on accurate diagnosis, thorough evaluation, and individualized care tailored to your dog's specific needs. By collaborating closely with your veterinarian, you can navigate the treatment journey with the utmost care and dedication, prioritizing your dog's ocular and overall well-being.
Incorporating a combination of medical, surgical, and supportive measures, the treatment approach for a dent behind the eye aims to address the underlying cause, alleviate associated symptoms, and facilitate the restoration of normal eye contours. Through proactive veterinary care and attentive support, you can navigate the treatment process with the dedication and compassion your canine companion deserves.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the presence of a dent behind your dog's eye can be a concerning indication of underlying health issues that warrant prompt attention and veterinary care. Understanding the potential causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this phenomenon is essential for advocating for your dog's well-being and ensuring the best possible outcome.
By delving into the intricate anatomy of a dog's eye, we gain valuable insights into the delicate structures and functions that can be impacted by the presence of a dent. From the cornea and iris to the vitreous body and retina, each component plays a crucial role in facilitating vision and maintaining ocular health. Any alteration in the normal contours of the eye, such as a dent, can disrupt these functions and necessitate thorough evaluation.
Exploring the potential causes of a dent behind the eye, including trauma, orbital bone abnormalities, tumors, inflammatory conditions, fluid accumulation, and dental abscesses, underscores the diverse factors that can contribute to this visible anomaly. Vigilantly monitoring accompanying symptoms, such as changes in eye appearance, abnormal discharge, pain or discomfort, vision changes, behavioral shifts, and systemic indicators, empowers pet owners to proactively identify and address potential health concerns.
Recognizing the appropriate timing to seek veterinary care is paramount, especially when persistent or worsening symptoms, pain or discomfort, vision changes, systemic symptoms, unexplained eye discharge, and behavioral shifts are observed. Timely intervention enables veterinary professionals to conduct thorough evaluations, provide accurate diagnoses, and implement tailored treatment plans to address the underlying causes of a dent behind the eye.
The treatment approach for a dent behind the eye encompasses medical management, surgical intervention, dental care, supportive measures, and ongoing monitoring and follow-up. By collaborating closely with veterinarians and prioritizing comprehensive care, pet owners can navigate the treatment journey with dedication and compassion, ensuring that their canine companions receive the best possible support.
Incorporating a combination of medical, surgical, and supportive measures, the treatment approach aims to address the underlying cause, alleviate associated symptoms, and facilitate the restoration of normal eye contours. Through proactive veterinary care and attentive support, pet owners can advocate for their dog's ocular and overall well-being, navigating the treatment process with the dedication and compassion their canine companions deserve.