Home>Health & Wellness>Behavior & Cognitive Care>Why Is My Dog Experiencing Anxiety


Behavior & Cognitive Care
Why Is My Dog Experiencing Anxiety
Published: January 29, 2024
Learn about the causes and signs of dog anxiety, and discover effective behavior and cognitive care solutions to help your furry friend feel calm and secure. Explore expert tips and advice for managing your dog's anxiety.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Canine anxiety is a prevalent issue that affects many dogs, leading to distress and discomfort. As responsible and caring pet owners, it's crucial to recognize the signs of anxiety in our furry companions and take proactive steps to help them cope with these challenging emotions.
Understanding the underlying causes of anxiety in dogs is essential for providing effective support and creating a nurturing environment for our beloved pets. By delving into the intricate world of canine behavior and emotions, we can gain valuable insights into the triggers and manifestations of anxiety in dogs.
In the following sections, we will explore the multifaceted nature of canine anxiety, shedding light on the common causes, signs, and symptoms of this condition. Additionally, we will delve into practical strategies and techniques that can be employed to alleviate anxiety in dogs, promoting their overall well-being and happiness.
By delving into the intricate world of canine behavior and emotions, we can gain valuable insights into the triggers and manifestations of anxiety in dogs.
Read more: Why Is My Senior Dog Biting?
Understanding Canine Anxiety
Canine anxiety is a complex and often misunderstood condition that can significantly impact a dog's well-being. Similar to humans, dogs can experience a range of emotions, including anxiety, which may stem from various sources. Understanding the intricacies of canine anxiety is crucial for pet owners to provide the necessary support and care for their furry companions.
Anxiety in dogs can manifest in different forms, such as separation anxiety, noise phobias, and general anxiety triggered by specific situations or environments. It's essential to recognize that each dog is unique, and their anxiety may be influenced by a combination of genetic predispositions, past experiences, and current circumstances.
One of the primary components of understanding canine anxiety is recognizing the behavioral cues exhibited by anxious dogs. These may include excessive panting, pacing, trembling, restlessness, excessive barking or whining, destructive behavior, and withdrawal. Additionally, some dogs may display physiological symptoms such as dilated pupils, increased heart rate, and gastrointestinal disturbances when experiencing anxiety.
Furthermore, it's important to acknowledge that dogs are highly perceptive animals, capable of picking up on subtle environmental cues and changes in their surroundings. Factors such as changes in routine, unfamiliar visitors, loud noises, or even the absence of their human companions can trigger feelings of unease and distress in dogs, leading to heightened anxiety levels.
Moreover, understanding the cognitive aspects of canine anxiety is crucial. Dogs, like humans, can experience irrational fears and worries, which may intensify their anxiety responses. By acknowledging the cognitive dimensions of anxiety in dogs, pet owners can approach the issue with empathy and patience, fostering a supportive and reassuring environment for their pets.
In essence, understanding canine anxiety involves delving into the emotional, behavioral, and cognitive aspects of this complex condition. By gaining insights into the multifaceted nature of canine anxiety, pet owners can cultivate a deeper understanding of their dogs' emotional well-being and provide the necessary care and support to help alleviate their anxiety.
Common Causes of Anxiety in Dogs
Understanding the common causes of anxiety in dogs is pivotal in addressing and mitigating this prevalent issue. Dogs, like humans, can experience anxiety stemming from various sources, and recognizing these triggers is essential for providing targeted support and intervention.
-
Separation Anxiety: Dogs are inherently social animals, forming strong bonds with their human companions. When left alone for extended periods, some dogs may experience separation anxiety, leading to distress and behavioral issues. This can manifest as excessive barking, destructive behavior, and restlessness.
-
Environmental Changes: Dogs are sensitive to changes in their environment, and alterations in their surroundings can trigger anxiety. Moving to a new home, encountering unfamiliar surroundings, or disruptions in their routine can induce feelings of unease and insecurity in dogs.
-
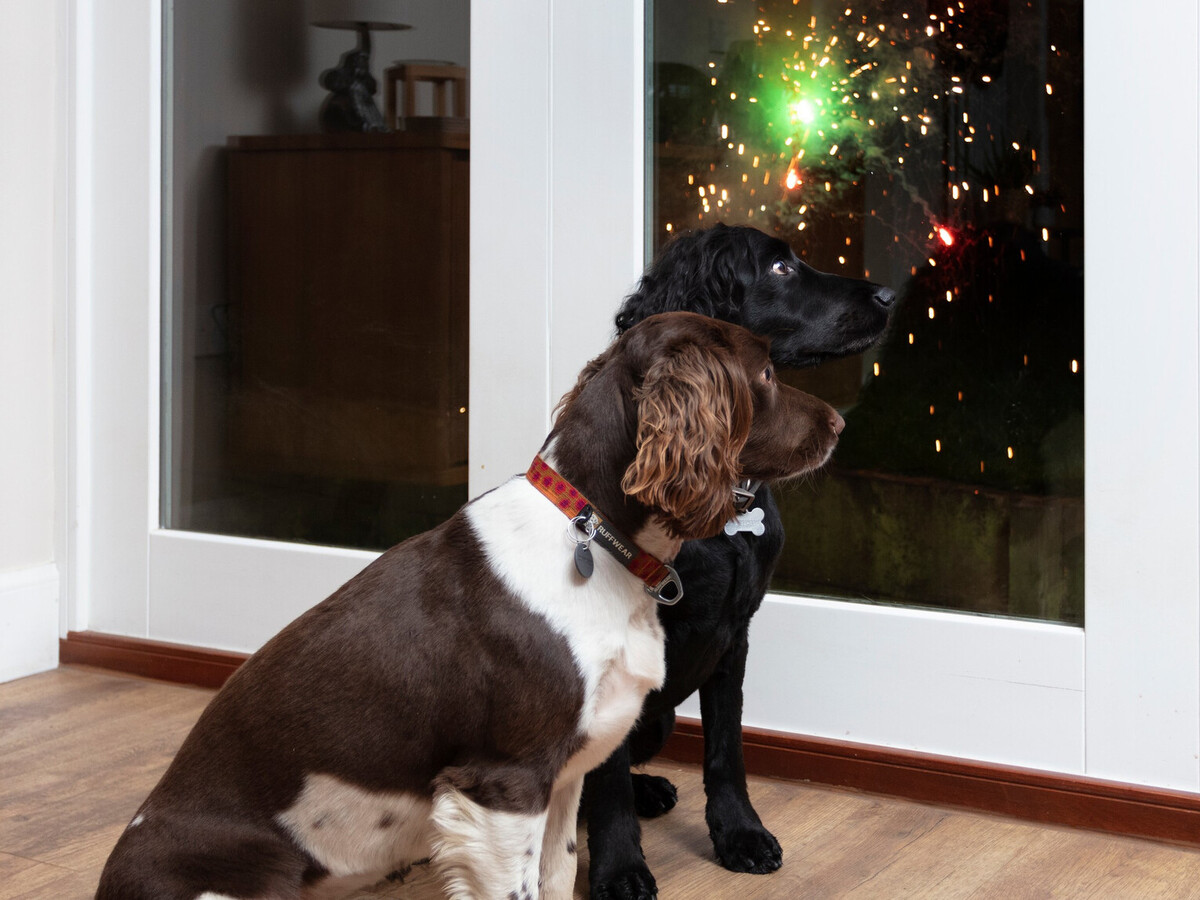
Loud Noises and Phobias: Many dogs exhibit anxiety in response to loud noises such as thunderstorms, fireworks, or construction sounds. This noise phobia can evoke intense fear and anxiety, causing dogs to seek refuge or exhibit erratic behavior.
-
Traumatic Experiences: Dogs that have undergone traumatic experiences, such as abuse, neglect, or accidents, may develop anxiety-related issues. These past traumas can significantly impact a dog's emotional well-being, leading to persistent anxiety and fear responses.
-
Lack of Socialization: Inadequate socialization during a dog's formative stages can contribute to anxiety in social settings. Dogs that have not been exposed to diverse environments, people, and other animals may exhibit anxiety when encountering unfamiliar stimuli.
-
Health Issues: Underlying health conditions can also precipitate anxiety in dogs. Pain, discomfort, or medical ailments may manifest as anxiety-related behaviors, highlighting the importance of addressing potential health concerns in anxious dogs.
-
Genetic Predispositions: Certain breeds may have a genetic predisposition towards anxiety-related behaviors. Understanding breed-specific traits and tendencies can provide insights into the potential susceptibility of individual dogs to anxiety.
By recognizing these common causes of anxiety in dogs, pet owners can take proactive measures to create a supportive and nurturing environment for their furry companions. Addressing these triggers with empathy and understanding can significantly alleviate anxiety in dogs, promoting their emotional well-being and overall quality of life.
Signs and Symptoms of Anxiety in Dogs
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of anxiety in dogs is crucial for proactive intervention and support. Dogs, like humans, can exhibit a diverse array of behavioral and physiological cues when experiencing anxiety. By keenly observing these manifestations, pet owners can gain valuable insights into their dogs' emotional well-being and take appropriate measures to alleviate their distress.
Behavioral Signs:
-
Excessive Panting and Pacing: Anxious dogs may display rapid and excessive panting, often accompanied by restless pacing. These behaviors signify heightened stress and unease in the dog's emotional state.
-
Trembling and Shaking: Visible trembling or shaking, especially in the absence of cold or fear-inducing stimuli, can indicate underlying anxiety in dogs. This physical manifestation reflects the dog's emotional turmoil and discomfort.
-
Excessive Vocalization: Dogs experiencing anxiety may engage in excessive barking, whining, or howling. This vocalization serves as a communication of their distress and a plea for reassurance and comfort.
-
Destructive Behavior: Anxious dogs may exhibit destructive behavior, such as chewing furniture, digging, or scratching doors and windows. These actions often stem from attempts to alleviate their anxiety or express their emotional turmoil.
-
Withdrawal and Avoidance: Some dogs may display withdrawal from social interaction or exhibit avoidance behaviors when feeling anxious. This can include seeking seclusion, avoiding eye contact, or retreating to a confined space.
Read more: How To Help My Dog Overcome Noise Anxiety
Physiological Symptoms:
-
Dilated Pupils: Enlarged or dilated pupils in the absence of dim lighting can indicate heightened arousal and anxiety in dogs. This physiological response is a clear indicator of their emotional distress.
-
Increased Heart Rate: Anxious dogs may exhibit an elevated heart rate, which can be palpable through physical examination. This heightened cardiovascular activity reflects their heightened emotional state.
-
Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Anxiety in dogs can manifest as gastrointestinal issues, including diarrhea, vomiting, or loss of appetite. These symptoms underscore the profound impact of anxiety on a dog's physical well-being.
Cognitive and Emotional Indicators:
-
Excessive Licking or Self-Grooming: Dogs may engage in excessive licking or self-grooming as a coping mechanism for their anxiety. This behavior serves as a self-soothing strategy to alleviate their emotional distress.
-
Hyper-Vigilance and Startle Response: Anxious dogs may exhibit hyper-vigilance, constantly scanning their environment for potential threats. Additionally, they may display exaggerated startle responses to minor stimuli, reflecting their heightened anxiety levels.
By attentively observing these signs and symptoms of anxiety in dogs, pet owners can gain valuable insights into their dogs' emotional well-being and take proactive steps to provide the necessary support and comfort. Understanding these manifestations is pivotal in creating a nurturing environment for anxious dogs, promoting their emotional resilience and overall well-being.
How to Help a Dog with Anxiety
Helping a dog cope with anxiety requires a compassionate and proactive approach aimed at addressing the underlying triggers and providing a supportive environment. By implementing practical strategies and fostering a nurturing atmosphere, pet owners can significantly alleviate their dog's anxiety and promote emotional well-being.
Create a Safe and Comforting Environment
Establishing a safe and comforting environment is paramount in helping a dog manage anxiety. Designate a cozy and secure space within the home where the dog can retreat when feeling distressed. This area should be equipped with familiar bedding, toys, and comforting items to provide a sense of security and solace.
Read more: Why Is My Diabetic Dog Shaking So Much
Consistent Routine and Predictability
Maintaining a consistent daily routine can offer a sense of predictability for anxious dogs, reducing uncertainty and promoting emotional stability. Regular feeding times, exercise schedules, and designated rest periods can instill a sense of security and structure, alleviating anxiety associated with unpredictability.
Positive Reinforcement and Calming Techniques
Utilize positive reinforcement techniques to encourage calm and relaxed behavior in anxious dogs. Rewarding desirable behaviors with treats, praise, and affection can reinforce a sense of security and confidence. Additionally, incorporating calming techniques such as gentle massage, soothing music, or aromatherapy can help alleviate anxiety and promote relaxation.
Physical and Mental Stimulation
Engaging the dog in regular physical exercise and mental stimulation is instrumental in managing anxiety. Physical activity not only promotes overall well-being but also helps reduce stress and anxiety. Interactive toys, puzzle feeders, and engaging activities can provide mental stimulation, diverting the dog's focus from anxiety-inducing triggers.
Professional Guidance and Support
Seeking professional guidance from a veterinarian or certified animal behaviorist is essential for addressing severe or persistent anxiety in dogs. These experts can offer tailored strategies, behavior modification techniques, and, if necessary, medication options to alleviate the dog's anxiety and improve their quality of life.
Read more: Why Does My Senior Dog Keep Whining?
Patience, Understanding, and Reassurance
Above all, demonstrating patience, understanding, and reassurance is crucial in helping a dog navigate anxiety. Providing a comforting presence, gentle reassurance, and empathetic understanding can significantly alleviate the dog's distress. Avoid reinforcing anxious behaviors and instead, offer calm and reassuring responses to promote a sense of security.
By implementing these supportive measures and creating a nurturing environment, pet owners can play a pivotal role in helping their dogs manage anxiety effectively. With patience, empathy, and proactive intervention, anxious dogs can experience a significant improvement in their emotional well-being, leading to a happier and more balanced life.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding and addressing canine anxiety is a multifaceted endeavor that requires empathy, insight, and proactive intervention. By delving into the intricate world of canine emotions and behavior, pet owners can gain valuable insights into the triggers, manifestations, and supportive strategies for alleviating anxiety in their furry companions.
Recognizing the common causes of anxiety in dogs, such as separation anxiety, environmental changes, loud noises, traumatic experiences, and health issues, provides a foundation for targeted support and intervention. By acknowledging these triggers and their impact on a dog's emotional well-being, pet owners can create a nurturing environment that promotes resilience and emotional stability.
Moreover, being attuned to the signs and symptoms of anxiety in dogs, including behavioral cues, physiological manifestations, and cognitive indicators, enables pet owners to keenly observe their dogs' emotional state and provide timely support. By recognizing these manifestations, pet owners can take proactive steps to alleviate their dog's distress and promote a sense of security and comfort.
Helping a dog cope with anxiety involves creating a safe and comforting environment, maintaining a consistent routine, utilizing positive reinforcement and calming techniques, providing physical and mental stimulation, seeking professional guidance when necessary, and demonstrating patience, understanding, and reassurance. By implementing these supportive measures, pet owners can significantly alleviate their dog's anxiety and foster emotional well-being.
Ultimately, the journey of supporting a dog with anxiety is rooted in empathy, patience, and a deep understanding of their emotional needs. By approaching canine anxiety with compassion and proactive intervention, pet owners can create a nurturing and supportive environment that empowers their dogs to navigate anxiety and lead fulfilling, balanced lives.
In essence, the bond between a pet owner and their dog is a profound and reciprocal relationship, characterized by love, trust, and unwavering companionship. By recognizing and addressing canine anxiety with empathy and insight, pet owners can further strengthen this bond, fostering a harmonious and enriching connection with their beloved furry companions.