Home>Health & Wellness>Common Health Issues>How To Help A Dog With Seizures From Lyme Vaccination

Common Health Issues
How To Help A Dog With Seizures From Lyme Vaccination
Published: January 31, 2024
Learn how to support a dog experiencing seizures from a Lyme vaccination and other common health issues. Find effective ways to help your furry friend.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Pawsomeoldies.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
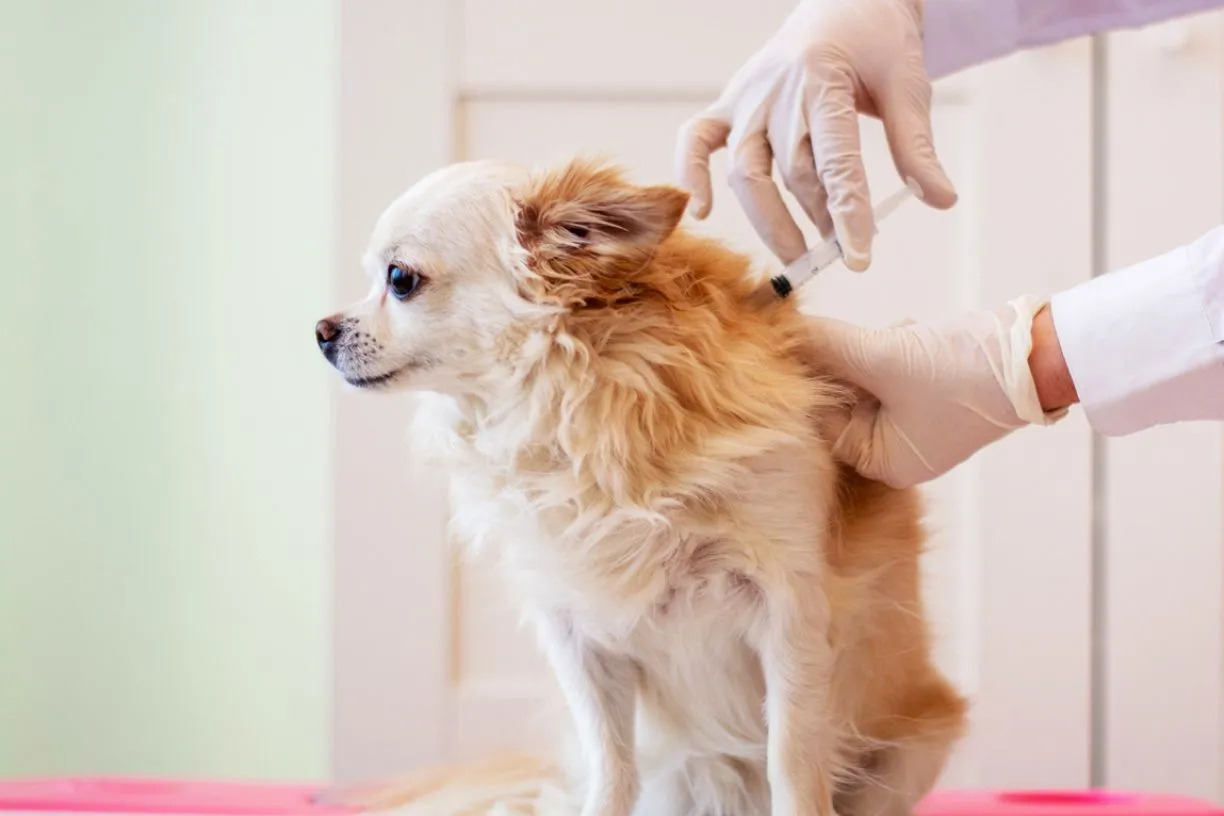
Lyme disease is a prevalent concern for dogs, especially those residing in or frequently visiting areas with high tick populations. To safeguard our furry companions from this potentially debilitating illness, many pet owners opt for Lyme vaccination. While this preventive measure is generally safe and effective, some dogs may experience adverse reactions, including seizures, following the vaccination.
Understanding the potential link between Lyme vaccination and seizures in dogs is crucial for pet owners. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of seizures and knowing how to respond can make a significant difference in ensuring the well-being of our beloved pets. Additionally, seeking prompt veterinary care and taking preventive measures can help mitigate the risk of seizures in dogs following Lyme vaccination.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Lyme vaccination and seizures in dogs, shedding light on the signs of seizures, steps to take during a seizure, the importance of seeking veterinary care, and strategies for preventing seizures in dogs after Lyme vaccination. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can be better prepared to support your canine companion and provide the necessary care in the event of a seizure following Lyme vaccination.
Understanding Lyme Vaccination and Seizures in Dogs
Lyme vaccination is a preventive measure designed to protect dogs from contracting Lyme disease, a tick-borne illness caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. The vaccine works by stimulating the dog's immune system to produce antibodies against the bacterium, thereby reducing the risk of infection and the potential development of Lyme disease.
While Lyme vaccination is generally considered safe, some dogs may experience adverse reactions, including seizures, following the administration of the vaccine. Seizures are neurological events characterized by abnormal electrical activity in the brain, leading to a range of physical and behavioral manifestations. In the context of Lyme vaccination, the occurrence of seizures in some dogs has raised concerns among pet owners and veterinarians, prompting a closer examination of the potential link between the vaccine and neurological reactions.
It's important to note that the relationship between Lyme vaccination and seizures in dogs is a subject of ongoing research and discussion within the veterinary community. While the exact mechanisms underlying this potential association are not fully understood, it is believed that certain dogs may be predisposed to experiencing seizures as a result of their unique genetic makeup or underlying health conditions. Additionally, individual variations in immune responses and neurological sensitivity may contribute to the manifestation of seizures following Lyme vaccination.
Pet owners should be aware that the occurrence of seizures after Lyme vaccination is relatively rare, and the majority of dogs vaccinated against Lyme disease do not experience such adverse reactions. However, it is essential to remain vigilant and informed about the potential risks and symptoms associated with post-vaccination seizures, as early recognition and intervention are crucial for ensuring the well-being of our canine companions.
By gaining a deeper understanding of Lyme vaccination and its potential implications for canine health, pet owners can make informed decisions regarding their pets' preventive care and be better prepared to address any adverse reactions that may arise. In the following sections, we will explore the signs and symptoms of seizures in dogs, the appropriate steps to take when a dog is experiencing a seizure, the importance of seeking veterinary care, and strategies for preventing seizures in dogs following Lyme vaccination. This knowledge will empower pet owners to provide the best possible support and care for their furry friends in the event of a seizure after Lyme vaccination.
Signs and Symptoms of Seizures in Dogs
Seizures in dogs can manifest in various ways, and recognizing the signs and symptoms is crucial for pet owners. While seizures can be a distressing experience for both the dog and its human companions, understanding the typical manifestations of a seizure can help in providing timely and appropriate care.
-
Uncontrolled Movements: During a seizure, a dog may exhibit uncontrolled movements, such as convulsions, twitching, or jerking of the limbs. These involuntary motions are often accompanied by muscle rigidity and may affect specific parts of the body or involve the entire body.
-
Altered Consciousness: Dogs experiencing a seizure may appear disoriented or unaware of their surroundings. They may exhibit a dazed or vacant expression, and their responsiveness to external stimuli may be significantly reduced.
-
Excessive Salivation: Seizures can trigger excessive drooling or foaming at the mouth in affected dogs. This foaming may result from heightened salivary production during the seizure episode.
-
Loss of Bodily Functions: In some cases, dogs may lose control of their bladder or bowels during a seizure. This loss of bodily function is a common occurrence and is attributed to the neurological impact of the seizure activity.
-
Vocalization: Dogs may vocalize during a seizure, emitting sounds such as whining, whimpering, or barking. These vocalizations may be involuntary and can vary in intensity and duration.
-
Prolonged Seizure Activity: While seizures typically last for a relatively short duration, some dogs may experience prolonged or recurrent seizure activity, known as status epilepticus. This condition requires immediate veterinary attention.
It is important to note that the signs and symptoms of seizures in dogs can vary in their presentation and intensity. Additionally, some dogs may exhibit pre-seizure behaviors or auras, which can serve as early indicators of an impending seizure. These pre-seizure signs may include restlessness, pacing, excessive salivation, or unusual vocalizations.
By familiarizing themselves with the signs and symptoms of seizures in dogs, pet owners can be better equipped to identify and respond to a seizure episode in their canine companions. In the event of a seizure following Lyme vaccination, prompt recognition of these manifestations can facilitate the provision of supportive care and the timely involvement of veterinary professionals.
Steps to Take When Your Dog is Having a Seizure
Witnessing your beloved dog experiencing a seizure can be a distressing and alarming situation. However, it's crucial to remain calm and take immediate steps to ensure the safety and well-being of your canine companion. Here's a detailed guide on the appropriate actions to take when your dog is having a seizure:
-
Stay Calm: While it's natural to feel anxious or frightened when observing your dog's seizure, maintaining a calm and composed demeanor is essential. Your dog can sense your emotions, and a soothing presence can provide comfort during this challenging time.
-
Create a Safe Environment: Clear the immediate surroundings to prevent your dog from injuring itself during the seizure. Remove any sharp objects, furniture with sharp edges, or other potential hazards. If the seizure is occurring on a elevated surface, carefully guide your dog to the floor to minimize the risk of falling.
-
Do Not Restrain Your Dog: It's important to refrain from restraining or holding down your dog during the seizure. Allow the seizure to run its course while ensuring that your dog is in a safe and secure space. Restraining your dog can lead to accidental injury or heightened distress.
-
Note the Duration: While it may feel like an eternity, seizures typically last for a relatively short period, usually a few minutes. Use a timer or mental note to track the duration of the seizure. If the seizure persists for an extended period, seek immediate veterinary assistance.
-
Minimize Stimulation: Reduce external stimuli by dimming the lights and minimizing noise in the vicinity. Create a calm and quiet environment to help alleviate any potential triggers or exacerbating factors.
-
Reassure Your Dog: Offer gentle and reassuring verbal cues to your dog, such as speaking in a calm and soothing tone. Your presence and comforting words can provide a sense of security to your pet during the seizure episode.
-
Monitor Breathing and Heart Rate: While observing the seizure, pay attention to your dog's breathing and heart rate. If you notice any irregularities or signs of distress, it's important to relay this information to the veterinarian.
-
Document the Seizure: Take note of the time the seizure started, its duration, and the specific behaviors and movements exhibited by your dog. This information can be valuable for the veterinarian in assessing the nature of the seizure and determining appropriate care.
By following these steps, you can provide essential support to your dog during a seizure and help ensure a safe and controlled environment. Remember that seeking veterinary care following a seizure is crucial, especially if it occurs after Lyme vaccination, to assess any underlying causes and determine the best course of action for your dog's well-being.
Seeking Veterinary Care for Seizures After Lyme Vaccination
Seeking prompt veterinary care is paramount when a dog experiences seizures following Lyme vaccination. While seizures can be a distressing occurrence, involving a veterinarian is essential to assess the underlying causes, provide appropriate treatment, and ensure the well-being of the affected dog.
Upon observing a seizure in your dog after Lyme vaccination, it is crucial to contact your veterinarian immediately. Communicate the details of the seizure, including its duration, the specific behaviors exhibited by your dog, and any other relevant observations. Based on the information provided, the veterinarian can offer guidance on the next steps, including whether immediate intervention is necessary.
In some cases, the veterinarian may recommend bringing the dog in for an emergency evaluation, especially if the seizure persists for an extended duration or if there are concerns about the dog's overall health. During the veterinary assessment, the veterinarian will conduct a thorough examination to determine the potential triggers or underlying conditions contributing to the seizures. This may involve neurological assessments, blood tests, and other diagnostic procedures to gain insights into the dog's health status.
Furthermore, the veterinarian will review the dog's medical history, including details of the Lyme vaccination, to assess any potential correlations between the vaccination and the onset of seizures. This comprehensive evaluation is essential for identifying any adverse reactions or sensitivities that may have led to the seizure episode.
Based on the findings of the assessment, the veterinarian will develop a tailored treatment plan to address the dog's specific needs. This may involve medication to manage seizures, supportive care to aid in the dog's recovery, and recommendations for future preventive measures. Additionally, the veterinarian will provide guidance on monitoring the dog's condition at home and recognizing any potential recurrence of seizures.
In some instances, the veterinarian may collaborate with specialists, such as neurologists or internal medicine experts, to ensure a comprehensive approach to managing the dog's seizures. This multidisciplinary approach can provide valuable insights and access to specialized care, further optimizing the dog's treatment and long-term well-being.
By seeking veterinary care for seizures after Lyme vaccination, pet owners can access professional expertise, diagnostic resources, and tailored interventions to support their dogs through this challenging experience. The collaboration with a veterinarian is instrumental in ensuring the best possible care and outcomes for dogs affected by post-vaccination seizures, ultimately promoting their health and quality of life.
Preventing Seizures in Dogs After Lyme Vaccination
Preventing seizures in dogs after Lyme vaccination involves a proactive approach to minimize the risk of adverse reactions and support the overall well-being of canine companions. While the occurrence of seizures following vaccination is relatively rare, pet owners can take certain measures to mitigate potential triggers and promote a safe and healthy post-vaccination experience for their dogs.
-
Consultation with Veterinarian: Prior to administering any vaccinations, including the Lyme vaccine, it is essential for pet owners to consult with their veterinarian. A thorough discussion about the dog's medical history, existing health conditions, and any previous adverse reactions to vaccinations can provide valuable insights into the dog's suitability for the Lyme vaccine. The veterinarian can offer personalized recommendations and address any concerns related to the vaccination process, thereby minimizing the likelihood of unexpected reactions, including seizures.
-
Vaccine Schedule and Administration: Following the veterinarian's guidance, adhering to a well-structured vaccine schedule is crucial for preventing adverse reactions in dogs. Ensuring that the Lyme vaccine is administered in accordance with recommended protocols, including appropriate dosages and intervals between vaccinations, can contribute to a more controlled and favorable vaccination experience for dogs. Additionally, proper administration techniques, such as injection site management and post-vaccination observation, play a key role in reducing the risk of adverse events.
-
Health Monitoring and Post-Vaccination Care: After receiving the Lyme vaccine, diligent monitoring of the dog's health and behavior is essential. Pet owners should observe for any unusual symptoms or changes in the dog's well-being in the days following vaccination. Providing a comfortable and stress-free environment for the dog, along with adequate rest and hydration, can support the dog's recovery and minimize potential stress-related triggers for seizures.
-
Individualized Risk Assessment: Recognizing that each dog is unique, pet owners should consider an individualized risk assessment in consultation with the veterinarian. Factors such as the dog's breed, age, overall health status, and previous vaccine responses can influence the likelihood of adverse reactions, including seizures. By taking into account these individual considerations, pet owners can make informed decisions regarding the timing and administration of the Lyme vaccine, tailored to their dog's specific needs and sensitivities.
-
Holistic Health Support: Promoting holistic health and wellness in dogs can contribute to their resilience and ability to tolerate vaccinations effectively. This includes maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and appropriate parasite control measures to support the dog's overall immune function and vitality. Additionally, minimizing environmental stressors and providing mental stimulation can enhance the dog's well-being, potentially reducing the susceptibility to adverse reactions following vaccinations.
By proactively addressing these preventive measures, pet owners can play a proactive role in safeguarding their dogs' health and minimizing the risk of seizures after Lyme vaccination. Collaboration with a trusted veterinarian and a commitment to personalized care can contribute to a positive vaccination experience for dogs, promoting their long-term health and vitality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the potential occurrence of seizures in dogs following Lyme vaccination underscores the importance of informed decision-making, vigilant monitoring, and proactive care to safeguard the well-being of our beloved pets. While the link between Lyme vaccination and seizures in dogs is a subject of ongoing research and discussion, pet owners can take proactive steps to recognize, respond to, and prevent seizures in their canine companions.
Understanding the signs and symptoms of seizures in dogs, including uncontrolled movements, altered consciousness, excessive salivation, and vocalization, empowers pet owners to identify and respond to seizure episodes effectively. By creating a safe and supportive environment during a seizure and seeking prompt veterinary care, pet owners can ensure the best possible outcomes for their dogs following a seizure, especially after Lyme vaccination.
The collaboration with a trusted veterinarian is instrumental in addressing post-vaccination seizures, as it enables comprehensive assessments, tailored treatment plans, and access to specialized care when necessary. Seeking veterinary guidance before vaccination, adhering to recommended vaccine schedules, and monitoring the dog's health post-vaccination are essential components of preventing adverse reactions, including seizures, in dogs.
Furthermore, recognizing the individualized risk factors and health considerations of each dog, along with promoting holistic health and wellness, can contribute to a positive vaccination experience and minimize the likelihood of seizures following Lyme vaccination. By embracing a proactive and informed approach to preventive care, pet owners can play a pivotal role in supporting their dogs' long-term health and vitality.
Ultimately, the well-being of our canine companions remains a top priority, and by staying informed, proactive, and attentive to their unique needs, pet owners can navigate the complexities of Lyme vaccination and potential seizure risks with confidence and compassion. Through collaboration with veterinary professionals and a commitment to personalized care, pet owners can provide the best possible support for their dogs, ensuring a safe and nurturing environment as they continue to enrich our lives with their unwavering companionship and love.
